.
Increased nervousness, aggression and apathy are the most common symptoms of prolonged stress. Prolonged stress on the psyche leads to the following consequences: a person’s physiology, moral state, and social relationships suffer.
Apathy is one of the manifestations of prolonged stress
The consequences of stress depend on the stress tolerance of the individual, the type of occupation and status of the person. Long-term and short-term stress can change the behavior and character of a man, woman, teenager or child.
Stressful state
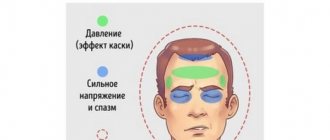
The consequences of this condition appear after prolonged stress on the nervous system. The central nervous system functions in two processes - relaxation and a state of excitation. Violation of one process entails a number of symptoms: irritability, headaches, insomnia, absent-mindedness and aggression. The consequences of severe stress are chronic changes in behavior, treated with tranquilizers, sedatives and deep psychoanalysis.
What does stress lead to? The reaction of the human body is unpredictable. The symptoms of the consequences depend on the person’s life, his environment and the factors that trigger stress. Why stress is dangerous:
- irreversible changes in the victim’s personality;
- pathologies of internal organs;
- development of mental disorders;
- adaptation disorder;
- destruction of the relationship between the stressed person and his environment.
Stress and its consequences depend on the frequency of stressors (events, people, memories that frighten a person). Fear is normal. Short-term emotional protection creates minimal harm to the body.
Constant tension is dangerous for mental and physiological health: the more often a person is in fear, the harder it is to get rid of the root cause of stress.
Causes of stress
Negative emotions arise against the backdrop of difficult life situations. The reasons for a difficult moral situation can be hereditary factors, hormonal changes in the body, physical changes, psycho-emotional stress, disruption of the daily routine, and relationship problems.
It will not be possible to avoid the causes of stress in the modern world, but every person can develop stress resistance.
The body's protective reactions can be regulated through breathing exercises, sports, yoga or other activities that require concentration and strength.
Reaction to stress
The reaction to stress is the consequences that have to be dealt with. Frequent panic attacks or insomnia create the preconditions for the development of a mental disorder. The frequency of human diseases directly depends on the frequency of reactions to stress. A weakened body cannot resist even the slightest threat: infectious or viral diseases. Symptoms of stress:
- cardiopalmus;
- headache;
- confusion;
- memory loss;
- increased sweating;
- pain in the chest and heart;
- abdominal cramps;
- chills;
- speech disorder.
Headache is one of the symptoms of nervous tension
Smells, sounds, memories, or hallucinations of the traumatic event may lead to the development of symptoms. The “stimulus” ended, but the signs of fear remained.
The negative experience experienced forces the psyche to defend itself: a person falls into forced apathy and escapes (the brain partially blocks memories or distorts the perception of reality). Psychoanalysis and a set of exercises help to get rid of the effects of stress.
List of possible diseases
Severe stress can have unpredictable consequences. The blow is delivered on a physical and emotional level.
Implications for mental health
The following disorders occur in the nervous system:
- increased anxiety;
- irritability;
- neuroses;
- emotional instability;
- intolerance;
- overexcitement;
- hypochondria;
- prostration;
- depression;
- fast fatiguability;
- insomnia;
- memory impairment.
A person experiences inexplicable, often uncontrollable attacks of aggression, mood swings, and loses interest in familiar things that previously pleased him.
Implications for physical health
The effect of constant stress on a person is as follows.
- Increased blood glucose levels. It is necessary for the body to obtain energy. But with constant stress, the sugar level constantly rises, the tension leads to disruptions in the functioning of internal organs, in particular the pancreas, it ceases to cope with its functions, which leads to the development of diabetes.
- The thymus gland is responsible for the production of leukocytes, which also suffers from stress. When immunity decreases, this organ contracts uncontrollably, which leads to disruption of the formation of leukocytes. This further reduces the body's defenses.
- When adrenaline is released, the capillaries expand, and when there is strong nervous tension, they burst. This causes the formation of hematomas and blood stagnation. The surface of the skin becomes unnaturally pale with a bluish tint. The blood supply to organs is also disrupted.
- Involuntary muscle tension leads to tissue destruction at the cellular level. Regular alternation of tension and relaxation negatively affects the functioning of internal organs. Glucosteroids accumulated in muscle tissue promote the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids, which leads to dystrophy.
- Cells suffer from metabolic disorders; toxins accumulate in them, which provoke intoxication of the body. It is difficult to remove them naturally. Cell growth is disrupted, the skin becomes thinner, easily damaged, and wounds take a long time to heal. Bones also suffer due to a lack of calcium, their fragility increases, and osteoporosis develops.
Against the background of constant emotional stress, fertile ground arises for the development of cancer. Stress provokes problems in the gastrointestinal tract, causing stomach ulcers. This is the main risk factor causing heart and vascular diseases, heart attacks, strokes, hypertension and angina.
The complexity of the situation lies in the fact that modern people lead an inactive lifestyle. Biologically active substances remain in the body for a long time in high concentrations, which prevents the nerves and body from calming down due to lack of muscle activity.
Destructive reactions are caused not only by long-term, but also by short-term stress. A single large shock has been shown to have negative effects long after the impact. At the same time, the consequences of stress are irreversible; in some cases, brain cells are destroyed.
Health effects of stress
Stress and its consequences are dependent concepts: severe trauma takes longer to resolve. A tense state disrupts the rhythm of life. It is difficult for the patient to navigate what is happening, to recover from severe stress without feeling devastated. The victim’s internal organs also suffer from mental stress: the cardiovascular system, stomach and intestines, endocrine system.
The human body weakens, and irritability gradually turns into apathy. People with stress from work or problems in their personal lives develop indifference to loved ones and the world around them. Due to constant stress, sleep is disturbed: the brain does not relax, confusion appears, and the severity of reactions weakens.
Psychosomatic diseases
The psychosomatic consequences of a severe stress state appear against the background of weakened immunity. Reduced activity and lack of appetite deplete the body: reduced immunity cannot resist diseases. Consequences of severe emotional stress:
- stroke;
- stomach and intestinal ulcers;
- chronic insomnia;
- decreased concentration;
- migraine;
- depression;
- sexual dysfunction;
- asthma;
- atherosclerosis.
The pathologies that arise depend on the state of the human body before the stress experienced. Increased anxiety, aggression and neuroses are accompanied by inflammation of chronic diseases. Eczema and dermatitis occur in people who cannot cope with anxious thoughts.
Stress is dangerous due to mental illnesses, such as split personality, penetrating trauma syndrome. For sick people, reality changes and adapts to their fears.
Children who have experienced domestic violence suffer from attention deficit disorder: the child exhibits symptoms of a fictitious disease. Over time, this syndrome develops into severe chronic diseases. A stressful state reduces professional activity. During home treatment and taking sedatives, the conductivity of brain neurons decreases. Memory is impaired, work ability decreases, and concentration is lost.
Asthma may be psychosomatic in nature
Chronic fatigue and chronic stress
In psychology, there are three types of human behavioral reactions to stress. The first reaction is conventionally called “foot on the gas” - the person is angry and constantly agitated. Under the pressure of circumstances, he literally boils, only negative emotions arise in him. The second state - “foot on the brake” - is characterized by isolation and withdrawal of the victim from the outside world. He closes himself, hides behind a mask of indifference. The last and most dangerous reaction to stress is “feet on both pedals.” The person is tense and constrained, it is difficult for him to pull away, but he is not able to throw out his emotions.
Chronic stress occurs against the background of any reaction of the body: the decisive factor is the duration of the symptoms of a serious condition. The body is weakened by violent emotions and attempts to escape consciousness. Long-term stress leads to complete emotional burnout.
Some people become lethargic under stress
Symptoms of burnout
The consequences of emotional instability, burnout, are accompanied by special symptoms. Signs of emotional burnout are divided into 3 groups:
- Cognitive. The victim exhibits memory problems. He only focuses on negative situations. Constant anxious thoughts accompany emotional burnout. Changing the victim's mindset is the most difficult task. The anxiety does not go away during the day, and at night the anxiety results in nightmares. The person feels tired, insensitive, lethargic.
- Emotional. The consequences of burnout are expressed in the acquired character traits of the victim: he is capricious, demanding, and quick-tempered for any reason. A person suffering from stress is overcome by feelings of loneliness and isolation. Depression and sadness are the main symptoms of burnout.
- Behavioral. The behavioral consequences of burnout are more common in adolescents and children. The victim is undernourished or overeating, hides from other people, and suffers from insomnia. The victim of stress cannot and does not want to complete the assigned tasks.
The effects of burnout manifest themselves in one or more symptoms. Loss of control over their emotions by expressive people occurs with increased aggression: a person destroys himself, his environment, and relationships.
In women, burnout is expressed by frigidity and sexual coldness. In men, burnout can manifest as sexual dysfunction.
Chest pain and tachycardia are two symptoms that indicate chronic stress. Fatigue coupled with aggression or inaction characterize chronic stress. Only a specialist can determine how advanced the disease is. It is very difficult to get rid of a protracted problem without the help of a specialist.
Destruction of relationships
Stress itself cannot lead to antisocial behavior of the victim; the consequences of a stressful state are responsible for the destruction of relationships in the family and at work. Psycho-emotional changes affect the perception of the world and people around you. A person in a state of constant tension is not able to objectively assess the situation. Conflict is a consequence of chronic stress: an aggressive attitude turns into a constant response. Irritability leads to a narrowing of the social circle. If a person feels morally bad, he splashes out negativity on loved ones, friends or colleagues.
Intrafamily relationships also suffer from the effects of stress. Communication between spouses is disrupted. Hot temper and suspiciousness disrupt harmony in the family: a person tries to relieve tension by splashing out negative emotions. In intimate terms, the victim is cold and uninitiative. Lack of sex life affects the relationship of spouses.
Prolonged stress is dangerous for work relationships. Conflict and temper lead to confrontation in the workplace, dismissal and loss of stable income. People with an apathetic state due to depression lack zeal for work - the employee receives constant criticism from colleagues and superiors, which aggravates his condition. The body launches additional defense mechanisms: the employee quits, falls into even greater depression, and loses the meaning of life.
Family relationships suffer greatly from stress
Causes
Stressful situations can arise due to the influence of any factor. However, scientists usually divide possible causes of development into two main categories - external and internal.
If we try to consider the reasons why stressful situations arise, we can highlight the following factors:
- Too high professional load.
- Not having a good intimate or personal life.
- Facing misunderstanding from family and friends.
- Urgent need for finance.
- Having a pessimistic mood.
- Low self-esteem.
- A situation in which the demands on both oneself and the environment are too high.
- The state of internal struggle of the individual.
Low self-esteem is one of the causes of stress
However, you should not think that such conditions can be caused exclusively by situations with a negative attitude. According to experts, the effect of stress on the body can also be observed in the case of an excess of positive emotions. This can happen when you move up the career ladder quite quickly or after the couple gets married.
As soon as it is possible to establish which events provoked stress, the cause must be eliminated as soon as possible. You should not be afraid of changing your life and reduce negative influence factors to a minimum.
Combating the effects of chronic stress
Comprehensive exercises will help get rid of severe nervous tension: a person undergoes emotional therapy and performs physical exercises. Complex activities lead a person to inner harmony. To treat chronic stress use:
- Yoga. Yoga classes allow you to concentrate your attention, focus your thoughts and let go of anxiety. Daily yoga practice has a beneficial effect on the physical condition of the body.
- Breathing exercises. Breathing techniques can be used at home, at work and even on public transport. Holding your breath and breathing calmly will ensure the supply of oxygen to the brain. Through breathing, a tense body relaxes and internal processes are normalized.
- Relaxation techniques. Massage and acupuncture will improve the functioning of the digestive system, blood circulation and muscle tone. Relieving tension will help you get rid of the effects of work stress.
- Lifestyle organization. Normalization of nutrition and a healthy lifestyle changes thinking. If a person takes care of himself, his stress level decreases.
To combat stress, it is not necessary to attend paid classes.
A person who has suffered emotional burnout can do home exercises. Morning jogging and a balanced diet will improve internal metabolic processes.
Quiet activities such as reading, knitting, art therapy are useful to improve morale. Concentrating energy and attention on one process has a beneficial effect on people with anxious thoughts.