Parents worry when their child’s health deteriorates. Headache is quite common in childhood. Its appearance may signal the development of various pathologies. The location of the pain is of particular importance. Let's consider what it means if a child has a headache in the forehead and how to help the baby.
What causes pain
Children experience headache attacks less often than adults. The reason for this is the immature nervous system and its great compensatory potential. Most types of forehead pain are not associated with pathological changes in the brain. In order to fight the syndrome, you need to understand what provokes it. A headache in the forehead area in a child begins due to:
- Poor diet.
- Neurological problems.
- External irritants.
- TBI (traumatic brain injury).
- Intoxication of the body.
- Migraine.
Internal factors
If the mother did not eat well while carrying the baby, then the sugar level in her blood may be low. This affects the development of the fetal brain: after birth, the baby will suffer from painful attacks of cephalalgia. Children with allergies may experience a headache when eating citrus fruits, chocolate, nuts, cola, or seafood. It is necessary to monitor the child’s nutrition and be as careful as possible when choosing foods.
A mother should not be surprised that her child’s forehead hurts, daily offering him carbonated drinks, sausages, smoked meats, chips, and other foods that contain preservatives. Headache attacks are provoked by supplements including aspartame, tyramine, calcium chloride, nitrite.
Migraine occurs in approximately 20% of children. The attack lasts from 1 to 5 hours. Doctors associate the nature of the disease with a certain gene inherited from the mother. If a mother experiences frequent headaches, she is likely to pass this on to her child. Pulsating temporal pain, nausea, and dizziness occur due to a lack of serotonin in the brain.
It is not yet possible to completely recover from migraines, but you can relieve the pain syndrome: sleep in the open air, take antispasmodics, do a head massage.
It happens that a child has a headache in the frontal part with the development of colds and bacteriological diseases, with neuralgia. The affected triangular nerve causes recurring, sharp pain. With a sharp turn of the head, coughing, sneezing, they can intensify. Neuralgia is treated with heating.
External factors
Children often hit their heads when falling, which results in brain injuries. Visible signs of TBI may include temporary loss of consciousness, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. It happens that the baby hit himself, cried and calmed down, and after a while he shows other signs. He is capricious, sleeps poorly, his vision becomes dark and his head hurts. Infants can arch their backs, throw back their heads, their fontanel swells and pulsates - this means that the bruise has caused serious consequences.
Important! After hitting a child's head, parents need to actively rub the bruise site. This will prevent the formation of edema and hematomas. Be sure to apply a cold compress (a piece of ice, a coin, water) and consult a doctor.
Stress, nervous exhaustion, and psychological stress also cause cephalalgia. A day full of emotions, noisy active games, uncontrolled TV watching, long games on a tablet or computer have a negative impact on the child’s well-being. A stuffy room, bright lighting, and loud rhythmic music can also cause headaches in children.
Why does a child have a headache in the frontal region and how to solve the problem?
Headaches of various types and origins are a fairly common phenomenon among children, and much more common than most adults tend to think.
Children have headaches similar to those of the adult population: in the forehead, crown, back of the head, temples... A typical migraine, similar to that which some adults suffer, is now typical for preschool children, and reduces the quality of life of children in all other age categories. This headache occurs in girls and boys.
Just like in an adult, not every headache in a child has the characteristic signs of a migraine, in which the head hurts in the temples and forehead. Even in the pediatric population, tension headaches are common, usually of vertebrogenic origin, i.e.
an ailment caused by disorders of the cervical spine, which can largely imitate a typical migraine. This type of disease is characterized by a concentration of pain in the frontal region, temples and eyes.
Why does a child have a headache?
The situation when a child has a headache is today not considered such an ominous sign of illness as it was previously. About 40% of 7-year-old children and up to 70% of 15-year-olds experience pain in the forehead and temples.
Between the ages of 13 and 18, frontal headache sometimes affects 59% of boys and 84% of girls. Although most of these problems in a child are not a sign of any serious illness, they should be given due attention.
Acute headache in a child in the temples and forehead, associated with symptoms of infection, fever, weakness, along with laboratory tests indicating inflammation, indicate meningitis. If encephalitis occurs, the main symptoms include impaired consciousness, high body temperature and neurological disorders (partial paralysis).
A headache in the frontal part of a child may also conceal a traumatic hemorrhage in the brain. It is manifested by impaired consciousness, nausea, vomiting, increased sensitivity to light and convulsions. In addition, sudden pain in a child may develop as a result of a brain tumor.
In addition to sudden attacks, chronic pain also occurs in children. If it persists but does not get worse, it is usually not a symptom of a serious illness. The attack can last from 30 minutes to 7 days.
Such a headache in a child, as in an adult, is bilateral, localized in the forehead or temples, characterized by mild or moderate intensity, does not worsen with physical activity and is not associated with vomiting.
This symptom is often accompanied by depression and occurs in a child who is having problems at school or at home.
Chronic headaches in a child may be associated with inflammation of the paranasal sinuses or blurred vision; often concentrated in the frontal and temporal parts, sometimes in the eye area. The trigger is watching TV or playing on the computer; After vision is restored, it goes away.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the problem does not awaken the child from sleep, or is not very intense.
This type of illness may indicate increased intracranial pressure and brain damage; may be accompanied by problems when walking, swelling of the optic nerve is visible on the back of the eye. In this case, the doctor always refers the patient to CT and MRI.
Increased intracranial pressure can be caused by medications, but first of all, the presence of an underlying disease should be determined, for example, obesity, adrenal disease, inflammation of the sinuses and middle ear.
What if my head hurts periodically?
The most common cause of recurrent headaches in children is migraine. The disease is characterized by the localization of pain in the forehead and temporal part, and is often one-sided. Directly, pain is preceded by increased activity of the child, irritability, fatigue.
The first sign of an attack is usually a visual aura, represented by flashes before the eyes and blurred vision. The pain is usually intense, throbbing, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sometimes abdominal pain, intensifying during physical activity; The headache usually lasts for 2-12 hours and subsides after sleep.
Painless periods occur between attacks.
Treatment of the child consists of adequate drinking regimen, taking anti-emetic and sedatives, and sometimes, if possible, Paracetamol and Ibuprofen to relieve pain. In cases where a child’s attacks recur more often than 4 times a month and significantly affect the quality of life, preventive treatment with special medications is prescribed.
Acute sinusitis is not a common cause of headaches. However, in a child, you should pay attention to the sudden onset of pain on the face with fever, runny nose and soreness in the nose. The diagnosis is confirmed by x-ray or CT.
Recurrent headaches in the forehead and temporal area in a child are caused by high blood pressure. If there are fluctuations or constant high blood pressure with pain, severe kidney, heart, endocrine diseases or cancer should be excluded.
Migraine in a child
The diagnosis of migraine can only be established after excluding other possible causes of headaches in a wide range of options: from inflammatory diseases of the meninges or sinuses, to visual and spinal disorders, the consequences of trauma, and even intracranial bleeding or brain tumors.
Considering the above and the risk of serious illnesses, we can once again emphasize that headaches, first of all, should be considered as a symptom of the disease, and not the disease itself.
If a doctor, after a thorough examination of a sick child, diagnoses migraine (headache is caused mainly by poor circulation in the vessels of the meninges), appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Currently, there are a number of effective therapeutic methods for the acute phase (relief of the attack, including accompanying symptoms) and prevention of migraine.
Treatment should be entrusted to a specialist. Of course, you cannot self-medicate (i.e., treat by parents). Instead of conventional analgesics, specific drugs in doses adapted to the child’s body are more suitable for use.
Tension headache in children
We are talking about the most common cause of headaches in children, the origin of which mainly lies in stress. This disease occurs in approximately 80% of cases.
As noted above, in some cases, tension headache manifests itself as a migraine, but sometimes, especially in young children who cannot talk about their feelings, there is restlessness, sometimes hyperactivity, irritability, nausea, and vomiting.
A typical symptom is increased sensitivity to the point of painful reaction in these children when the muscles in the neck and shoulders are compressed.
In particular, chronic problems of this kind can sometimes be incorrectly assessed, even by some doctors, as minimal brain dysfunction, ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) or as a behavioral disorder. In the chronic form of the disease, sleep disturbances appear. The child has difficulty falling asleep, has restless or too deep sleep, a typical manifestation is waking up in the morning in a tired, overwhelmed and irritated state.
Headache and spine
Headaches caused by disorders of the cervical spine occur not only in adults, but also in the younger generation. A common cause is a child falling from a height or a head injury, sometimes even several years ago.
The problem may lie not only in the actual injury, but also in the sudden movement of the cervical spine, which leads to its hidden damage and subsequent blocking.
Another common cause of spine-related headaches is poor posture and posture of the head and neck.
Pain of this type is most often localized in the back of the head, spreading to the forehead. Sometimes my neck and shoulders hurt.
The warning against cervical spine manipulation in adults is doubly true in the younger population.
In place, a light approach to relaxing the muscles in the neck and shoulder area, allowing subsequent spontaneous correction of the cervical spine and its connection with the skull.
In order for treatment to be effective and safe, it should be entrusted to a specialist with extensive experience in treating children's spine.
If the cause of the problem is poor posture, you must first release the blocked cervical spine, and then immediately begin systematic actions aimed at correcting your posture, from the soles of your feet to your head. This treatment should be carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of each child, including his age and physical condition.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/596a6a468146c12e34f9afda/597635d450c9e567255cc3fb
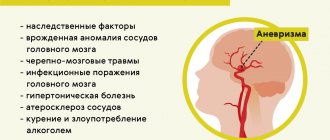
Possible diseases
When a child complains of pain in the forehead, we can assume the presence of certain diseases:
- Changed intracranial pressure. Intracranial pressure (ICP) increases in children prone to surges in blood pressure. Pain in the forehead and temples can be intense, radiate to the back of the head, and encircle the entire head. An attack can be triggered by a change in weather, severe fatigue, stress, or disruption of the thyroid gland. Most children with ICP have difficulty learning, they have poor memory, decreased concentration, and impaired vision. Parents should monitor their child for blood pressure surges and give him medications prescribed by the doctor. Intracranial hypertension is treatable, the main thing is not to let the disease take its course and consult a doctor in time
- Diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, frontal sinusitis). With sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, frontal sinusitis, natural breathing is blocked, the sense of smell is lost, and thick green mucus is constantly released from the nasal passage. In severe cases, the mucus may not come out. The temperature remains normal or rises slightly. At the same time, the forehead hurts, especially in the morning and evening hours. The inflammatory process in the nasal sinuses requires immediate qualified treatment
- Bacterial, viral pathologies (malaria, influenza, typhus, meningitis, botulism). Dull pain in the forehead in infectious diseases is accompanied by fever, cough, runny nose, muscle and joint pain, and lacrimation. General intoxication of the body can cause unbearable pain in the head, especially in children 11-13 years old. A sudden attack of pain can trigger meningitis. This infectious disease affects the lining of the brain, causing vomiting and tension in the muscles of the back of the head.
- Acute disease of the nervous system. With disorders of the nervous system in children, persistent drowsiness, apathy, and headache are observed. Parents need to contact doctors so as not to worsen the condition. If such signs are ignored, the patient may fall into unconsciousness or coma.
When a child has a headache in the frontal region and a body temperature above 38.5 degrees, it is necessary to give him an antipyretic. It will not eliminate the cause of the disease, but will relieve dangerous symptoms until the ambulance arrives.
Pain in the eyebrow above the eye in children
If the eyebrow hurts slightly, then most people do not pay attention to the condition that has arisen. But the reasons why an eyebrow hurts are not always harmless; sometimes the symptom that arises is the first sign of the development of a serious illness. Let's consider what can hurt above the eyebrow and whether you always need to see a doctor.
Frontit
The pathology most often appears as a complication of sinusitis, but can also occur as an independent disease. The frontal sinuses are located in the eyebrow area, on either side of the center of the face.
Causes
Provoke the development of the disease:
- frequent hypothermia;
- cold infections;
- diseases of the maxillary sinuses;
- chronic rhinitis.
If the brow ridges hurt with sinusitis, then the cause of the pain in the eyebrows is penetration from the maxillary sinuses into the frontal sinuses.
Symptoms
Signs of frontal sinusitis are similar to manifestations of sinusitis:
- headache;
- a runny nose appears;
- temperature rises;
- the pain intensifies when pressing on the eyebrow.
The headache is localized in the area of the brow ridges and intensifies when bending forward.
Patients often note that not only their eyebrows hurt, but also their eyes and bridge of the nose.
Treatment
The main therapy is aimed at cleansing the frontal sinuses from accumulated exudate and suppressing the inflammatory process. For treatment use:
- antibiotics;
- drops to reduce swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- antipyretics;
- analgesics and NSAIDs.
If there is a strong accumulation of purulent exudate, puncture of the frontal sinuses is indicated to administer an antiseptic and remove the accumulated pus.
Where to contact
When the pain above the eyes in the eyebrow area intensifies when pressed, you should visit an otolaryngologist.
Cervical osteochondrosis
Disease in the upper part of this spine can cause pinching of a nerve root in the back of the head.
Who will help
When your eyebrow hurts due to osteochondrosis, you need to visit a vertebrologist or neurologist.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Innervation of the facial muscles is carried out by 3 branches of the facial nerve: upper, middle and lower. Damage to the upper nerve plexus results in pain in the eyebrows and eyes.
Provoking factors
The causes of damage to the upper part of the trigeminal nerve are different. Commonly encountered ones include :
- hypothermia;
- bruises of the eyebrows and forehead;
- infectious inflammation of soft tissues (most often provoked by the herpis virus);
- neoplasms;
- vascular spasms.
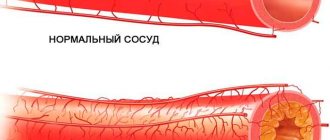
Often the cause of the development of neuralgia of the upper part of the nerve is atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels or disturbances of cerebral blood flow.
Who to contact
If you have pain above the eyebrow caused by neuralgia, you should visit a neurologist. If there is a history of injury to the eyebrow, then additional consultation with a traumatologist will be required.
Source: https://avia-biletiks.ru/bolit-brov-nad-glazom-u-detej/
Cluster (bundle) tension pains
The malaise has a high intensity that even an adult cannot endure. Cluster pains are short-term (from 15 minutes to 3 hours), but often recur. This type of headache is rare in children, affecting boys more often. Accompanied by nasal congestion, nausea, increased sweating, excitability, anxiety, watery eyes, sensitivity to bright light and sharp sounds.
The attack passes as suddenly as it begins. The cause of frequent unbearable boring pain in children may be a disorder of the nervous system, vascular pathologies, eye diseases, or ENT diseases. Doctors have not fully studied all the causes of cluster pain. Treatment is usually carried out by inhaling oxygen through a mask and drugs that stop attacks.
When a child has a headache in the forehead area, you need to distract him from the pain, offer warm sweet tea, give a Glycine tablet under the tongue, which relieves brain spasms, and do a simple massage from the back of the head to the shoulders. This will improve blood circulation and normalize the condition of the baby.
Clinical manifestations
In children over 5 years of age, the problem usually makes itself felt after lunch. Quite rarely, the baby experiences headaches in the morning.
Discomfort usually develops gradually and is bilateral. More often the pain is constant rather than sharp. The onset of the attack can be classified as moderately severe.
Regardless of the cause of headache in children 5 years old, the discomfort can be determined by the following:
- tearfulness;
- moodiness;
- loss of appetite;
- indifference to communication and games;
- agitation or apathy;
- complaints of headache.
Symptoms
If the child does not yet know how to talk and explain that he has a headache, the malaise can be determined by:
- Unreasonable irritability.
- Excessive tearfulness.
- Redness of the sclera of the eyes.
- Lethargy.
- Vomiting like a fountain.
- Tremor of the limbs.
- Frequent yawning.
- Pulsation of the fontanel.
- An increase in the size of the skull (with hydrocephalus, this is the main symptom in newborns).
Children who have reached 4-5 years of age are not always able to report their well-being. Parents should pay close attention to their behavior. If a child avoids active games, goes to bed, and often touches his head, these may be clear signs of cephalgia. It is necessary to pay attention to the localization of pain, the frequency and time of its occurrence, and accompanying ailments (nausea, fever, runny nose, vomiting, photophobia).
Dangerous symptoms
An unexpected headache in a child in the frontal region can appear due to viral, infectious, dental diseases, or more serious illnesses (brain tumor, otitis media, pathology in the cervical spine). You should not waste time and delay visiting a doctor if:
- Sudden and increasing attacks of cephalalgia.
- Impaired coordination.
- Pain in the head area at night and in the morning.
- Retardation, incoherent speech.
- Elevated temperature.
- When seizures occur.
Preventive recommendations
To reduce the risk of headaches, you should follow the following advice from doctors:
- expose the child to less nervous tension, create a favorable climate in the family;
- maintain proper nutrition;
- limit time spent at the computer;
- adhere to the work and rest schedule.
A headache is only a symptom that indicates a specific disease. The basis for successful treatment and minimizing the risk of negative consequences is timely consultation with a doctor and initiation of therapy.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a child has pain in the frontal part of the head, the pain recurs regularly, this condition cannot be ignored. Moreover, give drugs that adults use to save themselves from headache attacks. The only painkillers approved for children are Ibuprofen and Paracetamol. But whenever pain appears, they should not be used.
Only a doctor can determine the cause of cephalgia and prescribe appropriate treatment. Problems related to headaches are dealt with by: pediatrician, neurologist, otolaryngologist, dentist, hematologist. The doctor refers the child to:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
In case of a concussion and suspected traumatic brain injury, diagnostics are carried out to identify hemorrhages, hematomas, swelling, and abnormal changes in brain structures:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
- Echoencephalography.
- Radiography
- CT (computed tomography).
The treatment course is determined based on research results. If a child has a forehead pain due to a migraine, medications are prescribed to stop the attacks. Neuralgia is treated with medications and physical procedures. Headache, dizziness, loss of balance, nausea indicate severe physical fatigue. In such cases, the best medicine is proper rest.