Chronic headache, dizziness, unpleasant noise in the ears - similar phenomena occur in older people, and in middle-aged, young, and children. Often, contemporaries do not take episodes of cephalalgia very seriously, attributing the development of pain syndrome to overwork or mild malaise. Meanwhile, a headache of even moderate or weak intensity may indicate serious problems in the circulatory system.
Vascular headache (VHA) is a common phenomenon inherent in a variety of diseases of the cardiovascular system and neurological defects. The high frequency and intensity of pain in this form of cephalgia is due to the anatomical features of the body. In the structures of the cranium there are many nociceptors - special receptors, the irritation of which causes the sensation of pain.
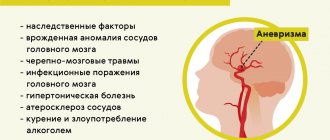
Causes of pain
Attacks of vascular headache occur when:
- Hypertension. A persistent increase in blood pressure levels disrupts the tone of blood vessels, causing thickening of their walls and narrowing of the lumen. As a result, blood circulation in the skull area is disrupted, which causes cephalgia.
- Hypotension. A sharp decrease in blood pressure negatively affects the condition of the blood vessels of the brain. In severe cases of the disease, the permeability of the arterial walls is impaired, which causes headaches.
- Atherosclerosis of the head and neck. When atherosclerotic plaques are deposited on the walls of the arteries, blood flow is disrupted. Functional areas of the brain are deficient in oxygen and nutrients. The body's reaction is severe cephalgia.
- Anomalies in the development of veins and arteries of the brain. Cavernous angioma and arteriovenous malformation are more often observed. Pathologies are expressed in the proliferation and interweaving of blood vessels, forming a benign neoplasm. The feeling of discomfort and pain is associated with impaired blood flow.
Another reason that causes cephalalgia of a vascular nature is VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia). This deviation causes a violation of the regulation of the tone of the venous walls.
How is diagnosis done?
To make sure that the headache is vascular in nature, a routine consultation with a specialist is not enough. The patient will have to undergo a full examination, which includes the following manipulations:
- Ensure constant monitoring of changes in blood pressure.
- Donate blood for a detailed analysis.
- Provide measurement of pressure inside the skull.
- Take an x-ray of the skull. If the need arises, spinal radiotherapy may also be required.
- Sometimes a CT scan will be helpful.
- Cerebral angiography helps in making an accurate diagnosis.
- It is often necessary to resort to magnetic resonance imaging.
- A thorough examination of the condition of the fundus will also be useful.
Symptoms of the disease
With these disorders, the following symptoms occur:
- Compressive, bursting or throbbing pain in the head;
- Dizziness;
- Loss of coordination;
- Impaired perception of the surrounding world;
- General malaise;
- Noise in ears;
- Nausea;
- Flashing of flies before the eyes;
- Fainting conditions.
Unpleasant sensations spread to different parts of the head: occipital, frontal, temporal. Sometimes the pain radiates to the ear, cervical spine, or eye sockets.
Cephalgia can take on the character of a migraine, spreading to only one part of the head.
Treatment of headaches
Treatment does not consist in suppressing the symptom, but in eliminating the cause that provoked it.
To identify the disease, the patient is prescribed the following diagnostic measures:
- Clinical and biochemical blood test;
- MRI or CT scan of the brain;
- ECG;
- Duplex scanning of the arteries of the head and neck.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a course of therapy.
For hypertension, which causes pain in the blood vessels in the head, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and calcium antagonists are prescribed.
To treat hypotension, medications containing caffeine and herbal tonics are prescribed.
If a patient is diagnosed with atherosclerosis, then he is prescribed statins - drugs that lower cholesterol levels in the body. Products containing Omega-3, herbal-based sedatives and tablets for stabilizing blood pressure are indicated.
If you have atherosclerosis, follow a special diet. Vegetable and animal fats, sweets, meat, and fatty dairy products are excluded from the diet.
Malformation of cerebral vessels is usually treated surgically. If the symptoms of the pathology are not pronounced, conservative treatment is prescribed. In other cases, resection of malformations or embolization of abnormal vessels is performed.
This pain in the head area is always associated with serious pathologies, so if such a symptom appears regularly, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. The exact cause will be determined after a set of diagnostic procedures.
Clinical picture
To relieve vasospasm, let’s analyze the nature of this process. Remember, medications can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. When talking about the critical condition of the body, neurologists refer to all types of connections: capillaries, arteries, veins, arterioles. They are smooth on the inside and are reduced according to the following algorithm:
- The signal arrives through nerve endings or is transmitted through hormonal cells in the blood;
- There is a change in electrolyte ions, which are responsible for the charge of the membrane;
- The process of reduction begins;
If a failure occurs at one of these stages, this leads to destabilization of the brain process. The drugs will help relieve spasms when used correctly.
It is impossible to exclude the possibility of a reaction to a sharp change in temperature (going out in frosty weather without outerwear) in the form of a reflex, or the disease could be a reaction to any other pain in the body, to poor blood circulation in the cervical region.
Which doctor should I contact?
Often, after physical exertion or mental stress, people feel worse. The nature of the pain can be varied. Compressive, pressing, throbbing pain in one side of the head is possible.
Pain during exercise is often functional in nature. They can occur for many reasons:
- Changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure;
- Stressful state during physical activity;
- Heat and stuffiness in the room;
- Dehydration is often the cause of headaches;
- Eat a large meal before training;
- Overweight people often suffer from hypoxia during exercise.
The likelihood of illness is higher in people with specialties: programmer, accountant, driver, who spend many hours at the computer or constantly strain the muscles of the eyes and neck.
Persistent cephalgia, which occurs regularly, requires mandatory consultation with a doctor in order to exclude serious pathology and prescribe the correct treatment in a timely manner.
The initial appointment should be made by a therapist. He will conduct a general examination, measure blood pressure, write out directions for tests and refer you to specialists.
If you have unpleasant sensations in the head and neck area, it is good to have a home blood pressure monitor, with which you can track pressure surges in different life situations. A rise in blood pressure after physical activity can often be the cause of pain.
The doctor gives a referral to an otolaryngologist to rule out chronic otitis media, sinusitis or inflammation of the maxillary sinuses (sinusitis).
The doctor can give a referral to an ophthalmologist to identify changes in the fundus and possible vision defects.
Most of the causes of discomfort in the head are associated with neurological symptoms, so diseases accompanied by head pain syndrome are treated by a neurologist.
Vasoconstriction in babies
Complaints about cephalalgia are more common in adults, but headaches also appear in childhood.
Headaches in young children are caused by adaptation to new living conditions, accompanied by increased intracranial pressure. This phenomenon is especially characteristic of infants who have suffered birth trauma and hypoxia.
You can suspect a headache in a small child if he shows lethargy, stiffness, restlessness, often spits up, spontaneously shudders and throws his head back. In this case, it is worth consulting a pediatric neurologist.
In older children, cephalgia can be caused by the following reasons:
- Infectious diseases (otitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, etc.). In this case, if a child complains of severe pain in the head, a thorough examination is required in order to promptly recognize possible serious complications, such as meningitis.
- Head injuries. Due to their mobility, children often fall, and the consequences of the injuries they receive sometimes do not have pronounced symptoms. If, some time after a fall or hit to the head, a child complains of cephalalgia, he should be seen by a doctor.
- Stressful situations associated with adaptation to kindergarten, school, etc.
- Migraine. Doctors believe that there is a hereditary predisposition to this disease, so if the mother is familiar with it, it can also appear in the child.
- Visual impairment and incorrectly selected glasses.
- Poor circulation in the brain, provoked by changing weather conditions, eating foods with a high content of artificial additives that cause vasoconstriction (for example, processed meat products, cheese), prolonged exposure to a stuffy room, and dehydration.
Pathology of the arteries and veins of the head is also observed in children, but much less frequently. The causes of narrowing of blood vessels are lack of physical activity, mental stress, and poor diet. In infants, the disease is caused by congenital underdevelopment of the circulatory system, pathology of the kidneys and heart.
This disease can be found in both older people and children. People living in big cities suffer especially often from vascular spasms. Unfavorable environmental conditions, the entry of toxins into the body, and lack of oxygen contribute to the appearance of spasms.
With age, blood flow in the vessels worsens due to a decrease in their elasticity. In children, the causes of vasospasms are somewhat different.
Vascular pathologies in children’s bodies are caused by the same reasons as in adults. That is, the walls of the blood vessels that are responsible for feeding the brain are also affected.
What tests are usually prescribed?
At an appointment with a neurologist, a physical examination of the patient is performed: basic neurological reflexes are checked and the neck muscles are examined.
The doctor writes out a referral for tests: general blood test, biochemical blood test, blood sugar test.
A general blood test with an increase in ESR or an increased content of leukocytes indicates inflammation in the body.
Blood biochemistry may indicate a deficiency of one of the vital elements, which leads to discomfort in the head area.
Low blood glucose levels are often accompanied by cephalgia, dizziness and weakness.
The doctor may write a referral for additional tests:
- The gas composition of arterial blood can reveal cerebral hypoxia.
- A blood test for hormones determines various abnormalities in the functioning of the hypothalamus.
A neurologist can give a referral to one or more diagnostic methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - excludes the presence of various neoplasms (tumors and cysts), aneurysms. The photographs clearly show post-traumatic defects, neurodegenerative abnormalities, and changes in blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis.
- Computed tomography (CT) is the most informative method for studying the brain. It gives a clear idea of pathological changes in the skull and brain, pathology of bone tissue, blood vessels and brain structures. Provides information about the consequences of traumatic brain injuries. The disadvantage of this method is the significant radiation dose during the study.
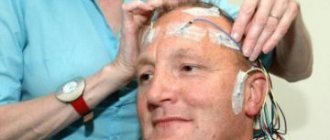
- Electroencephalography gives an idea of the presence of pathological changes in blood vessels and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Doppler ultrasound (ultrasound of the head and neck) - shows the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries; narrowing and tortuosity of the arteries, leading to brain hypoxia; peripheral vascular resistance.
- Rheoencephalography (REG) - gives an idea of the tone and blood flow of blood vessels. Using REG, the following are diagnosed: hypertension, atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- MRI of the cervical spine - the presence of cervical osteochondrosis can cause pain in the head and neck, which intensifies when turning the head.
- Rheovasography of cerebral vessels (RVG) - shows the quality of blood flow through the great vessels, evaluates collateral circulation.
- Radiography will be less known. In the image you can only see the bone structures of the skull, soft tissues are not visible.
There is no need to panic when scheduling such a serious examination. The doctor excludes rare severe pathologies and looks for the causes of the pain process.
Based on the studies, if no serious organic lesions are found, the cause of the disease is usually diagnosed. It develops as a result of: vascular spasms, cerebral hypoxia, hypertonicity of cerebral vessels, hormonal imbalances, vegetative-vascular dystonia or osteochondrosis, provoked by physical or psycho-emotional stress.
The mechanism of occurrence of VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (IBC code 10) refers to pathological changes in the central nervous system code G with a clarifying diagnosis - 44. 1 headaches of a vascular nature, not classified in other ranges without additional clarification.
That is, for unspecified reasons. This means that the development of VSD is influenced by both unfavorable external circumstances and internal disorders in the body. By changing, blood pressure increases the movement of blood into the vascular beds of the brain, which leads to stretching of the walls, and as a result, the tone and elasticity of the tissues decreases.
In this case, both arterial and venous channels are affected.
Enlarged vessels put pressure on the meninges, causing depression of sensitive nerve endings, which leads to pain and a throbbing headache.
The main sign of the development of VSD is high or low blood pressure and a headache that appears suddenly, is characterized by moderate intensity, and is accompanied by discomfort and nausea. When moving or external stimuli, the migraine worsens.
Upon visual inspection, it is noted:
- Temporary or permanent pain;
- Meteor dependence;
- Redness of the capillary network of the eyeball;
- Feeling of nasal congestion;
- Swelling, heaviness, swelling of the eyelids;
- Sore throat;
- Emotional disorder, constant tension;
- Pale skin;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Darkening in the eyes;
- Decreased hearing and vision.
In this case, the signs of headache depend on the type of vascular disorder:
- Cardiac - a symptom of arrhythmia, tachycardia, extrasystole;
- Hypotensive - muscle weakness, chilliness, fainting, pallor;
- Hypertension—rapid heartbeat, fatigue.
Groups of drugs effective for episodic attacks of pain
Medicines to treat this pathology are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They have an analgesic effect, relieve inflammation, and eliminate swelling.
Often prescribed:
- Ibuprofen-400 mg per day;
- Ketoprofen-100 mg/s;
- Naproxen-500 mg/s;
- Meloxicam-7.5-15 mg/s;
- Celecoxib-200 mg/s.
Most NSAIDs have a negative side effect: with long-term use, they negatively affect the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, including the development of drug-induced gastritis.
Medicines Meloxicam and Celecoxib are new generation drugs that do not have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. The disadvantages of using these drugs include the relatively high price.
Analgesics are often used at home to relieve an attack. They do not treat the disease, but only relieve pain. Drugs in this group are suitable for stopping episodic attacks, but their systematic use leads to the occurrence of abuse syndrome.
During an attack of pain, you can take Paracetamol-100 mg, Citramon, Analgin-500 mg or Mig 200-400 mg.
If the examination revealed the appearance of cephalgia after exercise as a result of increased blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe medications prescribed at an early stage of the development of hypertension. These include: vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, calcium channel blockers.
Self-prescribing antihypertensive drugs is unacceptable. Self-medication leads to serious consequences.
For muscle tension, drugs from the group of muscle relaxants are used as part of complex treatment. They relax the spasmodic muscles of the head and neck, relieving pain of a spastic nature, and help restore blood flow.
Often prescribed:
- Mydocalm-150-450 mg per day;
- Sirdalud (Tizanidine) - 4 mg/s;
- Baclofen-15 mg/s.
Nootropic drugs are often prescribed as part of complex treatment: Phenibut, Nootropil, Glycine. Nootropics have an activating effect on brain function and increase its resistance to damaging factors. The drugs improve cerebral circulation and eliminate the consequences of traumatic brain injuries.
Sedatives in combination with basic drugs lead to muscle relaxation and decreased vascular tone. Taking tranquilizers helps relieve pain, but this type of medication quickly causes drug dependence with withdrawal symptoms.
Sedatives that are not addictive: Afobazol, Atarax; alcohol tinctures of valerian, motherwort, Maryina root.
For severe attacks, a combination of drugs is used: Sirdalud 2 mg + Aspirin 500 mg or Analgin 250 mg + sedative.
The use of vitamin B complexes has proven itself. Vitamins B1, B6, B12 have a beneficial effect on the central nervous system and restore the structure of nerve tissue. Vitamin complexes are often prescribed: Neuromultivit, Milgamma, Neurovitan.
If attacks of pain recur more than 10 times a month, a course of treatment with Ibuprofen at a dose of 400 mg per day for 2-3 weeks and treatment with muscle relaxants is prescribed for 2-4 weeks.
There is no single scheme for pain relief. Depending on the cause, each patient needs an individual selection of drugs.
Treatment of chronic disease
Sometimes cephalalgia becomes chronic. The pain occurs every day, continuously, with varying degrees of intensity.
Tricyclic antidepressants are prescribed for a long course of 2-6 months. They relieve pain and help normalize the psycho-vegetative state of the nervous system.
Amitriptyline 10-100 mg/s is most often prescribed, the dose is increased gradually. The drug relieves pain well, but has many negative side effects and is addictive.
As an alternative, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are prescribed: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline. The course of treatment is at least 2 months. These drugs have less toxicity.
In addition to prescribing drug therapy, the doctor will recommend massage, a course of physiotherapy or acupuncture.
Contraindications for use
Any medications have both indications for use and contraindications. The instructions attached to them indicate possible side effects resulting from their use, cases in which their use is not recommended.
General, frequently noted contraindications to the use of painkillers:
- Individual intolerance to the drug or drug components.
- Pregnancy, lactation period. This is due to the high ability of drugs to penetrate the placenta and be secreted into milk, which adversely affects the life of the fetus or newborn child. In extreme cases, when it is impossible to get rid of long-term pain in any other way, it is possible to use Paracetamol.
- Ulcer, erosive lesions of the digestive organs.
- Hepatitis.
- Dermatous manifestations.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Hematopoiesis disorder.
- Allergy.
- Impaired liver and kidney function. The use of medications is recommended only under the direct supervision of a physician.
- Childhood.
Acetylsalicylic acid is not used under the age of 14 years due to the risk of developing Reye's syndrome. This is a form of acute liver failure found in pediatrics.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have an extensive list of contraindications for their use, especially for inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The exception is Paracetamol. It has a gentle effect on the body, without blocking the process of prostaglandin synthesis in peripheral tissues.
Frequent use of medications for pain is contraindicated for all categories of people.
The result of long-term medication use will be:
- Strengthening, more frequent attacks of pain, migraines;
- Development of pain into a chronic form;
- Development of pathologies of the digestive system;
- Provoking an allergic reaction;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
Venous encephalopathy
Pain syndrome due to impaired venous outflow is caused by prolonged venous stagnation due to cardiovascular, respiratory failure, and spinal diseases.
Characteristic clinical manifestations:
- morning, night bursting pain;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- syndrome of diffuse small focal brain lesions;
- asthenization;
- impaired consciousness during coughing attacks.
The phenomena of edema gradually develop, which further aggravates trophic disorders and causes paresis of the microcirculatory bed.
Dangerous combination with other medications
Taking several medications together can cause an undesirable reaction in the body: weaken the effect of the drug, overly enhance its effect, cause side effects, or even sometimes lead to death. People suffering from chronic diseases should take this seriously.
The combination of the following drugs is not recommended:
- NSAIDs and Cardiac aspirin. These drugs compete with each other in the body for the same enzyme. Their combined use reduces the effectiveness of aspirin. Both drugs have side effects on the stomach lining, which increases the risk of ulcers and stomach bleeding.
- NSAIDs and Warfarin. Causing a side effect in the form of decreased blood clotting, NSAIDs in interaction with Warfarin increase the risk of developing dangerous bleeding.
- Painkillers and antidepressants. The combined effects of such drugs provoke the formation of gastric and intestinal bleeding. Accompanying symptoms: anxiety, increased body temperature, increased breathing and heart rate.
- Strong sedatives, Phenazepam, and antibiotics. The group of antibiotics is most dangerous in its interaction with other drugs. This is due to the serious negative side effects that can occur when consuming them.
Taking painkillers requires caution and care. Avoid systematic use of medications without a doctor’s recommendations, and do not combine medications with other medications to avoid side effects.
Do not prescribe a course of treatment on your own, without prior consultation with specialists. Compliance with these rules will allow you to get rid of pain without negative and dangerous consequences for the body.
Arterial hypotension
A tendency to low blood pressure is dangerous because the risk of developing coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic stroke, and dementia increases. It may be a variant of the norm, for example, in athletes.
In the case of a pathological course of hypotension, it can develop acutely or be chronic, persistent or intermittent.
Headache with hypotension is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- staggering when walking;
- increased fatigue;
- blurred outlines of objects when looking in front of you;
- increased breathing;
- the appearance of anxiety, fear;
- tremor in the fingers.
Complications of various types of headaches
Headaches are:
- Primary
- Secondary.
Complications of primary headache
In particular, she has no complications. It includes hemicrania, tension-type headache, PHB, trigeminal autonomic cephalgia.
Migraine is a one-sided, throbbing pain that occurs due to bright light, noise, fatigue, eating foods such as chocolate, spices, cheese and wine. The disease is based on irritation of the nervous system of the head and neck, after which the blood joints narrow and sharply expand. Main complications of migraine:
- Status migraine is a severe attack. The disease causes swelling of the brain, seizures, stroke, heart attack,
- Migraine infarction - a migraine attack with an aura lasting 60 minutes,
- Migraine-associated seizures,
Complications of secondary headache
It occurs as symptoms of other diseases such as head trauma, cerebral vascular damage, infection, mental illness, damage to homeostasis and others. It disappears when the underlying disease is treated.
Intracranial hypertension
Intracranial hypertension is an increase in intracranial pressure. When pressure increases to 30 mmHg, blood circulation in the brain is disrupted. If it rises above 50 mm Hg, death is possible. A person experiences a pressing headache, nausea (in the morning), fatigue, drowsiness, depression of consciousness and prolonged hiccups. Pathology can cause structural damage.
Intracranial hypertension has serious complications:
- Cerebral ischemia, resulting from compression of the brain substance,
- Dislocation – displacement of brain structures,
- Wedging.
Giant cell arteritis (Horton's disease)
Giant cell (temporal) arteritis is an inflammation of the lining of the red blood joint, which affects the arteries of the temporal region of the head. The causes of the disease have not been fully identified. The disease occurs due to immune disorders. Pathogens enter the body and produce antibodies that cause inflammation.
Complications:
- Blindness. Vision loss is irreversible. Occurs as a result of impaired blood supply,
- Stroke. Rarely found
- Aortic aneurysm. Can happen at any time and lead to internal bleeding.
Meningitis
Meningitis is a lesion of the meninges. Pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, protozoa and fungi) cause disease. When sick, patients experience headaches and nausea.
Complications after meningitis:
- Paralysis,
- Blindness,
- Deafness,
- Ischemic stroke,
- Intellectual impairment
- Paresis,
- Convulsive syndrome,
- Hydrocephalus,
- Epilepsy,
- cerebral edema,
- SIADH
- Speech disorders
- Brain abscess
- Aneurysm,
- Transverse myelitis,
- Sphincter dysfunction.
The chance of death from bacterial meningitis is 10%. The mortality rate for viral meningitis is much lower (only 1%).
Glaucoma
Glaucoma – intraocular pressure (IOP).
The process begins with deterioration of peripheral vision. If left untreated, the nerves of the eye die.
The disease can occur due to old age, farsightedness, diabetes, hereditary predisposition, etc.
Complications:
- Blindness,
- Nerve dystrophy.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary sinuses that occurs as a result of complications of rhinitis. Inflammation occurs when viruses and bacteria enter the maxillary sinuses.
Complications:
- Chronic sinusitis lasting 12 weeks
- Frontitis - inflammation of the frontal sinus,
- Meningitis,
- Osteomyelitis,
- Hearing and vision problems.
Brain hematoma
A brain hematoma is an injury in which blood enters the skull from the joint. As a result, blood compresses the brain. This condition threatens human life and therefore requires timely treatment. The causes of the disease are arterial hypertension, tumors and injuries.
Intracranial hematoma causes disturbances in the brain. The blood squeezes the brain and oppresses it.
Complications:
- Deterioration of blood supply and blood outflow,
- Increased intracranial pressure,
- Problems with the movement of cerebrospinal fluid,
- Disorders related to movement and feeling. Appears due to limited signal transmission.
Factors provoking vascular disease
Stressful situations, constant mental stress and neuroses have a negative effect on the human body. An unhealthy lifestyle is another cause of stenosis of blood vessels. Poor circulation is caused by:
- Smoking, alcoholism.
- Gaining excess weight.
- Sedentary work.
- Not getting enough sleep.
- Lack of adequate loads.
- Oxygen deficiency: due to constant presence indoors, living in a polluted city.
- Foods oversaturated with trans fats.
Why is the gray matter poorly supplied with blood due to these factors? The reason is that vessels of different sizes in the brain become thinner, deformed, and atherosclerotic plaques grow on their walls. A person may have a genetic predisposition to narrowing the lumen of blood vessels in the brain. But the disease will not develop if you adhere to a diet and allow feasible exercise.
Brain vascular pathology can develop at a young age, even in a child, but most often it occurs in older people. The prognosis is most favorable for young patients. The chances of recovery also increase when the disease is diagnosed in the early stages and competent therapy is prescribed to the patient in a timely manner.
What is dangerous, what does a decrease in the lumen of veins and arteries lead to? Narrowed arteries can cause the development of the following pathologies in humans:
- decreased intelligence;
- feeling of annoying noise in the ears;
- memory problems;
- systematically recurring migraines;
- absent-mindedness, etc.
The most common anomaly of the development of arteries and veins of the brain is arteriovenous malformation and cavernous angioma. If the first signs of the disease appear in the form of a headache, they speak of a pseudotumor or torpid variant of the course.
In this way, the disease manifests itself in childhood. Periodically, the headache is accompanied by generalized convulsive seizures or equivalents in the form of a fleeting loss of consciousness without convulsions.
The danger of these two diseases is that sooner or later a cerebral hemorrhage will develop. This occurs more often in young, able-bodied people.
The risk of developing fatal complications or disability after hemorrhages from arteriovenous malformations and cavernous angiomas is so high that if this disease is detected, it is necessary to immediately decide on its radical treatment.
Literature
- L. G. Akhmadullina: Headache
- D. Marcus: Headache
- Evgeny Rozner: Headache. Migraine
- Gyuzal Tabeeva: Headache. Management
- Alekseev, Alyabyeva, Amirov: Glaucoma. National leadership
- V. I. Morozov, A. A. Podshivalin, G. E. Chigvintsev, G. A. Yulmetov: Natal damage to visceral organs
- V.N. Shtok: Headache. Practical guide
- A. I. Ermolaeva, G. A. Baranova: Headache
- A. M. Satybaldyev: Giant cell arteritis. Part 1. Terminology, classification, clinical manifestation, diagnosis
- Kolosova O. A., Osipova V. V.: Classification of headaches
Predisposing factors
Provoking factors for the occurrence of headaches of a vascular nature are:
- stress;
- physical inactivity;
- autonomic dysfunction;
- somatized depression;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- endocrine pathology;
- heredity;
- ecology;
- smoking, alcohol, other bad habits;
- impaired glucose tolerance;
- venous dysfunction;
- diet violation.
With various somatic pathologies, headaches have certain nuances and course features.
What types of headaches require immediate emergency care?
Headache can appear for simple reasons that do not require attention, and in some cases it can indicate the development of serious conditions that pose a threat to human life.
It is recommended to call an ambulance if you experience pain in your head:
- are too intense and do not disappear after taking painkillers;
- appear and intensify with any movement of the head;
- accompanied by nausea, dizziness, darkening of the eyes;
- appeared as a result of traumatic injury;
- accompanied by confusion;
- occur in parallel with speech impairment and numbness of one part of the body or face;
- accompanied by a violation of orientation in time and space.
Symptoms may indicate critical conditions that require emergency medical attention.
Why do the vessels of the limbs hurt?
For normal brain function, it needs nutrition, which is provided through constant blood circulation. For this purpose, numerous capillaries pass through the brain tissue. As a result of exposure to negative factors on the body, blood flow may be disrupted due to prolonged tissue contraction or spasms of the vascular walls.
Vasospasm or, as it is also called vasospasm, is a temporary narrowing of its lumen, which is transient in nature. The cause of this condition is a reflex contraction of the muscle tissue of the vessel wall.
Capillaries or small arteries are primarily susceptible to vasospasm. As a result, blood flow through them is limited or completely stopped.
Oxygen starvation of brain cells leads to various disorders in the functioning of the human nervous system.
Often, pain in the eyes is accompanied by redness of the blood vessels of the eyeball. The red color of the vessels sometimes indicates the presence of a disease, especially when the pain does not go away for a long time.
There are many reasons that cause pain and redness in the blood vessels of the eye. But the persistence and duration of this phenomenon confirms the seriousness of the problem requiring medical intervention.
We list some causes of pain in the blood vessels of the eye:
- the eyes are in constant tension;
- personal insensitivity or incorrect use of contact lenses;
- allergy;
- infectious infection;
- high blood pressure;
- disruption of the endocrine system.
In addition, the blood vessels in the eye may burst due to physical or nervous stress. The cause of burst blood vessels in the eyes can also be a typical lack of sleep. In this situation, it will be enough to normalize the daily routine.
To relieve tension in the eye vessel, it is enough to carry out a gentle massage, stroking the eyelids with your fingertips. It is recommended to simply cover your eyes with your palms and relax them for two to three minutes.
Your daily routine has a big impact on your eye health. Sleep should last at least 8 hours, this time is enough to restore the mucous membrane of the eye. Your eyes should also rest throughout the day. Work at the computer should be interrupted for a 10-minute rest.
Why you should always seek help from a doctor for headaches
If a person has been bothered by discomfort in the head area for a long time, it is recommended to consult a doctor. After conducting a series of examinations, collecting anamnestic data and complaints, he will be able to establish the cause of their occurrence, make a diagnosis and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen.
Headache is a rather complex symptom; it can be primary (in the form of migraine, tension headaches and pain not associated with structural lesions) and symptomatic (occurs against the background of injuries, vascular disorders, infectious lesions, the use of drugs and other chemicals, metabolic disorders, pathologies of the skull, eyes, cranial, facial structures).
Pain can be caused by pathologies of the cervical spine, depression, VSD, and arterial hypertension. These conditions require proper therapy, otherwise the disease becomes chronic and can cause severe complications.
Pain in the head with VSD, venous insufficiency and increased blood viscosity
Very often, cephalalgia is diagnosed with a disease such as vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). In the last ten years, this deviation has been observed in every third patient of the older age group to varying degrees (mild, moderate, severe). With this pathology, there is a significant decrease in blood pressure while the patient is completely calm. Headache with vascular dystonia is aching in nature, diagnosed at any time of the day and occurs suddenly, it is almost impossible to eliminate it.
VSD can be inherited or be an acquired disorder, depending on the environmental situation and diet. In most cases, dystonia affects people with increased mental or physical stress. Therefore, you need to properly plan your work and rest schedule.
Headaches due to vegetative-vascular deviation can also be diagnosed in patients who are in a supine position for a long time, since in such a situation there is a violation of the venous outflow. In this case, the patient will complain of dull, bursting pain. This type of illness also develops in those who sit at the computer for a long time. In this case, cephalalgia begins to torment already in the morning hours.
Do not forget about such a pathology as increased blood viscosity (hyperviscose syndrome). In this situation, the patient’s body constantly forms blood clots that can clog blood vessels, causing tissue death and the development of ischemic stroke. Cephalgia of the aching type occurs suddenly, it is almost impossible to get rid of it.
Most often, headaches are observed with vegetative-vascular dystonia, which can cause discomfort to the patient for a long period and be permanent. This disorder is irreversible and cannot be completely cured. Specialists can only help the patient improve his condition with the help of a variety of medications and achieve long-term remission.
Why you should never rely on folk remedies for such pain
Traditional recipes are not the best treatment method. In ancient times, they were used out of despair; traditional medicine was inaccessible.
Pain in the head area in most cases requires medication. And if they become a symptom of dangerous diseases, then surgical intervention is required.
Recipes from folk sources are not considered a panacea; they can be used as an auxiliary method of therapy, because they do not affect the cause of pathological symptoms. Such treatment should be agreed with a doctor.