Raynaud's syndrome is a disease in which the blood supply to the vessels of the hands or feet is disrupted. This disease gradually causes trophic changes in tissues. Raynaud's disease and syndrome occurs in 3-5% of people, women are predominantly susceptible to its development. In 85% of cases, Raynaud's syndrome is a sign of another disease.
Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital have experience in treating Raynaud's syndrome, so they are ready to offer patients with signs of this pathology a comprehensive examination and subsequent treatment. When conducting diagnostics, specialists find out the reasons that provoke arterial circulation disorder in the vessels of the extremities.
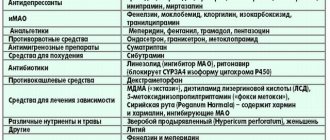
Raynaud's syndrome: ICD 10
In the ICD 10 classification, Raynaud's syndrome is classified as a peripheral vascular disease coded under code I73. This disease is coded I73.0. Raynaud's syndrome often develops against the background of connective tissue pathologies; for example, when diagnosing arthritis or scleroderma, in some cases this disease is detected. This relationship is explained by the fact that the walls of blood vessels consist of connective tissue, in diseases of which their structure is disrupted.
Raynaud's syndrome, the symptoms and treatment of which are interrelated, is characterized by damage to the capillaries and arterioles, their walls become inflamed and noticeably narrowed. A sharp narrowing of blood vessels is also caused by provoking factors such as stress and cold. Manifestations of Raynaud's syndrome occur in patients most often in separate parts of the body: toes and hands, chin, tip of the nose, where blood circulates more slowly.
Raynaud's syndrome, the ICD 10 code for which is I73.0, has synonymous names: Raynaud's phenomenon, Raynaud-Leriche syndrome and Raynaud's disease. When making a diagnosis, rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital use the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision.
Causes and risk factors for developing Raynaud's disease and syndrome
Predisposing factors are:
- heredity,
- constitutional deficiency of vasomotor innervation of terminal vessels,
- psychogenic factors,
- injuries of the central nervous system,
- chronic poisoning with nicotine, alcohol,
- endocrine disorders,
- infectious diseases,
- overwork and overheating.
Meteotropic influences and occupational hazards are of particular importance:
- people living in damp and cold climates,
- chemical workers,
- miners, fishermen, loggers.
Also, a high incidence is observed in people who often overexert their hands and fingers: milkmaids, typists, pianists, etc.
Raynaud's syndrome in women
Raynaud's syndrome symptoms and treatment in women begins at an earlier age. Among people suffering from this disease under the age of 50, there is a fivefold predominance of the disease in women. Common manifestations of Raynaud's syndrome are: pallor, bluishness of the skin and loss of sensation in certain areas of the limbs or face.
Some women ignore the signs of the disease at an early stage, resulting in the development of other serious diseases, the successful treatment of which determines the timely detection of the disorder. Raynaud's syndrome develops in several phases:
- the vasoconstrictor phase is characterized by the appearance of pallor of the skin, which can last up to 15 minutes;
- the cyanotic phase lasts several minutes, pallor during this phase is replaced by cyanosis;
- the phase of reactive hyperemia is characterized by redness of the skin.
This sequence is not observed in all patients during an attack. The duration and order of the phases depends on the course of the disease and the general condition of the body.
Prevention
| This section is missing references to information sources. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You may edit this article to include links to authoritative sources. This mark was set on April 10, 2021 . |
Prevention of the disease is to always keep the limbs warm. To do this, you need to wear multi-layered clothing, especially protect your hands and feet. Mittens are more practical than gloves, as they keep your fingers warm. Currently, special electrically heated gloves and socks and hand warmers are available for sale. Some people are able to prevent attacks of Raynaud's disease by moving their arms in quick circles, which pump blood into the limbs using centrifugal force. Warm water helps to warm you up, but you need to make sure that it is not too hot. People with Raynaud's disease should not smoke.
Raynaud's disease can be prevented by avoiding triggers and starting treatment at the first sign. But in severe cases, surgery may be required. Raynaud's disease is an early symptom of other diseases such as systemic sclerosis, characterized by thickening of the skin. However, Raynaud's disease should not be considered a general sign of its onset.
Raynaud's syndrome in men
If the signs are ignored and there is no treatment, Raynaud's syndrome progresses. During attacks, men and women experience common symptoms:
- pain syndrome, the development of which is preceded by insufficient blood supply to tissues and metabolic disorders;
- blanching of the skin is noted in the first minutes after the action of the provoking factor. Pale skin is associated with a sharp spasm of blood vessels and impaired blood circulation;
- a feeling of numbness and tingling that disappears after normalization of blood circulation;
- cyanosis of the skin appears after a pale color, which is explained by stagnation and blood filling of the veins;
- redness of the skin is caused by blood flow to the vessels that have experienced spasm.
Raynaud's syndrome, symptoms and treatment are similar in women and men, can develop with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Clinic are engaged in scientific activities and study world experience in the treatment of Raynaud's syndrome.
Symptoms
Raynaud's syndrome is much more common in females (approximately 5 times more common than in males). Basically, the first manifestations of the disease occur at a young age - from 15 to 30 years, in 25-27% of cases - after 40 years. It is estimated that about 3-5% of the world's population suffers from this disease. Naturally, in countries with cold climates the disease is much more common. Raynaud's syndrome is characterized by paroxysmal progression and stages. Since the spasm primarily affects peripheral vessels, the symptoms of the disease occur most often in the hands, less often in the feet, tip of the nose and tongue, chin, and earlobes. How does a typical attack of Raynaud's syndrome proceed? Let's find out.
As a result of vascular spasm (vasoconstriction), blood flow in the peripheral parts (usually the index and ring fingers for some reason) slows down. Blood circulates worse, which is accompanied by paleness of the fingers (even the color of alabaster). Poor blood supply causes a lack of tissue nutrition, metabolic disorders at the local level, which is accompanied by pain. Along with pain (or instead of it), numbness, tingling, and a crawling sensation in the fingers may appear, which is also associated with nutritional deficiency. The skin becomes cold to the touch. On average, this state lasts about 10-15 minutes. Then the vasoconstriction phase is replaced by a second phase, cyanotic (cyanotic).
CM. SEE ALSO: Vibration disease: symptoms, treatment and prevention
The cyanotic phase is so named due to the changing color of the skin: the paleness of the fingers is replaced by their cyanosis. This occurs as a result of stagnation of blood in the veins, which have a bluish tint. The overflow of the veins with blood causes the fingers to turn blue. The fingers remain cyanotic until the arterial spasm ends. The second phase is more associated with a feeling of numbness and tingling than with pain. Painful sensations in this phase are dulled compared to the first phase. The duration of the second phase ranges from several minutes to several hours. Then comes the third phase - the phase of vasodilation (vasodilation). It is also called reactive hyperemia due to the change in skin color from bluish to red.
The third phase occurs after the disappearance of vascular spasm. Blood flow is resumed with the same force, stagnant blood from the veins is pushed further along the bloodstream in fresh portions, tissue nutrition is restored. This is all accompanied by redness of the skin of the fingers, a feeling of heat, and an increase in the temperature of the skin in this area. Pain and other sensory disturbances disappear. After some time, the skin acquires its normal color.
The three-phase course of an attack of Raynaud's syndrome described above is classic, but it is not always found in this form. In real life, the picture is not always complete. Typically, the initial stages of the disease occur only in the form of a slightly pronounced first phase, when vascular spasm is not yet so strong. Gradually, as the process progresses, two other stages appear, but their severity may vary individually. The duration of the attack is also subject to significant fluctuations: from 10-15 minutes to several hours. The frequency of attacks varies from several per year to daily. Much depends on the reactivity of the body, the cause of Raynaud's syndrome and the duration of its existence, the presence of concomitant diseases. The area of the lesion also tends to increase as the disease progresses: after the ring and index fingers, the hands are completely involved, and similar changes occur in the feet and face. An interesting (and still incomprehensible to doctors) is the fact that the thumb is not involved in the pathological process in Raynaud's syndrome.
Raynaud's syndrome is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. Periodically occurring vascular spasms still do not go away without leaving a trace. Without timely treatment, functional disorders are replaced by organic ones. What does this mean? This means the following: disruption of blood flow sooner or later leads to the development of trophic disorders. Trophic changes are no longer paroxysmal in nature, they are permanent, which significantly darkens the patient’s life. The fingers swell, the skin cracks, long-term non-healing ulcers appear, and felons often occur. In severe cases, necrosis (death) of superficial tissues with their rejection is possible, and gangrene develops (and then you cannot do without a surgeon!). Of course, the stage of trophic disturbances is the result of a far-advanced process, which, today, is rare.
There are some differences in the clinical course of the syndrome and Raynaud's disease. Most often, Raynaud's disease occurs at a young age, occurs with symmetrical damage to the extremities, and trophic changes develop quite rarely. Raynaud's syndrome can be accompanied by significant asymmetry of the lesion (for example, one finger on the left hand and the entire hand on the right), and progresses faster (which is associated with the presence of the primary source of clinical manifestations, the underlying disease).
In addition to changes in peripheral tissues, patients with Raynaud's syndrome may complain of fluctuations in blood pressure, pain in the heart and abdomen, pain in the spine, sleep disturbances, and migraine headaches.
Diagnosis of Raynaud's syndrome
A patient with signs of Raynaud's syndrome should consult a rheumatologist for a consultation; also in the Yusupov Hospital, if there are signs of this disorder, a consultation with a vascular surgeon is required. During a comprehensive diagnosis, specialists conduct research to identify concomitant pathologies that could cause Raynaud's disease.
The diagnosis of Raynaud's syndrome is determined by specialists after collecting anamnesis, studying symptoms and a comprehensive examination of the patient. When diagnosing Raynaud's syndrome, the following laboratory tests are used:
- blood chemistry;
- complete blood count to determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- A general urinalysis can identify organic and functional kidney damage;
- immunological tests;
- coagulogram, which studies blood clotting. In Raynaud's syndrome, the capacity of platelets and red blood cells is increased, and there is also increased blood viscosity.
The diagnostic center at the Yusupov Hospital has European equipment for examining the materials obtained. High accuracy of diagnostic results is ensured not only by modern devices, but also by the professionalism of the Yusupov Hospital staff. Raynaud's syndrome, the treatment of which by rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out according to an individual plan, can be controlled by various methods depending on the course of the disease.
Diagnostics
The characteristic clinical picture of Raynaud's syndrome usually does not cause diagnostic difficulties. However, to confirm the presence of this disease, one of the following examination methods is necessary: capillaroscopy, rheovasography, Doppler ultrasound. These instrumental methods allow you to confirm vasospasm. Vasospasm can be induced using a cold test (immersing your fingers in cold water for several minutes). Recently, a diagnostic method such as wide-field capillaroscopy of the nail bed has come to the fore, since this study allows a detailed examination of the microvascular bed. In addition to instrumental diagnostic methods, a general blood test, a coagulogram (determining indicators of the blood coagulation system) are prescribed, and immunological blood parameters are examined. Most activities are carried out to establish the causative factor: it is necessary to find out whether it is Raynaud's syndrome or Raynaud's disease. And if this is Raynaud's syndrome, then, first of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease that has become the source of clinical manifestations.
CM. SEE ALSO: Vibration disease: symptoms, treatment and prevention
Raynaud's syndrome: treatment
An integrated approach to eliminating the causes of Raynaud's syndrome allows you to cure the disease without surgery. With the development of secondary Raynaud's syndrome associated with connective tissue pathologies, the patient is prescribed medications to eliminate the symptoms and causes of the disease.
With independent Raynaud's syndrome, drug and surgical treatment is carried out in exceptional cases. Raynaud's syndrome, the symptoms and treatment of which are interrelated, requires the exclusion of provoking factors such as vibrations, stress, smoking, and cold. Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital also include physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment plan. Professional psychologists with many years of experience teach patients techniques for relieving stress and tension, and relaxation.
Treatment of Raynaud's disease
Modern medical capabilities make it possible, if not to cure completely, then to significantly reduce the severity of the symptoms of Raynaud's disease. They use medication, physiotherapy, reflexology (acupuncture). Treatment of diseases that lead to the development of symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome is important.
Measures to prevent exacerbation of Raynaud's disease:
- to give up smoking;
- prevention of hypothermia (try not to overcool your hands, feet and face, dress according to the weather, make sure your shoes are dry, wear mittens in winter, etc.);
- adherence to sleep and rest patterns.
Highly qualified rheumatologists at MedicCity will help you cope with the manifestations of various rheumatological diseases. Our clinic diagnoses and treats rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, gout, osteoarthrosis, osteoporosis, Sjogren's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic vasculitis, dermatomyositis, systemic scleroderma, rheumatism, etc. The most modern treatment methods are used. Trust the professionals!
Treatment of Raynaud's syndrome in Moscow
Patients of the Yusupov Hospital receive high-quality medical services, as doctors and staff take a responsible approach to fulfilling their duties. Raynaud's syndrome, the symptoms of which appear unexpectedly in patients, raises many questions and concerns. Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital clearly explain to patients the features of this disease and the most optimal methods of treating it.
The therapy clinics of the Yusupov Hospital, where they provide care to patients with Raynaud's syndrome, have modern equipment to identify circulatory disorders and associated pathologies that can worsen a person's quality of life. When treating the disease, specialists use modern approaches and means that have a minimum number of side effects.
For a comfortable stay for patients, the Yusupov Hospital has a pre-registration system by telephone, so there is no long wait required to visit a specialist.
Treatment prognosis
Raynaud's disease cannot be completely cured. A person suffering from this disease is forced to follow the recommendations described above throughout his life and periodically resort to physiotherapy methods. Depending on the severity of the disease, drug therapy can be either continuous or prescribed in courses.
If Raynaud's syndrome is diagnosed, and the underlying disease is curable, then it is quite possible to get rid of vascular spasms. As a rule, recovery leads to the disappearance of the factors that provoke the syndrome.
Among vegetative-vascular diseases of the distal extremities, Raynaud's disease occupies a leading position. Data about it are quite contradictory. As a rule, the disease is not life-threatening, but it limits opportunities and requires constant drug therapy.
Raynaud's syndrome Scleroderma - what is it and how to treat it? Diabetic foot - drug treatment and foot care at home Hypertension Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities Hemolytic anemia
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatments are rarely used for Raynaud's disease. They are recommended only in cases where the risk of necrosis of the soft tissues of the fingers of the upper or lower extremities is very high.
Several types of surgery are used:
- Truncal sympathectomy. With this intervention, a section of the sympathetic nerve in the arms and legs, which is responsible for vascular spasm in the extremities, is crossed. The frequency and duration of attacks of the disease are reduced.
- Chemical injections. Surgical injections of medications (anesthetics or botulinum toxin type A) can block the transmission of nerve impulses in the sympathetic nerves responsible for narrowing the blood vessels of the arms and legs.
A significant disadvantage of these operations is that the resulting effect can be quite short-lived.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy is a method of treating the body using various physical stimuli that have a beneficial effect on cell and tissue biology.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of Raynaud's syndrome includes the following procedures:
- Magnetotherapy. Inductors are placed on the cervical and thoracic spine. Duration of exposure is 15 minutes. Daily, 15 sessions per course.
- Electrophoresis. It is carried out with sedatives (diazepam, sodium bromide), with antispasmodic drugs (papaverine, aminophylline, dibazol). The impact is on the feet and palms. Lasting 10 minutes, sessions daily, course of 10 procedures.
- Ozokerite, paraffin applications. The exposure temperature is 38 – 40 degrees in the form of “stockings”, “socks”, “collar”. The duration of the procedure is 15 – 25 minutes. Sessions every day, for 10 – 15 days.
- Mud therapy (hydrogen sulfide, bromine-iodine, nitrogen-thermal mud). Procedures are prescribed lasting 20 minutes, in courses of 10 sessions daily.
- Sulfide baths. The main component of sulfide baths is hydrogen sulfide, which penetrates the skin, thereby improving microcirculation in tissues and stimulating metabolism. The procedures are carried out for 10 - 15 minutes, in courses of 5 - 10 sessions every day.
Reasons for development
Despite the fact that the disease was first described more than 150 years ago, the final causes and mechanism of development are not fully understood. One of the leading factors is considered to be burdened heredity, although primary cases have also been noted in families. The main causes of pathology are:
- frequent hypothermia or frostbite of the extremities;
- numerous finger injuries;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- imbalance of sex hormones;
- severe psychotraumatic situations;
- increased blood viscosity (increased pure red blood cells, “cold” globulins, impaired lymph composition);
- working with vibrating mechanisms;
- autoimmune diseases (scleroderma, periarteritis nodosa, lupus, vasculitis, rheumatoid polyarthritis);
- additional cervical ribs, osteochondrosis, scalene muscle or carpal tunnel syndrome.
During examination, the detection of primary Raynaud's syndrome in women over 30 years of age is much more common than in men. This is associated with the characteristics of hormonal status. Patients whose work involves constant tension in their hands are at risk. And if, when describing the pathology, such changes were found in laundresses, then pianists and typists, today computer typists and writers are susceptible to the disease.