Forced laughter as the main symptom and other manifestations
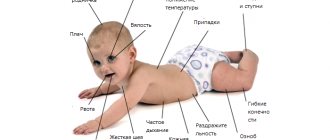
Unlike normal laughter, laughter with Joker syndrome is not caused by external circumstances and is not accompanied by positive emotions. It occurs suddenly, for no apparent reason, and is not controlled by the patient. In essence, it is a spasm - a violent contraction of the facial muscles, which other people mistake for an emotional reaction.
Subjectively, this symptom is unpleasant and causes patients a lot of suffering:
- The attack develops suddenly, the person often does not have time to take air into his lungs and begins to choke, laughter turns into coughing.
- The presence of such manifestations makes it impossible to work in a number of specialties.
- Forced laughter negatively affects socialization, since others may consider the patient dangerous or inadequate.
Other manifestations:
- Along with violent laughter, violent crying often develops. Possibly grimacing.
- Some patients have difficulty opening their mouth wide or closing their eyes.
- The voice becomes dull, weak, hoarse, sometimes disappears, whispering speech. It is difficult to pronounce a number of sounds.
- Due to weak swallowing muscles, solid food gets stuck in the mouth and liquid food comes out through the nose.
- Reflexes of oral automatism appear, which are normally observed only in newborns.
Joker smile, grimace
Pseudobulbar syndrome in children
Pathology can be diagnosed in children of any age, including newborns. The clinical picture is no different: the child has difficulty swallowing, chokes on milk, is whiny, restless, and his voice becomes hoarse. Older babies have difficulty chewing. Possible manifestation of hemiparesis, an extrapyramidal disorder characterized by muscle hypertonicity. Already in the first month of life, the manifestations of the syndrome are striking. Oral automatism, pathological crying or laughter are noticeable in children under one year and older.
Treatment should be started as soon as possible. Massage sessions are recommended, which can and should be done even for newborns. Children receive a massage of the orbicularis oris muscle. If necessary, he is fed through a tube. Drug therapy will be prescribed by the attending physician. From the arsenal of physiotherapy, electrophoresis with proserine is indicated for the cervical spine. A sign of successful treatment is the appearance of reflexes in the baby.
The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of brain damage. If there are any suspicious symptoms, you need to show your baby to the doctor as soon as possible. If your child is not treated promptly, difficulties with swallowing and chewing may persist for the rest of his life.
Causes
Pseudobulbar syndrome develops with combined damage to the brain pathways. The immediate cause is multiple bilateral foci of ischemia or minor hemorrhages.
In damaged areas, the nervous tissue degenerates and ceases to conduct signals. Due to impaired nerve conduction, the motor nuclei located in the medulla oblongata are not regulated by higher nervous structures, but act autonomously, sending untimely and inadequate commands to the facial muscles, muscles of the larynx and pharynx. The result is violent movements and functional impairment.
In adults
Experts in the field of neurology believe that in adults this condition is most often caused by atherosclerosis and hypertension. Other possible reasons:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- diffuse and multiple gliomas;
- specific and nonspecific neuroinfections;
- degenerative pathologies (Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis);
- demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis);
- metabolic disorders;
- vasculitis in some rheumatological diseases (for example, SLE);
- previous coma or clinical death.
Pseudobulbar palsy and its manifestations
In children
In children, the pathology is usually provoked by cerebral palsy and is combined with paresis, spasticity, and dyskinetic disorders. Sometimes the reason is:
- epileptiform syndrome (seizures or asymptomatic changes in the electrical activity of the brain caused by other conditions, including infections and birth injuries);
- bilateral aqueduct syndrome (congenital lesion of the liquor-conducting tract).
In some cases, in children, the disease develops against the background of injuries and tumors.
Diagnostics
To determine pseudobulbar syndrome in children, it is necessary to differentiate its symptoms from nephritis, parkinsonism, bulbar palsy and nerves. One of the distinguishing features of the pseudoform will be the absence of atrophy.
It is worth noting that in some cases it can be quite difficult to distinguish PS from Parkinson-like paralysis. This disease progresses slowly, and in the later stages apoplectic strokes are recorded. Moreover, signs similar to the syndrome appear: violent crying, speech disorder, etc. Therefore, a qualified doctor must determine the patient’s condition.
Difference from bulbar syndrome
The main difference from bulbar syndrome is the level of damage. In pseudobulbar syndrome, the pathways that transmit signals from the cortex to the nuclei of the medulla oblongata are affected. With bulbar syndrome, the nuclei themselves are damaged. Accordingly, in the first case, the brain structures that are responsible for vital functions continue to work, in the second, they stop functioning.
Both pathologies present with similar symptoms, but pseudobulbar syndrome is not life-threatening. Bulbar - can be fatal.
Clinical picture
Such patients may laugh or cry against their own will.
Pseudobulbar syndrome is characterized by a combination of impaired swallowing, speech, the appearance of violent grimaces (laughter and crying) and symptoms of oral automatism.
The appearance of choking and pauses before swallowing is explained by paresis (weakness) of the muscles of the pharynx and soft palate. In this case, the disturbances are symmetrical and not as severe as with bulbar palsy. There is no atrophy or twitching of the affected muscles. And the pharyngeal reflex can even be increased.
Speech impairments with pseudobulbar syndrome affect only pronunciation - speech becomes unclear and blurred. This is called dysarthria and can be caused by paralysis or spastic muscle tone. In addition, the voice becomes dull. This symptom is called dysphonia.
The syndrome necessarily includes symptoms of oral automatism. Moreover, the patient himself does not notice them; these signs are detected during special tests during a neurological examination. Mild irritation of some areas leads to contraction of the mental or perioral muscles. These movements resemble sucking or kissing. For example, such a reaction appears after touching the palm or corner of the mouth, or tapping the back of the nose. And with a light blow to the chin, the chewing muscles contract, closing the slightly open mouth.
Violent laughter and crying often occur. This is the name given to characteristic short-term contractions of facial muscles, similar to emotional reactions. These involuntary grimaces are not associated with any impressions and cannot be stopped by an effort of will. Voluntary movements of the facial muscles are also impaired, which is why a person may open his mouth when asked to close his eyes.
Pseudobulbar syndrome is not isolated; it appears against the background of other neurological disorders. The overall picture depends on the root cause. For example, damage to the frontal lobes is usually accompanied by emotional and volitional disorders. In this case, a person may become inactive, lacking initiative, or, conversely, disinhibited in his desires. Dysarthria is often combined with memory loss and speech disorders (aphasia). When subcortical zones are damaged, various motor disorders often occur.
What treatment does neurology offer?
A mandatory component of treatment is therapy of the underlying disease. For hypertension, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed; for atherosclerosis, drugs are prescribed to lower cholesterol levels and prevent the formation of blood clots. For neuroinfections, antimicrobial therapy is indicated. For tumors, surgery is performed and radiation therapy is used.
For all variants of pseudobulbar syndrome, medications are useful to activate neurometabolism (nootropics) and improve microcirculation in the brain.
Treatment for children includes sessions with a speech therapist to correct phonation disorders and work with a speech pathologist. Additionally, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and breathing exercises are performed. Neurology considers the use of stem cells to be a promising method of therapy.
Therapy
Pseudobulbar syndrome, which is treated at home, should be treated from the very first symptoms. This is the only way to try to stop the progression of the disease or slow down its development.
If the disease progresses, then the main therapy will be aimed at normalizing fat metabolism and reducing cholesterol. Drugs that improve metabolic processes in the brain and have a positive effect on the bioenergetics of neurons are helpful. In this case, encephabol, aminalon, cerebrolysin, prozerin, and oxazil are used.
If you ignore the first symptoms and do not consult a doctor, then it will be almost impossible to restore all brain functions. This means that the child will suffer all his life from the fact that he will not be able to swallow food normally, but not only that. In this case, children become disabled.
But if treatment for pseudobulbar syndrome in children is started in a timely manner, and it involves not only the use of medications, but also stem cells, then there is every chance of a complete recovery.
What's the difference?
To better understand the difference between bulbar and pseudobulbar syndromes, it is necessary to remember that the first pathology is caused by a disorder of the peripheral neuron, and the second by the central motor neuron.
In addition, with pseudobulbar palsy, the paralyzed muscles do not become atrophied.
For reference, motor neuron disease is a neurodegenerative, progressive disease that affects motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain.
Due to the gradual death of NS cells, constantly increasing weakness of all muscle groups develops.
In this case, the upper motor neurons with their processes descend into the spinal cord, where a synapse occurs (contact with the neurons of the spinal cord) and mediators are released that transmit signals unusual for neurons.
If a person is diagnosed with leukodystrophy, is there a chance of saving the patient’s life or is this unrealistic?
What is cerebral astrocytoma - symptoms, treatment and life prognosis - all this information is in our material.
Goals and methods of therapy
Sometimes the patient requires emergency medical care to save his life with bulbar palsy.
Its main goal is to eliminate the threat to life before transporting the patient to the hospital, where adequate treatment will then be prescribed.
Depending on the nature of the pathology and clinical symptoms, the doctor is able to predict the effectiveness of treatment of the disease, as well as its outcome.
This process consists of several stages, the first of which is the resuscitation and support of functions impaired due to paralysis.
To restore breathing, artificial ventilation is performed, and vitamins, adenosine triphosphate and proserine are prescribed to trigger the swallowing reflex. Atropine is used to reduce salivation.
The next step of treatment is symptomatic therapy, which can alleviate the general condition of the patient , and then comes the direct treatment of the disease that caused the development of the syndrome.
Since the patient is not able to eat on his own, he is fed through the use of an enteral feeding tube.