What is serotonin syndrome?
Serotonin
is a neurotransmitter produced by specialized cells in the brain, spinal cord, and intestines. Serotonin helps regulate:
- mood and behavior
- memory
- dream
- sexual desire and function
- digestion
- appetite
- blood flow
- body temperature
Some people may develop serotonin syndrome after taking drugs that increase serotonin levels. Doctors don't know the exact prevalence and incidence of serotonin syndrome because the condition has a wide range of nonspecific symptoms, making diagnosis difficult.
Recent evidence suggests that the incidence of serotonin syndrome is increasing along with the increasing use of antidepressants.
Diagnostic measures
Unfortunately, there are no specific diagnostic methods for this syndrome. Laboratory data can only reveal developed complications. Basically, monitoring of the patient is necessary.
If we talk about determining the amount of serotonergic drugs in the blood plasma, then most often they show the norm. And in the presence of toxic concentrations of drugs in the blood, this does not always lead to serotonin syndrome.
But, nevertheless, some diagnostic measures can help identify this condition in its early stages - first of all, these are the symptoms of the disease.
When starting to take appropriate medications, when increasing the dosage or adding additional drugs, you should monitor the patient's condition.
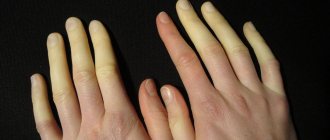
Incipient serotonin syndrome may be indicated by one or more frequently encountered signs - agitation, impaired reflexes, heavy sweating, mental disorders, loose stools, fever, myoclonus, tremor, etc.
A method is also used to exclude other causes of the development of such a condition. These include encephalitis, neuroleptic manifestations, hyperthermia, poisoning and antidepressant withdrawal syndrome, etc.
Causes
Typically, serotonin syndrome occurs when people take medications, supplements, or illicit drugs that increase serotonin levels. Drugs that increase serotonin levels:
- antidepressants
- SSRIs
- serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- tricyclic antidepressants
- migraine drugs
- triptans, such as almotriptan (Axert), naratriptan (Amerge), and sumatriptan (Imitrex)
- anticonvulsants
- carbamazepine (Tegretol, Equetro, Carbatrol)
- valproic acid (Depaken, Konvulex, Valporal)
- opioid painkillers
- tramadol (Ultram)
- oxycodone (OxyContin, Percodan, Percocet)
- tapentadol (Nucynta, Nucynta ER)
- cough medicines
- dolasetron (Anzemet)
- tropizerton (Navoban)
- granisetron (Sancuso)
Other substances that increase serotonin levels:
- drugs including ecstasy, cocaine and amphetamines
- herbal supplements such as St. John's wort and ginseng
- dextromethorphan - an ingredient found in cough medicines such as Delsym, Robitussin, and Mucinex DM
- ritonavir (Norvir), an antiretroviral drug
- lithium
Reasons for the development of a dangerous condition
Possible combinations of drugs that trigger the development of serotonin syndrome are varied.
The likelihood of this condition is high with simultaneous use of:
- MAO inhibitors with: SSRIs, thyroid hormones, drugs with destromethorphan, weight loss drugs (Fepranon), Imipramine, Carbamazepine, lithium drugs, narcotic substances ecstasy,
- SSRIs with Tramadol, Levodopa, Sumatriptan, Dihydroergotamine.
In addition, serotonin syndrome can occur due to non-compliance with the dose and poisoning of SSRIs at the beginning of their use. It is impossible to predict in advance the development of a pathological condition from a normal dosage of a medicine.
The possibility of developing the syndrome exists when there is a sudden change in the use of one antidepressant to another. This most often occurs when changing from SSRIs to MAO inhibitors. The fact is that the period of removal of some drugs from the body can be several weeks. And if the patient immediately after stopping them starts taking another serotonergic drug, serotonin syndrome may develop. You should always take breaks between taking different medications, taking into account the period of their elimination from the body.
Serotonin syndrome - symptoms
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome usually begin 1 to 6 hours after taking the drug and almost always within 24 hours. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome:
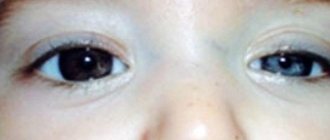
- dilated pupil
- dry mouth
- agitation or restlessness
- anxiety
- hallucinations
- excessive sweating
- blood pressure changes
- rapid heartbeat or tachycardia
- nausea
- vomit
- diarrhea
- muscle spasm
Severe symptoms that doctors associate with serotonin syndrome:
- high body temperature or hyperthermia
- rave
- muscle rigidity
Providing medical care
In order for the treatment to give a positive result, it is necessary to discontinue all medications that the patient had previously taken. That is, those that have a negative effect on serotonin metabolism.
To ensure that the drugs are completely removed from the body, sorbents are prescribed or gastric lavage is performed. Then the doctor prescribes treatment, which is symptomatic. This is necessary to improve the patient’s condition and restore the body. Next, medications are prescribed to relieve agitation.
Infusion therapy using droppers is also necessary. In order for the autonomic nervous system to be restored, potent drugs are sometimes necessary.
If the patient experiences respiratory failure, as well as at elevated temperatures, a breathing tube is inserted to perform pulmonary ventilation. If the case is extremely severe, then serotonin antagonists are administered.
It is very important to prevent further development of the syndrome, so doctors recommend seeking help in the initial stages of the development of serotonin syndrome. If the symptoms of the disease are not relieved within the first 12 hours, negative consequences are possible.
Here is an approximate scheme of symptomatic treatment of a patient with serotonin syndrome:
- benzodiazepines (Sibazon, Lorazepam) reduce muscle tone and rigidity, relieve mental agitation and epilepsy attacks;
- drugs from the Paracetamol group to reduce body temperature;
- in severe cases, muscle relaxants ;
- intravenous infusions are necessary if there is significant fluid loss.
Mechanical methods in the form of cool rubbing or rubbing with vinegar will also help;
If timely assistance was not provided on time, the following complications may develop:
- renal failure;
- development of coma;
- negative effect on the heart muscle and blood vessels;
- destructive process in muscle tissue;
- acid-base metabolism in the body is disrupted (metabolic acidosis);
- the process of blood clotting is disrupted.
Diagnostics
A doctor can diagnose serotonin syndrome by reviewing a person's medical history, symptoms, and medications. Your doctor may also use laboratory tests to rule out conditions that cause similar symptoms to serotonin syndrome, such as hormonal imbalances and infections. Examples of tests that doctors may use to diagnose serotonin syndrome include:
- blood analysis
- electrolyte test
- creatine test
- Analysis of urine
- kidney, liver or thyroid function tests
- drug and alcohol tests
- brain scan
- lumbar puncture
Necessary diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis is made based on observation of the clinical manifestations of the pathology. It is necessary to differentiate this pathology from other ailments with similar symptoms:
- neuroleptic malignant syndrome;
- overdose of narcotic painkillers;
- psychosis in the acute phase;
- hypertensive crisis;
- encephalitis;
- tetanus.
If the presence of signs indicates a mild form of serotonin syndrome, then emergency care is provided in the hospital, which consists of the following actions:
- drugs that cause pathology are discontinued;
- wash the stomach;
- to reduce intoxication, sorbent substances are prescribed.
The patient's condition improves within 6–12 hours. In severe cases, additional measures are necessary:
- Prescribed "Methysergide", "Cyproheptadine" - opponents of serotonin receptors.
- Lorazepam and Sibazon are used if epilepsy attacks are present and muscle stiffness is observed.
- High fever is brought down by cold rubbing and taking Paracetamol.
- To relieve the patient of fever and relax the muscles, muscle relaxants are prescribed. They help cope with blood clotting problems.
- To normalize the water balance, intravenous diffuse solutions are used.
- To maintain normal blood pressure and heart, appropriate means are used.
Treatment of serotonin syndrome allows you to relieve existing symptoms in a short time and return the patient to work.
Serotonin syndrome - treatment
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome usually resolve on their own once the person stops taking the drug or substance that caused the condition. People with severe symptoms may require hospitalization and close monitoring. For people with severe serotonin syndrome, doctors may recommend the following treatments:
- immediate discontinuation of the drug causing the reaction
- medications that reduce serotonin levels
- medications that reduce muscle stiffness or muscle spasms
- IV infusions to improve hydration and reduce fever
Serotonin and its syndrome
Serotonin is often called the hormone of happiness for the reason that its levels rise during moments of euphoria and ecstasy, and decrease during depression.
However, the body does not require the hormone serotonin to maintain a good mood; it also has other functions:
- regulates the emotional component,
- provides the opportunity for healthy sleep,
- responsible for the presence of appetite,
- regulates memory and learning abilities,
- affects the production of melanin.
Melanin is a compound that is responsible for skin pigmentation, hair color, and more. Also, it is responsible for the rate of aging and can lower blood glucose.
Important! Melanin is extremely important for travelers - it allows the body to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
An insufficient amount of serotonin in the body reduces resistance to stress factors and leads to depression.
If its content is insufficient, certain medications (antidepressants) are prescribed. However, with a long period of their use, as well as when the permissible dosage is exceeded, seretonin syndrome develops.
Serotonin syndrome is an excess of serotonin in the synaptic cleft (a certain distance between the membranes of a pair of neurons) or due to overexcitation of serotonin receptors located on the membrane of neurons.
Common serotonin disorder syndrome has three groups of characteristic manifestations:
- psychical deviations,
- neuromuscular abnormalities,
- manifestations of vegetative changes.
Diagnosing serotonin syndrome at this stage of development of medical science is possible solely according to clinical signs.
No laboratory or instrumental techniques have been developed to confirm the presence of serotonin syndrome.
There are no reliable statistics on the number of cases of this syndrome in the Russian Federation. There are only approximate data that may not fully correspond to reality for the following reasons:
- People with signs of serotonin syndrome do not always seek help from doctors.
- When there are signs of serotonin syndrome, doctors do not always make this diagnosis.
- It is impossible to prove the presence of serotonin syndrome using laboratory methods.
- Drugs can cause this reaction in the body. But a diagnosis that would indicate that the syndrome appeared because of them is even rarer.
The use of antidepressants, as well as some narcotic drugs, can lead to a disruption of the serotonergic system and a day after the start of use, a serotonin failure occurs.
It occurs due to the fact that the body experiences serotonin deficiency after an excess of its amount the day before.
Prevention
Doctors can prevent serotonin syndrome by monitoring people taking high-risk medications and prescribing treatments that have a low risk of interacting with a person's current medications.
Risk groups include people who:
- recently started taking or increased the dose of a drug that increases serotonin levels
- taking herbal supplements or illicit drugs that increase serotonin levels
- have end-stage kidney disease
Treatment
Depending on the severity of the manifestations, the treatment tactics for serotonin syndrome are chosen. There are three degrees of severity of the syndrome:
- Light heaviness. Often goes unnoticed. Manifested by a slight increase in heart rate, sweating and tremors.
- Medium severity. Heart rate is greatly increased, blood pressure is increased, temperature is up to 40, nystagmus, mydriasis, mental and motor hyperactivity.
- Severe degree of the syndrome. Almost all manifestations are present, the patient loses consciousness and may fall into a coma.
Depending on the degree of severity, a decision is made regarding treatment tactics. The main tactics are as follows:
- Complete withdrawal of medications that lead to an excess of serotonin.
- Removing drug residues from the body.
- Serotonin receptor antagonists are used.
- Further measures depend on symptomatic manifestations.
In most cases, serotonin syndrome is a consequence of the use of serotonergic drugs without due caution.
In some situations, it is possible to assume its occurrence with a high degree of probability. Sometimes excess serotonin occurs after the first use of antidepressants.
Serotonic syndrome is a fairly serious phenomenon that can be fatal, so only doctors can prescribe antidepressants.