Doctor Vadim Berezhnoy
Founder of the MediGlobus platform. Medical expert, Head of the department of coordinating doctors.
Chiari syndrome is a condition in which brain tissue moves into the spinal canal. The incidence of the disease is approximately 1 person per 1,000 population. Most cases of pathology are asymptomatic. Some forms of the disease cause complications that are life-threatening and life-threatening to the patient. How to identify the disease in time and cure it - read the article.
What is Arnold-Chiari disease?
Chiari syndrome
is a structural defect in the cerebellum that is characterized by downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum.
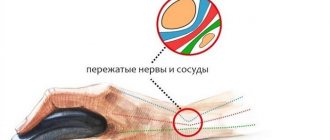
The pathology negatively affects functions controlled by damaged areas of the brain and blocks the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Structural defects of the brain and spinal cord occur during fetal formation. They are the result of genetic mutations or poor nutrition of the mother during pregnancy. In this case, Chiari syndrome refers to primary or congenital defects.
Acquired or secondary Arnold-Chiari malformation develops later in life. It occurs due to traumatic injury, disease or infection.
Primary Chiari syndrome is more common than secondary one. More than 60% of all cases of the disease are congenital.
Pathogenesis
In addition, the disease can develop:
- If your mother suffered from sexually transmitted and infectious diseases.
- Uncontrolled number of medications taken during pregnancy.
- Use of tobacco, drugs, and alcoholic beverages.
Of course, this is just a guess, there is no exact indicator. But in any case, if a pregnant woman does not monitor her diet and lead an unhealthy lifestyle, this will certainly negatively affect the development of her fetus.
Symptoms of Arnold-Chiari syndrome
Headache
is a hallmark of the disease. It occurs suddenly after coughing, sneezing or straining. Other symptoms of pathology include:
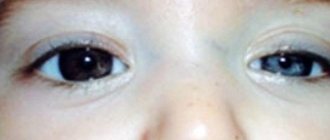
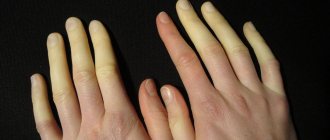
- pain in the neck; hearing problems; muscle weakness; numbness of the limbs; dizziness; difficulty swallowing or speaking;
- nausea and vomiting; tinnitus; rachiocampsis; insomnia; depression; violation of fine motor skills.
In patients, symptoms of the disorder vary depending on the compression of the tissue and nerves. Some people with Arnold-Chiari syndrome experience no symptoms of the disease.
In infants, Chiari syndrome causes:
- difficulty swallowing; irritability when feeding; excessive drooling; faint cry; frequent urge to vomit;
- limb weakness; neck stiffness; breathing problems; developmental delays; problems with weight gain.
Degrees of Chiari syndrome
| Arnold-Chiari syndrome type 1 | The initial degree of Chiari syndrome occurs when the inferior part of the cerebellum extends into the foramen magnum. This pathology occurs most often. In childhood it is asymptomatic. The first signs of the disorder appear in patients over 25 years of age. Typically, the disease is discovered incidentally during testing for another condition. |
| Arnold-Chiari syndrome type 2 | The onset of the disease occurs in early childhood. The disease is more severe than grade 1 Arnold-Chiari malformation. It causes life-threatening complications. Its treatment requires surgery. |
| Chiari malformation type 3 | The pathology includes a form of dysraphism where part of the cerebellum and/or brainstem pushes through a defect in the back of the head or neck. This anomaly is extremely rare. It is associated with high early mortality or severe neurological impairment in surviving patients. If treatment is carried out, then early surgical closure of the defect is necessary. Symptoms of type 3 Chiari syndrome appear in infancy. |
| Chiari syndrome type 4 | This syndrome is the most severe and rare form of the disease in which the cerebellum fails to develop normally. This part of the brain is in its natural position, but parts of it are missing. Most children born with this anomaly do not survive infancy. |
Methods for diagnosing Arnold-Chiari syndrome
Many people with Chiari disease have no symptoms
. Therefore, the disorder is often discovered during the diagnosis or treatment of another disorder.
To identify the syndrome, the doctor conducts a physical examination, tests memory, coordination, balance, reflexes, motor skills, etc. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes one of the following tests:
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | An examination that produces three-dimensional images of body structures through the use of magnetic fields and computer technology. The method provides an accurate view of the brain, cerebellum and spinal cord. It is used to determine the type of Chiari syndrome and the degree of progression. When looking at the back of the brain and spinal cord, MRI provides more information than a CT scan. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | A diagnostic test that creates images of the body's organs and structures using computer-generated X-ray reconstruction. It is used to determine the size of the ventricles of the brain. The method is most informative when assessing bone abnormalities at the base of the skull and cervical canal. However, computed tomography is not very useful for analyzing the contents of the posterior fossa or spinal cord. |
| Fluoroscopy | A test used to monitor the swallowing process. This test can determine the presence of an abnormality indicating lower brain stem dysfunction. |
| Brainstem auditory evoked potential (BAER) | Test to check hearing aid function and brain stem connections. It is used to detect disorders in the brain stem. |
| Myelogram | X-ray of the spinal canal using a contrast agent. During the procedure, areas of compression of the spinal cord or nerves are determined. |
| Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) | A method that is used to assess the response of the central nervous system to stimulation of fibers of the peripheral nervous system. It determines the presence of neurological disorders. |
Diagnosis of the disease
There are cases when this anomaly does not manifest itself in any way and there are no symptoms at all. Then you can find out about the disease with the help of a special medical examination and even during a routine examination by a doctor.
Diagnosis of the disease
If a doctor suspects Arnold-Chiari disease, he will prescribe the following procedures: electroencephalogram of the brain, echoencephalography (ECHO-EG) and rheoencephalography. All these studies make it possible to measure intracranial pressure and see even the most minor pathologies. However, a definitive diagnosis cannot be made from such images.
Additional examination is being carried out. The patient is referred for magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography. It is advisable to remain motionless during this procedure in order to obtain an image close to the original. Since small children cannot be forced not to move for a couple of minutes, a drug is injected into their bloodstream, which puts the baby into medicated sleep. Tomography helps to detect a defect in the bone structure and will reveal various formations in the patient’s skull.
What is spina bifida, how to treat it and how to avoid this disease
Also, to establish a diagnosis, a tomography of the spine is prescribed, which shows whether there are any other pathologies. Pregnant women are prescribed a repeat ultrasound.
All procedures should be carried out strictly according to the doctor’s recommendation. A true specialist will not make an accurate diagnosis without conducting a proper examination.
How is Arnold-Chiari syndrome treated?
Some types of Chiari syndrome do not manifest themselves in any way and do not interfere with a person's daily life. In these cases, doctors recommend regular monitoring of the abnormality using MRI. If the disease causes various complications, then surgery and drug therapy are indicated.
Surgical intervention
is the only treatment available that can relieve symptoms or stop the progression of damage to the central nervous system. More than one surgery may be required to treat this condition.
The most common intervention for Albert-Chiari syndrome is posterior fossa decompression.
. During surgery, the doctor creates more space for the cerebellum and relieves pressure on the spinal cord. Surgery involves making an incision at the back of the head and removing a small area of bone at the bottom of the skull. Some patients require fusion of the cervical spine.
Findings from the National Institutes of Health show that this surgery is most effective when it is performed in utero rather than after birth. Perinatal surgery reduces the risk of hydrocephalus and restores the normal position of the cerebellum and brain stem.
Reasons for the development of the anomaly
Doctors have different opinions about the causes of the anomaly. There are several theories that explain how the defect develops.
Neurologists identify two pathologies that lead to the formation of Chiari malformation:
- The development of the fetus in the womb may be disrupted - the cranial fossa will be smaller than the anatomical norm, parts of the brain will acquire normal parameters.
- The dimensions of the departments are increased, while the parameters of the posterior cranial fossa and BZO meet the standards. The expanding brain rushes towards the hole.
Summary
Chiari syndrome is a structural defect in the cerebellum.
It is characterized by downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum. The abnormality causes pressure on the brain stem and negatively affects functions controlled by these areas. To identify the disease, the doctor conducts a physical examination, testing the patient's memory, coordination, balance, reflexes and motor skills. To confirm the Albert-Chiari diagnosis, he prescribes an MRI, CT scan, or other studies. Surgery is the only treatment available that can relieve symptoms or stop the progression of central nervous system damage. More than one operation may be required to completely eliminate this condition. The most common intervention for Chiari syndrome is decompression of the posterior cranial fossa. The leading destinations for the treatment of Albert-Chiari syndrome are Turkey, Israel, Germany, Spain, South Korea and the Czech Republic. To organize a trip abroad for diagnosis and treatment of Arnold-Chiari syndrome, please contact the coordinating doctors of the international MediGlobus platform. Leave a request - our specialists will answer you as soon as possible.
NeurologyNeurosurgery
Doctor Vadim Berezhnoy
Founder of the MediGlobus platform. Medical expert, Head of the department of coordinating doctors.
Nina Vorobey
Editor
She has been writing medical texts for more than 2 years. Experience in the field of copywriting exceeds 6 years. Has an education in the field of “Social and Legal Protection”. Completed the medical course program. Studies communication techniques for negotiating with patients. In his free time, he attends trainings and seminars on medical psychology.