Parkinson's disease is one of the most complex neurological pathologies. It occurs mainly in older people; young people suffer from Parkinsonism in isolated cases. Treatment of the disease was unsuccessful for a long time, and the patients themselves were considered hopeless.
Breakthroughs in medicine and pharmacology have made it possible to create special drugs to help patients, however, for a significant category of patients, surgery for Parkinson's disease remains the only hope for improvement.
The feasibility of surgical treatment
Levodopa is currently used to treat Parkinson's disease.
They began to be used recently, which reduced the number of cases of surgical intervention.
However, surgical treatment of the disease is still carried out.
After several years of taking levodopa, patients begin to experience complications in the form of drug-induced dyskinesia or muscle fluctuation (purulent inflammation).
This significantly complicates further treatment and leads to disability. It is impossible to cure the side effects, so surgery is the only option.
Surgical intervention is indicated for patients diagnosed with trembling-rigid and tremulous forms of the disease. The age of the patient is of great importance.
In juvenile parkinsonism, the likelihood of a positive effect of the operation is higher and its implementation is more advisable than in elderly patients.
Moreover, patients over 65 years of age have many contraindications to surgical intervention. The decision on the feasibility and safety of the operation is made by a medical council, based on the results of the examination of the patient.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease are:
- Persistence of severe symptoms despite correctly selected drug therapy.
- Rapid progression of pathology, which requires increasing the dosage of medications. In this case, many side effects occur that reduce the patient’s quality of life.
- The patient's young age and desire to work, but the manifestations of the disease prevent him from continuing to work.
- Possible rapid loss of ability to work, which will make the patient disabled and dependent on his family.
Like any treatment, surgery has a number of contraindications. These include:
- Serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Diabetes.
- Presence of a pacemaker.
- Psychical deviations.
- Suicidal tendencies.
- Severe dementia.
- Oncological diseases.
- Severe visual impairment (surgery can lead to complete blindness).
- Severe arterial hypertension.
- Problems with blood clotting.
- Age over 70 years.
Surgery for Parkinson's disease - effect and contraindications:
Causes of Parkinson's disease
The exact causes of Parkinson's disease have not yet been established. Doctors identify predisposing factors, the presence of which increases the risk of developing the disease. Among them:
- Natural aging. Age-related changes contribute to a decrease in the number of nerve cells. As a result, dopamine levels in the basal ganglia decrease. This is considered a precipitating factor for the development of Parkinson's disease.
- Impact of adverse environmental factors. The death of nerve cells can occur due to toxic substances, heavy metals, and free radicals entering the body.
- Taking certain medications. Dopamine metabolism disturbances can be caused by certain drugs. The result is pathological symptoms similar to Parkinson's disease.
- Burdened heredity. The gene responsible for the transmission of Parkinson's disease has not yet been identified. However, in 20% of cases, if one of the relatives was diagnosed with the disease, subsequent generations are at risk.
- Brain damage. As a result of bruises, concussions, meningitis, encephalitis of various origins, the structure of the basal ganglia is disrupted. This increases the risk of developing Parkinson's disease.
- Concomitant somatic pathology. Some somatic diseases, such as atherosclerosis, malignant neoplasms, and thyroid diseases provoke the development of Parkinson's disease.
- Wrong lifestyle. Predisposing factors include: prolonged exposure to stress, poor and unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins, smoking and alcohol abuse.
Surgical methods
Currently, invasive and non-invasive surgeries are used. Invasive methods include thalamotomy and pallidotomy.
Thalamotomy
During the operation, partial destruction of the structure of the thalamus (the part of the brain responsible for transmitting sensory and motor information) is carried out.
Thalamotomy can only be performed on one side, so it is used in cases of unilateral tremor.
In 95% of cases, the tremor disappears, however, with this type of therapy, serious complications often develop in the form of speech impairment or its complete disappearance, abulia (lack of will), aspraxia (impaired purposeful movements).
Pallidotomy
This method is used if the patient has predominant movement disorders on one side of the body. The essence of the procedure is to insert a needle into the globus pallidus . The globus pallidus is the part of the brain in which the focus of movement disorders is formed.
During the operation, connections between this department and the thalamus are destroyed.
The effectiveness of pallidotomy is very high, more than 95% of patients report the disappearance or significant weakening of symptoms. In this case, the incidence of complications does not exceed 2%.
Deep brain stimulation
Among minimally invasive techniques, the method of deep brain stimulation has gained the greatest popularity. A neurostimulator is implanted into the patient's area under the collarbone.
It is connected to electrodes that are inserted into the deep structures of the brain that control movement. The patient can adjust the stimulator settings himself depending on his own feelings.
The advantages of neurostimulation over other methods are obvious:
- Ability to adjust settings.
- No need for medications.
- Reversibility (the device can be removed if necessary).
- The operation is also performed for bilateral symptoms.
- Lack of rehabilitation period.
The disadvantages of the method include high cost and the need to replace the device after 6-8 years.
Parkinson's treatment - deep brain stimulation (DBS), surgery, cost:
Stem cell transplantation
This treatment method has not been studied enough and is therefore not widely used. The essence of the treatment is the transplantation of neurons into the brain.
Neurons are obtained after differentiation of stem cells. They replace dead cells, which leads to the restoration of motor and other functions.
Currently, drug development is underway that can target Lewy bodies, which are the main markers of Parkinson's disease and dementia. However, this is still a distant prospect.
Read about other treatments for Parkinson's disease:
- admissibility of using folk remedies;
- effectiveness of hardware procedures;
- additional methods used at home.
Stages of development of Parkinson's disease according to Hoehn-Yahr
Doctors distinguish several classifications for Parkinson's disease. The Hen-Yahr scale is considered the most popular. It is based on a description of changes exclusively in motor activity. Other disorders associated with the disease are not affected. According to the Hoehn-Yahr classification, the following stages of Parkinson's disease are distinguished:
- Zero. The person is considered completely healthy, there are no clinical symptoms of the disease.
- First. Motor disturbances occur in one hand. The first stage is characterized by the appearance of sleep disturbances, emotional lability, changes in the sense of smell, and severe fatigue. As the condition worsens, trembling occurs in the fingers, which then appears at rest.
- One and a half (intermediate). Pathological symptoms appear either in one limb or in one part of the body. The tremor becomes constant. The trembling disappears only in sleep. As a result of tremor, fine motor skills are impaired and handwriting changes. The intermediate stage is characterized by stiffness and limitation of movements in the neck and thoracic spine.
- Second. Movement disturbances appear on both sides. Most often, tremor of the tongue or lower jaw occurs, and salivation increases. Movements in the joints become difficult, facial expressions worsen, and speech slows down. In the second stage of Parkinson's disease, the skin may be dry or oily. The patient is able to restrain involuntary movements in rare cases. Simple actions can be performed, but they are greatly slowed down.
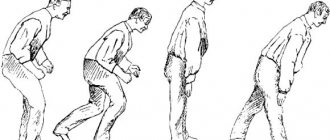
- Third. Characterized by changes in gait. The patient walks with small steps, the feet are parallel to each other. The face resembles a mask. In some cases, head tremors like nodding movements are possible. In the third stage, speech deteriorates. The patient becomes fixated on the same words, repeating them several times. Self-service is still possible, but difficult. All actions take more time. A “supplicant pose” is formed when the head is bent forward, the back is hunched, the arms are pressed to the body, and the legs are bent at the knees and hip joints.
- Fourth. It becomes difficult for the patient to change body position even during sleep. Instability occurs, balance is lost when getting out of bed. As a result, patients often fall and fractures occur. Speech at the fourth stage becomes quiet, slurred, and sometimes nasal. Such conditions worsen the emotional state, causing depression. Mental lability often leads to suicide attempts. The ability to self-care is lost.
- Fifth. The most severe stage of Parkinson's disease. It is characterized by progression of motor disorders. It is difficult for patients to stand up, sit and walk independently. Eating is impossible not only due to severe tremor, but also due to impaired swallowing. Patients cannot control urination and bowel movements, and incontinence occurs. Speech is incomprehensible and self-service is completely impossible.
Preparation for the procedure
Before surgery, the patient must undergo all examinations to confirm the absence of contraindications.
You should not eat or drink 15 hours before the procedure.
The operations are performed under local anesthesia.
The patient is fully conscious and in contact with the doctor . With invasive methods, a burr hole with a diameter of up to 1.5 cm is made in the skull.
Then, under X-ray control, a destruction instrument is inserted into the brain. The procedure lasts 1-2 hours. The clear consciousness of the patient gives the surgeon the opportunity to verify the correctness of the manipulations.
For many patients, symptoms of the disease disappear already in the operating room. Some take several months to recover.
The installation of the neurostimulator takes place in two stages, also under local anesthesia. For the stimulation mode to be set correctly, the patient must be fully conscious.
First, electrodes are inserted into the brain and test stimulation is performed. The patient tells the doctor about his feelings. If the result is positive, the neurostimulator is implanted under general anesthesia.
Get a personal medical program
Contact our medical team and we will provide you with a clear and detailed plan of action: an expert doctor will review your medical history, based on which a schedule of tests and tests will be drawn up. You will also receive a dossier of specialized doctors, current prices for all procedures. All information is provided free of charge. Call +972 (77) 4450480 | 8 (800) 707-6168 (Call from Russia is free)
REQUEST A TREATMENT ESTIMATE
Author of the article
: prof.
Abraham Kuten Other publications by the author
: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Postoperative period and complications
After invasive operations, the patient spends 10-15 days in the hospital.
The electrical activity of the brain is monitored on the 7th day, then after 3, 6, 12 months.
After treatment, the doctor adjusts the drug therapy.
Manifestations of the disease disappear over a period of several days to several months.
This depends on the stage of parkinsonism and the health status of the person being operated on.
There are no complications after neurostimulation. Unless the wound becomes infected if sanitary rules are not followed.
As for invasive techniques, the most dangerous is thalamotomy. The complication rate reaches 12%.
The most common side effects that occur are:
- dysarthria (distortion of pronunciation);
- dysphasia (disappearance of speech);
- abulia (lack of will, inability to perform actions and make decisions);
- memory impairment.
Possible complications of pallidotomy:
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- loss of voice;
- the appearance of convulsive seizures;
- depression;
- limb weakness.
Fortunately, these complications occur in only 2% of those operated on.




![Eating Well for Parkinson's Disease [2020 Guide]](https://3d-panneco.ru/wp-content/uploads/pravilnoe-pitanie-pri-bolezni-parkinsona-rukovodstvo-2020-330x140.jpg)



