Panic attack is a sudden attack of anxiety and overwhelming fear, accompanied by unpleasant physiological symptoms. There is an increase in blood pressure to critical levels, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, increased sweating, and involuntary urination.
Important! Panic attacks are not a disease as such, but indicate a malfunction in the body as a whole. You need to know what medicine for panic attacks can relieve an attack.
How can you tell if you're having a panic attack?
Panic attacks can occur both in absolutely healthy people in a state of real threat to life, and as a result of some mental, somatic and psychophysiological abnormalities in human health.
Frequent attacks occur in persons suffering from various forms of neuroses, vegetative-vascular dystonia and other manifestations of neurocirculatory dysfunction, and pathological fears. Persons with cardiovascular pathology, endocrine diseases, injuries and brain tumors are also susceptible to attacks.
Attention! Seizures during attacks are often confused with a hypertensive crisis or heart attack. In order to clearly differentiate a panic attack from other diseases, you need to know how an attack begins and develops.
The first thing a person feels is a general state of discomfort and incomprehensible anxiety, a feeling that something is wrong. At the same time, the heartbeat increases, hands become clammy, blood pressure rises, dizziness and a feeling of impending fainting appear. The body is seized with a slight trembling, the hands go numb, the legs weaken and give way. It becomes impossible to breathe and fear sets in. As the attack progresses, fear develops into overwhelming horror and an almost physical sensation of death. Very often, when faced with an attack for the first time, patients say: “I’m dying.”
Treatment of vagoinsular crisis
Vagoinsular crisis
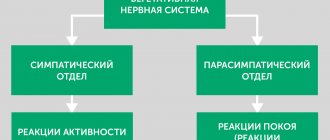
The vagoinsular variant of a panic attack is characterized by pathological excitation of the parasympathetic division of the ANS. Freezing, interruptions in the heart, sweating, dizziness, a feeling of “falling into nowhere,” decreased blood pressure, redness of the skin, increased intestinal peristalsis—these are all symptoms of a vagoinsular crisis. Psychotherapy and breathing correction are also used in its treatment.
And the medications are the following: atropine 0.1% 1 ml subcutaneously or platyphylline 0.2% 2-3 times a day subcutaneously, for low blood pressure - cordiamine 1% 2-3 ml, caffeine 10% 1 ml. If there are signs of low blood sugar - sweating, dizziness, feeling hungry, a 40% glucose solution of 20 ml is administered intravenously, it is recommended to drink sweet tea. If the patient has severe dizziness and vomiting, 0.5% haloperidol 2 ml intramuscularly relieves these symptoms.
In case of a mixed version of a panic attack, the doctor evaluates from the clinical picture which activity - sympathetic or parasympathetic - predominates, and based on this, forms the treatment. It should be noted that the relief of panic attacks is carried out under ECG control, blood pressure control, it is also necessary to do a blood test for glucose levels, insulin levels, and a urine test for catecholamine levels. The patient, even after one episode of panic attack, must be consulted by a neurologist and psychotherapist.
What happens in the body?
The mechanism for the development of an attack is as follows: sudden anxiety activates the adrenal glands, increasing the production of the stress hormone cortisol, which in turn causes a rapid heartbeat and has a vasoconstrictor effect. Constricted blood vessels increase the pressure of blood flow (increased blood pressure), spasms of smooth muscles begin, which explains sharp abdominal pain and involuntary urination. Tachycardia and increased muscle tone of the respiratory apparatus cause shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air.
First aid for a panic attack
If the attack occurs alone, then the first and most important thing to do is to go outside, where there may be passers-by. When people are nearby, the patient’s well-being immediately improves, and hope appears in the mind that they will have time to save him, call an ambulance and give him medicine for a panic attack.
If there is no possibility of contact with people, for example, the attack happened late at night, you need to wash your face with cool water, take a sedative for panic attacks, open the window, walk around the room, trying to breathe deeply and evenly through cupped palms. Check if the phone is turned on and pick it up. Knowing that you can call for help at any time will help you calm down faster. And the main thing is to switch your thoughts to positive memories, turn on a funny movie and read a book, focusing on reading.
Loved ones, if they are nearby, can speed up the cessation of panic attacks. To do this, it is advisable to take the patient’s hand and tell him in a confident voice that everything will be fine. If you have sedative tablets on hand, use them as a medicine for a panic attack, drop 10 to 30 drops and give to the patient with a glass of water.
Etiological treatment
Elimination of causes
At the heart of any disease is a cause, a factor that served as a “trigger” and provoked the onset of the disease. VSD also has the following factors or “triggers”: stress, nasopharyngeal infections, overexertion, hormonal abnormalities. If you influence the elimination of these factors, it is possible to achieve relief from the symptoms of the disease or get rid of it altogether. For example, with VSD and panic attacks provoked by stress, it is necessary to resolve all conflict situations and normalize relationships with friends and relatives.
If the development of VSD is based on an infectious onset, it is necessary to thoroughly sanitize the oral cavity, nasopharynx, and perform a tonsillectomy, if indicated. In case of VSD associated with overfatigue, it is necessary to exclude excessive loads. If a hormonal imbalance is suspected in the occurrence of vegetative-vascular dystonia, then the woman is recommended to undergo treatment together with a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Who can help get rid of the disease?
Once faced with an attack of uncontrollable fear and anxiety, a person begins to fear repetition. After all, attacks can begin at any time, even in a completely calm environment: in transport, at a lecture, at work, at home in front of the TV and even in sleep. With external security, inexplicable anxiety suggests one’s own mental inadequacy. With frequent attacks, a person may feel like he is going crazy. The question naturally arises: where to go, how to get treatment, and whether there is a cure for panic attacks.
First of all, you should contact a neurologist. A specialist in this profile will be able to determine the causes (usually there are several) of the pathology, differentiate it from other diseases (the main criterion is spontaneity, unsystematic attacks) and, what is very important, prescribe medication for panic attacks. The fact is that, depending on the severity of the disease, you may need strong drugs, available in pharmacies only by prescription.
In addition to drug therapy, the neurologist will advise the patient to see a psychotherapist to find the root cause of the development of abnormalities.
Important! This direction should not be ignored, since often the source of panic attacks is strong psycho-emotional trauma suffered in distant childhood and almost forgotten by the patient. In this case, the best cure for panic attacks is properly selected psychotherapy.
What result does the patient expect?
That's right, recovery. Fast, no side effects, forever. Just as the “clairvoyants” and sellers of dietary supplements promise, who went the furthest in their promises.
Do doctors manage to avoid this simplification? Not always. After all, they are ordinary people, they also use the media, get sick, listen to lectures about “new safe and effective drugs.”
Everyone wants it fast. The patient will recover quickly, the doctor will cure quickly. The pace of life is crazy, you have to do everything, there’s no time to get sick. The patient has no time to rest or pause. The doctor has no time to listen.
Well, yes, listen. About the fact that the husband has become inattentive, there is no sex, he’s a mess at work. You know, sometimes interesting facts pop up among this everyday life. Having both direct and indirect relation to health. But, unfortunately, these facts usually come up not in a doctor’s office, but in a friendly conversation. Where everyone is their own psychotherapist and psychologist, where there is an opportunity to speak out.
You can regret as much as you like about the irretrievably gone time, when medicine was more of an art, and the doctor could spend a lot of time in the patient’s house, knew all the relatives and their problems, which could be discussed after examining the patient. And is it worth it? After all, only very wealthy people could pay for such a “reception”.
And the doctor combined an internist and a psychotherapist.
However, note: now that internists (therapists, neurologists, cardiologists, etc.) have separated into separate specialties and no longer combine their duties with psychotherapy, their help has become much more accessible. But the need for the doctor to listen (i.e., in psychotherapy) remains.
And which doctor does the patient consider good? Regardless of specialty? That's right, someone who listens carefully.
In my practice, perhaps the most striking example of how pills without psychotherapy do not work is panic attacks (PA).
But in other anxiety-depressive conditions, similar processes occur.
Treatment of panic attack with pharmacological drugs
Drug treatment should be started only on the recommendation and under the supervision of the attending physician. But for your own peace of mind, it is better to know what medications your doctor can prescribe for panic attacks.
So, all medications for panic attacks that can improve the patient’s well-being are divided into 5 groups:
- Sedatives;
- Tranquilizers;
- Neuroleptics;
- Nootropics;
- Antidepressants.
Each group of drugs for panic attacks has its own characteristics of impact on the nervous and vascular systems of the body. At the same time, antidepressants, tranquilizers and sedatives are designed to calm the weakened nervous system, antipsychotics and nootropics affect internal processes at the molecular level. The doctor will determine how to treat the disease.
Sedative medications
The most common type of medication for treating anxiety and fear attacks in the early stages. There are more than a hundred drugs in this group; they are (usually) of plant origin or semi-synthetic (bromine-based). The concentration of the active substance in each individual medicine for panic attacks is insignificant, so they are sold in pharmacies without a prescription.
Medicine for panic attacks can be based on herbal raw materials: valerian, St. John's wort, mint, motherwort, lily of the valley, passionflower. Peony tincture, motherwort extract and sedative herbs (a balanced combination of herbs for preparing infusions and decoctions) are very popular.
Attention! The use of sedative medications reduces anxiety and irritability, improves sleep quality, and has a moderate cardiostatic effect.
When choosing over-the-counter medications for panic attacks, you should remember one feature: all alcohol tinctures have a sedative effect for 5 minutes to half an hour, and can quickly eliminate the onset of an attack.
Drugs in tablet form act more slowly, in a cumulative manner, that is, to achieve the effect you need to take a whole course.
Tranquilizers
Tranquilizers are drugs of synthetic origin, another name is anxiolytics, designed to have a pronounced sedative effect in the fight against neuropsychic disorders.
It is important to know! The main disadvantage of tranquilizers is that the body quickly becomes addicted.
That is why such medications for panic attacks are used in short courses (no more than two weeks). Pharmacies dispense medications only with a prescription. You should not resort to even mild tranquilizers without a doctor’s recommendation, since in addition to the therapeutic effect, they have a lot of contraindications and side effects. They are usually prescribed for the treatment of advanced forms of neuroses and, as doctors say, blooming neurasthenia, as a cure for panic attacks.
All tranquilizers are divided into 3 groups:
- Benzodiazepine-based medications. These include Nozepam and Phenazepam, Seduxen and Lorafen;
- Medicines based on diphenylmethane. These include the popular “Atarax” and “Amizil”;
- Medicines based on derivatives of different chemical groups. This includes the famous “Afobazol”, “Proroksan”, “Spitomin”, “Buspirone”, “Spucinat” and others.
Each of these groups of medications for panic attacks has its own indications and contraindications. You should not risk your health by choosing a medication for panic attacks on your own; let a doctor do it.
Antipsychotic medications
Neuroleptics are psychotropic medications, also known as antipsychotics, prescribed for the treatment of deeper mental disorders.
First generation antipsychotics (Amenazine, Galaperidol, etc.) are used mainly in addiction medicine and psychiatry, and second generation drugs (minor antipsychotics) are firmly established in practice for the treatment of neurotic disorders, including severe depression and as a cure for panic attacks. These include medications: Sonapax, Melleril, Thiodazine, Thioril, Truxal, Eglek, Neuleptil, Betamax and others.
Nootropic drugs
Nootropics are medications that regulate the activity of the central nervous system and improve brain functions in the field of higher mental activity.
Taking a nootropic medication increases the body's resistance to stress, helps cope with increasing mental and physical stress, improves memory and attention. In the medical treatment of panic attacks, it is used in combination with other methods of therapy. The most common nootropic drug with a calming effect is Glycine.
Antidepressants
Antidepressant drugs act on the neural network of the brain, restoring its function. Based on the name, the drugs are designed to combat depressive conditions of varying severity and can be used as a cure for panic attacks. With the ability to improve mood, they also reduce the overall level of anxiety and prevent the onset of an attack. Today, fourth-generation antidepressants Cymbalta, Milnacipran, Remeron, Effexor, Zyban, Wellbutrin, Adepress, Plizil and others have appeared in pharmacies. But drugs of 1-2 generations are still most popular (Imipramine, Amitriptyline, Clomipramine, Fluoxetine, Sertraline, Venlafaxine, etc.). This is due to the fact that proven drugs are cheaper, although they have a longer latent period of action (it takes time to achieve the effect). Fourth generation antidepressants are more expensive, but significantly improve in speed of action and in the number of side effects.
Pros and cons
There are pros and cons to drug therapy for panic disorders.
Doctors resort to antidepressants because they are a reliable remedy that will almost always help cope with the symptoms of this disease within a short period.
It is easier for the patient to take a pill and be calm than to constantly wait for sudden anxiety to strike again. Not every person is ready to attend psychotherapy sessions, much less deal with their fears on their own.
Another positive aspect of using antidepressants is that they are cheap compared to consultations with a psychotherapist.
But, like any other group of drugs, antidepressants have their weaknesses.
The main disadvantage of drug therapy for panic attacks is the side effects that the drug has on the patient’s body.
The most common symptoms are the following:
- dizziness and nausea;
- absent-mindedness;
- drowsiness and lethargy;
- irritability;
- loss of libido;
- lack of appetite and change in taste;
- deterioration of short-term memory.
Pregnant women and some older people with blood pressure problems are contraindicated.
The second reason why patients do not want to take antidepressants is that they are more likely to gain excess weight.
In addition, sometimes a patient taking drugs of this group becomes addicted. And during the withdrawal of the course, attacks of fear may be replaced by depression or increased irritability.
Given these features, antidepressants are not suitable for everyone. Patients who have an individual intolerance to these medications, as well as those for whom they do not bring relief, require consultation with a doctor. Based on the medical history and characteristics of the patient, he decides what can replace antidepressants without risking the patient’s health. In addition to these drugs, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are often prescribed for these nervous disorders.