Parkinson's disease is a serious disease of the nervous system that damages the neuronal cells of the brain. Parkinson's disease is progressive. From a medical point of view, it is manifested by motor disorders, namely, weak motor activity, limited movements, muscle mobility in a state of complete rest, tremors of the limbs. The disease is also accompanied by the development of mental disorders - a person’s mental abilities decrease, and the state of depression increases.
The causes of Parkinson's disease can be different; the disease cannot be treated. Only through drug therapy can the symptoms of Parkinson's disease be relieved.
Medical prescriptions include a structured lifestyle, as well as physical exercises for balance and stretching. Speech problems will be corrected by a speech therapist.
general information
Parkinson's disease affects men twice as often as women. In most cases, it develops after 60 years of age, but cases of early onset of the disease are recorded (at 30-40 years of age), as well as juvenile forms that develop in people in their twenties.
There are several hypotheses for the formation of pathology. It has now been precisely proven that one of the mechanisms of its development is the gradual degeneration of neurons and a decrease in the production of dopamine. It is an important neurotransmitter involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As a result, a specific set of disorders is formed, which makes it easy to make a diagnosis.
Forecast
How long do women with Parkinson's disease live? Are they more resistant to the disease than the male sex? What are the causes of death for the “weaker” sex? The life expectancy for this disease is well described by the table:
| Age at diagnosis | average life expectancy |
| Up to 40 years old | About 40 more years (average 35-43) |
| From 41 to 65 years old | About 20 years |
| After 65 years | 5-7 years |
As can be seen from the table, life expectancy decreases with age. And doctors have disappointing forecasts for women. Women with this disease live less than men. This is due to the fact that cognitive impairment develops in later stages. They affect the quality and length of life. Patients require additional conditions, care from relatives or social workers. In the later stages, older women need constant care, and even routine household services are difficult.
Causes
The exact causes of Parkinson's disease have not been identified. Scientists have been able to identify only a number of factors that increase the risk of developing neurodegenerative processes:
- natural processes of aging of the body, accompanied by a decrease in the ability of tissues to regenerate;
- genetic predisposition (this is especially true for forms with early onset);
- chronic lack of vitamin D, which protects neurons from the pathological effects of toxins;
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals, pesticides, alcohol;
- poor environmental conditions in the region of residence;
- taking certain medications (for example, chlorpromazine);
- chronic insufficiency of blood supply to the brain (due to atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, etc.);
- infections affecting the central and peripheral nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis, herpes viruses, influenza);
- brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- smoking;
- frequent and prolonged stress, chronic fatigue.
Make an appointment
How does the rigid form manifest itself?
Rigidity means stiffness of movement due to high muscle tone. Such changes are caused by simultaneous tension of antagonist muscles (extensor and flexor).
The rigid form of Parkinson's disease has several properties.
- The tone affects asymmetrically. It develops non-simultaneously throughout the body. Asymmetry is especially characteristic of the beginning of the development of pathology.
- The intensity of the increased tone may vary throughout the day. The muscles are least tense after rest. Nervous shocks increase muscle stiffness.
Trembling-rigid form - development and symptoms
Features of movements in parkinsonism
In its pure form, rigid Parkinson's disease is not common and can only exist at the very beginning of the disease. More often, increased tone is combined with other symptoms, according to which three types of Parkinson's disease are distinguished.
- The rigid-trembling form occurs in approximately 20% of patients. With this type of Parkinson's disease, increased muscle tone is complemented by a general decrease in motor activity.
Parkinson's disease (shaking palsy)
There may be no tremor in Parkinsonism
It is the combination of akinetic and rigid symptoms that is most often understood as the rigid form of parkinsonism. A special symptom of it is bradykinesia, or slowing of the movements of all muscles, which develops gradually.
Slowing of movements (bradykinesia)
Symptoms
Parkinson's disease is manifested by specific symptoms, which together form a clear picture of the disease:
- tremor: fine trembling begins in one hand and then spreads to both limbs and head; the movement of the fingers is somewhat reminiscent of counting coins; while performing purposeful movements (for example, while working at a computer);
- general slowness of movements (bradykinesia): the patient often freezes in one position;
- specific gait: a person moves with small, shuffling steps, as if he is constantly on very slippery ice;
- poor facial expressions: a mask effect is formed due to low mobility of facial muscles;
- monotonous, quiet speech;
- increased muscle tone (muscle rigidity): the figure becomes stooped, arms and legs are slightly bent, the head is tilted forward;
- postural instability: a person has difficulty starting and ending movements, resulting in decreased ability to maintain balance;
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system: oily skin, excessive secretion of saliva and sweat;
- decreased sense of smell;
- constipation, urinary disorders.
Unlike other neurodegenerative diseases, Parkinson's disease has little effect on intelligence in early and middle stages of development. As the pathology progresses, there is a decrease in the speed of thinking and speaking, decreased mood, depression and indifference to everything that happens.
Features of the disease
The disease is one of the disorders of the motor system, in which there is an increase in the tone of muscle tissue of the plastic type. In addition, there is a significant slowdown in voluntary movements.
The presented pathology can safely be classified as one of those that only progresses over time and, actively developing, at one point deprives a person of the ability to move or perform basic work.
Akinetic-rigid syndrome is characterized by a large number of unpleasant symptoms, the intensity of which increases over time. Before treatment is prescribed, the patient must undergo a thorough diagnosis.
The presented pathology is associated with impaired functionality of those parts of the brain that are responsible for performing motor actions. When making a diagnosis, special attention must be paid to hereditary predisposition.
Stages of development
Currently, doctors distinguish 5 stages of Parkinson's disease, manifested by a certain set of symptoms:
- Stage 0: no clinical manifestations;
- Stage 1: there are slight difficulties in moving one arm, a slight tremor, first with excitement, then at rest; the sense of smell and sleep are disrupted, fatigue and apathy appear;
- Stage 2: disturbances involve the second hand, trembling of the tongue and lower jaw appears; salivation; hypokinesia is formed; the ability to self-care is preserved;
- Stage 3: stiffness and impoverishment of movements increases, facial expressions are almost absent; a specific gait and posture is formed; during a conversation, the patient begins to get stuck on the same word; self-care is difficult, but possible;
- Stage 4: postural instability develops, the patient begins to fall frequently; the intellect begins to suffer, depression increases; At this time, suicide attempts are common; a person needs help to perform simple actions;
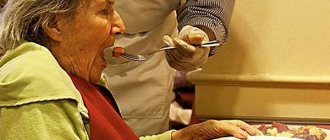
- Stage 5: manifestations reach their climax, the person cannot sit down, stand up and walk independently, eating is difficult due to swallowing disorders; loss of control over bowel movements and urination; the patient requires constant care.
Symptoms of pathology
Akinetic-rigid syndrome may have the following symptoms:
- Formation of muscle hypertonicity, which is present in the patient throughout the entire therapy.
- Not full extension of the upper limbs. At the same time, the arms are bent not only at the elbows, but also at the hands.
- Insufficient leg extension at the knees, which progresses over time.
- Lowering the head closer to the chest.
- Loss of intensity and variety of movements.
- Slowness of any motor actions.
- Tremor of the upper and lower extremities, as well as the jaw. With movement, these symptoms decrease slightly.
- Unintelligible speech. When talking, a person practically does not express any emotions.
- Problems with thinking.
- Lack of reactions of facial muscles even in everyday life.
- Obsession of communication.
- Inability to move independently.
Akinetic-rigid syndrome even affects a person’s handwriting: it becomes small, so it is quite difficult to make out.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is made based on the characteristic clinical picture. The patient is examined by a neurologist who notes typical signs. Complaints must be clarified and an anamnesis of the disease (history of the appearance of symptoms) and life history (information about previous injuries, chronic diseases, surgical interventions) is collected. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are used to clarify concomitant pathology and exclude other causes of neurological disorders.
Features of pathology treatment
So, treatment of akinetic-rigid syndrome depends on the severity of its development. In severe cases, a person may be hospitalized. Therapy includes:
- Taking muscle relaxants - special drugs that help relax muscles and reduce their tone. Among such drugs are: “Meprotan”, “Mydocalm”, “Flexin”.
- Use of medications prescribed for Parkinson's disease. These drugs make it possible to combat the manifestations of paralysis, and also allow you to resist motor dysfunction: Lisuride, Pyridoxine, Romparkin, Levodopa. Naturally, these medications are very strong and have many side effects. Quite a number of drugs can be used to treat the syndrome, since they are not always effective, and the disease itself has many different symptoms. There are no universal remedies for treating the disease.
During the rehabilitation period, which lasts almost the entire life, physiotherapeutic procedures are actively used. They make it possible to restore damaged muscle groups and strengthen them. This is especially true for the tissues of the spine and joints.
Psychological support from relevant specialists is also important. In particularly difficult cases, surgery may be recommended. Doctors perform stereotactic neurosurgery. It allows you to restore damaged tissue.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
At the moment, successfully selected treatment for Parkinson's disease can stop the process of degradation and reduce the severity of pathological symptoms. The disease begins to progress more slowly, which allows patients to stay in good shape longer.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is aimed at restoring the balance of dopamine in the central nervous system. The following drugs are used:
- Levodopa and its analogues: serve as the basis for the production of dopamine;
- dopamine receptor agonists: stimulate receptors similar to a natural neurotransmitter and reduce the severity of symptoms;
- MAO-B inhibitors: reduce the breakdown of dopamine;
- COMT inhibitors: prescribed in combination with levodopa and reduce its breakdown;
- anticholinergics: aimed at reducing symptoms.
There are combination products that combine several active ingredients for the fastest possible effect.
Non-drug treatment
Drug treatment is complemented by physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage. Physiotherapy is used to activate metabolic processes and increase blood flow in the brain. Depending on the patient’s condition and concomitant diseases, the following may be prescribed:
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound stimulation;
- electrosleep;
- mineral baths;
- acupuncture.
The massage is aimed at improving motor activity. Intensive muscle kneading and passive gymnastics reduce muscle stiffness and have a general strengthening effect.
Physical therapy exercises allow you to:
- reduce muscle stiffness and strengthen it;
- increase sense of balance;
- improve the patient's emotional state.
Most exercises are aimed at training the sense of balance. The complex is selected individually depending on the patient’s condition, age and concomitant diseases.
Surgery
The help of surgeons is relevant in the last stages of the disease. The most effective and safest operation is the installation of a brain stimulator. The intervention does not require opening the skull. Thin electrodes are inserted into the brain and a small stimulator is placed under the skin of the collarbone. The device is programmed for a specific pulse frequency; in addition, the patient and his relatives can change the settings depending on the condition. Using a stimulant allows you to reduce the dosage of medications and keep symptoms under control for a long time.
Other surgical treatment options require working on an open brain:
- thalamotomy: destruction of part of the thalamus, allowing to get rid of tremors, but maintaining other symptoms;
- pallidotomy: partial removal of one area of the brain (globus pallidus), significantly reducing all the main symptoms of the pathology.
Methodology for determining severity
An adequate assessment of the severity and disability of a person plays an important social role. The Hoehn-Yahr scale for assessing the severity of Parkinson's disease, introduced into practice in the late 60s of the twentieth century, has become widespread. According to this scale, five degrees of severity are distinguished, depending on the manifestations and consequences of the disease:
- Stage 0 – no signs of disease.
- Stage 1 – only one-sided symptoms.
- Stage 1.5 – unilateral manifestations involving skeletal muscles.
- Stage 2.0 – mild bilateral symptoms without imbalance.
- Stage 2.5 – bilateral signs, imbalance, but the ability to overcome evoked posterior movements (retropulsions) is preserved.
- Stage 3 – moderate bilateral symptoms. Presence of unexpressed postural instability. The patient does not require outside care.
- Stage 4 – severe manifestations, immobility. The ability to move or stand independently on “good” days or hours remains.
- Stage 5 – complete immobility.
Determining the progression of the disease is also important. There is a fast pace, which is characterized by a change of stages according to Hen-Yar within two years, a moderate pace - from three to five years per stage, a slow pace - overcoming one stage takes more than 5 years.
Complications
Restriction of muscle function in Parkinson's disease inevitably leads to a decrease in the intensity of blood flow and a decrease in the level of metabolism. Already in the middle stages of the development of the disease, the risk of blood clots and the development of dangerous conditions increases significantly:
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, heart failure;
- pulmonary embolism.
Bedridden patients often face severe complications associated with a recumbent position:
- congestive pneumonia;
- aspiration pneumonia (due to impaired swallowing, food enters the respiratory tract);
- bedsore infection and sepsis.
Most patients experience apathy and severe depression, which lead to suicidal thoughts. Some patients carry out plans and commit suicide.
Correctly selected treatment significantly reduces the risk of complications, which is why it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Development of the akineto-rigid form
At the very beginning of the disease, movement disorders do not appear. Gradually, not only rigidity develops, but also bradykinesia:
- the facial muscles are initially affected, which leads to weakened facial expressions and decreased blinking, and subsequently to a mask-like face;
Parkinson's disease - photo
Handwriting in Parkinson's disease
Gradually, it becomes more and more difficult for a person to take care of himself: to comb his hair, wash, fasten his clothes.
Patient care
Parkinson's disease in general and the akineto-rigid form in particular are also characterized by autonomic transformations and changes in the psyche:
- slow movement of food through the digestive tract and constipation;
- weight loss;
- weak sweating, which is especially dangerous during hot periods due to the high risk of overheating;
- increased sebum secretion and associated seborrheic dermatitis;
- increased urge to urinate and urinary incontinence;
- sexual dysfunction;
- depression;
- grouchiness;
- egocentrism;
- slow switching from thought to thought;
- obsession;
- irritability.
The combination of slow movement and increased tone ultimately leads to postural instability. This syndrome is associated with an inability to maintain balance and is manifested by various symptoms:
- forced periodic transition to a mincing step while walking;
- the need to take several steps in the event of a push that throws you off balance;
- loss of stability when trying to stand up or sit down.
Such changes can ultimately lead to a fall. Patients often suffer fractures.
With the akineto-rigid form, the prognosis is often unfavorable. This type of Parkinson's disease often results in complete immobility, difficulty swallowing, and breathing problems.
Prevention
Prevention of Parkinson's disease includes:
- proper nutrition with a minimum amount of preservatives and artificial additives, a sufficient amount of vitamin D, omega-3, antioxidants;
- regular physical activity to prevent physical inactivity;
- adequate sleep of at least 8 hours a day, adherence to a work and rest schedule;
- minimizing stress and fatigue;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- regular medical examinations, compliance with all doctor’s recommendations;
- timely contact a specialist if any suspicious symptoms appear.
Make an appointment
Early signs
“Parkinson's disease takes a long time to develop, and at first it can be unnoticed. Among the early ones, there are a number of non-motor signs, that is, not related to motor activity. They can appear 6-7, and sometimes 10-15 years before the first motor clinical symptoms. Patients begin to complain of completely different health problems: fatigue, constipation, depression, bladder problems, impaired sense of smell, restless leg syndrome.
There is no need to panic about the appearance of such signs, because people still turn to specialists with such problems: for constipation - to a gastroenterologist, for depression - to a psychotherapist, for bladder dysfunction - to a urologist. However, there is no need to delay it; patients are often brought to us for an appointment when they already have more pronounced symptoms: slowness of movement, problems with gait, changes in handwriting and hand tremors at rest. By the way, it is worth understanding that hand tremors are not at all a mandatory sign of parkinsonism; it happens that the pathology occurs without it at all,” notes Snezhana Milanova.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic will come to the rescue at any stage of Parkinson’s disease. We offer comprehensive treatment in accordance with modern standards:
- selection of drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, laser treatment, etc.;
- therapeutic massage courses;
- Exercise therapy directly in the clinic;
- training in physical exercises for exercise at home;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment if indicated;
- training relatives in the rules of caring for the sick;
- work with a psychologist and psychiatrist if necessary.
Life extension
When the patient has completed all the necessary diagnostic procedures, he will be given a final diagnosis. Sometimes this process is delayed, because... symptoms may be vague and similar to other diseases. Immediately after checking that a person has this particular disease, the doctor will prescribe therapy that will allow him to remain in a normal state and live as long as possible.
Treatment includes many ways to treat the disease. It is very important to follow all the measures prescribed by the doctor, because... Only this approach will achieve results. The patient is prescribed:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Physical therapy;
- Classic diet;
- Psychotherapy.
Along with this, you must take medications. They help treat the disease by reducing its impact on the brain. Various groups of drugs are prescribed. Most popular:
- "Lizuride";
- "Midantan";
- "Levodopa";
- "Pyridoxine";
- "Cyclodol".
Additionally, it is permissible to use folk remedies. To do this, you need to make an infusion of oats, thyme, lemon balm, peony, oregano or chamomile. If the disease progresses to stage 4 or 5, then you will need to care for the patient. If there are no relatives, this can be done by specialists at a rehabilitation center.
Recent medical developments make it possible to perform an operation that eliminates most symptoms and also normalizes the patient’s condition as much as possible.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic has experienced doctors, skilled nurses and modern equipment for diagnosing and treating various diseases. We offer:
- diagnostics using instrumental, functional and laboratory studies;
- consultations with experienced specialists in various fields;
- obtaining the opinion of foreign colleagues if necessary;
- individual selection of treatment;
- complex therapeutic regimens using medications, physiotherapy and other methods;
- extensive screening programs for early diagnosis of diseases;
- detailed consultations on disease prevention;
- any certificates and conclusions.
Parkinson's disease begins very slowly, but it is almost impossible to stop the process. If you or your family have suspicious signs, do not delay contacting a doctor. Sign up for diagnostics at the Energy of Health clinic.