Causes
Unfortunately, no reliable causes leading to Parkinson's disease have been identified. A certain role is given to environmental factors (especially contact with heavy metals), hereditary factors, the presence of repeated traumatic brain injuries and other undesirable effects, including taking certain medications. Some authors believe that the cause of Parkinson's disease is the presence of a prion infection.
Ultimately, the pathological cause of the disease is a disruption in the functioning of one of the areas of the brain - the substantia nigra. In this part of the brain, special neurotransmitters are produced - substances that allow communication between neurons, regulation of muscle tone, and much more. It is the disruption of the DOPA system that leads to all manifestations of the disease.
Differential diagnosis
Parkinson's disease must be differentiated from all diseases that are accompanied by parkinsonism syndrome: secondary parkinsonism, pseudoparkinsonism, “parkinsonism plus”. About 80% of parkinson's syndrome cases are due to Parkinson's disease.
One should remember certain clinical features of parkinsonism that should raise doubts about the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, for example: ineffectiveness of levodopa, absence of tremor, symmetry of motor disorders, early manifestations of signs of peripheral autonomic failure.
Symptoms
A classic sign of Parkinson's disease is tremor - shaking of the limbs and head. However, often this very symptom, which certainly exists, is considered the leading one and almost the only thing that leads many people to panic when trembling appears in their hands or head. However, it is not. The main and obligatory symptom of the disease is oligobradykinesia - insufficient range of movements, their scarcity, difficulty starting movement. Oligobradykinesia also leads to poor facial expressions and gestures. And only in the presence of this symptom can we talk about Parkinson’s disease. Two other typical and frequent manifestations - tremor and rigidity (muscle stiffness due to increased muscle tone) are often found in other diseases, but also have important diagnostic value.
Also, with Parkinson's disease, there may be disturbances in the motor sphere, for example, postural instability or the inability to independently stop movement, leading to a fall. It is this symptom that often becomes disabling in the later stages of the disease.
Often with Parkinson's disease there are cognitive impairments (impaired memory, concentration, learning ability), pelvic disorders (usually constipation), and mental disorders. In most cases, the disease, especially in the later stages, leads to a deeply traumatic effect on the patient (and often on relatives) and leads to the development of clinically or subclinically expressed depression. This also needs to be taken into account, because under the guise of depression, many of the patient’s problems may not be noticed: he simply will not talk about them on his own.
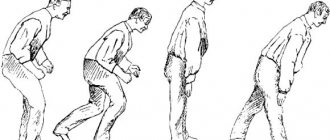
Often patients change in behavior (become pedantic, inconsistent, overly intrusive, and a persistently depressed mood develops). The quality and pattern of sleep is also disrupted in patients. Also characteristic are a typical posture (the posture of a petitioner), gait disturbances (walking in small steps) and many other signs.
If we take the most “popular” and well-known symptom – tremor – then it has its own characteristics. Tremor in Parkinson's disease is characterized by a unilateral onset, often in the arm, with a gradual transition to the other side, and then to another anatomical zone (legs, etc.). Tremor of the jaw and head is less typical and usually occurs in the later stages of the disease, and even then only in rare cases. The very appearance of the tremor is also striking; it resembles “counting coins” or sorting out pills. The tremor is usually low-amplitude, somewhat decreases in the process of performing a purposeful movement, which is especially noticeable during the finger-nose test; there is almost no tremor during the movement of the finger, while upon completion of the purposeful action (hitting the nose), a clearly visible tremor appears.
Famous people with Parkinson's disease.
Clinical picture
The following manifestations are characteristic[3]:
- Slowing of voluntary movements (bradykinesia), which reaches various degrees, up to the inability to sit down, stand up, or move (akinesia).
- Waxy increase in muscle tone (plastic tone according to Sherrington).
- Loss of friendly movements: no hand movements when walking, no turning of the head in the direction of gaze, etc.; Small friendly movements also appear, which give an individual characteristic to each voluntary movement.
- Violation of expressive movements, for example, gestures, facial expressions (amimia develops).
- As a result of changes in muscle tone, muscle contractures occur that fix the limbs and torso, which determines the patient’s peculiar posture.
With a sharp increase in muscle tone to the point of rigidity (akinetic-rigid Förster syndrome), the patient may be completely immobilized. During passive movements, the limbs remain in their assigned positions. As a result of pathological excitability of muscles under tension, Westphal's paradoxical phenomenon occurs.[3]
Poverty of movements and increased muscle tone of the plastic type are not detected in all patients with akinetic-rigid syndrome. Thus, when using some phenothiazine drugs in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders, motor disorders may occur as side effects - stiffness, immobility - without increasing muscle tone of the extrapyramidal type.[3]
Diagnostics
Diagnosing Parkinson's disease is challenging. Indeed, despite common misconceptions, not a single neuroimaging study, except positron emission tomography, can reliably establish a diagnosis. Neither MRI of the brain, nor even ultrasound examination of the substantia nigra allows us to speak about the presence of the disease with a high degree of probability.
The only research method that allows us to talk about the presence of the disease is positron emission tomography (PET). When performing PET, there is a decrease in the accumulation of a special radioactive drug - fluodopa in the striatum and substantia nigra. Moreover, detection of the disease is possible even at the preclinical stage. However, the prevalence of the study is very limited, the study is extremely expensive at the present stage and in Russia it can only be carried out in large research src=»https://neurosys.ru/wp-content/uploads/posts/2014-02/1392397744_parkinsona-diagnostika. jpg" class="aligncenter" width="350″ height="324″[/img] As a rule, the diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture. In this case, the presence of characteristic symptoms, the typicality of the clinical picture and complaints, as well as the sequence of progression of symptoms must be taken into account. Also, a neurological examination reveals the presence of bradykinesia, the “cogwheel” phenomenon and other specific symptoms of the disease.
A good response to therapy with levodopa-containing drugs also plays an important role in diagnosis. Symptoms usually disappear completely or almost completely at the first appointment.
Methodology for determining severity
An adequate assessment of the severity and disability of a person plays an important social role. The Hoehn-Yahr scale for assessing the severity of Parkinson's disease, introduced into practice in the late 60s of the twentieth century, has become widespread. According to this scale, five degrees of severity are distinguished, depending on the manifestations and consequences of the disease:
- Stage 0 – no signs of disease.
- Stage 1 – only one-sided symptoms.
- Stage 1.5 – unilateral manifestations involving skeletal muscles.
- Stage 2.0 – mild bilateral symptoms without imbalance.
- Stage 2.5 – bilateral signs, imbalance, but the ability to overcome evoked posterior movements (retropulsions) is preserved.
- Stage 3 – moderate bilateral symptoms. Presence of unexpressed postural instability. The patient does not require outside care.
- Stage 4 – severe manifestations, immobility. The ability to move or stand independently on “good” days or hours remains.
- Stage 5 – complete immobility.
Determining the progression of the disease is also important. There is a fast pace, which is characterized by a change of stages according to Hen-Yar within two years, a moderate pace - from three to five years per stage, a slow pace - overcoming one stage takes more than 5 years.
Rigid form of Parkinson's disease
The rigid form of Parkinson's disease is the most severe type of the disease. The pathological condition occurs in older people and ranks second in frequency after Alzheimer's psychosis. The progression of symptoms leads to complete immobility of the patient and stiff muscles; clinical manifestations are difficult to respond to therapeutic intervention. In rare cases, the disease occurs in young people and children.
Consequences and life prognosis
According to the above tables, the need for outside care can be noted already at stage 4 of the disease. However, at stages 2.5 and beyond, a person’s ability to work is practically lost.
The life prognosis for patients with Parkinson's disease is usually favorable. With proper care and adequate therapy, the average life expectancy practically does not decrease. Timely initiation of adequate therapy, non-drug methods of rehabilitation and the provision of psychological support allow patients to maintain social activity for a long time and maintain the quality of life at the proper level.
Related articles: Exercise therapy for Parkinson's disease Treatment of Parkinson's disease
Treatment
Treatment of the akinetic-rigid form of Parkinson's disease can be carried out using the following methods:
- drug therapy;
- surgical intervention;
- herbal treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy.
Dopamine-based medications that replenish the neurotransmitter deficiency must be taken constantly. Rigidity in Parkinson's is relieved by medication, but therapy is symptomatic.
During drug treatment, complications may arise in the form of violent movements and outbursts of aggression. In some cases, the patient “freezes” after physical activity and becomes completely motionless.
Surgical treatment using a laser allows you to stop the progression of the disease in the early stages. Traditional medicine methods and physiotherapeutic effects are of auxiliary value and are designed to relieve tension in stiff muscles.



![Eating Well for Parkinson's Disease [2020 Guide]](https://3d-panneco.ru/wp-content/uploads/pravilnoe-pitanie-pri-bolezni-parkinsona-rukovodstvo-2020-330x140.jpg)



