Basic recommendations for catering
- The diet for Parkinson's should be balanced. About half of the diet should be allocated to vegetables and fruits. The remaining two servings should be carbohydrates and proteins. It is better to use grains rich in vitamin B. And for protein foods, choose white meat and legumes.
- Food must be prepared at home. It is necessary to exclude semi-finished products, fast food, and snacks from the diet. For heat treatment we use steam, an oven or a slow cooker. Remove fried foods. Salt food after cooking.
- You need to eat at least 4-5 times a day. Portions should be small, it is recommended to chop the food. After chewing, you can wash down your food with water.
- The place for eating needs to be organized correctly. You can place a non-slip mat under the dishes and use special weighted cutlery. It is better to use plastic mugs; dishes with two handles or with a straw are convenient.
To prevent atherosclerosis, it is recommended to follow a Mediterranean diet. It uses a lot of olive oil, sea fish and fresh vegetables.
Drinks for Parkinson's disease: list of permitted and prohibited
The diet for Parkinson's disease should include the following drinks:
- Clean water in an amount of at least 1.5-2 liters;
- Fruit drinks or compotes with a small amount of sugar;
- Fermented milk drinks, weak tea.
It's better to limit:
- Full-fat milk, cream;
- Coffee and strong tea.
Exclude:
- Carbonated drinks with artificial additives.
Is it okay to drink alcohol if you have Parkinson's? No, alcohol worsens the course of the disease and causes an exacerbation of symptoms.
Porridges and cereals
The diet for Parkinson's disease should consist of one-quarter carbohydrates. It is recommended to use cereals rich in vitamin B:
- Buckwheat;
- Oatmeal;
- Millet;
- Steamed rice or knitted porridge.
It is better to cook porridge in a semi-liquid and viscous form. Avoid dry rice and semolina. They cause constipation.
Plant food
Diet for Parkinson's should be varied. This will help cope with loss of taste and food refusal. Vegetable diet:
- Cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, broccoli, cauliflower can be used regularly;
- Radishes, white cabbage, beans and peas should be limited.
Nuts are a valuable source of protein. Dried fruits and fruits will replace sweets and help cope with constipation. But you should avoid eating mushrooms. They are poorly digestible.
Meat food
Protein Diet for Parkinson's Disease: Proper nutrition includes eating white meat.
Allowed to use:
- Turkey;
- A rabbit;
- Chicken.
Sausages, lard, and smoked meats are excluded from the diet. It is better to limit red meat. Veal and lean beef are acceptable.
Cheeses and cottage cheese
Low-fat cottage cheese should be included in the patient's diet. It should be consumed at lunch or in the evening. Curd dishes are suitable for a snack. They must not contain artificial additives.
It is preferable to use soft curd cheeses. Other types are limited due to their high salt content.
Other products
Nutrition for Parkinson's disease: the patient's menu should be varied.
Allowed bakery products:
- Black and gray bread;
- Bran bread.
Oil and fats: It is preferable to use vegetable and olive oil. Use the creamy product minimally.
Sweets:
- Marshmallow without additives;
- Paste;
- Dried fruits;
- Berry-based jelly.
General rules
Parkinson's disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that is associated with the degeneration (destruction) of certain neurons (dopamine neurons) and dysfunction of the central nervous system.
The cause of the disease is unknown. Research has proven the role of many factors, including hereditary ones. It is believed that neuronal degeneration is caused by oxidative stress of neurons and apoptosis (death). There is an accumulation of calcium and iron in the cells, with a simultaneous lack of zinc. Clinical symptoms appear when 50-80% of neurons die. Parkinson's disease is characterized by a complex of symptoms that includes tremors (shaking of hands, head), muscle stiffness, stiffness of movements, decreased facial expressions, autonomic and mental disorders. Parkinson's disease cannot be cured. However, thanks to medications and nutrition, it is possible to slow down the progression of the disease, reduce its manifestations and improve the patient’s quality of life.
The role of nutrition should not be ignored. Considering that atherosclerosis is a risk factor for the onset and progression of the disease, it is clear that the diet for Parkinson's disease must meet the requirements of a cholesterol-lowering diet . It involves eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, greens, legumes, various seeds and nuts, whole grain bread, low-fat dairy products and lean meats (no more than once a week). The basis of the diet is fish and seafood, as well as olive, linseed, and sesame oil.
of ketogenic diets , a type of low-carbohydrate diet program, has also been confirmed The mechanism of ketosis is triggered by consuming carbohydrates at a level of 100 g per day or less, which is 3, 5, 4 times less than the daily requirement of a healthy person. Due to the deficiency of carbohydrates, fats are actively included in metabolism . When they are actively broken down, fatty acids and ketone bodies are formed and energy is released. Ketogenic diets are widely used for epilepsy , Dravet syndrome , Douse syndrome and other diseases of the nervous system and are considered as an alternative non-drug treatment option.
Ketone bodies affect brain structures: the production of antioxidants , the production of free radicals decreases, and neurodegenerative changes are inhibited. This is the basis for the use of this diet for Parkinson's disease . If the hypocholesterol diet can be used by everyone without restrictions, then the ketogenic diet can only be used on the recommendation of the attending physician. First of all, because it has many contraindications ( diabetes , heart disease, high cholesterol , kidney pathology). Then, it is very important to be able to correctly calculate the amount of nutrients in the diet. Another disadvantage is that it is difficult for patients to tolerate and is often accompanied by decreased ability to work.
Considering some of the pathogenetic aspects of this neurological disease, nutrition for Parkinson's disease should include:
- Antioxidant vitamin C , which slows the progression of the disease. Patients have an increased need for ascorbic acid, therefore, in addition to consuming foods containing it (rose hips, red peppers, sea buckthorn, Brussels sprouts, dill, wild garlic, cauliflower, red rowan, oranges, papaya, kohlrabi, strawberries), it is recommended to take dose 3000–6000 mg per day.
- B vitamins are very important for this disease. The production of dopamine in the body depends on the intake of vitamin B1 in the body. Pyridoxine is contained in potatoes, oat and buckwheat cereals, nuts, carrots, and spinach. The tablet drug should not be taken while taking Levodopa .
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is important for preventing the progression of neuronal damage and depression . Its suppliers are kidneys, liver, yeast, eggs, dairy products, cabbage, rose hips.
- We get vitamin B6 Sources of B12 are offal, fish, soy, seaweed, oysters. Folic acid (B9) is found in dark green vegetables (lettuce, spinach, asparagus), avocados, wheat, beans, liver, and the least in egg yolks.
- Vitamin B3 (nicotinic acid) supports the immune system, prevents depression and irritability. Contained in brewer's and bread yeast, cereals, bran, animal liver, peanuts.
- Berries, fruits and vegetables as sources of vitamins and minerals. Cherries, cherries and barberries are useful for this disease. If possible, consume all fruits and vegetables raw.
- Tocopherol (vitamin E) and lipoic acid have neuroprotective properties and antioxidant effects . High levels of lipoic acid are found in beef, liver, cream, sour cream and beans. Sources of vitamin E are nuts (almonds come first, hazelnuts, cashews, pistachios, walnuts), vegetable oils, wheat sprouts, dried apricots, prunes, sea buckthorn, rose hips, salmon, squid, pike perch, eel, oatmeal and barley. Taking vitamin E in high doses has a beneficial effect on the course of the disease. The recommended intake of this vitamin is 200 IU per day.
- Vitamin D , whose role has also been proven. We get this vitamin from fermented milk products, cottage cheese, vegetable and butter, cheese, raw yolks, seafood, fish liver (halibut and cod), fish oil, herring, tuna, mackerel, oatmeal, potatoes. The drug can be taken at a dose of 400-800 IU per day.
- Calcium for the prevention of osteoporosis . It is found in dairy products and sesame seeds. Magnesium provides neuromuscular impulse transmission (wheat bran, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, almonds, pine and walnuts, peanuts, spinach, beans, dates, sunflower seeds), potassium (honey, bee bread, apple cider vinegar, potatoes, soybeans, beans, peas, watermelon, melon, bananas, dried apricots, almonds, pine nuts) and sulfur as an antioxidant (the highest content in rabbit and chicken meat, pike, sea bass, sardine, pink salmon, flounder, peas, eggs, average content in lamb, beef, soybeans, peanuts, pork and duck liver).
- Coenzyme Q10 , which promotes the production of cellular energy, slows down the death of neurons and the progression of the disease. Coenzyme A ( vitamin B5 acts synergistically with coenzyme Q10 , balancing cell metabolism, reducing fatigue and eliminating depression. Suppliers of these vitamins are beef, lamb, chicken, liver, heart, sardines, mackerel, eggs, legumes, fresh vegetables and fruits, and brown rice.
It has been proven that caffeine has a positive effect on the neurological status of patients. Drinking coffee daily (no more than one cup per day) strengthens the blood-brain barrier, which reduces the toxic effects of various substances. There is another explanation for the reduced risk of parkinsonism: caffeine blocks adenosine A2A receptors , which regulate the release of glutamate , which damages motor neurons. Taking into account frequently occurring vegetative disorders ( constipation , stomach dysfunction, urinary disorders), adjustments are made to the diet.
It is recommended to drink one cup of coffee per day
In the treatment of constipation , a diet high in dietary fiber (vegetables and fruits in any acceptable form, wheat bran, flax seed) plays an important role. When consuming bran and flax seed, you must not forget about parallel drinking load (1.5 liters of liquid per day). Flax seeds can be consumed ground, 1-2 tsp. 2-3 times a day, after filling them with 100 ml of water. The diet should include foods that have a laxative effect and enhance intestinal motility: beets, prunes, peaches, apricots, apples, strawberries, plums. Increasing physical activity is of no small importance in the treatment of constipation.
In case of dysfunction of the stomach associated with deterioration in the evacuation of its contents, patients experience nausea, vomiting, pain in the stomach and a feeling of fullness. In this case, it is recommended to eat light meals in small portions: soups, vegetable purees, boiled rolled meat, boiled fish.
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) is also quite common in Parkinsonism. To correct this condition, additional culinary processing of food (for example, chopping or pureeing) is used. Rough and fried foods that are difficult to swallow are excluded, and boiled food with a creamy consistency is introduced. If vegetables and fruits are difficult to swallow raw, you need to switch to stewed and finely chopped or pureed. Fruits need to be peeled from hard skins. Any food should be taken in small pieces, chew it thoroughly and not take the next portion until the previous one has been swallowed. You need to eat more often and in small portions.
Reduce consumption:
- Squirrel. Low protein intake optimizes drug treatment with levodopa . Certain amino acids may compete with this drug at the blood-brain barrier and in the intestine, reducing its effectiveness. In this regard, the drug should be taken 40-60 minutes before meals. Plant foods contain little protein, but more carbohydrates, and animal foods contain a lot of fat, protein and cholesterol .
- Milk and dairy products. If they are limited, elderly patients need to take calcium supplements (1200 mg per day) and vitamin D (400–800 IU).
- Zhirov. Excessive fat intake has been shown to be a risk factor for developing the disease. In this regard, it is recommended to replace saturated animal fats with polyunsaturated and vegetable fats. Some authors note a deterioration in the condition of patients with increased consumption of arachidonic acid (lard, butter, red meat, fish, game meat, eggs). Because arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fat, it is mistakenly considered a “healthy fat.” But as we see, it enters the body as part of animal fats; if consumed excessively, it does more harm than good. In addition, it is a precursor of prostaglandins - mediators of inflammation and allergic reactions. Fatty foods also slow down the absorption of levodopa and its entry into the blood.
- Simple carbohydrates and salt.
- Products containing iron. Based on the role of iron in neuronal damage, some authors propose limiting the intake of this trace element in the diet.
- Certain food additives ( monosodium glutamate , aspartate , cysteine , hydrolyzed vegetable protein) can worsen the manifestations of the disease, and therefore it is recommended to avoid products containing them (these are industrially produced products).
- Avoid drinking alcohol. Many drugs do not combine with it. In addition, tremors may increase after drinking alcohol.
Diet
Medicines are taken in the morning 30-40 minutes before meals. For better absorption of drugs, breakfast should consist of carbohydrates. Proteins and fats compete in the intestines with Levadopa drugs and impair their absorption.
Diet for Parkinson's disease "Proper nutrition."
| 1 | The patient should have at least 5-6 meals; |
| 2 | Meals should consist of 3 full meals and 2-3 snacks; |
| 3 | The serving volume should not exceed 200-250 ml; |
| 4 | Food should be easily digestible, served in small pieces or pureed; |
| 5 | You should eat food 3-4 hours before bedtime. |
Fight constipation
A diet for Parkinson's disease does not imply an absolute abstinence from certain types of foods, but rather a balanced diet. Often, elderly and senile patients are prone to constipation. This may be due to impaired motility of the digestive tract due to Parkinson's pathology, taking medications, prolonged sitting, a decrease in saliva volume due to drooling, or physical inactivity. Nutrition and fluid balance algorithm:
- It is recommended to drink 1 glass (150-200 ml) of water at room temperature on an empty stomach. The drinking regime is regulated at the rate of 25-30 ml per 1 kg of person’s weight per day. With caution - in case of heart failure or kidney disease with excretory failure due to the possible development of edema.
- Foods for Parkinson's disease should be rich in fiber and coarse fibers for the productive formation of feces (brown bread, rice, corn, bran, oatmeal).
- Inclusion in the diet of foods that help softly loosen stools: prunes, dried apricots, raisins, baked apple, boiled beets, strawberries.
- Stimulation of the intestines through pectin-containing fruits and berries: apples, peach, banana, orange, cherry, grapes; vegetables: eggplant, carrots, cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes, pumpkin.
In addition to correcting nutrition, it is recommended to maintain physical activity during the day, perform abdominal massages and gymnastic exercises.
Method of cooking, portion size
The main factor in the development of the disease is cerebral atherosclerosis. If Parkinson's disease progresses, diet and nutrition are very important for prevention.
- It is important to keep vitamins in food for Parkinson's disease. Therefore, it is better to use raw vegetables and fruits;
- Boiling and steaming also leave most of the nutrients in the food;
- It is advisable not to fry or cook food over an open fire;
- It is convenient and useful to use a multicooker for stewing;
- Portions should be small.
When the disease occurs, the functioning of the masticatory muscles is impaired. Small portions of food do not tire the patient and allow him to enjoy eating.
Prohibited Products
Drinks with sweeteners and alcohol-containing drinks are prohibited. You should avoid eating fast food and refined sweets - cakes, pastries, chocolates. It is better to reduce the proportion of raw vegetables due to their hardness, which is associated with difficulties when swallowing.
The nature of the course and symptoms accompanying Parkinson's disease require the prescription of a special diet by the attending physician - a properly selected diet can reduce the discomfort associated with the manifestations of the disease.
Types of diets
For this disease, the following types of diets are used:
- Mediterranean;
- Ketogenic;
- Gluten-free.
The Mediterranean diet is the optimal nutritional option for patients. It is necessary to prevent the development of atherosclerosis and provide sufficient fiber. Nutrient balance: 60% carbohydrates, 30% fat and 10% protein.
Diet Basics:
- The diet includes a large amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, fruits, nuts, seeds, grains;
- Dairy products are used in the form of cottage cheese, yogurt and cheese;
- No more than 4 eggs per week are allowed;
- Fish and white meat are consumed in moderate quantities;
- Red meat is consumed in minimal quantities;
- The basic diet includes a lot of olive oil.
Pros:
- This type of nutrition is optimal in terms of calories;
- It is a good prevention for high cholesterol and systemic atherosclerosis.
Nutrition and diet cannot stop progressive Parkinson's disease. But the influence of ketogenic food on the development of chronic diseases of the nervous tissue is being actively discussed. Read the detailed description below. It should be noted that there is no long-term evidence base on the benefits of this diet.
The effect of a gluten-free diet on Parkinson's disease is controversial. Cereals containing gluten are removed from the diet. The patient’s diet is depleted, because plant foods are the main source of vitamin B. In addition, a gluten-free diet increases the cost of the patient’s diet.
Products prohibited for consumption
Fried and smoked foods, canned foods, and semi-finished products should be excluded from the menu of a patient with parkinsonism. It is not recommended to prepare food for several meals at once; it must be fresh each time.
Ingredients that should be completely excluded from the diet or at least limited:
- animal fats in the form of red meat, sausages;
- simple carbohydrates – baked goods, sugar, chocolate;
- margarine, butter;
- broths cooked with meat or bones;
- fatty fermented milk and dairy products;
- finished products with dyes, preservatives, flavor enhancers and any chemical additives. Monosodium glutamate is considered especially dangerous for the brain;
- strong black tea, instant coffee.
Baking should be excluded from the diet or at least limited.
Parkinson's disease significantly depletes the body. Consumption of the listed products further weakens it and does not allow you to fully fight the disease. You should also limit the amount of mushrooms, dried fruits, semolina, white rice, and pasta in your diet.
Ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet is a nutritional diet that is low in carbohydrates, high in fat and moderate in protein.
Examples of dishes:
- Breakfast: omelet with cheese and tomatoes;
- Lunch: salmon with asparagus (small amount);
- Dinner: meat stewed with zucchini.
According to research, on such a diet you can not only lose weight and improve your body health, but also get rid of the severe symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The ketogenic diet for Parkinson's reduces tremors and muscle stiffness.
Pros:
- Body weight decreases;
- Sugar and lipid levels are normalized;
- The severity of symptoms in Parkinson's disease is reduced;
Cons of the keto diet:
- Protein puts a high burden on the kidneys and can lead to organ failure;
- There are fewer vitamins and minerals on the menu, which will need to be introduced artificially;
- Low fiber content leads to constipation;
- The diet can lead to ketoacidosis: vomiting, acetone-smelling urine and sweat;
- There are no studies with a high degree of evidence (long-term and conducted on a large population);
- Possible progression of atherosclerosis;
- Possible development of bowel cancer.
Is the ketogenic diet suitable for every day for Parkinson's? No. You are allowed to use the keto diet for 5 days. For the next 25 you need to eat a varied diet. It is necessary to undergo regular examination by a doctor.
Basic principles
As such, there is no strict diet for parkinsonism.
Doctors recommend adhering to a low-cholesterol diet to reduce the risk of the formation of atherosclerotic vascular plaques.
In addition, calcium and iron accumulate in the patient’s cells against the background of zinc deficiency.
The patient's diet should be tailored to these features. The Mediterranean diet is best suited, where the basis is vegetables, herbs, seafood, and vegetable oil.
When drawing up a menu, you should take into account the person’s condition and the stage of the disease. Many patients suffer from constipation due to decreased intestinal motility.
To normalize digestion, you need to eat vegetables, fresh herbs, cereals, and dairy products.
Patients also experience difficulty chewing and swallowing food; in this case, the method of preparing dishes is important. It is preferable to cook puree soups, liquid porridges, and steamed cutlets.
Providing the body with vitamins and minerals plays an important role, since catabolism processes predominate in the body.
In the later stages of the disease, levodopa is prescribed, which interferes with the absorption of nutrients. Therefore, food should have a high content of the following microelements:
- Vitamin C , which has a powerful antioxidant effect. Contained in citrus fruits, bell peppers, rose hips.
- B vitamins . They stimulate the production of dopamine. Sources include: potatoes, carrots, oatmeal, spinach.
- Nicotinic acid (B3) improves immunity and restores nerve conduction. Present in cereals, nuts, liver.
- Lipoic acid acts as an antioxidant and is found in legumes, liver, and sour cream.
- Coenzyme Q10 stimulates the production of energy by cells, which prevents the death of neurons. Sources are: eggs, chicken, fruits, vegetables, fish.
- Caffeine . Blocks receptors that promote the release of glutamate (glutamate damages brain neurons). Doctors advise drinking 1-2 cups of natural coffee every day, provided that the patient does not have heart problems.
Thus, the basic principles of nutrition for parkinsonism are:
- Fractionality. Food is taken 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- Balanced in nutrients, enriched with vitamins.
- Compliance of the method of preparing dishes with the patient’s condition.
- Reducing the amount of animal fats.
- The influence of nutrition on the patient's body.
The choice of dishes for the patient is of great importance.
It is better to choose unbreakable plates that are fixed to the table with suction cups. For human safety, do not use forks, but spoons with a thick handle that is comfortable to hold in your hand. Sippy cups with straws are suitable for drinking.
Starvation
The Parkinson's diet should include sufficient calories. But scientists note that fasting for 2-4 days allows the immune system to work more actively and stimulates the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (allows the formation of new neurons).
How fasting is used:
- It is contraindicated in the later stages of the disease;
- Used only for normal or overweight people;
- It is short-lived - 1 day of fasting per week;
- Fasting is allowed after consultation with your doctor.
There have been no reliable studies on the benefits of fasting. The scientists' conclusions are based on studying the phenomenon in small groups of people.
Taking vitamins for Parkinson's
With the help of a balanced and vitamin-rich diet, the patient’s emotional and muscle tension can be reduced. Additionally, such food strengthens the nervous system and immunity, prevents the development of complications, and reduces the severity of side effects from taking medications.
With the help of a balanced and vitamin-rich diet, the patient’s emotional and muscle tension can be reduced.
The menu of a patient with Parkinson's should include foods containing the following vitamins:
- C – rose hips, bell peppers, cauliflower, citrus fruits, strawberries;
- B1 – oatmeal, nuts, spinach, potatoes;
- B2 – rose hips, cabbage, dairy products;
- B3 – cereals, bran, peanuts;
- B6 – grains, fish, berries, bananas;
- B9 – dark green vegetables, beans;
- B12 – fish, oysters, seaweed;
- E – nuts, vegetable oils, oatmeal, seafood;
- D – fermented milk products, vegetable oils, seafood.
If you eat properly and nutritiously, Parkinson's syndrome will progress more slowly, delaying the onset of disability. If it is impossible to sufficiently fill the diet with vitamins, it is recommended to start taking pharmaceutical medications. Their list and dosage is determined by the doctor.
Fasting days
The scientific community is actively discussing the benefits of fasting days for chronic degenerative brain diseases. Reducing the daily diet to 600 calories allows the body to activate the immune system, get rid of old damaged cells, and restore new neurons and connections.
Levadopa medications are not suitable for nutrition in Parkinson's - their compatibility with protein foods is extremely low. Therefore, the patient is recommended to have fasting days without protein. Their regularity should not exceed one day every two weeks.
Here is a detailed diet for Parkinson's disease, proper nutrition - the video will tell you in detail about the important points.
Grocery list
Prohibited
The following products are strictly prohibited for people suffering from Parkinson's disease:
- Fast food. Such foods contain a lot of trans fats, salt, and monosodium glutamate. Fats interfere with the absorption of levodopa medication and contribute to allergic reactions.
- Sausage, sausage products. They contain large amounts of salt, preservatives, and saturated fats.
- Simple carbohydrates (sugar, jam, sweets, cakes). Increases sugar levels.
- Mayonnaise, ketchup and other industrial sauce.
- Dishes prepared by smoking, marinating, and deep-frying.
- Coarse vegetables (radishes, radishes) due to difficult digestion.
- Full-fat dairy products (cheese, homemade sour cream, cream)
- Alcohol. After drinking alcohol, the symptoms of the disease intensify.
The rest of the products are not prohibited, but some of them should be consumed sparingly:
- Products containing iron. Iron has been shown to contribute to neuronal damage.
- Animal fats (pork, lamb, goose, lard). They increase the risk of progression of the pathology. Animal fats are replaced with vegetable ones.
- Protein food. Interferes with the absorption of levodopa.
- Nuts, seeds. Can be added to food in crushed form.
Allowed
The list of permitted products is quite wide. The lion's share of the diet consists of plant foods and fish. The menu must include:
- Fresh, stewed vegetables, herbs.
- Legumes (if they do not cause flatulence).
- Fruits and berries, especially those containing vitamin C (oranges, dogwoods, currants).
- Fish, seafood. Sea kale is also useful.
- Soups with vegetable broth. If the patient has difficulty swallowing, it is better to prepare puree soup.
- Cutlets from turkey, chicken, lean fish.
- Wholemeal bread.
- Low-fat dairy products (kefir, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, natural yogurt).
- Porridge with water (oatmeal, buckwheat, wheat).
- Eggs, omelettes.
- Nuts, dried fruits (scrolled through a meat grinder).
- Rosehip decoction, cranberry juice, herbal teas, clean water (up to 2 liters per day).
- Sunflower, olive, linseed oil.
- Jelly, jelly based on berries and fruits.
Products
Useful
Foods for Parkinson's that are useful and necessary in the diet:
- Cereals (they are rich in vitamins and minerals and are easily absorbed by the body);
- Vegetable oils (contain essential nutrients, slow down the development of vascular atherosclerosis, and serve as a valuable source of energy);
- Poultry (such protein foods are easily digestible and do not contain excess iron, which is toxic to nerve cells);
- Fish (sea and river varieties are used, but preference should be given to low-fat types);
- Eggs (an affordable and valuable source of protein and phospholipids);
- Fermented milk products with low fat content (yogurt, cottage cheese, kefir contribute to the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract).
Allowed
The menu for Parkinson's should be varied. It is necessary to supplement it with the following types of products:
- Sweets (marshmallows, honey, dried fruits, marshmallows);
- Tea and tea drinks (rooibos, hibiscus);
- Vegetables and fruits (greens, root vegetables, berries);
- Nuts (walnuts, cashews, macadamia, pecans).
Limited
If you want a healthy diet for Parkinson's disease, a sample menu should not include a lot of fat and food with synthetic additives. What foods should you not eat if you have Parkinson's disease?
- Fatty meat (impairs the absorption of medications);
- Alcohol (is a toxin for the nervous system);
- Caviar (contains a lot of salt);
- Mushrooms (poorly digested in the body);
- Semolina (causes constipation);
- Canned food;
- Sausages;
- Ready semi-finished products;
- Chocolate;
- Margarine;
- I'll bake it.
Strong tea and coffee should be limited. They overstimulate the nervous system. It is allowed to use drinks in a weak form in combination with low-fat milk.
Compatibility with protein foods
Protein is essential for the normal functioning of the body. But it interferes with the absorption of drugs (Levadopa) in the stomach and intestines. Therefore, protein snacks should be moved to the evening.
Authorized Products
- The weekly diet should consist of fish and seafood dishes. This could be tuna, mackerel, cod, sardines, saury, flounder. Sea kale is useful, which can be finely chopped and added to salads or stewed vegetables.
- If possible, use fresh vegetables. If eating them is difficult, switch to stewed or boiled and crushed. Restrictions on coarse vegetables - radishes, radishes, turnips. If tolerated well, legumes should be a mandatory component of the diet. They can be included in your diet daily. Green peas and green beans do not cause bloating. Beans and spinach have been shown to contain natural dopamine . Beans can be eaten as grain or green beans.
- Fruits and berries, as they contain fiber and pectins (especially citrus fruits, apples, viburnum, grapes, cranberries, dried dogwood berries). Pectins improve intestinal motility, reduce cholesterol , and cleanse the body of harmful substances (radioactive substances, pesticides, toxic metals).
- Bran, sesame seeds, fenugreek and flax are additional sources of fiber and healthy oils. They should be administered additionally if there is constipation .
- Vegetable soups (cabbage soup, beetroot soup, borscht) with vegetable broth. Vegetables are well ground when swallowing is difficult. Cereal soups are also good when boiled or pureed. You can prepare puree soups into which pureed meat or fish is added.
- Choose low-fat varieties of meat and poultry (give preference to turkey or chicken). It is enough to eat meat dishes once a week. Meat dishes should be cooked boiled and then chopped. You can cook steamed cutlets, pates and airy meat soufflé.
- Rye and bran bread. It may be easier to consume it in the form of soaked crackers.
- Milk, cottage cheese, fermented milk drinks low in fat and limited. Every day you can include up to 2 whole eggs, from which you can prepare omelettes (steamed and baked).
- Any cereal, but it is better to exclude pearl barley, as it is the coarsest cereal. Porridge is cooked in water and with the addition of milk. Dry and crumbly porridges are difficult to swallow, so you need to prepare “smear porridges” - boil well and add water to a semi-viscous consistency.
- To season ready-made dishes, use unrefined vegetable oils (olive, sesame, corn, flaxseed).
- All nuts and seeds contain healthy monounsaturated fats. You need to eat 30-50 g daily, but they are difficult to eat in their natural form, so you can grind them in a blender, add honey and get a tasty and healthy dessert. It’s a good idea to add chopped prunes and dried apricots here (especially if you are prone to constipation).
- Rosehip decoction, herbal teas, juices, still mineral water (up to 2 liters per day). Anti-stress and neurotrophic effects are exerted by herbal decoctions of catnip, skullcap, passionflower, and valerian root.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| greenery | 2,6 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 36 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| cashew | 25,7 | 54,1 | 13,2 | 643 |
| sesame | 19,4 | 48,7 | 12,2 | 565 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Sausages | ||||
| boiled diet sausage | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 170 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Vitamins
What can you eat if you have Parkinson's disease to reduce the toxic effects of medications? To do this, your diet includes fresh vegetables and fruits rich in antioxidants. It is recommended to eat greens.
Vitamin foods for Parkinson's disease:
- Apples (affordable, recommended to peel before eating);
- Fresh herbs (parsley, dill, lettuce, cilantro, arugula - finely chopped for salads);
- Spinach (can be eaten raw and for stewing);
- Oranges, tangerines, lemons (citrus fruits are rich in antioxidants, but compete with Levadopa drugs, consume 2-3 hours after taking the tablets).
Tips for choosing and adjusting your diet
Parkinson's disease is accompanied by symptoms that further aggravate the patient's condition. Many of them can be dealt with by making appropriate adjustments to the diet. In particular, if you have problems with swallowing, you should eat food that is as crushed as possible or completely ground.
For swelling
It is necessary to minimize the amount of salt consumed, due to which fluid is retained in the body. Cranberry juice, which has a pronounced diuretic effect, is introduced into the diet. Apples, dried fruits, and cabbage also help get rid of edema. Additionally, it is recommended to walk more, and when sitting, raise your legs on a chair or bench.
For edema, cranberry juice, which has a pronounced diuretic effect, is introduced into the diet.
For constipation
The emphasis in the diet is on fiber, grains, fruits and vegetables. Be sure to maintain a drinking regime. Additionally, you can eat dishes with prunes and vegetable oils. The effectiveness of the approach will increase if the patient’s physical activity is increased.
In case of lack of appetite
The lack of cravings for food must be dealt with comprehensively. The patient is advised to exercise and walk in the fresh air. Dishes should be varied, attractive, and exude a pleasant aroma. The menu for the patient is compiled taking into account his preferences. The calorie content of the diet can be slightly increased so that the patient is full at the moments when he wants to eat.
For nausea
The discomfort can be managed with medication, but you may want to try making a few dietary changes first. It is not recommended to drink food with food. Do not mix cold and hot foods. After eating, you should wait half an hour before brushing your teeth or rinsing your mouth. It is better to abstain from citrus fruits or their juice.
Alcohol
Parkinson's and alcohol are incompatible. Alcohol-containing drinks (beer, wine, liqueurs) are strong depressants. After using them, patients are susceptible to aggression and melancholy. In addition, being intoxicated increases the likelihood of falls and injuries. Patients should completely abstain from alcoholic beverages.
Alcohol is prohibited for Parkinson's disease. It is dangerous for the following reasons:
- Leads to depletion of nerve cells;
- Causes addiction;
- Stimulates aggression;
- Impairs coordination and postural instability.
List of prohibited products
Sweets, fatty and fried foods, and smoked foods are excluded from the diet. The following foods have a negative effect on the patient’s body:
- duck meat;
- fatty pork;
- sausages;
- caviar;
- margarine;
- canned foods;
- mushrooms;
- White rice;
- semolina;
- pasta.
It is prohibited to eat food that contains monosodium glutamate. This substance negatively affects the state of basal brain structures.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of such vegetables:
- sorrel;
- spinach;
- radish;
- radish.
Bananas are a prohibited fruit. The patient is not allowed to eat sweets: sweets, ice cream, chocolate, cakes. Drinking strong tea, cream, mayonnaise, lard, mustard, and cheese is also contraindicated.
Drinking alcohol increases the symptoms of the disease. Alcohol provokes depression and promotes the removal of beneficial vitamins and microelements from the body. Drinks containing ethanol destroy brain cells - alcohol and Parkinson's disease are incompatible.
Meals on special occasions
Edema
Edema in Parkinson's disease occurs rarely and may be associated with concomitant cardiac pathology. How should you change your diet if pastosity appears?
- Reduce fluid intake;
- Reduce the amount of salt in dishes.
Consultation with the attending physician is required.
Constipation
If you have constipation, you should drink plenty of fluids. The patient should increase daily activity and physical activity. A large amount of fiber is additionally introduced into the diet (vegetables, fruits, bran, prunes). Mild laxatives (lactulose) may be used periodically.
Lack of appetite
If there is depressive behavior and lack of appetite, you can allow the patient to try some of their favorite food. Before eating, you are allowed to eat a little pickled cucumbers, a piece of raw smoked sausage, and a slice of chocolate. The taste of familiar food will help you cope with a bad mood and return to a normal lifestyle.
Nausea
The symptom appears in the early stages during treatment with Levadopa. After 1-2 months, the body will adapt to the changes and the nausea will pass. After taking your medication, you can suck on a piece of candy or drink small amounts of lemon water.
Thirst
Thirst and dry mouth can be relieved by increased fluid intake (water, fruit juice, herbal tea, compote). You should tell your doctor about the new symptom.
Price of healthy food
The cost of healthy eating won't break your budget. The cost of fresh fruits and vegetables will be covered by reducing meat consumption. But the ketogenic diet is quite expensive. Meat and fish must be of good quality. The cost of such food for a week is 1.5-2 times higher than the usual budget. The gluten-free version of the diet also differs in price. Adapted cereals and flour are 2-3 times more expensive than regular wheat products.
Healthy foods
Parkinson's disease is an age-related phenomenon, and over the years the need for animal protein decreases many times. Meat products bring less benefits and more cholesterol and fat, so the emphasis is on plant-based protein.
If you are sick, your diet should include:
- cereal porridge;
- boiled lean meat;
- fish;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- black bread;
- rice;
- flax seed;
- corn;
- fresh berries.
How to distinguish Parkinson's disease from parkinsonism
Very often parkinsonism is equated with Parkinson's disease, but this is not true.
Vegetables must be stewed or boiled, and fruits must be peeled and peeled. It is advisable to cook soups in fish or vegetable broth, without frying them in oil.
A passive lifestyle often provokes constipation; plenty of fluids will help get rid of it. Every day the patient should drink at least 1.5-2 liters, the emphasis is on weak black tea, natural fruit drinks, unsweetened dried fruit compotes and ordinary clean water (mineral water is possible, but without gas).
If necessary, you will additionally have to take vitamin and mineral complexes, which will be selected by your doctor. This will help compensate for shortcomings in nutrition, saturating the body with all valuable substances.
What to do if you have no appetite?
If the patient does not want to eat, you should pay attention to a number of tips:
- Seek help from a specialist. Sometimes the main reason for the reluctance to eat lies in the depressed state of the patient.
- Do not drink allergic or harmful drinks.
- Eat small meals with frequent snacks.
- Prepare simple meals to save time and effort.
- 5Prepare light snacks to satisfy hunger, which may include vegetables and fruits.
- If possible, you can freeze a portion of the food and, if necessary, simply reheat it.
- After returning from work, you don’t have to go eat right away; you can take a break and recuperate.
- To increase the patient's appetite, it is advised to do light physical exercise. It could even be a walk.
Recommendations on how to awaken a patient’s appetite:
- You need to drink water after eating. With proper drinking regimen, you do not feel full before consuming foods.
- Every day the patient's diet should include a favorite dish.
- Allow the patient to eat foods that are high in calories.
Principles of healthy eating when ill
Both with this illness and with other diseases, systematic nutrition is a guarantee of good condition and speedy recovery. There is no need to treat with unconditional trust the advice of traditional medicine or the judgments of loved ones in the matter of choosing a diet. It is better to consult a nutritionist individually before starting a diet. The doctor will prepare a meal plan and inform you about the features of proper nutrition.
General rules and laws of nutrition:
- A varied diet for the patient, which should include all categories of products. Taking special vitamins is not excluded.
- Performing special gymnastic exercises, adhering to the regime. The doctor, based on the patient’s physical fitness and height, will tell you what weight the patient should be and how many calories should be consumed every day.
- The patient's diet should consist of fiber, cereals, pasta, rice, and fresh fruit.
- It is better to consume foods that contain little fat and low-quality substances.
- You should not consume sugar in large quantities. It is necessary to reduce the addition of salt to food.
- It is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of pure spring water daily.
- The consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited due to the incompatibility of certain medications with alcohol.
- It is important to ensure maximum balance of all food groups. In winter and spring, it is worth using medications with microelements.
Nutritional Features
As is known, therapy for parkinsonism is not capable of bringing recovery. It all comes down to constantly managing the symptoms. A person with Parkinson's has a weakened body, metabolic processes are slowed down, making it difficult for him to digest and assimilate large amounts of food. It is recommended to eat small portions, 5-6 times a day. This kind of nutrition is called fractional.
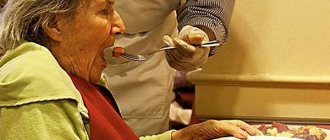
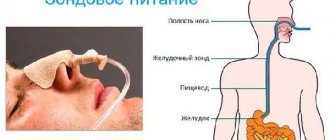
In the later stages of the disease, when it is difficult for a person to eat on his own, he will have to be fed. If you have severe tremors, you can use the achievement of modern medicine and technology - the electronic mechanical device “Parkinson's Spoon”.
Patients with pronounced symptoms of the pathology find it extremely difficult to chew and digest solid food. They may have difficulty swallowing, which can cause them to lose weight quickly. Therefore, you should give preference to semi-liquid or liquid food. The body will accept it well, and the patient will not experience discomfort.
Basic rules for eating
Parkinson's disease requires strict adherence to a diet. This is explained by the fact that patients take medications that need to be taken at a certain time, coordinating it with food intake.
In order for nutrition and therapy to be coordinated, it must be remembered that the patient should eat 2 hours after taking the medications, during which time they should be absorbed into the intestines. The effect of the medicine may not be obtained immediately, but after some time, because the rate of absorption by the small intestine decreases for various reasons.
Some patients experience difficulty swallowing food. In order for this process to proceed without complications, you need to ensure that the food is thoroughly chewed. This rule applies to both sick and healthy people. The more thoroughly the food is chewed, the faster and more complete the process of its absorption in the intestines. It is not for nothing that the Chinese advise bringing food in the mouth to such a state that it can be drunk. This is one of the principles of healthy eating.
Posture while eating is also important. Your back should be straight and you should lean forward slightly while swallowing. Food should be washed down with a small amount of water after each swallow.
Overeating is harmful, so it is better to eat in small portions, but more often.
If for healthy people the process of eating does not pose any difficulties, then for patients with Parkinsonism it is a whole problem. Hand trembling does not allow you to hold a spoon or fork, glass or plate in your hand. Therefore, family members need to ensure that the patient, with the help of certain devices, can do without outside help. This will help them avoid depression from their helplessness.
There are also requirements for the surface of the table; if possible, it should not be smooth: a plate or glass will not slide on a rough surface.
The handle of the spoon, as well as the mugs, can be wrapped in rags to make them more voluminous and easy to pick up. In addition, they will not constantly slip out of your hands.
Much attention is paid to the drinking regime. Patients are advised to drink at least 1.5 - 2 liters of water per day - that's 6 - 8 glasses
It is better to drink the last daily portion of water after lunch, rather than in the evening, because drinking liquid shortly before bedtime provokes frequent visits to the toilet at night and swelling in the morning.
Patients should control their weight. If their diet consists of only healthy and permitted foods (vegetables, fruits, cereals, protein, fiber), then the body receives the required amount of nutrients and elements. If the weight has decreased by 10% over 3 months, it means that the person needs more food. If you are malnourished, therapy does not have the desired effect.
Pros and cons of the diet
The Mediterranean type of diet has no contraindications and is therefore recommended for all patients.
Pros of this diet:
- variety, balance;
- easily tolerated by patients;
- can be used for a long time;
- restores metabolism, improves well-being.
There are practically no downsides, with the exception of significant financial costs for seafood and fresh vegetables in the winter season.
The ketogenic diet has more contraindications: diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease.
The advantages include high efficiency, a significant reduction in the symptoms of parkinsonism (tremor, muscle rigidity, autonomic disorders).
Among the disadvantages, they note that patients do not tolerate the keto diet well; due to the small amount of carbohydrates, they feel lethargy, loss of strength, and mood.
Proper nutrition for parkinsonism. Useful and dangerous foods for parkinsonism
It is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity and postural instability. This disease shares symptoms with Parkinson's disease, from which it takes its name. However, “Parkinsonism” is a separate set of symptoms, which is still different from the progressive and neurodegenerative Parkinson’s disease. The latter is the most common cause of parkinsonism. However, a number of other reasons can lead to its development, including toxins, certain metabolic diseases, and neurological conditions. This will be discussed in more detail below.
In 7% of people with parkinsonism, this syndrome developed after taking specific medications. It can manifest itself as a side effect of neuroleptic antipsychotics, thioxanthenes, phenothiazines, and sometimes antidepressants[1].
Causes that provoke the occurrence of parkinsonism
Not everyone with parkinsonism has Parkinson's disease. There are many other causes of parkinsonism, including:
- medications, such as those used to treat psychosis, underlying mental disorders, and nausea;
- exposure to toxins such as carbon monoxide, cyanide and organic solvents;
- certain brain lesions such as tumors or fluid accumulation;
- metabolic and other disorders such as chronic liver failure and hypoparathyroidism;
- brain injury;
- diffuse Lewy body disease;
- encephalitis;
- HIV AIDS;
- meningitis;
- multiple system atrophy;
- progressive supranuclear palsy;
- stroke;
- Wilson's disease.
Other causes of secondary parkinsonism include:
- brain damage caused by drugs used for anesthesia;
- carbon monoxide poisoning;
- poisoning with mercury and other chemicals;
- drug overdose[3].
Symptoms of Parkinsonism
Most often, parkinsonism is characterized by the same symptoms as Parkinson's disease. Among its symptoms are the following:
- 1 Tremor. Tremor or shaking usually begins in a limb, most often in the hand or fingers. One of the characteristic features of Parkinson's disease is tremors of the hand in a relaxed state (at rest).
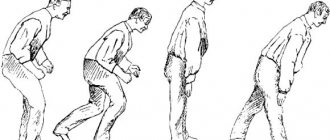
- 2 Slow movement (bradykinesia). Over time, Parkinson's disease can reduce a person's ability to move and slow them down, making simple tasks difficult and time-consuming. A person's steps may become shorter or it may be difficult for them to rise from a sitting position.
- 3 Tight muscles. Muscle stiffness can occur in any part of the body. Tight, tense muscles can limit your range of motion and cause pain.
- 4 Poor posture and balance. A person's posture may become slouched, or as a result, coordination may be impaired.
- 5 Loss of automatic movements. With Parkinson's disease, a person may have decreased or completely lost the ability to perform unconscious movements, including blinking, smiling, or swinging their arms while walking.
- 6 Changes in speech. A person with Parkinson's may speak softly, quickly, sloppily, or feel embarrassed before speaking. In most cases, speech becomes more monotonous[2].
Other symptoms that may also occur with parkinsonism include the following:
- marked memory loss that occurs during the first year of the disorder (including dementia);
- low blood pressure, difficulty swallowing, constipation, and problems urinating (sometimes due to multiple system atrophy);
- hallucinations and visual-spatial problems (for example, with orientation in the house or in the parking lot early in the development of the disease);
- abnormalities in eye movement[2].
Types of parkinsonism
Parkinsonism can be divided into three different types. This:
- 1 Primary parkinsonism. It is caused by Parkinson's disease. Includes sporadic and familial cases and accounts for about 80% of parkinsonism cases.
- 2 Secondary parkinsonism. This form of parkinsonism can be caused by a number of problems. These include drug addiction, infections, toxins, brain injury or tumors, normal pressure hydrocephalus, hypoxia, and metabolic dysfunction.
- 3 Atypical parkinsonism. This is a type of disease that includes additional neuropsychological and neurological deficits such as hemiatrophy-hemiparkinson syndrome, juvenile form of Huntington's chorea, corticobasal degeneration and others[4].
Complications of parkinsonism
Parkinsonism resulting from Parkinson's disease may be accompanied by additional complications. In most cases, they require separate treatment. Among them are the following:
- Difficulty in thinking. A person suffering from Parkinson's may experience cognitive problems (dementia) and difficulty thinking, which usually occur in the later stages of Parkinson's disease. Such cognitive problems are not very responsive to medications.
- Depression and emotional changes. The latter includes changes in emotional state such as fear, anxiety or loss of motivation. Doctors often prescribe additional treatment in such cases.
- Swallowing problems. A person may have difficulty swallowing as the disease progresses. Saliva can accumulate in the mouth due to slower swallowing, leading to drooling.
- Sleep disorders. People with Parkinson's disease often have trouble sleeping, including waking up frequently at night, waking up early, or falling asleep during the day.
- Bladder problems. Parkinson's disease may cause an inability to control urination or difficulty in doing so.
- Constipation. Many people with Parkinson's disease develop constipation, mainly due to a slow digestive tract.
- Changes in blood pressure. A person may feel dizzy due to a sudden drop in blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension).
- Fatigue. Many people with Parkinson's disease lose energy and become tired easily.
- Pain. It can occur in specific areas of the body or throughout the body[5].
Basic principles of nutrition
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disease that develops due to dysfunction of the dopaminergic system. The pathology is manifested by a slowdown in speed and a decrease in the volume of voluntary movements, muscle rigidity, disturbances in gait and other motor functions. A special diet used exclusively for Parkinson's disease has not been developed, but proper nutrition can curb the development of the disease and have a positive effect on the general well-being of the patient.
When calculating the daily calorie intake, it is taken into account that spasticity and tremors of the limbs, involuntary pathological movements are equivalent to moderate physical activity and require additional energy expenditure. The energy requirement per day is approximately 30 kcal per kilogram of body weight. The disease negatively affects the functions of the digestive tract. Frequently observed violations:
- Decreased sense of taste.
- Decreased appetite.
- Decreased sense of smell.
- Depressive state.
- Nausea, feeling of discomfort in the epigastrium (the area under the xiphoid process).
- Difficulty in bowel movements (constipation).
- Side effects of medications.
Concomitant chronic somatic and mental illnesses aggravate the course of Parkinson's disease. Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract against the background of psycho-emotional disorders quickly lead to weight loss. If a patient loses 10% of body weight over a 3-month period, the likelihood of malnutrition is high. The diet prescribed for Parkinson's disease involves the introduction of the following foods into the diet:
- Vegetables fruits.
- Cereals, cereals.
- With a high calcium content.
Foods that contain large amounts of fat and protein interfere with the entry of Levodopa (the main anti-Parkinsonian drug) into the blood. Protein foods take longer to digest. Remaining in the stomach, proteins are broken down into amino acids, which enter the small intestine, where absorption into the blood occurs.
Amino acids compete with similar substances in Levodopa for the transport vehicles through which they are transported into the blood. Moreover, amino acids occupy a priority position during transportation, which causes a slowdown in the absorption of the active substances of Levodopa. If medications are taken while eating a meal rich in fats and proteins, they enter the bloodstream 1-4 hours later.
To increase the effectiveness of the drugs, they are taken 1-2 hours before meals. If, against the background of drug treatment, there is a decrease in the volume of physical activity, it is better to eat protein dishes (meat, fish, eggs) in the evening, preferring a diet with a reduced protein content during the day.
Due to mutual suppression of drug action, you cannot combine taking Levodopa drugs with eating foods rich in iron. Taking into account the general principles of diet and adhering to the recommended diet, it will be possible to slow down the progression of the disease, maintain physical activity and the ability to self-care for many years. Basic principles:
- Prohibition of fasting.
- Reduce the amount of table salt (up to 6 g daily).
- Fractional meals (the daily amount of food is divided into 5-6 meals).
- The predominance of easily digestible foods in the diet that are quickly digested.
- Drink at least 6-8 glasses (1.5-2 liters) of clean water daily.
To reduce the discomfort from manifestations of dysphagia (impaired swallowing function), while eating you need to sit upright, swallow a portion of food, and lean a little forward. Eat food in small portions. Take the next portion into your mouth after the previous portion of food has been completely chewed and swallowed. To improve swallowing, drink each serving with a small amount of water. Nutritionists advise chewing food thoroughly.
Saliva contains substances (enzymes) that carry out the primary processing of food so that it is easier to digest and does not linger in the stomach. The amount of protein food is determined at the rate of 0.8 g/kg body weight. The ratio of proteins and carbohydrates is about 1:5. It should be borne in mind that increased acidity of gastric juice and overeating increase the time it takes to digest food, which slows down the effect.
Nutritional Features
Side effects of drugs and the consequences of the disease itself require a special approach to menu planning.
Nausea
This may be caused by a certain drug, and stops when it is replaced with another. The doctor may also prescribe special medications to eliminate this symptom. Additionally, you must adhere to certain rules:
- eat little and often;
- To neutralize morning sickness, eat a couple of crackers right in bed. You can replace them with other products containing proteins - a slice of cheese or boiled meat;
- refuse citrus fruits and drinks containing them, as this can provoke an attack of nausea;
- drink water and drinks in small sips, and preferably between meals;
- drink sweet drinks (contraindicated for diabetes and increased weight);
- give up fried, fatty and sweet foods;
- to reduce the smell emanating from food, eat it not hot, but at room temperature;
- do not engage in vigorous physical activity after eating;
- You should not brush your teeth immediately after finishing a meal.
Difficulty swallowing
In such cases, it is difficult to swallow hard, fried foods. Therefore, if you have Parkinson's disease, you need to follow proper nutrition. It is advisable to take each serving of food with a small amount of liquid. And it is better to give preference to soft, semi-liquid dishes, chopping all products:
- various porridges, puree soup;
- boil or bake vegetables and fruits;
- eat raw fruits with their peels removed, separately from other dishes, so as not to cause fermentation;
- milk and fermented milk products, yoghurts and ice cream;
- consume meat in the form of stewed cutlets, meatballs or casseroles.
It is forbidden:
- nuts and seeds;
- dry biscuits, crispy confectionery products;
- crispy scrambled eggs, fried potatoes;
- long spaghetti - it is better to replace them with pasta.
Fine motor skills disorders
Patients find it difficult to make small movements with their fingers, which is further aggravated by hand tremors. They cannot grasp small objects such as cutlery. Therefore, you need to increase the size of the items:
- wrap the handles of spoons, forks and cups with strips of fabric to increase their thickness;
- drink water and other drinks through a straw;
- To make scooping easier, use special gadgets - a curved spoon, a tilted plate.
Constipation
They are a common consequence of the disease due to impaired intestinal motility. Therefore, it is necessary to drink at least two liters of clean water per day (compotes, tea and other drinks are not taken into account). You also need to eat foods rich in fiber: vegetables, fresh fruits and berries, legumes, whole grain cereals, rice, bran, various greens.
In this situation, regular exercise and walks in the fresh air will help. You can massage the abdomen with stroking movements in a clockwise direction. Sometimes you can take a laxative.
Weight control
Weight should be measured 1-2 times a week. If the patient is prescribed steroids or diuretics, you need to weigh yourself daily. Constant loss or gain of weight is a reason to consult a doctor who can help you adjust your diet.
The patient may lose weight due to loss of appetite caused by depression, as well as deterioration of the sense of smell and taste. Causes may include nausea and physical discomfort while eating. To increase muscle mass, you need to increase your caloric intake, considering that the average person normally spends about 2,500 calories per day. On the advice of a doctor, you can take nutritional supplements, which come in the form of drinks or vitamins.
There is also the exact opposite problem - when the patient experiences an obsessive desire to eat and gains excess weight. To maintain a balance between getting the required amount of calories and getting rid of extra pounds with Parkinson's disease, you need to follow the right diet.
Prevention of osteoporosis
Parkinson's disease occurs in people between 40 and 70 years of age. At this age, bones become fragile, and the disease increases the risk of falls and fractures. Therefore, it is necessary to take calcium, magnesium and vitamins D and K. Vitamin D is also produced under the influence of sunlight, which makes walking on a sunny day especially necessary.