Unlike other tendon diseases, temporal tendonitis does not impair a person's ability to move, but it is accompanied by very painful and unpleasant symptoms.
Temporal tendonitis occurs everywhere and affects people of any age.
Tendinitis is an inflammatory lesion of the tendons.
Temporal tendonitis is an inflammation of the tendons of the masticatory muscles, which are attached to the temporal bone and provide function to the temporomandibular joint.
The disease can occur on only one side or involve the tendons on both sides.
Causes of temporal tendonitis include:
- Frequent loads on the joint, especially monotonous ones. The main loads placed on the temporomandibular joint are chewing and talking. Of course, during normal talking or chewing, tendon inflammation does not develop. But the habit of gnawing hard foods (nuts, seeds) sharply increases the load on the joint, leading to microtrauma of the tendons, followed by the replacement of their elastic fibers with coarse connective tissue fibers.
- Malocclusions and anomalies in the location of teeth. Incorrect placement of teeth in the oral cavity increases the load on the temporomandibular joint, even when chewing soft food.
- Injuries. This may include bruises, dislocations, and fractures of the lower jaw.
- Infection of surrounding tissues. Diseases caused by infectious pathogens are boils on the face, osteomyelitis of the lower jaw, dental caries, and sinusitis.
- Acute and chronic diseases of the temporomandibular joint (arthritis, arthrosis). The development of inflammatory changes in the tendons of the temporomandibular joint is facilitated by various disorders of mineral metabolism, endocrine diseases, systemic diseases (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus) and age-related changes - all of them are accompanied by a decrease in the elasticity of the tendons and mild trauma under normal loads.
The main symptom of temporal tendonitis is pain localized in the joint area, cheeks and radiating to the lower jaw, teeth, neck, and forehead.
The intensity and nature of the pain can vary: from dull aching to unbearably sharp.
Very often, patients are able to clearly establish the relationship between the occurrence of pain and previous chewing of hard foods, cracking of nuts and seeds.
The pain can be constant, intensifying when chewing, talking, opening the mouth, or it can only occur when there is a load on the joint, and be absent at rest.
Local symptoms
The most common local symptoms are:
- difficulty opening the mouth (due to pain);
- swelling on the affected side in the cheek and temple area.
- When you feel the cheek, you can identify a tense muscle roll and a painful cord of inflamed tendon.
Infectious temporal tendonitis is characterized by redness along the tendons.
General symptoms
With temporal tendonitis, general symptoms are rare, mainly in cases where inflammation of the tendons of the masticatory muscles was caused by an infectious factor.
Patients may complain of lethargy, loss of appetite, headache, and fever.
Diagnosis is based on a thorough collection of medical history and complaints, examination of the patient by a doctor - this turns out to be quite sufficient to confirm the diagnosis.
Additional research methods are not needed, and they are not informative: in a general blood test, if there are any changes, they are nonspecific (signs of inflammation), and no pathology can be detected on x-rays.
The greatest difficulty is the differential diagnosis between temporal tendonitis and other diseases with similar symptoms (dental problems, trigeminal neuralgia).
However, an experienced doctor should easily cope with this task, since the disease has a number of distinctive features:
- Temporal tendonitis differs from trigeminal neuralgia in the presence of a connection between the occurrence of pain and the load on the joint, painful swelling along the tendon.
- With caries, especially complicated, there may also be pain in the cheek with radiation to the neck, lower jaw, but there are indications of pain in the tooth, which intensifies not only when chewing, but also from thermal (cold, hot), chemical (acid) irritants , sweet food) of nature.
Treatment of tendinitis is carried out mainly on an outpatient basis; severe cases of the disease requiring hospitalization are practically never encountered.
The basic principles of treatment are presented below.
Ensuring functional rest of the temporomandibular joint
In the most acute period of the disease, with severe pain, patients are prohibited from opening their mouths, and they are not even allowed to talk.
Food is given in liquid form through a straw. After 1-2 days, they gradually switch to semi-liquid food, and a mechanically gentle diet (ground, soft food) is maintained for about a month.
Subsequently, it is recommended to avoid foods that require significant chewing effort.
Use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs
The peculiarity of the treatment of temporal tendonitis, in contrast to tendonitis of other localizations, is that all kinds of burning and warming ointments are not used.
When applied to the face, they greatly irritate the skin; caustic particles get into the eyes and nose and can cause lacrimation, rhinitis, and conjunctivitis.
Local remedies include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren emulgel, diclofenac).
More often, NSAIDs and painkillers are prescribed orally for a short course (for 5-7 days) - diclofenac, nimesulide, nurofen, ketorol and other drugs are used.
Antibacterial treatment
For temporal tendonitis of infectious origin, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs (amoxiclav, azithromycin, cephalexin, etc.) are prescribed orally or intramuscularly, less often - to the area of the inflamed tendon.
Physiotherapy methods
They relieve pain very effectively and significantly speed up the healing process.
In this case use:
- laser;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis with novocaine;
- lidase;
- ultrasound;
- shock wave therapy.
Specific prevention is to avoid harsh loads on the temporomandibular joint.
If there are risk factors, as well as after tendonitis, it is recommended to avoid nuts, seeds, hard meat, hard sausages, crackers and other products, the use of which is combined with intense chewing.
Almost every person has experienced temple pain. Many people do not consider it necessary to see a doctor even with regular and severe discomfort, but such a symptom may indicate serious morphological changes in the cardiovascular system or brain. Find out why your temple hurts when pressed and how to properly deal with this painful sensation.
Clinical picture of the condition
It is worth distinguishing a simple headache from sensations when pain occurs when pressure is applied. These symptoms signal different diseases; they are not equivalent to each other. If the cause of a migraine most often lies in impaired blood circulation in the brain and organic causes, then if the temple hurts when pressed, it is most likely due to problems with blood vessels, osteochondrosis, and heart pathologies.
Often pressure on the temple, accompanied by pain, is typical for older people and neurotic individuals. At the same time, symptoms such as increased anxiety, insomnia, sleep problems, irritability, unmotivated aggression, fixation on certain events, and difficulties in communication develop.
With such symptoms, it is highly recommended not to self-medicate. These may be manifestations of early dementia or neuropathy, encephalopathy. Drug treatment and competent selection of pharmacological agents will help stop the inevitable progression of the disease. And if the patient tries to self-medicate at home, the symptoms will increase, and after a few years the person may become incapacitated.
Possible causes of this symptom
Why do my temples hurt when pressed? This is not a separate disease, but often signals serious health problems: cerebral vessels, blood pressure, vestibular system, cervical spine.
The most common diseases in which the temple hurts when pressed:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- hypertension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- withdrawal syndrome;
- magnetic storms and increased atmospheric pressure;
- chronic stress and overwork;
- excessive physical activity (leads to overload of blood vessels and thinning of their walls).
Migraine, which every person has experienced at least once in their life, is also manifested by pain when pressing on the temple. Chronic migraine and vegetative-vascular dystonia have a lot in common, and only an experienced neurologist can distinguish one diagnosis from another based on the combination of a number of symptoms.
Causes of pain in the right temple
The etymology of pain in the right temple can be harmless or dangerous.
What causes “harmless” right-sided cephalalgia:
- insomnia, sleep disorder, uncomfortable bed or pillow, stuffy room can cause pain when you feel dizzy when getting up and feel sick in the morning;
- stress and overexertion, temporal pain is the scourge of office workers and people who do not know how to rest from everyday work; when pressing on the temple, cephalalgia intensifies;
- uncomfortable workplace, sedentary lifestyle;
- when descending, diving to depths or climbing to heights (mountains), on an airplane, when traveling in transport (especially with large crowds of people), cephalalgia, nausea, dizziness and tachycardia may appear;
- poor nutrition, fasting, long breaks between meals, bad habits, hangover;
- drug abuse, poisoning, intoxication;
- weather dependence.
Such pain can be easily managed with conventional medications. However, if they appear constantly or every day, then anesthetics will gradually begin to have a negative effect on the body or stop helping.
Frequent pain in the right temple indicates the presence of pathology or a serious illness. It is necessary to contact specialists and undergo a full examination.
The etymology and symptoms of pain are quite diverse. Why there may be a headache in the right temporal zone - we will consider all the details and the main causes below.
Head injuries
With TBI (traumatic brain injury) or brain dysfunction, tumors or abscesses, swelling, redness and sharp pain may appear in the affected area.
Often such pain does not differ in intensity. Trauma syndrome with dull pain, noise in the ear (depending on the location of the injury), nausea, vomiting and dizziness may appear only after some time.
For any TBI or bruises, it is recommended to immediately go to the emergency room for medical attention.
Perhaps your prolonged pain (even mild) indicates a violation of brain functions, the gradual development of a tumor or an imbalance in the circulatory system.
Colds
ENT diseases can be accompanied by acute respiratory manifestations, when the throat is very sore and the cough is suffocating. Inflammatory processes developing in the reflex organs and in the jaw - colds, flu, sore throat, frontal sinusitis, conjunctivitis, an inflamed tooth, sinusitis or otitis media can cause severe pain. The pain may pound and radiate to the ear, forehead or back of the head. If, with right-sided cephalgia, it radiates into the eye, then the organ or skin around it may swell.
Sometimes a cold causes pain that radiates to the tooth. This happens with caries and other untreated dental problems.
During pregnancy, it is recommended to relieve pain only after consultation with your doctor, so as not to harm the baby.
Migraine
Another name is hemicrania, which means "half head". The attack may begin suddenly or with an aura - the threshold of pain, which is expressed in sensitivity to light, smells or sounds.
If the attack is not stopped in time, it can last 2-3 hours, go away on the second day or last several days.
The pain is stabbing, varies in intensity, ache most often in the right temple, radiates to the eye (or inside the orbit) and to the jaw.
Attacks can be accompanied by vomiting, nausea, disorientation, and even provoke a migraine stroke.
What causes migraine:
- the disease often affects those suffering from lack of sleep or overwork;
- with surges in blood pressure, hypo- and hypertonicity of blood vessels;
- when choosing the wrong products;
- Abuse of caffeine or tyramine can be a symptom of an attack.
The nature of origin of hemicrania has not been studied. The disease is considered hereditary and usually occurs in women. However, studies in recent years have shown a large increase in migraine syndrome among men.
Problems with hormones
Painful sensations caused by hormonal disorders are varied - the head aches or throbs in the temple, when you press on the temporal area, the pain usually intensifies.
Main features:
- The right temple hurts very badly in women (up to 75%) during menopause, as well as with severe PMS (premenstrual syndrome);
- It is believed that the first attacks against the background of hormonal changes appear during puberty in boys and girls, sometimes during pregnancy;
- vegetative-vascular problems or intracranial hypertension can trigger migraines in adolescents or young people due to hormonal instability.
High blood pressure
Intracranial hypertension or ICP is characterized by the presence of an increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid).
With cerebrospinal fluid pressure on different parts of the brain, cephalgia can occur in any location.
Often accompanied by pressing, throbbing pain in the right temple, general malaise, weakness, tachycardia, shortness of breath, heart pain and tinnitus.
Causes:
- psycho-emotional character;
- changes in climatic conditions;
- magnetic storms.
Such disturbances must be taken seriously, as visual disturbances, loss of consciousness and convulsions are possible.
Cerebrovascular disorders
Cerebral angiodystonia is accompanied by pain in the right temporal zone, which radiates to the eye. Formed due to a violation of the elasticity of blood vessels or arteries.
Symptoms:
- sleep disturbance, dizziness;
- sudden changes in pressure;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- numbness of fingers;
- decreased brain activity and memory.
Stress experienced
Stress, depression, anxiety are overstrains of a psychogenic nature, leading to a surge or release of adrenaline. As a result, blood pressure increases.
If you stay in such an environment for a long time, you can end up not only with a serious nervous disorder, but also with loss of physical health.
Right-sided pain, when there is a knocking and shooting in the temple, is one of the first symptoms of the development of a serious illness.
Atherosclerosis
Often, pain in the right or left temporal region appears after the diagnosis of atherosclerosis. The disease is characterized by narrowing or blockage of the lumen of blood vessels due to the formation of cholesterol plaques.
Gradually, pain in the right temporal zone becomes constant, and analgesics cease to help. The pain intensifies when you press on the temple on one side of the head.
Patients experience unmotivated irritation, anxiety, decreased brain activity, memory and intelligence.
Neurological diseases
Temporal arteritis is an inflammation of the membranes of the carotid and temporal arteries. Usually observed in older people, more often observed after respiratory diseases.
Accompanied by grinding of teeth, strong clenching of the jaw, throbbing pain, intensifying in the evening. The disorder affects the temporomandibular joints.
If you press on your temple, you can feel some compaction. There is diplopia, decreased vision, chronic conjunctivitis, and possible blindness.
Eye fatigue
Excessive strain on the organs of vision, constant spending time in front of a monitor or working at a computer leads to overwork of the eye muscles.
And also reading in a poorly lit room or transport leads to an increase in intraocular pressure.
Considering the fact that most people are right-handed, we subconsciously strain our right eye more. Accordingly, pain occurs in the right temple.
Inflammatory processes of the trigeminal nerve
An inflamed trigeminal nerve is a powerful pain syndrome on one side of the face. Men suffer from this disease three times more often than women.
On the left side, pain is observed only in 28% of cases, all others experience pain on the right side. An attack usually begins with a tic in the cervical region, pain shoots into the temple, the face spasms and twitches. Sometimes the skin goes numb.
People suffering from such pain usually freeze for a while, cannot bend over or work, and are afraid to talk or chew. How to relieve pain of this nature can only be found out by consulting a specialist in this profile.
Poor sleep schedule
Adequate sleep is necessary to restore physical strength. Lack of sleep and fatigue lead to additional stress on the body. Workaholics are more likely to suffer from this syndrome.
Right-sided temporal pain is often caused by incorrect sleeping posture when the neck becomes numb. A pinched nerve in the cervical spine results in headaches and general malaise.
Meningitis
With meningitis - inflammation of the membrane and encephalopathy (inflammation of the brain matter) pain is always observed in the right temporal region.
The causes are varied - infections of meningococcus, streptococcus, influenza virus, measles, rubella, chickenpox or an encephalitis tick bite.
The pain is strong, pressing, even leading to epileptic seizures. A rash appears on the body starting from the lower extremities. If the rash reaches the face, then such symptoms are extremely unfavorable.
The disease is difficult to treat; pain and seizures can haunt the patient for the rest of his life.
Intracranial pressure
If intracranial pressure readings are significantly higher than normal, the patient feels a dull, prolonged pain in the back of the head and temples, which intensifies with strong pressure. People with increased intracranial pressure describe this condition as “as if water has accumulated in the skull and the head is about to burst.” This condition sometimes occurs immediately after waking up. In some patients, on the contrary, symptoms worsen in the late evening.
In some cases, changes in atmospheric pressure can provoke surges in intracranial pressure. This can cause the patient to wake up at night from a severe migraine, while pressure on the temples and back of the head will cause acute pain. Chronic stress and overwork can also cause increased intracranial pressure.
In the absence of drug treatment and lifestyle changes, intracranial pressure can lead to organic changes that cause permanent chronic ailments. In the future, this may threaten the patient with the possible development of encephalopathy, various neuropathies, and a decrease in cognitive functions.
Why does my temple hurt when I chew: reasons
16.10.2018
Medical statistics provide data that 70% of people of different ages and gender periodically suffer from headaches localized on the left side. However, not everyone goes to medical institutions, so the number can only be taken as conditional.
Meanwhile, such symptoms should not be ignored, since their causes may indicate the presence of serious pathologies that require immediate treatment.
Types of pain
Patients who consult a doctor describe a wide variety of conditions, accompanied by associated symptoms. Headaches can be aching, pressing, shooting, sharply expressed and blurred.
Each type of cephalalgia is characterized by certain symptoms, and additional signs indicating a certain type of pathological process occurring in the body. Often the pain is accompanied by strong pulsation in the temples, which patients associate with the blows of small hammers, which prevent them from being distracted and falling asleep.
According to the nature of the mechanism of pain formation, they are divided into:
- On vascular, caused by spasm of the aorta or its expansion, as well as decreased tone of the veins.
- Muscular, which occur when the activity of transmission of nervous excitation increases.
- Neuralgic.
- Liquorodynamics associated with fluctuations in intracranial pressure.
- Central, when the above listed mechanisms of pain are absent.
- Mixed, caused by several processes occurring simultaneously.
As you can see, there are many causes and types of pain. That is why it is important to carefully collect anamnesis during diagnosis. The doctor will have to find out exactly how the headache hurts, what sensations the patient experiences before, during and after the attack, what can trigger the onset of exacerbations, and what additional symptoms are noted.
However, this information is not enough to establish the causes, so laboratory and hardware examinations are carried out.
To understand the pathological processes and understand what can cause pain in the temporal region, you need to have an idea of the anatomical structure of this part of the skull.
It consists of several bones - parietal, zygomatic and frontal. Muscle and subcutaneous fat tissue, nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels. The temporal bone connects to the lower jaw, forming a joint that takes an active part in chewing movements, swallowing, and speech functions.
All of the listed structures - muscles, nerves, bone tissue, veins, arteries, lymphatic vessels, meninges - can become inflamed. In addition, pain can be caused by various pathologies of nearby organs - hearing, vision, smell.
In addition, the causes of cephalalgia can be intoxication with chemicals, alcohol, drugs, medications, as well as increased radiation.
Among the external factors that cause headaches, it should be noted poor nutrition, physical inactivity, fasting while following an irrational diet or lack of adequate nutrition, and prolonged stay in a room with limited oxygen access. As well as nervous stress and overstrain of a mental and physical nature, can cause the development of cephalgia, including bilateral temporal pain or pain concentrated on the right or left.
As well as diseases of the kidneys, liver, pancreas, as well as metabolic disorders occurring in the body, causing obesity.
Changes in hormonal levels can also lead to the development of cephalalgia - diabetes, the formation or disruption of the menstrual cycle, menopause, pregnancy can trigger headaches. As you can see, there are quite a few causes of cephalalgia.
To save the patient from suffering, it is necessary to correctly determine what caused it, and treatment should be aimed at eliminating the root causes, and not relieving symptoms. For this purpose, diagnostics are carried out, including laboratory and hardware tests, questioning and examination of patients.
Possible causes and associated diseases
Headaches affect 75% of the world's population. This condition becomes a frequent reason for seeking medical help. However, international practice shows that a large percentage leaves the problem unattended and does not consult a doctor.
With all the variety of uncomfortable sensations, patients often complain of soreness in the temple area. This may be associated with various pathologies, so before starting therapy it is necessary to carry out a diagnosis to differentiate:
- arterial hypertension;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- migraine.
Often the temple may hurt during depression. In women, this condition is caused by hormonal surges, for example, before menstruation or during menopause. If a patient complains that her temple hurts when chewing, the reasons should be sought in other pathologies. For this purpose, laboratory and hardware examinations are carried out, and a detailed anamnesis is collected.
Pain in the temporal region cannot be ignored, since arthritis can lead to blindness without proper therapy. Patients complain that their temple hurts when I chew. They experience redness of the scalp.
The temporal arteries become denser and protrude, the pulse cannot be felt in them, and pain is felt when pressed. In addition to the main symptoms, the condition is accompanied by additional ones.
Patients may complain that their tongue or tooth hurts when chewing food and swallowing.
Meanwhile, this is not the only reason when unpleasant sensations are concentrated on the left side of the head in the area of the temple, eye and upper jaw. This condition is typical for migraine, in which accompanying symptoms are weakness, heightened sense of smell, causing nausea and vomiting. In addition, the pain is aggravated by exposure to sharp sounds and bright light.
Weather-dependent people may also get a headache on the left side when the weather and atmospheric pressure changes, on days of magnetic storms.
Other external factors can also influence a person’s condition. For example, when climbing mountains or diving to great depths, discomfort is noted in the temporal region. This is due to the pressure difference.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae, caused by salt deposition, is another cause of cephalgia in the temporal region. The mechanism of the disease is compression of the blood vessels supplying the brain and disruption of intracranial pressure and the flow of cerebral fluid. In this condition, there is a lack of oxygen. This causes aching pain on the right or left.
A stroke can also cause similar symptoms, which are accompanied by disturbances in orientation, consciousness, speech, and partial paralysis. It should be noted that stroke - vascular rupture occurs more often in the left hemisphere.
In addition, brain tumors can cause unilateral temporal pain. The condition is accompanied by decreased memory, impaired vision, hearing, and absent-mindedness.
Infections such as tonsillitis, sinusitis, flu, otitis media, and inflammation of the dental nerves can also cause pain on the left side. They become more intense when bending, turning and sudden movements.
Characteristic signs of sinusitis are increasing pain during a change in ambient temperature, for example, when a person goes out into the cold or, on the contrary, returns from the street to a warm room.
Tilts of the head also cause the condition to worsen. Since the inflammatory process is localized in the cranial sinuses, where pus accumulates, pain is felt in the nose, cheeks, and forehead, which create discomfort when chewing food.
Pinching of the trigeminal nerve on the left or right side of the face also causes severe pain radiating to the ear, eye, masticatory muscles, and neck.
Pain in the temple when chewing may indicate various pathologies of the temporomandibular joint, which is one of the most mobile in the human body. In the presence of pathologies, for example, malocclusion, dislocation or other injuries, chewing is painful, and every opening of the mouth is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and discomfort.
Additionally, these symptoms can be caused by dental problems.
If your temple hurts a lot when chewing, you should consult a doctor to determine the root cause. Only a correct diagnosis will allow you to select an adequate method of therapy and relieve the disease.
Pain in the temples when chewing, the cause of which has not been identified, can continue for weeks and months, causing significant discomfort to patients. In addition, if left untreated, it can cause serious complications.
That is why you should not ignore cephalalgia and take analgesics uncontrollably. Such drugs will only calm you down temporarily, but will not solve the problem. The root cause will remain, which means the pain will return again.
Only timely therapy will help get rid of suffering and maintain health.
Dental gaps such as caries, periodontitis, pulpitis, as well as malocclusion during the eruption or removal of wisdom teeth can cause pain in the temples.
Help in such a situation lies in the treatment of existing pathologies. The dentist will determine the cause and provide the necessary treatment.
It should be noted that pain caused by jaw joint dysfunction and malocclusion will require long-term therapy by an orthodontist.
Dental problems that cause pain when chewing include cellulitis and abscesses. These are purulent formations that can be caused by various diseases of the oral cavity and teeth. Treatment consists of surgical opening of the abscesses, which is carried out differently in each specific case.
Various types of traumatic brain injuries can also be accompanied by discomfort and pain in the temporal lobe. If you receive a blow to the jaw, a fracture or dislocation is possible, in which opening the mouth and chewing will be accompanied by severe unbearable pain.
First aid for injuries consists of fixing the jaw and then going to a medical facility.
Patients often ask why their temple hurts when chewing, when the doctor is unable to diagnose any of the listed pathologies. The answer is simple. The fact is that such a condition is often observed with nervous strain and chronic fatigue. Excessive mental and physical stress can cause headaches in the temple area.
Therefore, patients with such complaints are recommended to normalize their daily routine, establish a correct work and rest schedule, and get 8 hours of sleep.
A change of environment helps relieve strong psycho-emotional stress. Patients are advised to avoid stressful situations and are prescribed a course of psychotherapy.
If necessary, drug therapy is carried out aimed at restoring the nervous system.
Tension pains are precisely those complaints that are caused by stress, overwork and chronic fatigue. Men are more likely to suffer from them. They suffer from severe paroxysmal headaches that can last from several minutes to a week. In this case, unpleasant sensations arise suddenly, occur severely and cause discomfort.
Pathologies such as arthrosis can cause pain in the temple area, which intensifies with chewing movements. It is characterized by degenerative changes in the joint, which are caused by the absence of molars, incorrect position of wisdom teeth, and inflammatory processes occurring in the bone tissue.
Arthritis can also impair chewing function by reducing jaw mobility.
Diagnostics
To find out why your temples hurt so much when you chew, you need to undergo an examination. Modern medicine has various diagnostic methods that make it possible to accurately determine the causes of discomfort in the upper part of the head. And, therefore, prescribe adequate treatment.
Diagnosis of injuries comes down to collecting an anamnesis, during which the doctor needs to find out the nature of the injuries received. During the examination, you should pay attention to the condition of the skin, determine the presence of hematomas, tumors, abrasions and scratches.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Unstable functioning of the heart and blood vessels is a common cause of headache when pressed. These are serious conditions in which self-medication is unacceptable and consultation with a cardiologist is necessary. Does your temple on the right side hurt when pressed and do you feel pulsation of the veins? Most likely the cause is arrhythmia. This condition also often causes dizziness, darkening of the eyes, and short-term fainting. The patient feels weak and nauseated. Does your temple on the left side hurt when you press? Perhaps the reason is surges in blood pressure. It must be measured regularly to rule out hypertension.
With the combination of all these symptoms, we can talk not only about arrhythmia, but also about angina pectoris and cardiomyopathy. When blood pressure rises, the nature of the pain in the temples is stabbing or throbbing. If the indicators are lowered, then nagging discomfort, dizziness appears, and a short-term loss of consciousness may occur.
In some cases, problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system are caused by changes in atmospheric pressure, weather changes, and chronic stress. This condition cannot be left to chance. It can lead to chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Causes
There are many reasons why temple pain occurs. They can be external and internal. External causes include those, having eliminated which, a person returns to a normal state. They are not associated with organic lesions, and if they lead to them, it is only after prolonged exposure.
- Intoxication. Pain occurs due to poisoning by toxic substances contained in toys, finishing materials, and products. A strong odor causes pressing pain in the temple, it spreads to the forehead and back of the head, intensifying due to irritation of the eyes, tissues of the larynx, and nose. A long stay near a source of toxic substances leads to constant pain, a feeling of swelling in the head, and dysfunction of the respiratory system and heart.
- Changing environmental conditions. When traveling to places with a different climate, in high mountains, or during long flights, temporal pain appears, which disappears soon after returning home. They are often observed in people prone to vegetative-vascular dystonia or vascular pathologies.
- Starvation. Provokes pain in the temporal region, weakness, refusal of certain foods or food entirely.
- Overwork. Pressure in the temples appears as a result of excessive fatigue, severe mental stress, and sleep disturbances. In addition to the temple, pain often affects the eye area. Fatigue is indicated by swelling, circles under the eyes, absent-mindedness, and nervousness.
- Food. Chips, spices, chocolate, smoked meats, and foods high in monosodium glutamate provoke the development of painful sensations. At the same time, spasm of the facial muscles may occur.
The list of internal reasons is more impressive. These are mainly diseases related to the brain.
Migraine
The disease is neurological in nature and is considered primary. It occurs independently, and not against the background of any disease. Some researchers, however, associate it with damage to the trigeminal nerve. Soreness appears on one side and is described as pulsating.
It can be so strong that a person loses his ability to work, becomes very irritable, lethargic, and depressed. He does not tolerate loud sounds or bright lights and prefers to be in a dark room. You may become intolerant to certain smells.
The pain intensifies with movement, overwork, stress, eating disorders, and sleep. Often accompanied by nausea. The attack lasts several days.
Cluster pain
If migraine occurs more often in women, then cluster pain occurs more often in men. There are no anatomical or physiological prerequisites for it. Sometimes it is correlated with jet lag, smoking and excess weight. The name comes from the nature of the pain - it appears in series.
The number of short-term attacks can reach three per day. Moreover, they can occur for several months in a row. After which a long break is possible. The duration of one attack is from 15 to 60 minutes.
The pain is very strong and sometimes difficult to bear. The onset of the attack is associated with the fact that the ear is blocked on one side, for example, on the left. This is immediately followed by acute pain in the temple and behind the eye. It may spread to the forehead. Bursted blood vessels cause redness of the sclera. Tears appear. If there is pain in the left temple, the nose swells on this side, and difficulty breathing occurs. Blood rushes to the face, sweating increases.
Attacks are more likely to recur in autumn and spring. Severe pain can lead to a suicide attempt.
Tension pain
Soreness in the temples is caused by prolonged tension in the muscular tissue of the neck and head, caused by a monotonous posture. Another reason is stress. Pressing pain appears on both sides. The attack sometimes lasts six hours.
When muscles are strained day after day, the pain becomes chronic.
Arterial hypertension
With repeated increases in blood pressure to 140/90 or higher, arterial hypertension is diagnosed. Vasoconstriction occurs under the influence of adrenaline, due to blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques. Neoplasms and hematomas can compress them. Increased pain in the temples is provoked by strong emotions, climate change, stuffiness, noise, and overwork. At the same time, painful sensations appear in the back of the head, noise in the head, sleep disturbances, and spots before the eyes. The pain is characterized as if something is pressing on both sides of the temples.
Often the disease develops on its own and occurs as a result of dysregulation of vascular tone. In some cases, it appears as a consequence of diseases of the kidneys, endocrine system, or injuries. Blood pressure increases due to menopause, pregnancy, excess weight, and physical inactivity.
Intracranial hypertension
An increase in pressure in the cranial cavity is usually associated with the formation of an excessive amount of cerebrospinal fluid, disturbances in its circulation, and accumulation in certain areas. This condition is caused by neoplasms, hemorrhages, hematomas, inflammatory processes, and swelling.
Pressing pain is accompanied by disorders of consciousness, vision, temporary blindness, and paresis. Sometimes convulsions occur, breathing is impaired, and the person feels sick. The pain increases after being in a horizontal position for a long time. Spread to other parts of the head.
Hormonal disorders
If a woman has pain near her temple when pressed, then perhaps it is due to diseases of the hormonal system. With thyrotoxicosis, the symptoms are varied - migraines and pain in the back of the head and temples when pressed can occur. If there is a deviation in TSH levels, hair loss (alopecia), asthenia, dysphoria, irritability, and anxiety are also possible.
Another reason why temples hurt when pressed is premenstrual syndrome. This condition is not a disease and occurs in approximately 30% of women aged 16 to 43 years. To avoid it, before the onset of menstruation, you should rest more, avoid physical activity, hypothermia, and stress. In some cases, a course of vasodilator drugs will help. A prescription for such medications can be obtained from a neurologist.
Local diseases
If it hurts just below the temple when pressed (the sensation is not located in the temple itself, but next to it), then most likely the cause is local diseases. These are meningitis, sinusitis, inflammation of the nasopharynx and sinuses, ARVI, and other infectious diseases. This is due to an increase in temperature and the accumulation of mucus in certain parts, which with its volume puts pressure on the tissues of the skull.
To treat such conditions, antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs should be used. These are “Kagocel”, “Sinupret”, “Arbidol” and others. An immunologist can prescribe a medicine that would be ideal for a particular patient and does not cause side effects.
If the temple on the right side hurts when pressed (at the same time there is nasal congestion, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes and other symptoms of ARVI and influenza), then the inflammatory process occurs on the right side of the nasopharynx, tonsils and sinuses. It is necessary to more actively use medicinal aerosols and sprays specifically for the treatment of the right nostril and the side of the throat. Does your temple on the left side hurt when you press? Accordingly, the inflammatory process is more active on the left.
Vegetovascular dystonia
This disease is a complex of functional disorders, which is based on dysregulation of vascular tone of the autonomic nervous system. This is a common reason why the right temple hurts when pressed. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by pain in the temples and without pressure. In the early stages, it is simply an unpleasant squeezing sensation, as if the head is in a vice. In parallel with this, the patient often experiences anxiety, unmotivated fear, phobias, and depressive disorders appear.
There is an opinion among patients that a neurologist makes a diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” if he cannot correctly diagnose it. Allegedly, the symptoms of VSD are so extensive that they can be attributed to every second resident of our country. A competent neurologist will only laugh at such a statement: the diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” has clear symptoms and really exists, although it is difficult to treat with medication. The patient's condition with this disease can be significantly alleviated not by pills and injections, but by changing lifestyle and giving up bad habits (in particular, smoking cigarettes).
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Has several stages. At the initial stage of development, this disease makes itself felt only by mild dizziness. In some cases, vision decreases (because the optic nerve is pinched). At the second stage, the patient begins to experience headaches, and short-term loss of consciousness is possible. The main difference between osteochondrosis and increased intracranial pressure is that the neck and shoulders hurt, and the cartilage crunches when you rotate your head.
If, in parallel with these symptoms, the patient’s temple hurts when pressed, then we can confidently say that the problem is precisely osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The treatment of this pathology is carried out by an orthopedist and a neurologist. The following medications are prescribed:
- Intramuscular injections of drugs that include cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine, thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid.
- Over-the-counter mild nootropics.
- Vasodilators.
- Medicines designed to compensate for the deficiency of collagen and elastin in the body.
Pain in the temples: why it occurs, the nature of the pain, concomitant diseases and treatment
Headaches localized in the temples are familiar to almost every person - statistics claim that at least 98% of people have experienced this unpleasant syndrome.
If an ordinary pain syndrome can be tolerated and even withstand its fairly intense effects, then pain in the temples forces even the most tolerant people to take medications.
This is due to the fact that it is in the temporal region that a large number of nerves and vessels are located: the slightest pressure on the nerve endings leads to severe pain.
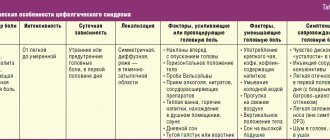
Nature of pain in the temporal part of the head Causes of pain in the temples - Migraine - Some infectious diseases - Cerebral angiodystonia - High intracranial pressure - Atherosclerosis - Dysfunction of the autonomic system - Cluster pain - Temporal arteritis - Hypertension - Trigeminal neuralgia - Hormonal disorders in women - Pathological changes in the temporomandibular joint - Head injuries 3. Treatment of pain in the temples
Migraine
We recommend reading: Migraine – causes, symptoms and basics of treatment
This disease causes not only an acute attack of pain in one or another part of the head with a pulsating sensation in the temple, but also nausea, vomiting, and aversion to bright light and noise. Migraine can only manifest itself as intermittent pain in the temple, accompanied by irritation and nervousness.
Often, patients are not aware of the presence of migraine, so if the above symptoms occur, it is necessary to consult a doctor - medicine has developed a specific treatment for this disease, and the use of painkillers brings virtually no relief.
Arteritis of the temporal region
Arteritis is an inflammatory disease of the arteries.
A rather rare disease in which a small lump forms on the temple, hurts when pressed and pulsates. It occurs most often in people over fifty years of age. The appearance of arteritis in young people is possible in isolated cases only in the presence of a genetic predisposition.
Arteritis is treated by a neurologist, surgeon, and therapist. At the same time, the patient may suffer from migraines, a feeling of fluid accumulation in the brain, and surges in blood pressure.
Hangover and withdrawal symptoms
The morning after a stormy party brings not only headaches and nausea, but also serious stress on the arteries and blood vessels. The body struggles with the consequences of severe ethanol intoxication. Due to the suppression of the tone of the vascular walls, people often complain that it hurts near the temple when pressed. Depending on the individual characteristics of the sick person, the pain may be located in the back of the head or forehead. In some cases, the left temple hurts when pressed, but the right one does not.
In this case, there is only one treatment - try to remove toxic products from the body as quickly as possible. To do this, you can use Enterosgel, preparations with activated carbon in the composition. After severe intoxication, it is necessary to take a course of vitamins with magnesium, selenium, and iodine.
Often such patients complain: “I press on my temple and it hurts.” They often exaggerate the scale of the problem. If pain in the back of the head and temple occurs after alcohol abuse, you should not run to the doctor and look for serious pathologies. It’s enough to simply eliminate ethanol-containing drinks from your diet once and for all.
Temporal bones hurt, what is it?
Unlike other tendon diseases, temporal tendonitis does not impair a person's ability to move, but it is accompanied by very painful and unpleasant symptoms.
Temporal tendonitis occurs everywhere and affects people of any age.
Tendinitis is an inflammatory lesion of the tendons.
Temporal tendonitis is an inflammation of the tendons of the masticatory muscles, which are attached to the temporal bone and provide function to the temporomandibular joint.
The disease can occur on only one side or involve the tendons on both sides.
Causes of temporal tendonitis include:
Pain
The main symptom of temporal tendonitis is pain localized in the joint area, cheeks and radiating to the lower jaw, teeth, neck, and forehead.
The intensity and nature of the pain can vary: from dull aching to unbearably sharp.
Very often, patients are able to clearly establish the relationship between the occurrence of pain and previous chewing of hard foods, cracking of nuts and seeds.
The pain can be constant, intensifying when chewing, talking, opening the mouth, or it can only occur when there is a load on the joint, and be absent at rest.
Local symptoms
The most common local symptoms are:
- difficulty opening the mouth (due to pain);
- swelling on the affected side in the cheek and temple area.
- When you feel the cheek, you can identify a tense muscle roll and a painful cord of inflamed tendon.
Infectious temporal tendonitis is characterized by redness along the tendons.
General symptoms
With temporal tendonitis, general symptoms are rare, mainly in cases where inflammation of the tendons of the masticatory muscles was caused by an infectious factor.
Patients may complain of lethargy, loss of appetite, headache, and fever.
Diagnosis is based on a thorough collection of medical history and complaints, examination of the patient by a doctor - this turns out to be quite sufficient to confirm the diagnosis.
Additional research methods are not needed, and they are not informative: in a general blood test, if there are any changes, they are nonspecific (signs of inflammation), and no pathology can be detected on x-rays.
The greatest difficulty is the differential diagnosis between temporal tendonitis and other diseases with similar symptoms (dental problems, trigeminal neuralgia).
However, an experienced doctor should easily cope with this task, since the disease has a number of distinctive features:
- Temporal tendonitis differs from trigeminal neuralgia in the presence of a connection between the occurrence of pain and the load on the joint, painful swelling along the tendon.
- With caries, especially complicated, there may also be pain in the cheek with radiation to the neck, lower jaw, but there are indications of pain in the tooth, which intensifies not only when chewing, but also from thermal (cold, hot), chemical (acid) irritants , sweet food) of nature.
Treatment of tendinitis is carried out mainly on an outpatient basis; severe cases of the disease requiring hospitalization are practically never encountered.
The basic principles of treatment are presented below.
Ensuring functional rest of the temporomandibular joint
In the most acute period of the disease, with severe pain, patients are prohibited from opening their mouths, and they are not even allowed to talk.
Food is given in liquid form through a straw. After 1-2 days, they gradually switch to semi-liquid food, and a mechanically gentle diet (ground, soft food) is maintained for about a month.
Subsequently, it is recommended to avoid foods that require significant chewing effort.
Use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs
The peculiarity of the treatment of temporal tendonitis, in contrast to tendonitis of other localizations, is that all kinds of burning and warming ointments are not used.
When applied to the face, they greatly irritate the skin; caustic particles get into the eyes and nose and can cause lacrimation, rhinitis, and conjunctivitis.
Local remedies include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren emulgel, diclofenac).
More often, NSAIDs and painkillers are prescribed orally for a short course (for 5-7 days) - diclofenac, nimesulide, nurofen, ketorol and other drugs are used.
Antibacterial treatment
For temporal tendonitis of infectious origin, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs (amoxiclav, azithromycin, cephalexin, etc.) are prescribed orally or intramuscularly, less often - to the area of the inflamed tendon.
Physiotherapy methods
They relieve pain very effectively and significantly speed up the healing process.
In this case use:
- laser;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis with novocaine;
- lidase;
- ultrasound;
- shock wave therapy.
Specific prevention is to avoid harsh loads on the temporomandibular joint.
If there are risk factors, as well as after tendonitis, it is recommended to avoid nuts, seeds, hard meat, hard sausages, crackers and other products, the use of which is combined with intense chewing.
Which doctor should I consult if my temple hurts when pressed?
First you need to get a voucher to see a therapist. He will prescribe the standard necessary tests - a biochemical blood test, a general urine test. After receiving the results, the overall clinical picture will become clearer. If leukocytes are elevated, then the cause of pain in the temple is most likely caused by inflammatory processes in the sinuses, lymph nodes, and nasopharynx. This condition is easily treatable.
If the tests are normal, the therapist will give you a coupon for a consultation with an endocrinologist and a neurologist. For patients who find it unpleasant to be in a public clinic and do not have time to wait their turn, there are paid diagnostic centers. There you can make an appointment directly with an endocrinologist, surgeon and neurologist. In this case, tests and procedures will also be paid.
How is diagnosis carried out and possible treatment options?
To find out the exact reason why it hurts above the temple when pressed, you will have to undergo a series of studies. If a patient goes to a clinic at his place of residence, he is required to provide all procedures free of charge (everything will be paid for by the insurance company with which the sick person is registered under the medical policy). As mentioned above, if the patient does not have time to wait for an appointment with a coupon in public medical institutions, he can go to private diagnostic centers and undergo diagnostics for a fee.
To diagnose the severity of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, MRI and CT are prescribed. After determining the stage, the neurologist prescribes treatment. These can be either ordinary vitamin-mineral complexes, physiotherapy and exercise therapy, or serious prescription anesthetic drugs. It all depends on how far the pathological condition has gone.
To diagnose vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is enough for a neurologist to compare a number of symptoms. There is no research that could help accurately identify this disease. In some cases, it makes sense to undergo an MRI of the brain vessels. The cost of such a study is about seven thousand rubles in paid diagnostic centers. MRI of cerebral vessels is informative and will help establish an accurate diagnosis not only for VSD, but also for organic brain disorders, intracranial pressure, and encephalopathy.
Diagnostics
Determining the cause of temporal pain occurs based on data from blood tests and instrumental examinations.
General analysis indicators allow you to see signs of inflammation, infectious diseases, and anemia. Biochemical data indicate signs of atherosclerosis, temporal arteritis, and kidney diseases causing arterial hypertension. A coagulogram allows you to detect features of the blood clotting process, which allows you to draw a conclusion about the risk of thrombosis and hemorrhage.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- Radiography. It is carried out primarily to exclude inflammation in the sinuses, injuries, and neoplasms.
- MRI. The data obtained helps to see and evaluate brain structures, tissue density, the presence of tumors, necrosis, hematomas, thrombosis, and the condition of blood vessels. Can be performed on young children and pregnant women. Children are performed under anesthesia.
- CT scan. As a result of a layer-by-layer study, a flat or three-dimensional picture is obtained that allows one to detect inflammation, tumors, and hemorrhages. The study helps to see neoplasms, vascular patterns, features of the skull bones, brain membranes, injuries, hematomas.
- Angiography. This is a special type of radiography with the introduction of a contrast agent, which allows you to see the pattern of blood vessels, aneurysms, and expansions.
- Ultrasound of the head. Based on the results of the study, organic lesions are assessed, irregularities in shape, size of blood vessels, and individual areas of the brain are identified.
- Electroencephalography. Indicates the presence of signs of epilepsy.
- Spinal tap. The specialist takes a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, analyzes it for changes in composition, and assesses intracranial pressure.
- Blood pressure monitoring. To clarify the diagnosis of arterial hypertension or hypotension, daily blood pressure monitoring using a special sensor is indicated.