The brain is considered the most poorly understood in the body. Scientists, possessing modern technologies, even now cannot thoroughly understand the etiology of disorders of brain structures. Most departments closely intersect with each other - any disorder in one of them leads to a malfunction in the rest.
When pronounced disorders appear, a head examination is performed. Often the cause of pathological processes is a Verge's cyst or cystic growth of the transparent septum of the brain. This is a kind of knot with compacted walls and cerebral fluid inside. What do cystic neoplasms threaten the victim with, and how should they be treated?
What kind of pathology is this
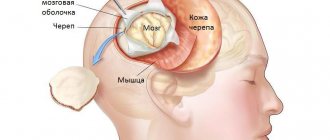
It is known that the brain is covered with dura, arachnoid (arachnoid) and soft membranes. The septum pellucidum separates the anterior part of the brain from the corpus callosum. It includes 2 plates consisting of brain tissue. Between them there is a slit-like cavity. Its shape is comparable to a square filled with liquor.
The formation of the septum occurs in the initial stages of intrauterine development. The distance between the plates determines the gestational age. Therefore, signs of congenital abnormalities can be noticed already during this period.
Due to excessive concentration of cerebrospinal fluid, a cystic neoplasm can form between the plates. Doctors assure that the appearance of such growths does not affect human health. But the whole point is the size of the cyst: the rapidly growing formation begins to put pressure on adjacent tissues and vessels, which contributes to a rapid increase in intracranial pressure.
Primary (or congenital) Verge's cyst can be combined with other pathological conditions:
- Malformations . The cause of this type of disorder is the choroid plexus of veins and arteries in the nervous system.
- Arnold-Chiari malformation , in which the cerebellar tonsils descend and compress the medulla oblongata.
- Neuronal heterotopia , characterized by impaired movement of nerve cells.
- Hypoplasia of the optic nerve . There is a decrease in the content of axons in the structure of the affected nerve fibers.
Reasons that contribute to the formation of cysts
The appearance of cavities between brain tissues can be caused by the following factors:
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Inflammatory processes spreading to the membranes of the brain;
- Past infectious diseases (especially meningococcal infection);
- Concussions and brain injuries;
- Brain hemorrhages.
In infants, the presence of a cyst is often associated with intrauterine infection.
Sometimes an anomaly of the transparent septum of the brain is combined with a number of abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous system. These include:
- Hydrocephalus;
- Hypoplasia of the optic nerves;
- Vascular malformations;
- Arachnoid cysts located in other areas of the organ.
After the neoplasm acquires significant size, it begins to put pressure on nearby vessels and tissues. From time to time the cyst blocks the interventricular spaces.
Causes
The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid is caused by:
- Congenital anomalies . Almost 100% of premature babies are diagnosed with this pathology. In a newborn baby, a cyst of the septum pellucidum often resolves over time, is asymptomatic and benign. The causes of the development of pathology in the fetus are associated with infectious intrauterine diseases or injuries of the mother.
- Acquired (secondary) causes . These could be injuries, concussions, inflammation affecting the lining of the brain, and hemorrhages. Such cysts can grow to enormous volumes and threaten not only the well-being, but also the life of the patient.
A Verge's cyst can become malignant if its catalyst is a pathological focus in another organ. Such brain tumors grow very quickly and are practically untreatable.
Locations
In addition to the genesis of formation, the location of the cyst also plays a significant role. Often the formation is localized between the vault of the corpus callosum and the anterior part of the brain. However, in some patients the cyst may occur in the anterior part of the interventricular septum. In addition, sometimes it is localized in the cerebellar area. Since such formations are generally located in the “safest” places, they are usually asymptomatic. Signs of pathology appear only with intensive growth of the formation, which is more typical for acquired pathology.
Symptoms and clinical signs
If it grows uncontrollably, a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain can cause the following unpleasant symptoms:
- Attacks of aching cephalgia that are not relieved by analgesics.
- Feeling of squeezing, bursting, squeezing of the head.
- Deterioration of visual acuity, hearing problems.
- Ear noise on one or both sides.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Trembling and numbness of the limbs.
Symptoms caused by the growth of a cyst depend on its location and size. Compression of neighboring organs can lead to their destruction and serious consequences. If the victim has the above symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Timely and adequate treatment will help to avoid complications associated with the growth of the cyst and prevent the development of a cancerous tumor.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear if the cyst is medium to large in size. It can be:
- visual impairment;
- hearing loss, tinnitus;
- headache that is not relieved by medication;
- pulsation in the head area;
- nausea that does not go away after vomiting;
- problems with coordination;
- changes in skin sensitivity;
- involuntary movements of arms and legs;
- violation of muscle tone;
- lameness;
- paralysis;
- convulsions;
- hallucinations, mental disorders.
What is the danger of Verge's cyst?
The consequences of growth in the transparent septum of the brain largely depend on its nature and size. If a cyst appears and grows very quickly, the patient develops chronic increased intracranial pressure. He often loses consciousness, due to a lack of oxygen supply to the brain, many body functions are disrupted, convulsive seizures occur, vision deteriorates greatly, hearing deteriorates, and motor functions suffer.
The acquired anomaly leads to circulatory disorders and dropsy of the brain. A malignant tumor can be fatal.
The most dangerous consequences of the disease include:
- Atrophy of brain tissuecaused by compression of the meninges and the formation of adhesions, interfering with normal blood circulation. In advanced cases, the pathological process leads to loss of performance.
- Dropsy of the brain . As the cyst grows, it impedes the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to impaired drainage of fluid from the brain cavity. The disease negatively affects the activity of all vital organs and systems.
- Stroke . The Verge cyst itself does not cause pathological processes in the vessels, but often provokes a violation of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid and blood. And its constant growth threatens rupture of arteries and massive internal bleeding.
The normal size of a Verge cyst is calculated individually in each case. Experts believe that if the pathology does not grow and does not in any way affect the functioning of parts of the brain, then there is no need for specific treatment of the patient.
Kinds
Cystic cavities are differentiated according to the following characteristics:
- Localization. The arachnoid cyst of the brain is located between the soft tissue and the membrane. Cerebral - directly in the brain tissue. An arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst rarely causes symptoms. This is explained by the fact that the subarachnoid cyst does not directly affect the brain itself, but is located between it and the outer membrane.
- Location. A lacunar cyst develops in the frontal lobes. In the pineal body - pineal. There may also be a cyst of the posterior cranial fossa, left temporal lobe, right, etc. A retrocerebellar cyst is located in the cerebellum. In severe cases, neoplasms can affect the entire hemisphere (hemisphere). This can cause critical conditions. Damage to the occipital, frontal region, and pyrineural septum is dangerous. Sometimes the spinal cord may be affected.
- Etiology. Takes into account the reasons for the appearance of cysts. Primary is formed due to genetic disorders. This is a congenital anomaly that affects the tissues of the head. At some stage of fetal development, brain tissue is formed with disturbances. The baby may be born with a cyst or it will grow later. If the baby develops normally, parents may not even be aware of the congenital anomaly for many years. Often newborns with it are no different from healthy peers. Secondary - the result of birth injuries, operations, stroke, coronary artery disease, infections, etc. Most often, one lobe of the brain may be affected.
Any cyst can capture healthy tissue or displace it. In severe pathogenesis, brain tissue can be compressed and pinched. On one side they are pressed by the cyst, on the other by the bones of the skull. The consequence is that the functions of the department that is affected are disrupted. This is dangerous as it threatens health and life. This option requires immediate medical attention.
Sometimes neoplasms can spread to the spine. This can provoke dangerous consequences.
When a brain cyst appears, size and growth rate are of no small importance. Most often these are tiny tumors. They do not compress brain tissue and practically do not interfere with normal life. But large tumors require urgent treatment and constant monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Due to a post-ischemic cyst, the blood supply can be seriously impaired. The tissues do not receive proper nutrition and atrophy, and zones of necrosis form.
It is necessary not only to detect the neoplasm itself, but also to find out for what reasons it appeared. Only by knowing the reasons can you effectively build a treatment regimen.
Diagnostics
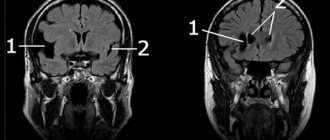
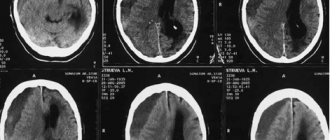
At the first signs of the disease, you should seek medical help. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the specialist refers the patient to magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Using a scan, you can see not only the pathological formation, but also identify its location, size, and structure.
To identify the cause that contributed to the formation of the cyst, a number of additional procedures are prescribed:
- A detailed blood test to identify inflammatory processes and associated abnormalities.
- Blood test for clotting and cholesterol levels to eliminate the risk of thrombosis.
- Electrocardiography assessing heart function.
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels. It is carried out to identify vascular abnormalities.
- Study of blood flow through the vessels of the brain, allowing you to evaluate blood flow in real time.
The main goal of diagnosis is to assess the detected neoplasm: whether it is benign or malignant, how quickly it grows, and where it is located. Only after this, specialists decide on further treatment tactics.
Treatment
The main therapy for Verge's cyst is based on:
- Observation.
- Conservative treatment.
- Surgical intervention.
The patient is observed for some time. If the detected cyst does not cause discomfort and does not affect the patient’s well-being, he is recommended to have a magnetic resonance scan twice a year. When the pathology does not grow, other treatment methods are not used. If it increases, a conservative technique is used.
The main goal of conservative therapy is to slow down the growth of the formation. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- Nootropic drugs.
- Osmotic diuretics.
- Drugs that stimulate cerebral circulation.
- Medicines that help resolve blood clots and hematomas.
By taking these medications, the patient should feel improvement. Symptoms of the disease either partially or completely disappear. If after the therapy no positive dynamics are observed, surgical intervention is used to restore the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid.
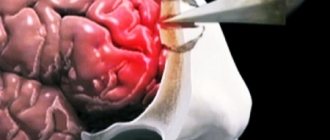
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- A probe is inserted into the area of the problem cavity.
- Using an endoscope, small incisions are made, thanks to which the accumulated cerebrospinal fluid flows out.
- A drainage tube is inserted into the problem area to avoid re-formation of the cyst and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
This treatment gives a 100% result if the formation is single-chamber. With a growth consisting of several cavities, in 20% of cases the cyst appears again. After surgery, the patient should be periodically examined so that if the pathology re-grows, it can be detected at an early stage and therapy can be started in a timely manner.
Self-medication is not acceptable here, since a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain can cause the most serious consequences if not treated correctly. It is especially dangerous to drink various infusions and decoctions: they can sharply worsen the patient’s well-being and accelerate its growth.
Prevention
There are no preventive measures to prevent the appearance of Verge's cyst. But patients are recommended:
- Avoid head injuries.
- Treat infectious diseases in a timely manner.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Pregnant women need to do tests and ultrasounds in a timely manner, regularly visit an obstetrician-gynecologist and follow all his recommendations.
If a patient is diagnosed with such neoplasms, then there is no need to panic. In most cases, the prognosis for detecting a cyst in the early stages is favorable. The main thing is to undergo a series of prescribed procedures and get ready for recovery.