High blood pressure
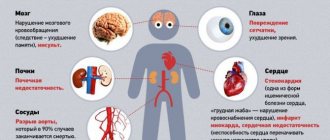
Another serious reason why the forehead hurts between the eyebrows is increased intracranial pressure. This happens to those who suffer from high blood pressure. This category includes hypertensive and hypotensive patients. This also includes people who are sensitive to changes in weather phenomena. People who suffer from high blood pressure should definitely buy a device to measure it. If the pressure rises, then special measures should be taken to normalize it. These include taking special medications.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or take medications that have not been prescribed by a doctor. You should control your blood pressure. It is also necessary to contact a medical institution for consultation, examination and prescription of medications, which will be selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the human body. When pain occurs between the eyebrows, you must first measure the pressure and take the necessary measures to stabilize it. If you cannot cope on your own, then you need to call a doctor.
Causes of pain in the eyebrow area
There are many reasons why eyebrows hurt, the most common problems are:
- mechanical injury;
- a bite of an insect;
- allergy;
- inflammation of the frontal sinuses;
- migraine;
- ICP;
- glaucoma.
In all these cases, the pain syndrome has its own characteristics, which is an important diagnostic sign.
Unrelated to pathologies
- Sometimes the pain above the eyebrow is not due to any disease, but due to injury, a bite or an allergic reaction.
- In this case, the pain never radiates to the temple, eye or other area, since the lesion is strictly local in nature, usually without involving the deep layers of the sclera, eye muscles or vitreous body in the process.
Mechanical injury
These include the consequences of a fight: bruises, abrasions, scratches, fractures. The pain in this case is intense, often pulsating at rest, moderate, and upon palpation sharply intensifies to an unbearable level.
This problem is also often observed after tattooing.
A bite of an insect
Usually ends with severe inflammation and swelling. A wasp, gadfly, ant and many other insects can bite. A characteristic feature is damage on only one side.
However, if a person was attacked by a beehive, then multiple lesions will be observed in a variety of areas. In this case, the headache in the eyebrow area is localized exactly at the site of the bite.
Allergy
An allergic reaction is a common reason why the eyebrow above the eye hurts. Typically, this pathology is observed after an insect bite (described above). In addition, allergies can occur to paint fumes and other chemicals.
Usually the conjunctiva and upper eyelids are involved in the process. In this case, the pain syndrome is mild, but quite severe swelling is observed.
An important sign is the development of pathology as a result of a certain irritant.
Cold
cold pimple on the head
The name of a whole group of viral and bacterial diseases of the respiratory system. Common signs are fever, runny nose, cough and sputum production.
It is transmitted by airborne droplets and strongly depends on the lifestyle and state of a person’s immunity.
The pain spreads throughout the forehead without clear localization. The intensity is moderate.
Possible diseases
It often hurts between the eyebrows due to a serious illness that requires urgent treatment.
Inflammation of the frontal sinuses
The most common cause is inflammation of the sinuses - frontal sinusitis or ethmoiditis. Pathology develops due to viral or bacterial infection.
In the first case, the exudate is serous or catarrhal (clear, watery or mucous). In the second situation, the discharge is purulent (thick, cloudy, yellow, white or greenish).
If your forehead hurts between the eyebrows, but there is no runny nose, this does not exclude an infectious infection, since exudate can be released, but not flow out of the sinus.
At first, the unpleasant sensations are localized in one place, but then the entire face is involved in the pathological process. An important sign is severe pain in the morning, which subsides in the evening.
Frontitis is characterized by pain in the bridge of the nose, which sharply intensifies when pressing on the area between the eyebrow and eye near the nose, and redness of the eyes, photophobia, and swelling of the eyelid are detected.
The nature of the pain above the eye with ethmoiditis is very similar, but differs in less swelling, is localized in the bridge of the nose and eyebrows, but does not intensify with pressure.
Migraine
Migraine is a neurological pathology. The main symptom of the disease is periodic or constant pain on one side of the head (on both sides - extremely rarely).
It intensifies with physical or mental stress, as well as as a result of changes in humidity or temperature. In addition, fear of light or sound is an important symptom.
This pathology occurs as a result of mechanical trauma, hypothermia, vascular disorders, hemorrhage, nerve inflammation, neoplasm, and infectious damage to the membranes of the brain.
An important difference is the lack of dependence on blood pressure or ICP. That is, pain in the frontal part of the head depends entirely on mental and physical work.
Glaucoma
These include various diseases that are associated with increased pressure in the eyes, which causes visual impairment, decreased sensitivity of the retina to light, and optic nerve atrophy.
Glaucoma is primarily divided into open-angle and closed-angle. If left untreated, eye disease pathology leads to blindness.
However, even modern therapy does not eliminate the disease, but only stops it. Sooner or later, the disease leads to loss of vision, which is associated with compression of the capillaries that nourish the retina.
A characteristic symptom of the pathology is eye pain, as well as redness due to vasodilation.
Increased ICP
Increased intracranial pressure is observed when the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is disrupted. Develops due to various pathologies.
In this case, the head hurts above the eye, in the back of the head and in all other places; it has a pressing or bursting character. Accompanied by nausea and photophobia. The pain increases sharply with sneezing and coughing.
- The diagnosis is made by examining the fundus of the eye, where swelling of the blood vessels is detected.
- Later, in the absence of treatment, the pain becomes unbearable, a person without drug support becomes irritable, depressed, and suicidal tendencies are possible.
- If the pathology is not treated, the disease will lead to brain atrophy and death.
Associated symptoms
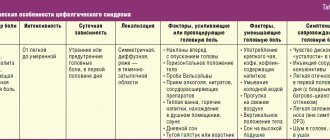
All diseases when the forehead hurts above the eyes, with their characteristic signs and distinctive features are given below in the table:
DiseaseDescription of pain syndrome Other symptoms of diseases
| Injury | Immediately after the injury, the pain may be absent due to adrenaline, at rest it is intense, pulsating, and sharply intensifies with palpation. | A bruise, bruise, or abrasion is found at the site of the impact. The fracture is diagnosed by x-ray. |
| A bite of an insect | The pain has a clear localization, is noted immediately after the bite, and later subsides. The pain syndrome does not increase with pressure. | The area around is swollen. Often a black or red dot is found at the site of the bite. |
| Allergy | The eyes, eyelids, orbits and the area around them hurt. The pain is mild and may feel like discomfort. | Swelling of the eyebrows and upper eyelid and redness of the eyes are detected. The difference is the presence of symptoms on both sides of the face. |
| Viral acute respiratory infections | When you have a cold, the pain spreads across the entire forehead, but without a clear localization (from the temples to the bridge of the nose). With rhinitis, discomfort affects the inner surface of the nose. | The temperature is 37.5-38.5 (C), the patient feels well, appetite and activity remain. The sputum is mucous and watery. |
| Bacterial acute respiratory infections | Temperature 38.5-39.5 (C), feeling poor, lack of appetite, patient passive. The sputum is thick, opaque, white or yellow. | |
| Frontit | Pain in the bridge of the nose; when pressing on the area between the eyebrow and eye near the nose, it sharply intensifies. | Associated symptoms: conjunctivitis, photophobia and lacrimation. |
| Ethmoiditis | Headache between the eyebrows, in the eye sockets, bridge of the nose, behind and above the eyes. | High temperature, discharge of thick purulent exudate from the nose. Constant severe nausea and vomiting. |
| Migraine | Throbbing pain in the head occurs as a result of mental or physical work. Localized only on one side (but not always). | There is a fear of light, sounds, and fatigue. |
| Glaucoma | The pain is not felt in the eyebrows and forehead, but as if behind the eyes or above them. | Various vision pathologies appear. Redness of the eyeball is detected as a result of vasodilation. |
| High ICP | The pain is diffuse, bursting, and has no clear localization. Increases sharply with bending, coughing and sneezing. | There is a fear of light, sounds, and fatigue. |
Cluster pain in men and not only
Why does my forehead hurt between my eyebrows? In addition to the above symptoms, there is another reason for this. It is characterized by the fact that a person feels throbbing pain, painkillers do not help, and the eyes turn red. This type of sensation has a name, namely, these pains are called cluster pain.
Cluster pain occurs due to the fact that a person has problems with blood vessels. It is worth saying that this type can be provoked by certain factors. These include changes in climate conditions, drinks containing alcohol, and smoking. There are cases when this type of pain occurs due to the consumption of a certain type of alcohol, for example red wine. People who know exactly what may cause headaches of this nature are advised to avoid consuming this product or drink. Typically, this type of pain accompanies men over the age of forty who have a bad habit associated with smoking.
Typical nature of pain between the eyebrows, above the eyes
There are 4 types of cephalgia, each with different causes and symptoms. Determining the type of headache is the first step to solving the problem:
- Tension. With this type, the headache occurs in the area of the temples, in the frontal region, or between the eyes. The soreness is characterized as a hoop around the head. The intensity is practically unchanged and does not increase.
- Migraine. With a migraine, a person feels a throbbing pain in the head on the left or right side, accompanied by nausea and hypersensitivity to light. Visual disturbances (flashes of light, zigzag lines in the field of vision) may also appear.
- Cluster. A person experiences sudden, intense (often unbearable) pain around the eye on one side.
- Attacks caused by sinusitis. Sinusitis manifests itself as a dull, throbbing pain in the forehead and eyebrows, above the nose (in the bridge of the nose). Pressure may also be felt above the eye under the eyebrow. The pain intensifies when the head is tilted.
Migraine
Why does my forehead hurt and put pressure on my eyes? The reason for this is migraine. This is another ailment that often accompanies the fair sex. In this case, pain may be present in the space between the eyebrows.
But more often it occurs in the temporal part. There are options when migraines cause pain in the eye areas. Nausea is also often present, and the person may vomit. This type of pain is a female pathology. Men don't have migraines.
Flu and other infectious diseases
Why does my forehead hurt when I have a runny nose? The most common cause is influenza. These pain sensations occur in a pronounced form. It happens that a person cannot lift his head from the pillow or open his eyes. The patient's eyes become very sensitive to daylight. You should know that a person’s condition, in which he experiences symptoms such as aching bones, headache, fever, and increased body temperature, can be caused by other infectious diseases. Such ailments include meningitis, malaria and typhus.
Rhinitis of various forms
Chronic rhinitis leads to insomnia
The inflammatory process in the nasopharynx causes swelling of the nasal sinuses, thereby making breathing difficult. This reduces the amount of oxygen reaching the brain and causes headaches. In this case, when you have a runny nose, it hurts between the eyebrows. As a rule, the pain syndrome occurs for a long time; the person often blows his nose, which causes pressure on the nasal sinuses, causing a headache. Despite all the harmlessness of rhinitis, it should be treated and prevent the development of a chronic form, which can lead not only to headaches, but also to sleep disturbances, as well as exhaustion of the body.
All these reasons cause pain, which goes away along with a runny nose, with proper treatment and does not cause any complications. There are a number of infectious diseases accompanied by a runny nose and headache.
Sinusitis and frontal sinusitis
A headache between the eyebrows can occur due to the presence of diseases such as sinusitis and frontal sinusitis. In these cases, it is imperative to take all necessary measures to eliminate this disease.
This is due to the fact that the body may not be able to cope with the recovery process on its own. Then a person may experience complications that are much more difficult to get rid of. Below we will explain in more detail why the forehead hurts and the temples feel pressure.
Causes
Diagnosing rhinitis
It is impossible to name a definite cause of pain in the forehead during a runny nose; there are several pathologies that can cause such a symptom:
- colds;
- viruses;
- flu;
- hypertension;
- rhinitis;
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- ethmoiditis;
- sphenoiditis;
- otitis;
- infectious diseases.
With any of these diseases, characterized by the appearance of a runny nose, a headache may occur, localized in different places:
- if your forehead hurts from a runny nose, this is due to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the body and the development of an inflammatory process, sinusitis or otitis may be suspected;
- if, in addition to the forehead, the bridge of the nose hurts, we can talk about sinusitis;
- If your eyebrow hurts due to a runny nose, you should definitely consult a doctor, this may indicate serious complications.
Headaches of any etiology cannot be ignored, but there are a number of causes that are not dangerous and can be easily treated at home.
What symptoms begin to bother a person with these ailments?
This disease occurs in three stages, such as initial, acute and chronic. In all of them there are headaches in the nose and between the eyebrows. In addition, there are other symptoms that can indicate at what level of spread the disease is.
The frontal sinuses are located between the eyebrows. When they become inflamed, the patient begins to experience pain. As a rule, the inflammatory process begins when a person does not take special measures to improve the health of his body, for example, during a cold. Or the treatment was chosen incorrectly. Therefore, it does not bring the desired result. There is also no need to endure the disease on your legs. When a person is sick, he should remain in bed. This is not just a recommendation, but an important element of the treatment process. It should be remembered that each organism is individual. Some people have a stronger immune system, while others have a weaker one.
Therefore, in some people, the body copes with the disease on its own, without any consequences. But it is better to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Because it is unknown how the body may behave in one case or another.
Pain between the eyebrows: causes and nature of pain
Headaches in the forehead area are very unpleasant and can become an obstacle to a person’s normal activities. They have different reasons, it should not be underestimated.
Frequent attacks of cephalgia reduce the quality of life and may indicate a serious illness. If you haven't had headaches before and suddenly start experiencing persistent pain, consult your doctor.
A visit to a specialist is also required if there is severe pain between the eyebrows or the intensity of the migraine suddenly worsens.
Typical nature of pain between the eyebrows, above the eyes
There are 4 types of cephalgia, each with different causes and symptoms. Determining the type of headache is the first step to solving the problem:
- Tension. With this type, the headache occurs in the area of the temples, in the frontal region, or between the eyes. The soreness is characterized as a hoop around the head. The intensity is practically unchanged and does not increase.
- Migraine. With a migraine, a person feels a throbbing pain in the head on the left or right side, accompanied by nausea and hypersensitivity to light. Visual disturbances (flashes of light, zigzag lines in the field of vision) may also appear.
- Cluster. A person experiences sudden, intense (often unbearable) pain around the eye on one side.
- Attacks caused by sinusitis. Sinusitis manifests itself as a dull, throbbing pain in the forehead and eyebrows, above the nose (in the bridge of the nose). Pressure may also be felt above the eye under the eyebrow. The pain intensifies when the head is tilted.
Causes associated with manifestations of pathology and disease
According to doctors, pain above the eye in the eyebrow area is rarely caused by just one cause. However, trigger factors need to be identified. There are primary pains, mainly caused by a neurological disorder, and secondary pains, where the pain between the eyebrows is caused by serious factors such as brain tumors and similar problems.
Meningitis and encephalitis
Meningitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the meninges, the membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord from various negative effects.
Symptoms of meningitis:
- headache (part of the head from the crown to the eyebrows may hurt);
- nausea;
- muscle stiffness;
- fever;
- sensitivity to light;
- fatigue;
- muscle pain;
- excessive sleepiness;
- muscle cramps;
- rash;
- vomit;
- anxiety;
- petechiae;
- unconsciousness.
Important! Meningitis can occur after eyebrow tattooing or piercing using non-sterile instruments.
Encephalitis is a viral disease caused by flaviviruses. The disease affects the nervous system, including brain tissue.
Stage 1 symptoms include:
- muscle and joint pain;
- fatigue;
- increased drowsiness;
- slight pain in the forehead.
After a few days, these problems recede on their own, the person’s condition improves, returning to a picture of full health.
The 2nd phase of the disease is characterized by the occurrence of severe headache accompanied by fever. The patient experiences sensitivity to light, nausea, and vomiting. Symptoms of nervous system damage include:
- neck muscle stiffness;
- muscle spasms;
- nervous paralysis;
- dizziness;
- sleep disorders;
- memory impairment;
- disorientation.
This acute condition lasts 2–3 weeks. Then the patient's health gradually improves.
Migraine
Migraine affects people of working age 25–55 years, and is more common in women. The disease manifests itself in several phases, unlike stress pain, it worsens with physical activity and stress.
Triggers include:
- stress;
- physical activity;
- weather change (atmospheric pressure);
- food (cheese, chocolate, citrus fruits, alcohol, monosodium glutamate);
- lack of sleep;
- fatigue;
- hormonal factors.
With migraines, pain usually occurs on the left or right side. The pain is pulsating, the person cannot continue activities, needs peace and quiet.
Acute frontal sinusitis and sinusitis
Let's look at the symptoms of the acute course of the disease:
- A feeling of pressure on the area between the eyebrows, which is accompanied by acute pain. These sensations begin to intensify if you press on the area between the eyebrows. Also, the pain will be stronger when turning the head and tilting it. The patient has difficulty moving his eyes.
- A large amount of pus is released from the nasal sinuses in the morning and afternoon, which is accompanied by a pungent odor.
- The patient's temperature can reach 39 degrees. It is accompanied by fever and chills.
- The patient has a cough. It appears due to the fact that mucous secretions mixed with pus flow down the larynx, and the person begins to cough.
- Lost appetite.
- Apathy towards everything that is happening sets in.
- Sleep is disturbed. This is due to the fact that the patient is worried about pain, nasal congestion, temperature, etc.
Sinusitis
Maxillary sinuses with sinusitis
This is the most common disease, the main symptom of which is a runny nose and headache. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, which are located on both sides of the bridge of the nose, almost under the eyes. This is where the inhaled air, cold and containing dust or harmful substances, enters. And if a person has a weak immune system, the maxillary sinuses become inflamed and pus begins to accumulate in them.
Therefore, if the bridge of your nose and forehead hurt when you have a runny nose, you should consult a doctor; it could be sinusitis. The headache is usually pressing, bursting; if you shake your head, it may seem as if fluid is flowing from one side to the other. If you lie on your back, the pain usually goes away; in addition, there are other symptoms of sinusitis:
- constantly elevated temperature, signaling an inflammatory process;
- thick purulent green or yellow discharge with an unpleasant odor from the nasopharynx;
- conjunctivitis, irritation and redness of the eyes;
- general weakness of the body;
- painful sensations when pressing on the nasal sinuses.
Sinusitis requires serious comprehensive treatment, otherwise complications may develop.
Features of the chronic stage of frontal sinusitis and sinusitis
The chronic course of the disease is characterized by the fact that its symptoms appear rather weakly.
Why does your forehead hurt with sinusitis? There is pain between the eyebrows. But they may not bother a person for a certain time. After a period of calm comes an exacerbation. Then the symptoms of the disease appear more clearly. This is the essence of the chronic course of the disease. It fades away and then appears again. There are certain factors that can cause exacerbation of chronic sinusitis. These irritants relate to environmental influences.
Treatment of sinusitis and sinusitis
The simplest treatment option for frontal sinusitis and sinusitis is the implementation of health measures at the initial stage of the disease. The essence of the treatment is to rinse the sinuses with saline solution. Before this, the canals should be cleared of mucus and pus. In addition to saline solution, there are other special means for rinsing the nose. They differ in composition and can be prescribed by a doctor individually when a patient visits a medical facility. Although first the person will be examined. And then they will do the necessary examination and prescribe treatment.
It is worth mentioning that if you start treatment at an early stage, you can rid the body of these ailments through such simple drugs as Aspirin and Pentalgin. But advanced forms will require the purchase of more drugs at a higher cost. Surgical intervention in the body is also not excluded. Recently it has been used less frequently. But when treatment through medications and rinses does not help, the patient is prescribed a surgical method of treatment. It is aimed at cleansing the sinuses of fluid accumulated in them. During the operation, the person will need to stay in the hospital for a certain time. This is necessary to prepare the patient for surgery and monitor him after surgery.
Attention should be paid to the fact that the acute form of frontal sinusitis and sinusitis is similar in external manifestations to a disease such as frontal sinusitis of an allergic nature. This suggests that in no case should you independently assess your condition and make any diagnosis for yourself, and then carry out treatment measures. The wrong direction in therapy can lead to the fact that a person will not recover from the illness that bothers him. Complications may also arise, which will then be difficult to get rid of.
The disease can become chronic if during its acute period the forehead sinuses were poorly cleansed. In addition, the patient may not complete the course of treatment. This option is quite common, because many people, at the first signs of relief, stop taking measures to improve the health of the body. This is not recommended, since if the disease becomes chronic, there is a possibility that it will bother the person throughout his life.
Particular attention should be paid to children. The fact is that a person as an adult can talk about what bothers him. But children do it with difficulty. Therefore, if you suspect any pathology, you should take the child to the doctor.
Diagnosis of the disease
Often a person does not know what to do and which doctor to contact if the eyebrow hurts on its own or in cases where pressure is applied to it.
It’s best to start with a therapist who will listen and ask about symptoms and past illnesses. He will conduct an initial examination and, if necessary, refer you to specialists.
As a rule, this is a neurologist, ENT specialist or ophthalmologist. If head injuries have occurred, a surgeon may be needed.
After this, diagnostics will be carried out. A variety of methods can be used: blood sampling for analysis, x-rays and probing of the sinuses, ultrasound, CT or MRI of the nasal sinuses. If meningitis is suspected, an electroencephalogram, CT scan, and cerebrospinal puncture are prescribed.
Only after this the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.