general information
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Charcot's disease) is a serious pathology of the nervous system, in which there is damage to the so-called motor neurons in the spinal cord, as well as in the cerebral cortex. This is a chronic and incurable disease that gradually leads to degeneration of the entire nervous system. In the final stages of the disease, a person becomes helpless, but at the same time he maintains clarity of mind and mental health.
ALS disease, the causes and pathogenesis of which have not been fully studied, does not differ in specific diagnostic and treatment methods. Scientists continue to actively study it today. It is now known for sure that the disease develops mainly in people between the ages of 50 and approximately 70 years, but there are also cases of earlier lesions.
Muscle weakness and joint stiffness
What's happening? When the number of signals from motor neurons to muscles decreases, the latter are used less and less and lose mass over time. This leads to a feeling of weakness and can cause problems with balance and gait, which increases the risk of falling.
What can be done? A decrease in muscle mass cannot be stopped by physical exercise, because... the disease progresses irreversibly. However, exercise helps maintain joint flexibility and mobility, which helps maintain muscle function, balance, and body posture. To get a referral to a physical therapist who can create an appropriate exercise program, you must contact your primary care physician. A nutritionist can also help and advise you on how to eat properly to maintain your body weight and further slow down the rate of muscle loss.
Learn more about ways to combat muscle weakness and fatigue
Classification
Depending on the location of the primary manifestations of the disease, experts distinguish the following forms:
- Lumbosacral form (impaired motor function of the lower extremities occurs).
- Bulbar form (some nuclei of the brain are affected, which entails central paralysis).
- Cervicothoracic form (primary symptoms appear with changes in the usual motor function of the upper extremities).
On the other hand, experts distinguish three more types of ALS disease:
- Mariana form (primary symptoms appear very early, a slow course of the disease is observed).
- Classic sporadic type (95% of all cases of the disease).
- Family type (differs in late manifestation and hereditary predisposition).
Pain
What's happening? ALS does not directly cause pain or discomfort. But they can be the result of a number of other reasons. For example, pain occurs as a result of muscle spasms, general spasticity, muscle tension, skin pressure, or constipation. Therefore, it is important to find out the cause of the symptom.
What can be done? There are recommendations for optimal body positions, support, prevention of local compression and drug therapy. In case of prolonged pain, you should contact a medical facility. The doctor can choose the appropriate pain reliever.
Find out more about pain relief options
Why does ALS occur?
The causes of this disease, unfortunately, still remain poorly understood. Scientists currently identify a number of factors, the existence of which increases the likelihood of getting sick several times:
- ubiquin protein mutation;
- disruption of the action of neurotrophic factor;
- mutations of some genes;
- increased free radical oxidation in the neuronal cells themselves;
- presence of an infectious agent;
- increased activity of so-called excitatory amino acids.
Swallowing problems
What's happening? When the muscles of the face, mouth and larynx are affected, swallowing becomes difficult. Disruption of the normal process of eating and swallowing is called dysphagia. As a result, a person receives less nutrients and fluids, which can lead to weight loss.
What can be done? It is necessary to contact a speech therapist and nutritionist, who will assess the degree of swallowing impairment and changes in body weight, and also talk about possible solutions to the problem. Including, in order to increase the intake of proteins and carbohydrates from food, you need to adjust your diet. There are also alternative methods that can serve as support or complete nutritional replacement.
Learn more about swallowing problems and nutrition in ALS
ALS disease. Symptoms
Photos of patients with this disease can be viewed in specialized reference books. All of them have only one thing in common - the external symptoms of the disease in the later stages.
As for the primary clinical signs of pathology, they very rarely cause caution on the part of patients. Moreover, potential patients often explain them by constant stress or lack of rest from the work routine. Below are the symptoms of the disease that appear in the early stages:
- muscle weakness;
- dysarthria (difficulty speaking);
- frequent muscle spasms;
- numbness and weakness of the limbs;
- slight muscle twitching.
All these signs should alert everyone and become a reason to contact a specialist. Otherwise, the disease will progress, which increases the likelihood of complications several times.
Muscle cramps and spasms
What's happening? Due to the deterioration of signal transmission from motor neurons, muscle tension or spasms develops. This leads to impaired motor activity and coordination of movements, as well as an increased risk of falls. Sudden muscle spasms can be extremely painful.
What can be done? To eliminate this symptom, as a rule, it is enough to change the position of the body while resting in a bed or chair. Exercise partially solves the problem. In addition, your doctor may prescribe medications to relax your muscles.
Find out more in the material “Pain in ALS”
Course of the disease
How does ALS develop? The disease, the symptoms of which were listed above, initially begins with muscle weakness and numbness of the limbs. If the pathology develops from the legs, then patients may experience difficulty walking and constantly stumble.
If the disease manifests itself as a dysfunction of the upper extremities, problems arise with performing the most basic tasks (buttoning a shirt, turning a key in a lock).
How else can you recognize ALS disease? The causes of the disease in 25% of cases lie in damage to the medulla oblongata. Initially there are difficulties with speech, and then with swallowing. All this entails problems with chewing food. As a result, the person stops eating normally and loses weight. In this regard, many patients become depressed, since the disease usually does not affect cognitive functions.
Some patients have difficulty forming words and even concentrating normally. Minor disturbances of this kind are most often explained by poor breathing at night. Medical workers should now tell the patient about the characteristics of the disease and treatment options so that he can make an informed decision about his future in advance.
Most patients die from respiratory failure or pneumonia. As a rule, death occurs five years from the moment the disease is confirmed.
Fatigue
What's happening? Decreased physical muscle functionality requires greater energy expenditure to maintain daily activity. Other causes of fatigue include breathing problems, shortness of breath, decreased food intake, and dehydration.
What can be done? Make a plan to complete your tasks for the day. This will help maintain a balance between activity and adequate rest. A physical therapist can offer more detailed techniques for solving the problem of fatigue. It is also important to consult with a nutritionist about increasing calorie intake and fluid intake.
Find out more about ways to combat fatigue
Learn more about weight maintenance
Diagnostics
Only a specialist can confirm the presence of this disease. In this matter, the primary role is given to the competent interpretation of the existing clinical picture in a particular patient. Differential diagnosis of ALS disease is extremely important.
- Electromyography. This method allows you to confirm the presence of fasciculation at an early stage of its development. During this procedure, a specialist examines the electrical activity of the muscles.
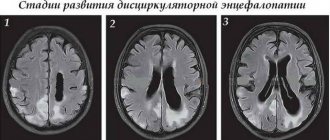
- MRI allows you to identify pathological foci and evaluate the functioning of all nervous structures.
Saliva and phlegm
What's happening? When swallowing is impaired, excess saliva accumulates in the oral cavity, which leads to drooling and the associated feeling of discomfort. The consistency of the secretion can be either watery or thick. Increased viscosity is associated with a decrease in the amount of fluid entering the body. In this case, saliva is removed with great difficulty. Dry mouth may also develop due to medications, dehydration, mouth breathing, or mucosal candidiasis.
What can be done? Options for solving this problem include dietary adjustments, drug therapy, and the use of aspiration devices for cleaning the oral cavity (suction).
Learn more about how to control salivation
What should the treatment be?
Unfortunately, medicine today cannot offer effective therapy against this disease. How can you overcome ALS? Treatment should be aimed primarily at slowing the progression of the pathology. For these purposes, the following activities are used:
- special massage of the limbs;
- if the respiratory muscles fail, artificial ventilation is prescribed;
- in case of development of a depressive state, tranquilizers and antidepressants are recommended. In each specific case, drugs are prescribed individually;
- joint pain is relieved by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Finlepsin);
- Today, experts offer all patients the drug Riluzole. It has a proven effect and is an inhibitor of the release of so-called glutamic acid. Once ingested, the drug reduces neuronal damage. However, even this remedy is not able to completely cure the patient; it only slows down the course of the ALS disease;
- To facilitate the patient's movement, special devices (canes, chairs) and collars are used to completely fix the neck.
Emotional reactions
What's happening? Some people with ALS experience a range of emotional states, including anxiety, fear, anger, sadness, depression and denial. These reactions are normal.
What can be done? Awareness of your emotional states is the first step to solving problems associated with feelings. If these conditions are too pronounced and persist for a long time, we strongly recommend that you seek help from a doctor. In some cases, drug therapy and/or psychotherapy are effective.
Learn more about emotional disturbances in ALS
Stem cell treatment
In many European countries, patients with ALS are now treated with their own stem cells, which also helps slow the progression of the disease. This type of therapy is aimed at improving the primary functions of the brain. Stem cells transplanted into the damaged area restore neurons, improve oxygen supply to the brain and promote the appearance of new blood vessels.
Isolation of the stem cells themselves and their direct transplantation are usually carried out on an outpatient basis. After therapy, the patient remains in the hospital for another 2 days, where specialists monitor his condition.
During the procedure itself, cells are injected into the cerebrospinal fluid through a lumbar puncture. Outside the body, they are not allowed to reproduce on their own, and reimplantation is carried out only after detailed cleaning.
It is important to note that this type of therapy can significantly slow down the disease of ALS. Photos of patients 5-6 months after the procedure clearly prove this statement. It will not help you get rid of the disease completely. Unfortunately, there have also been cases where treatment has no effect at all.
Emotional lability (pseudo-bulbar effect)
What's happening? Some people with ALS have bouts of uncontrollable laughter and/or crying that are difficult to control. These reactions do not occur in all patients, and they are involuntary.
What can be done? To relieve symptoms, you can turn to drug therapy. These reactions may cause some concern for others, but if they know that these manifestations are part of the symptoms of ALS, it will be easier for them to cope with it.
Learn more about emotional lability in ALS