A stroke is a disruption in the blood supply to a certain area of the brain. The main human organ is supplied by a huge number of vessels, both small and quite large. Depending on which blood vessel was affected, a common and extensive stroke is distinguished. The first option has already been discussed on the AntiStroke website in this article. And here let's look at what a major stroke is, its types, consequences and treatment in detail.
What is a major stroke
A major stroke is an acute disruption of the blood supply to a large area of the brain. This type of stroke differs from a regular one in that a large number of parts of the brain are affected. And if the disease is not stopped in time, the cells will begin to die throughout the affected area. In most cases, a major stroke occurs as a result of damage to the branches of the carotid artery (one of the largest vessels in the human body). As a consequence of this, a large area of the brain is affected, which can lead to either death, or the person remains disabled for the rest of his life.
Features of a major stroke
- the functioning of the branches of the carotid artery is disrupted;
- Most of the brain is affected;
- in most cases, the person remains disabled or dies due to complications;
- full recovery after a major stroke occurs only in exceptional cases;
- this type of disease in most cases occurs as a secondary disease (a person already has some disease that provokes a major stroke).
What affects life expectancy after an attack?
Prognosis for the future life of patients after an attack depends on several aspects:
- Type of pathology.
- Degree of damage to brain tissue.
- Localization of affected areas.
- Age and gender.
- Duration of the immobilized state.
- Presence of concomitant pathologies.
Size of the pathological focus
The length of time a person can live depends on the extent of necrosis of brain tissue. So, if the damage was extensive, then the cells will not be able to fully recover even a year after the stroke. And since at this time the functioning of the body will be defective, the functioning of the organ systems will be disrupted more quickly, and this will create an increased risk of a new stroke, which shortens the remaining life expectancy.
Consequences of pathology
The average life expectancy of patients who develop serious pathologies such as paralysis, numbness or mental disorders after a stroke is significantly reduced due to the inability of such patients to lead full life activities. Thus, paralysis can become a predisposing factor for the formation of bedsores and blood poisoning, and mental disorders can become a predisposing factor for neurological diseases, which brings the patient’s death closer.
Age
It is much more difficult for older people and newborns to suffer a stroke. This is due to the fact that their cells do not have the ability to quickly renew themselves, and in the future they can develop:
- Inflammation of the cerebral cortex.
- Pathological lesions of the vascular bed.
- Bleeding in the brain.
- Heart attack.
In such patients, even if they survive the attack, with the slightest excitement or increase in blood pressure, a new attack starts, and they will not be able to live long.
Duration of immobility
A bedridden patient after a stroke rarely has sufficient motivation to actively participate in rehabilitation, which is especially pronounced in cases of paralysis or paresis. In this regard, he does not complete the entire course prescribed by the doctor, and his muscles continue to lose tone, the blood supply to the body deteriorates, thrombosis and necrosis develop, and blood poisoning occurs.
Because of this, inflammatory processes often develop, and the patient becomes especially sensitive to infections. As a result, a paralyzed patient lives much shorter and has a higher risk of having another stroke.
Main reasons
A major stroke does not occur out of nowhere; this disease is always provoked by some reason. Depending on this, an ischemic or hemorrhagic major stroke occurs. For example, in the first case, the cause may be a spasm of the carotid and vertebral arteries, blockage of a large vessel with a blood clot. In the case of hemorrhagic stroke, the disease can occur due to high blood pressure (blood pressure), physical or mental stress, and so on. The types of stroke will be discussed in more detail below.
0
Causes of hemorrhage
But there are several common precipitating factors that can cause both ischemic and hemorrhagic major stroke of the brain:
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- inactive lifestyle;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- high blood cholesterol levels;
- smoking, drug and alcohol use.
In most cases, the prevention of any stroke is based on compliance with the principles of a healthy lifestyle (healthy lifestyle). Therefore, if a person cares about his health, then he should lead an active lifestyle, give up bad habits, and as he gets older, see a doctor.
Its symptoms
Symptoms of hemorrhagic major stroke:
- unexpected blow to the head;
- redness of the facial skin;
- high pressure;
- rare, barely palpable pulse;
- one of the pupils is abnormally dilated;
- speech disorder;
- possible loss of consciousness;
- hoarse, less often bubbling, breathing;
- paralysis of the arm and/or leg on the opposite side from the one where the extensive stroke occurred (for example, the disease damaged the right hemisphere, which means there will be paralysis of the left arm and/or leg);
- tongue retraction;
- the person cannot swallow;
- stiffness (tension) of the neck muscles;
- leg muscle stiffness.
Symptoms of ischemic extensive cerebral stroke:
- loss of consciousness for a short period of time;
- rapid pulse, in most cases irregular;
- the patient has chills;
- low-grade fever (temperature gradually increases over time);
- pale skin all over the body.
It is immediately worth noting that when a stroke occurs, there is first an asymptomatic stage. Then the signs begin to manifest themselves, but the person either cannot talk about them or they do not believe him. And only at a critical moment do most symptoms appear, when it may already be too late. Therefore, if a person already has 2-4 signs of a major stroke, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, especially if the person is at risk.
Classification
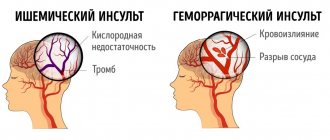
Extensive or severe stroke of the brain is of two types: ischemic and hemorrhagic. These varieties are further divided into several subspecies: in the first case there are five more, in the second case there are two more. Above, these two types have already appeared more than once in the text, so it’s time to find out what a hemorrhagic extensive stroke is and what an ischemic extensive cerebral stroke is in more detail.
Ischemic
Ischemic major stroke of the brain can be of 5 types:
- atherothrombotic – due to atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries (develops slowly);
- cardioembolic – partial or complete blockage of blood vessels in the brain (develops quickly);
- lacunar – damage to perforating arteries (develops over several hours);
- hemodynamic – a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- microocclusive – a violation of the coagulation and anticoagulation system of the human body.
In fact, ischemic stroke occurs slightly more often than hemorrhagic stroke, but the consequences of this stroke are milder. And this type of disease can be treated more easily if medical assistance is provided in a timely manner.
Mechanism of ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs due to blockage of a blood vessel in the brain. As a consequence of this, a certain area of the main organ does not receive blood with oxygen and nutrients. This means that the cells begin to “starve” and then gradually die. Most often, ischemic stroke occurs due to blockage of a vessel by an embolus or thrombus.
Hemorrhagic
There are only two types of hemorrhagic major stroke: intracerebral and subarachnoid. If in the first case a person can more or less recover and return to his usual way of life, then in the second case the disease more often ends in death. Indeed, with a subarachnoid extensive stroke, a large amount of blood enters the subarachnoid membrane, where it damages vital centers.
Mechanism of hemorrhagic stroke
If an ischemic stroke is accompanied by blockage of a vessel, then a hemorrhagic stroke occurs as a result of a rupture of a cerebral artery and the release of blood outside the vessel. Of course, the nutrition of a certain area of the main organ stops, which means that after some time necrosis will begin (if help is not provided in time). And if blood gets into the subarachnoid membrane, then minutes will count.
Possible consequences and complications
Generally speaking, a person will face a long rehabilitation period after suffering a massive cerebral stroke. If the main organ of the human body is severely damaged, the patient may fall into a coma for an indefinite amount of time. If this was avoided, then the complications and consequences of a stroke will directly depend on in which hemisphere of the brain the blood supply to the organ is disrupted.
Coma state during stroke
Extensive stroke - the consequences depend on how quickly professional medical assistance was provided. In most cases, a person falls into a coma during a hemorrhagic stroke, and the person loses consciousness almost instantly. And if the blood leaks into the brain stem, the patient will die within a few days without regaining consciousness.
With an ischemic stroke, a coma occurs abruptly. Unlike the hemorrhagic variety, in this case the loss of consciousness can be rapid or slow, depending on the speed with which the brain vessel is clogged.
With any stroke, it is important that the person regains consciousness within 1-2 days, preferably within a few hours. Otherwise, the doctor gives an unfavorable prognosis for recovery, even if the coma passes soon.
Damage to the left cerebral hemisphere
The left hemisphere of the brain is responsible for logical and analytical abilities. With a stroke of this part, paralysis of the right leg and/or arm occurs, the functioning of organs located on the right side is disrupted, problems with memory and psyche appear, the person cannot read and write, and it becomes difficult for the patient to speak clearly. Fortunately, most functions can be fully restored if you follow your doctor's recommendations.
Damage to the right cerebral hemisphere
The right hemisphere of the brain is responsible for human emotions, spatial orientation, creative activity, and so on. Therefore, with a stroke of the right half of the brain, paralysis of the left side of the body, memory loss, mild excitability or drowsiness, and possibly an unbalanced emotional state are observed, while the person is not able to “read” the emotions of other people. As is the case with damage to the left hemisphere, with proper comprehensive treatment, most functions of the right side of the brain can be restored.
Mental disorders
Develop with damage to the temporal lobe. Cognitive disorders can be:
- subjective – memory and attention deteriorate, but patients do not experience any particular discomfort;
- lungs – have little effect on quality of life after a stroke;
- moderate – the patient’s daily life becomes difficult, even performing simple tasks takes a lot of time;
- severe - the patient is completely dependent on others, dementia, hysteria, and so on may occur.
Forecast
In fact, it is impossible to give a rehabilitation prognosis without knowing the patient’s medical history and the nature of the disease. Since it depends on a huge number of factors: how long the stroke lasted, what type of disease, whether the person has chronic diseases, age, qualifications of medical personnel, availability of modern medical supplies, the patient’s desire to follow the doctor’s recommendations, how quickly first aid was provided, etc. Further.
In most cases, people after an extensive stroke remain disabled to one degree or another, since it is not always possible to completely restore lost function after extensive necrosis. However, modern treatment methods make it possible to compensate for the consequences and complications of a stroke, bringing the patient closer to his usual lifestyle. But for this it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and set yourself up for the best outcome.
Chances of surviving past 80
Unfortunately, a large number of elderly people are not able to survive a major cerebral stroke. In most cases, the body cannot cope with the shock, and the person falls into a coma from which he never recovers. Therefore, it is important, at least from the age of 40-50, to prevent stroke: follow a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, and see a doctor at least once every six months to a year.
How long do they live after severe brain damage?
It is impossible to answer the question of how long people live after a major stroke. Since a person can live either a few days after an impact or several decades. This again depends on a variety of factors, including the patient’s lifestyle and the characteristics of his body. To increase your chances of a long and good life after a stroke, you should follow a healthy lifestyle and follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Features of impact in pensioners
WHO statistics indicate that the disease affects those who have already reached 60 years of age, because at this age the risk of its development increases.
Several factors contribute to this:
- renal failure;
- rheumatism;
- high blood pressure;
- any severe viral illness;
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- risk of thrombosis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- physical inactivity.
Reference! Elderly people have some peculiarities in the course of stroke. As a rule, it is more difficult, because at this age there are other health problems.
Features of the course:
- the body suffers from “ age-related diseases ”, and therefore symptoms increase more rapidly;
- there is a high risk of death. Over time, brain tissue is damaged more rapidly. In addition, there is minimal chance of recovery from neuralgic problems. Due to age, not all patients turn to a specialized specialist on time;
- of an ischemic type of stroke is characteristic ;
- after 60 years, the cause of the disease is atherosclerotic plaques .
Important! Regardless of age, you should immediately consult a doctor if you experience certain symptoms. This greatly increases the chances of recovery.