Causes
To make a final diagnosis and begin treatment, a cerebrospinal fluid analysis and an MRI are necessary. However, this is not where diagnosis should begin, since the first step is to find out the main causes of encephalopathy inherent in a specific clinical picture. Here are some commonly diagnosed pathologies:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- trauma, brain damage;
- intrauterine infections;
- arterial hypertension;
- chronic oxygen starvation of the brain;
- impaired intracranial pressure;
- diabetes;
- pathological childbirth of pregnant women;
- cervical injuries of varying degrees during natural delivery;
- impaired blood supply;
- traumatic shock.
Diagnostics
The first step in making a diagnosis is the collection of the patient’s anamnestic data. The patient must remember all past infectious and chronic diseases, bruises (including childhood ones), since the clinical picture of brain damage does not appear immediately.
After a thorough history taking, it is necessary to conduct a general laboratory test of blood and urine (at the discretion of the attending physician). This helps to identify the hidden course of an infectious or chronic disease.
Types of additional brain examination:
- radiography;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- nuclear magnetic resonance;
- electroencephalography (EEG);
- duplex brain scan;
- Doppler ultrasound of head vessels;
- neurosonography.
Based on the results of laboratory tests, an x-ray of the main organ of the central nervous system is often prescribed. Carrying out this diagnostic method is necessary when identifying changes in hormonal levels (disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary system) and traumatic brain injuries. Using X-rays, it is possible to detect residual signs of old bruises and changes in the structure of the sella turcica.
EEG and nuclear magnetic resonance are necessary to assess the functioning of the brain as a whole, as well as to identify disturbances in the conduction of neural connections in the affected areas.
MRI and CT allow a layer-by-layer examination of the tissues of the main organ of the central nervous system, which helps determine the exact location of the damage and identify tumor processes.
Newborns and children with open fontanelles often undergo an ultrasound examination of the head - neurosonography. Using ultrasound, it is possible to establish the nature and localization of changes in the main organ of the central nervous system after birth trauma, hypoxia or asphyxia during childbirth, as well as intrauterine infection.
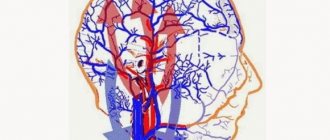
Ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels shows the anatomical features of the arterial and venous beds, their patency, places of blockage, and blood flow speed in the vessels of the main organ of the central nervous system.
To complete the picture, consultations with specialists will be required. The doctor refers children with RE to a speech therapist, child psychologist, psychotherapist, surgeon, or ophthalmologist.
Symptoms
Symptoms of residual encephalopathy in children usually appear after a significant period of time from the initial pathology. Infectious or inflammatory diseases, traumatic brain injuries or arterial hypertension can provoke their development.
Features of perinatal residual encephalopathy
Clinically, perinatal EC is manifested by a number of syndromes:
- hydrocephalic-hypertensive;
- epileptic;
- meningeal;
- convulsive;
- psychovegetative;
- focally scattered microsymptoms.
The initial signs of the disease are usually general cerebral symptoms: dizziness, nausea, vomiting and headache - first paroxysmal and then constant. The severity of hypernesia-hydrocephalic syndrome is determined by the degree of increase in intracranial pressure - from mild anxiety and reaction to bright light, to crises accompanied by vomiting without relief, lethargy and complete adynamia.
In more than half of the cases of EC in children, psychovegetative disorders are manifested, manifested by complaints of a neurasthenic nature. Children become irritable, their range of interests narrows, their mood becomes unstable, and their memory deteriorates. With post-traumatic and infectious EC, autonomic lability predominates in the clinic, and with perinatal EC, symptoms of dystrophic disorders, often accompanied by allergic pathology, dominate.
The clinical picture of focal symptoms depends on the location of the brain lesion and is manifested by hearing and vision impairment, cranial nerve paresis, and asymmetry of tendon reflexes.
The most severe consequences of perinatal EC are cerebral palsy and epilepsy.
Clinic of acquired residual encephalopathy
It is characterized by gradual development and depends on the location and severity of cerebral lesions. The most common symptoms of RE include:
- violations of operational and long-term memory;
- psycho-emotional lability, mood instability;
- decreased concentration;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- decreased mental performance;
- intense headaches that are difficult to relieve with medications;
- sleep inversion (daytime sleepiness and nighttime insomnia).
An objective examination of the neurological status of patients reveals nystagmus, the appearance of pathological reflexes, positive coordination tests (instability in the Romberg position), hyperreflexia and muscle hypertonicity. In some cases, signs of damage to the cranial nerves are recorded (hearing loss develops, visual acuity decreases, ptosis and gaze paresis are possible).
Neurological symptoms are often accompanied by autonomic disorders. The progression of RE encephalopathy leads to the development of one or more neurological deficit syndromes: parkinsonian, vestibulo-atactic, pseudobulbar, hyperkinetic.
In the later stages of RE, a decrease in intelligence and disorders in the emotional and volitional sphere are possible.
Forecast
REP neurology in the initial stages is treatable. Despite the fact that lost neurons are not restored, complex therapy makes it possible to stop the process of destruction of cerebral tissue and maintain the normal functional activity of the organ.
If the pathology is discovered in the later stages, when the changes are already irreversible, the person will have severe impairments of higher brain functions for life. Such patients are unable to care for themselves and require constant care from relatives or medical personnel.
What is residual encephalopathy
The word “residual” is translated from Latin as residual. Residual encephalopathy indicates that pathological processes in the brain remaining after treatment of other diseases have led to the development of a serious complication. In some cases, several years pass after a previous illness before a person is diagnosed with encephalopathy.
ICD-10 code
According to the international classification of diseases ICD-10, residual encephalopathy has the code G93.4. If the complication arose after a head injury, then use the coding T90.5 or T90.8. When a doctor makes a diagnosis and indicates the disease code, it is necessary to specify in parentheses the reason for the disease, the degree of brain damage and the symptoms that bother the patient.
Signs of residual encephalopathy appear slightly at the initial stage. The nature of the violations can be varied. With encephalopathy, the nervous and cardiovascular systems suffer, weakening of memory, attention, and coordination disorders occur. A person should see a doctor if the following symptoms are present:
- insomnia;
- frequent headache;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- increased excitability;
- constant fatigue;
- anxiety.
With complications, the patient quickly gets tired, convulsions, partial or complete paralysis occur. There are often cases when, with residual encephalopathy, the victim falls into a coma. A decrease in mental abilities is directly related to impaired blood circulation in the brain. If residual phenomena are left unattended, the process may become irreversible.
It is customary to divide the reasons that caused the residual nature of changes in the brain into acquired and congenital. This is due to the fact that the factors and characteristics of brain damage received in childhood or in adulthood are different. Among the reasons that can lead to residual encephalopathy, doctors name:
- injury leading to concussion and death of brain cells;
- undergone surgery to remove a malignant brain tumor;
- meningitis;
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- stroke;
- bad habits – consumption of alcohol, psychotropic substances, narcotic substances;
- exposure to ionizing radiation;
- diabetes;
- difficult pregnancy and childbirth.
The occurrence of residual encephalopathy can be influenced by disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and liver, which contribute to an increase in the level of urea in the blood. The substance has a destructive effect on brain cells. Another common cause of the development of residual encephalopathy is vascular atherosclerosis, leading to a cessation of oxygen supply.
Residual encephalopathy in children
Signs of perinatal encephalopathy in children are caused by the consequences of intrauterine disorders that are congenital in nature. The reason may be:
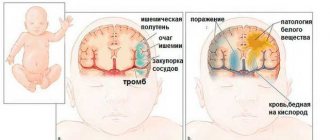
- fetal hypoxia;
- intrauterine infection;
- negative heredity;
- birth injuries;
- the lifestyle that the mother led when she was pregnant.
With timely diagnosis of encephalopathy, it is possible to cure the child without consequences. The acquired form in children can cause:
- head injury;
- viral infection;
- exposure to radiation.
A child, unlike an adult, cannot talk about his problems, so you need to carefully monitor his behavior in order to prevent the consequences of perinatal encephalopathy before they become irreversible. If this is not done on time, the disease threatens to develop into hydrocephalus, mental retardation or cerebral palsy. Frequent, causeless crying, irritability, and lack of normal sleep in the child may be a cause for concern for parents.
Complications and consequences
residual encephalopathy in a child
Complications and consequences associated with residual encephalopathy are severe and frequent. Their occurrence directly depends on the qualifications of the doctor and on how quickly the patient sought help.
develop as consequences
- hydrocephalic syndrome (when the fluid that forms under the cerebral cortex becomes too much, and the brain simply cannot remove it normally);
- vegetative-vascular dystonia (disorders affecting blood vessels);
- residual brain dysfunction (the disease is associated primarily with mental disorders in its cortex);
- cerebral palsy (a complex of chronic diseases associated with abnormalities in the brain);
- epilepsy (convulsive seizures, which are accompanied by a faint state of the patient).
Complications, prevention
Complications of residual encephalopathy are dangerous not only because of the deterioration in the patient’s quality of life. They can lead a person to incapacity and disability. With severe damage to the central nervous system, cerebral edema, spasm of the respiratory muscles, and dysfunction of the cardiovascular center may develop. The patient should be under constant medical supervision to prevent complications.
Residual encephalopathy occurs as a residual phenomenon not only of other diseases, but of traumatic brain injuries, concussions, etc. Of course, it is impossible to say that every person is guaranteed to be insured against TBI. In this sense, one of the preventive measures can be called the desire to minimize dangerous situations, take care of one’s own and others’ safety at home, at work, in transport, etc.
On the other hand, the prevention of diseases that may eventually become causes of REC plays an important role. Patients with such diseases are at risk. This must be understood in order to take measures to treat these diseases - potential “harbingers”.
There is also a connection between encephalopathy and poisons, radiation, and drugs, which have a catastrophically destructive effect on brain cells. All these unfavorable factors need to be excluded from their lives by everyone who wants to be healthy.
A person’s lifestyle affects the state of his brain not only spiritually, but also in a direct physical sense. It is no coincidence that observations show that long-term smokers have worse memory. And what effect alcohol and drugs have on intelligence and behavior can be judged by anyone who has at least once observed such a person taking poison. And the picture is completely different if a person manages to give up any bad habit. This suggests that the best prevention of encephalopathy of any kind is a healthy lifestyle.
Classification of encephalopathies
The disease often manifests itself in adulthood and is a consequence of insufficient oxygen supply to the meninges. The main types of encephalopathy are:
- Congenital disease. The pathological process begins its gradual development from the 28th obstetric week, persists throughout the entire period of pregnancy, and is diagnosed in a newborn patient. It takes on new forms and becomes a difficult to treat disease in pediatric neurology.
- Acquired encephalopathy. This is a complication of the underlying disease, which is often characterized by an infectious, inflammatory nature. In addition, this may be a consequence of organic damage to the cerebral cortex or trauma. Dystrophic changes in tissue in this case have several varieties, depending on the predominant pathogenic factor. The doctor studies the symptoms, conducts a comprehensive examination, and then names the features of brain damage.
Perinatal
The disease develops in newborns and requires immediate medical attention. Congenital encephalopathy also has several varieties according to the etiology of the pathological process. More often this is perinatal encephalopathy in children, which is also called hypoxic or ischemic. The disease begins in the prenatal period, and is diagnosed in newborns. Perinatal encephalopathy is congenital, while periventricular encephalopathy occurs after birth due to oxygen deprivation.
Acquired
The disease can develop in newborns, but is more often found in adults. Acquired encephalopathy is treatable, but the patient remains forever at risk and must comply with mandatory preventive measures. Since the nerve endings of the brain are already affected, the prognosis of specialists can be very unpredictable and not always favorable. Depending on the nature of the provoking factor, doctors identify a number of body disorders. This:
Post-traumatic encephalopathy is a consequence of severe skull injuries, develops over an impressive time interval, changes the consciousness, habits and behavior of the clinical patient. Discirculatory encephalopathy is the result of a violation of blood flow through the vessels. There are venous, atherosclerotic and hypertensive forms of the characteristic disease. In addition, angioencephalopathy and microangioencephalopathy may develop. The diagnosis is made using techniques such as REG, EEG, Echo-EG. In addition, for encephalopathy, an X-ray with functional tests of the cervical spine and more is required. Toxic encephalopathy is a consequence of severe intoxication of the body with toxic substances, alcoholic beverages, harmful chemicals, medications and narcotic drugs. It can be successfully treated with conservative methods, but the process of regeneration of foci of brain necrosis is very long. The radiation form of this disease becomes a complication of ionizing radiation, an increased dose of radiation to the body. More often this is a consequence of the specifics of professional activity, the harmful influence of environmental factors on the body. The diabetic variety of the characteristic disease rapidly progresses, as one of the unpleasant consequences of the development of diabetes mellitus in the body, and is prone to frequent relapses. Correction of blood sugar using medications or more radical methods is indicated. Leukoencephalopathy is provoked by a disturbed chemical composition of the blood, while hepatoencephalopathy is based on chronic renal failure. Both forms affect the brain and cause mental disorders with systematic relapses. Hashimoto's encephalopathy is an extremely rare pathology with a disorder of neuroendocrine metabolism in the brain. In modern medical practice, this is a little-studied disease that is difficult to treat. The spongiform form of the disease is an abnormal degeneration of certain parts of the brain
Characteristic mutations are visualized during mandatory MRI for diagnostic purposes. The mitochondrial form of the disease is accompanied by a disturbance in neuropsychic development, and the pathology is preceded by serious mitochondrial dysfunction. If you are interested in residual encephalopathy - what it is, it is important to clarify that this is a massive death of cells in the central nervous system. Necrotizing encephalomyelopathy is caused by impaired metabolism and provokes the death of neurons.
What is REP?
20.04.2019
The abbreviation REP stands for residual encephalopathy. The disease develops secondarily, after injuries or other pathologies of the central nervous system.
The disease is characterized by active death of cerebral neurons, which are not subsequently restored.
There are congenital and acquired forms. Congenital develops under the influence of various negative factors on the fetus during intrauterine development, and acquired - due to damage to brain tissue after birth.
The congenital form, in turn, is divided into types:
- anoxic;
- bilirubin;
- diabetic;
- metabolic;
- ray.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, mild, moderate and severe forms are distinguished. In addition, the disease can be latent for a long time, and the manifestation of the first signs occurs several years after exposure to damaging factors. In children, REP often develops as a consequence of poor-quality treatment of perinatal encephalopathy.
In addition to disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, residual encephalopathy often provokes severe pathologies of other organs and systems, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of life and disability of a person.
Rap neurology: what is it, causes of the disease
A neurologist diagnoses REP in cases of disorders of brain function that occur after diseases that provoke damage to nerve cells. The most common causes of REP are:
- mechanical damage to cerebral tissue due to bruises, concussions, bone fractures, intracranial hemorrhages, etc.;
- perinatal encephalopathies resulting from pathologies of intrauterine development or damage to the central nervous system in the first days of life;
- encephalitis of infectious nature;
- autoimmune processes in the central nervous system;
- increased urea content in the blood due to kidney or liver diseases;
- disturbance of cerebral hemodynamics as a result of atherosclerosis, ischemic stroke, embolism, etc.;
- neuronal damage due to diabetes mellitus;
- intoxication, especially in case of poisoning with neurotoxins, salts of heavy metals, ethyl alcohol, psychotropic drugs;
- systematic use of drugs.
Considering that residual encephalopathy can be provoked by several factors at once, when making a diagnosis, the doctor must carefully study the patient’s anamnestic data.
Other therapies
Treatment with pharmaceuticals should be supplemented with physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage. To stimulate blood circulation, patients with residual encephalopathy are prescribed contrast showers and baths with essential oils, reflexology, and magnetic therapy.
It is advisable to use electrophoresis (with drugs that improve microcirculation), local darsonvalization, and electrical stimulation. In parallel with physiotherapy, massage procedures are carried out. Exercises for physical therapy are selected by the doctor together with the patient, taking into account his age, condition and other individual characteristics.
Developmental activities, art therapy, and hippotherapy provide good results in the treatment of children with REP. Such treatment methods normalize brain function, improve mood, and promote social adaptation.
Symptoms of the condition in children
Residual encephalopathy in children has many manifestations. The most common of them are:
- violations of the intellectual-mnestic sphere, expressed in mental retardation, poor performance at school;
- hydrocephalus external or internal;
- motor disorders in the form of paresis and paralysis;
- convulsive syndrome.
The presence of certain signs depends on the degree of damage to the brain substance and the location of the main foci of ischemia in it. At the initial visit to the doctor, only one of the syndromes may be observed, but in the absence of adequate therapy, residual encephalopathy tends to progress and over time, existing symptoms will worsen and new ones will appear.
How not to miss alarming symptoms?
The first “bells” of the disease in infants are extremely difficult to identify; a weak or delayed cry after birth, suppression of the sucking and grasping reflexes, and hemodynamic disturbances: heart rate and blood pressure should be alarming. Later the following symptoms are observed:
- irritability, tearfulness;
- sleep disorders - the child either sleeps around the clock or wakes up every half hour;
- hypertrophied reaction to a sharp sound, turning on the light;
- periodic shaking of the whole body;
- frequent persistent regurgitation or hiccups after feeding;
- throwing the head back;
- eye rolling;
- convulsions;
- increased or decreased muscle tone in the limbs.
If the pathology was not assessed in time, then encephalopathy can be suspected in older children:
- delayed psychomotor development;
- appetite disorders;
- dyssomnia (sleep disorders);
- frequent headaches and dizziness;
- mental disorders (apathy, tendency to depression, aggressiveness, decreased criticism);
- an increase in the size of the skull due to hydrocephalus.
Tips for parents
The only thing that can be advised to parents in view of such a disease as residual encephalopathy is to be more attentive to their children. When the first signs of pathology appear, you must immediately contact a specialist, since the sooner therapy is started, the greater the chance of reducing the effect of hypoxia on neurons.
Also, falls of children and infections cannot be ignored - they can cause the death of brain cells, and therefore require timely diagnosis and adequate treatment. The health of children is priceless; it is better to contact the pediatrician once again with a question of interest than to later try to cope with a neglected process.
Complications
What complications occur in children with REP? A neurological diagnosis means that the pathology cannot be ignored, since without appropriate treatment, patients develop:
- severe mental disorders;
- hydrocephalus;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- paralysis of individual muscle groups or limbs;
- parkinsonisms;
- epileptic seizures.
Considering that dead nerve tissue does not have the ability to regenerate, visiting a doctor late increases the risk of complications.
In early childhood, minimal signs of brain dysfunction may be observed, which are manifested by hyperactivity, inability to engage in certain activities for a long time, and increased excitability. If the condition is not corrected in time, problems with the behavior and emotional state of the teenager will arise during puberty.
Treatment approaches
Treatment of residual encephalopathy is always comprehensive and is aimed not only at correcting existing symptoms, but also at restoring damaged nerve tissue, protecting functioning neurons from hypoxia and other adverse factors. Treatment methods are always selected individually, taking into account the reasons that caused diffuse brain pathology, the age of the child and the observed clinical picture.
Most often, all manipulations can be performed on an outpatient basis with periodic visits to the doctor. In severe cases of the disease or its steady progression, a hospital stay may be necessary.
Basic treatment methods
The following methods are used in the treatment of residual phenomena of encephalopathy:
- physical therapy;
- physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, DDT, paraffin therapy, mud therapy);
- reflexology (acupuncture);
- manual therapy and massages;
- diets with limited salt intake;
- occupational therapy and speech therapy for older children;
- exposure to medications;
- neurosurgical interventions (for example, shunting for hydrocephalus).
The positive effect of the carried out set of measures can be noticeable only after several courses of treatment. In some cases, the child has to resort to the help of specialists for many years. After recovery or when the progression of the pathology stops, children are registered at a dispensary.
Medications
Drug therapy prescribed for residual encephalopathy is designed to improve cell nutrition, facilitate oxygen access and restore the affected areas of the brain. For this use:
- vascular drugs (Cytoflavin, Trental, Nicotinic acid) - normalize microcirculation;
- neurometabolites (Cerebrolysin, Cerebrolysate, Cortexin) – contain a complex of amino acids necessary for neurons;
- neuroprotectors (Cerakson, Pantogam, Gliatilin) – protect against hypoxia, restore cell membranes, improve impulse transmission;
- antioxidants (Mexiprim, Mexipridol, Mexicor) – suppress lipid peroxidation and the action of free radicals;
- B vitamins (Milgamma, Neurovitan) – are the “building blocks” of the nervous system;
- anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Topiromat, Valprocom) – necessary for the development of symptomatic epilepsy;
- diuretics (Diacarb, Veroshpiron) - reduce increased intracranial pressure against the background of hydrocephalus.
The use of nootropics (Piracetam, Lucetam, Picamilon, Nootropil) is possible only in the absence of convulsive syndrome.
Drug treatment
The approach to the treatment of encephalopathy must be comprehensive. Therapeutic measures are aimed at restoring brain trophism and its functional activity. To improve microcirculation and normalize metabolic processes, nootropics (Cinnarizine, Piracetam, Cavinton) are used. Additionally, B vitamins (thiamine, folic, nicotinic acid) are prescribed, which activate metabolism in the central nervous system and help strengthen nerve connections.
Eliminate headaches with the help of analgesics (Analgin, Ibuprofen), but if they are not effective, take drugs with a stronger effect (Ketanov, Pentalgin). For inflammatory processes accompanied by severe pain, corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) are prescribed.
REP in neurology is accompanied by epileptic paroxysms. Epilepsy attacks are treated with anticonvulsants (Valproic acid, Phenobarbital, Klonopin).
If the patient suffers from increased anxiety, irritability and other signs of emotional instability, medications with a mild sedative effect are prescribed (Glycine, Novo-passit, Pantogam, peony tincture). For severe psycho-emotional disorders, tranquilizers and antidepressants (Azafen, Phenibut, Gidazepam) are used.
Therapeutic measures
The pediatrician selects therapy individually in each individual case, depending on the severity of the disease, the traumatic factor, the age of the child and other characteristics. In particularly severe cases, the child is sent to a hospital.
Most often, treatment consists of massage and exercise therapy, infusion therapy (use of calcium, magnesium, ascorbic acid, glucose solution) and some other medications if necessary. So Phenoarbital and Diazepam will help avoid seizures. Baclofen is prescribed to relieve muscle hypertonicity. Taking B vitamins will help improve metabolism in brain cells.
Additionally, herbal medicine can be used - the child is prescribed herbal infusions of lemon balm, plantain, dandelion, mint and other medicinal plants. We should also not forget about walks in the fresh air and a nutritious, balanced diet.
Many experts claim that acupuncture and manual therapy are also highly effective methods for this pathology.
In addition, children with a similar diagnosis are necessarily prescribed a diet that involves minimal consumption of salt, foods high in cholesterol, and exclusion of chocolate from the diet. It is recommended to enrich the child’s diet with ascorbic acid, vitamins, and foods high in iodine.
Most often, after completing a timely course of treatment, children experience a complete recovery. But it is not always possible to do without consequences - the greater the number of damaged cells, the higher the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome.
Even after treatment has already been completed, the child needs rehabilitation. Children who have had encephalopathy are advised to:
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- swimming lessons;
- phytotherapy;
- periodic courses of nootropic drugs;
- doctor's supervision;
- periodic rest in specialized sanatoriums.
When a diagnosis of encephalopathy is made, parents should prepare themselves for a fairly long-term treatment. Depending on the degree of development of the disease, therapy can take from two to three years.
Treatment methods and drugs
Treatment methods for each child are selected individually. It all depends on the causes, location of lesions in the brain, severity of conditions and clinical manifestations of the disease. However, the most commonly used drugs are:
- improves blood circulation in the brain (stugeron, vinpocetine);
- anticonvulsant (antiepileptic) drugs (carbamazepine, depakine);
- non-steroidal (non-hormonal) anti-inflammatory drugs (metamizole, ibuprofen);
- steroid (hormone) anti-inflammatory (dexamethasone, prednisone);
- multivitamin complexes (vitrum);
- sedative (negrustin, glycine);
- nootropics (Cortexin for children).
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods are of great importance. Massage and physical therapy help improve muscle tone and blood flow. Physical therapy helps eliminate skeletal muscle movement disorders. Group and individual lessons organize children and correct their behavior in a favorable way.
Residual encephalopathy is a very serious pathology in children. However, its timely detection helps to restore lost functions and fully restore the child’s nervous system. It is necessary to prevent perinatal damage to the fetus and closely monitor the condition of the child after birth if there is a risk of developing EC.
Symptoms of the disease
The severity of the symptoms of this pathology and their combination depend on:
- on the age of the child and the degree of maturation of the nervous system;
- on the location and extent of damage to brain tissue and its glial structures;
- on the causative factor and the duration of its effect on brain cells;
- from the presence of concomitant diseases that can aggravate the pathological effect of the main etiological factors (intoxication, metabolic or vascular disorders).
Common signs and symptoms of encephalopathy in children are:
- frequent headaches, anxiety, moodiness, constant screaming (in young children);
- hyperactivity, uncontrollability, disinhibition, obsessive states;
- sleep disorders, which are manifested by drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night;
- neuroses in the form of behavioral disorders or phobias in the form of panic fear of any objects, obvious or imagined, as well as environmental phenomena;
- decreased memory (usually impaired short-term memory for remembering words, numbers or names of objects), cognitive activity and intelligence of the child;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- development of hydrocephalic syndrome (in children of the first year of life).
In this case, the symptoms become permanent with worsening signs of encephalopathy in children, the following are noted:
- frequent fainting;
- dizziness;
- asthenia;
- deterioration of attention and memory;
- changes in motor coordination;
- movement disorders (flaccid paralysis, paresis);
- mental and vegetative disorders;
- significant decrease in intelligence;
- behavioral disorders;
- developmental delay.
Discirculatory or toxic
In this form of the disease, organic changes in neurons develop due to the development and progression of vascular diseases, congenital anomalies of cerebral vessels, or toxic effects on neurons of poisons, microbial toxins, drugs or chemicals.
This pathology can be triggered by the influence of the following factors on the child’s brain:
- systemic or infectious vasculitis, embolism, hereditary angiopathy, persistent hypotension, arrhythmias;
- congenital anomalies of cerebral vessels (aneurysms, atriovenous malformations, congenital stenoses);
- blood diseases (leukemia, thrombocytopenic purpura, coagulation disorders);
- viral and infectious diseases with persistent and long-term neurotoxicosis, complicated by septic processes;
- progressive somatic and endocrine pathologies that cause persistent changes in blood vessels, microangiopathy (diabetes mellitus, pathology of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland);
- abuse of alcohol, nicotine, narcotic and toxic drugs (by the mother during pregnancy or adolescence).
Epileptic
Epileptic encephalopathy develops against the background of an increase in convulsive or non-convulsive seizures, leading to the progressive death of nerve cells in the lesion, the formation of new foci of epileptiform activity and disruption of connections between neurons.
Impaired brain function manifests itself in progressive cognitive disorders, decreased memory and intelligence, behavioral disorders, severe asthenia, and sleep disorders.
There are two forms of epileptic encephalopathy:
- epileptic encephalopathy I or destructive epileptic encephalopathy – develops against the background of progressive established epilepsy in a child with frequent, prolonged seizures, recurring status epilepticus;
- Epileptic encephalopathy II is manifested by typical mental disorders, behavioral changes, social maladaptation and cognitive disorders characteristic of destructive epileptic encephalopathy in the complete absence of characteristic epileptic seizures.
Perinatal or residual encephalopathy perinatally caused
This form of the disease comes from the Latin residual, meaning “residual.”
Thus, this type of encephalopathy may be a residual phenomenon of previously suffered pathological processes in the brain.
Quite often this disease is observed after perinatal encephalopathy.
You can read more about this pathology in this article:
Residual encephalopathy may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, most often up to 3-5 years, and only after this period symptoms begin to appear. The effectiveness of treatment of childhood encephalopathy with early diagnosis, complete and comprehensive treatment, and compliance with all recommendations of specialists in most cases is completely cured within a year and has virtually no consequences in adult life.
Diagnosis of REP: interpretation and treatment
The diagnosis of REP is quite rare. Most often, this pathology is detected in childhood. The disease is one of the types of encephalopathies. It is accompanied by the gradual death of cells of the central nervous system. How dangerous is this pathology? And is it curable? We will consider these questions in the article.
What it is
What does a diagnosis of REP mean? The meaning of this abbreviation is residual encephalopathy. The disease is characterized by the death of neurons and impaired brain function. The word “residual” means “residual.”
This pathology is always secondary. It occurs as a residual phenomenon after suffering diseases of the central nervous system. This complication occurs when brain diseases are insufficiently or incorrectly treated.
Parents of children are often interested in what a diagnosis of REP in a child means. The decoding of this medical abbreviation is similar, it is residual encephalopathy. With adverse effects on the embryo or birth injuries, perinatal encephalopathy occurs.
This disease is diagnosed in children in the first weeks and months of life. If the treatment of such a pathology was carried out poorly, then REP may develop in the future as a residual phenomenon.
Often this complication does not appear immediately, but after several months or even years, and it can be difficult to diagnose.
Causes
The diagnosis of REP is usually made to patients if they show signs of brain disorders after suffering pathologies of the central nervous system and other diseases that adversely affect the state of neurons. Residual encephalopathy most often occurs due to the following diseases and conditions:
- Severe head injuries accompanied by concussion or skull fractures.
- Congenital perinatal encephalopathy. This condition develops after birth injuries and a pathological course of pregnancy in the mother of the child.
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain.
- Excess urea in the body. This deviation is often observed in diseases of the liver and kidneys.
- Stroke and other cerebrovascular accidents. The cause of the pathology can also be vascular atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes mellitus. Endocrine disorders and excess glucose in the body adversely affect the condition of the nervous tissue.
- Toxin poisoning. Heavy metal compounds, certain medications, and alcohol have an adverse effect on the brain.
- Use of narcotic and psychotropic drugs. Even with timely detoxification, patients often retain signs of brain pathology.
Often the causes of this type of encephalopathy are several unfavorable factors. The physician must take a thorough history of the patient before diagnosing REP. This disease can develop after a fairly long period of time after suffering pathologies.
Symptoms
Residual encephalopathy in an adult patient is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Sudden memory loss. The patient becomes forgetful. He may have difficulty remembering even recent events.
- Decrease in intelligence. The patient's thinking process is disrupted due to the death of neurons and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Emotional lability. The patient's mood often changes, and there is increased irritability and tearfulness.
- Sleep disorders. Patients suffer from insomnia at night, and during the day they feel drowsiness and lethargy.
- Convulsive seizures. Seizures become more frequent as the disease progresses.
- Speech, vision and hearing disorders. The patient slurs his words. Vision and hearing deteriorate due to the death of nerve cells.
- Impaired coordination of movements. The patient's gait becomes unsteady, and he often loses his balance.
- Asthenia. The patient complains of constant fatigue and high fatigue.
- Headache. Migraine-like attacks occur. In this case, the pain syndrome is not relieved by analgesics.
These manifestations of pathology increase as the disease progresses. The more neurons die, the more severe the impairment of brain function.
What signs indicate a diagnosis of REP in a child? This disease can sometimes be difficult to identify in young children. After all, the baby cannot complain about feeling unwell. Parents should be alert to the following manifestations:
- tearfulness;
- increased reaction to external stimuli;
- frequent nausea and vomiting;
- weak sucking reflex;
- increased muscle tension;
- arrhythmia;
- exophthalmos (bulging eyes).
In older children, the disease is accompanied by the same symptoms as in adults. Residual encephalopathy has an extremely negative effect on the child’s intelligence. Children lag behind in mental and physical development, experience difficulties in assimilation and memorization of information, and it becomes difficult for them to study. Often, sick children experience sudden fainting.
Complications
How dangerous is a neurologist's diagnosis of REP? Without treatment, this type of encephalopathy can lead to the development of the following complications:
- severe dementia in adult patients;
- mental retardation in children;
- dropsy of the brain;
- neurocirculatory dystonia;
- paralysis;
- Parkinson's disease;
- epilepsy.
The likelihood of complications increases if the patient seeks help too late, when a significant number of nerve cells have died.
Pediatric neurologists often talk about minimal brain dysfunction when diagnosing REP. What does this mean? This complication is expressed in mental disorders in young patients. The child becomes restless, hyperactive, excitable, and often makes erratic movements. These manifestations intensify during puberty against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
Diagnostics
Before diagnosing REP, the doctor questions the patient and examines his medical record. It is necessary to identify all neurological pathologies that the patient suffered in the past. Additional research methods are also prescribed:
- electroencephalogram;
- MRI and CT of the brain;
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels.
Drug treatment
Treatment of this type of encephalopathy should be comprehensive. To restore normal brain function, patients are prescribed nootropic drugs:
- “Cinnarizine”;
- “Piracetam”;
- "Cavinton";
- “Noopept”;
- “Pantogam”
- "Phenibut";
- "Phenotropil".
These medications improve cerebral circulation and metabolism. It is useful to take them together with B vitamins. This will help restore normal functioning of the central nervous system.
For severe headaches, analgesics usually do not help. Therefore, patients are prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- “Ketanov”;
- “Nise”;
- “Ibuprofen.”
For severe pain, treatment with corticosteroids: Prednisolone or Dexamethasone is recommended.
If the patient experiences frequent epileptic seizures, it is recommended to take anticonvulsants: Finlepsin or drugs based on valproic acid.
For increased irritability and mood swings, doctors prescribe mild sedatives: Afobazol, Glycine, Persen. These medications will help reduce emotional instability. In severe cases, antidepressants and tranquilizers are indicated.
Drug treatment is supplemented with therapeutic massage sessions. This helps stimulate cerebral circulation. Therapeutic gymnastics is also useful. When performing exercises, you need to pay special attention to the collar area. Active neck movements help improve brain nutrition.
A child suffering from residual encephalopathy needs developmental activities. When correcting mental disorders, it is very important to train memory and attention. In cases of severe developmental delay, home schooling is indicated for school-age children.
Forecast
If the diagnosis of REP was made in a timely manner and the patient completed the full course of therapy, then the disease can be cured. Lost neurons can no longer be restored. But if the process of brain cell death has just begun, then therapy will help maintain the normal function of the central nervous system. Therefore, treatment is effective only at the initial stage of the pathology.
In advanced cases, it is no longer possible to restore lost brain functions. Even after treatment, the patient retains signs of memory impairment, thinking disorders and emotional lability. In children, this can lead to severe mental impairment.
Prevention
How to prevent the occurrence of residual encephalopathy? Prevention of this dangerous disease consists of observing the following measures:
- Injuries and pathologies of the central nervous system must be carefully treated.
- During pregnancy, women need to be under regular supervision by an obstetrician-gynecologist. It is also necessary to avoid any adverse effects on the embryo.
- We must try to prevent traumatic brain injuries in children.
- It is necessary to protect yourself from poisoning with toxic substances, and also stop drinking alcohol.
- Patients who have suffered pathologies of the central nervous system need to be regularly monitored by a neurologist and undergo all necessary examinations.
These recommendations will help avoid the occurrence of residual encephalopathy. It is important to remember that this disease is much easier to prevent than to cure.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/406627/diagnoz-rep-rasshifrovka-i-lechenie
Symptoms of encephalopathy
Recognizing the onset of encephalopathy is problematic. After all, the condition that precedes its development can be characterized by symptoms that are common to humans and are temporary in nature, such as headache, dizziness, and tinnitus. At first, this may be mistakenly associated with changes in weather, excessive physical or mental stress, or severe stress. But if you do not pay attention to them, you can allow the disease to progress, since even such symptoms can indicate a deterioration in cerebral circulation.
By nature, the symptoms of encephalopathy are very diverse. But its most common signs, with the exception of the above three, are:
- general weakness;
- increased fatigue;
- tearfulness;
- lack of initiative;
- sudden mood changes;
- depression;
- hot temper;
- clouding of consciousness, memory destruction;
- deterioration of vision and hearing functions;
- poor sleep;
- obsessive desire to die.
Encephalopathy of the brain
When visiting a doctor, such patients often have difficulty pronouncing some words, their speech is verbose, their range of interests is narrowed, and there is a desire to sleep during the daytime. These are the common and most common symptoms of encephalopathy. You should also know that each type of disease has its own set of symptoms.
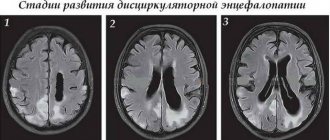
Thus, the development of discirculatory encephalopathy is characterized by 3 stages, characterized by a certain set of signs:
- compensated stage. Here, the appearance of general symptoms is observed, such as dizziness, memory loss, and headaches.
- subcompensated stage. Symptoms are more pronounced and clear:
- constant headache;
- incessant ringing in the ears;
- worsening sleep;
- tearfulness;
- state of depression;
- lethargy;
decompensated stage. The main symptoms of this stage are life-threatening morphological changes in brain tissue.
Progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy can lead to the development of dementia. Symptoms of this encephalopathy:
- headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- memory impairment;
- dizziness;
- the appearance of phobias;
- psychopathy;
- the occurrence of hallucinations;
- asthenia.
Consequences of alcoholism
Toxic and, above all, alcoholic encephalopathy is dangerous due to the destructive effects of toxic substances on the vessels of the human brain, manifested by the following symptoms:
- long-term, acute psychoneurological personality disorder;
- an increase in the volume of the ventricles of the brain;
- congestion of the meninges with blood;
- cerebral edema.
Post-traumatic encephalopathy is dangerous due to the latent course of symptoms that appear long after the injury:
- behavioral disorders;
- impaired thinking;
- absent-mindedness;
- memory loss.
It should be noted that the severity of these symptoms will be stronger, the more severe and dangerous the injury. Radiation encephalopathy is characterized by 2 types of disorders: asthenic and psychological. Symptoms that characterize progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy:
- violation of higher brain functions;
- a disorder of consciousness that can lead to dementia;
- epileptic seizures and ataxia are rare.
This leukoencephalopathy is the most “aggressive” of a large number of encephalopathies, its prognosis is disappointing - death.
Symptoms of metabolic encephalopathy:
- confusion;
- absent-mindedness;
- drowsiness;
- lethargy;
- speech disorder;
- the occurrence of hallucinations;
- disturbance of worldview;
- coma - as the disease progresses.
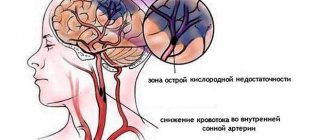
Causes of residual encephalopathy
A number of painful conditions can influence the development of the disease:
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI);
- inflammatory processes in the brain;
- infectious diseases;
- stroke;
- hypertension, especially in combination with vascular atherosclerosis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia with vegetative crises;
- kidney diseases;
- liver diseases;
- systematic intoxication with alcohol and other harmful substances (drugs, poisons, potent drugs in excessive doses); Drug addicts and chronic alcoholics are especially susceptible.
In children, REP can be congenital and occur for an additional number of reasons.
Most often these are complications during pregnancy that affect the development of the child. Perinatal pathologies are different, as are the factors that cause them. This is an unfavorable environment, ionizing radiation affecting the pregnant woman and the fetus, the use of alcohol, drugs, and medications harmful to the pregnant woman by future parents. Toxicoses of pregnancy, especially late gestosis, can negatively affect the development of the fetus. Danger awaits the unborn child if a woman has suffered an infectious or inflammatory disease during the formation of nervous tissue in the embryo. Any disturbances in the blood supply to the fetus that cause oxygen starvation of brain cells can lead to the development of pathologies in the future. Similar consequences cannot be excluded in the case of iron deficiency anemia and complicated childbirth.
There may also be a genetic predisposition to brain disorders. It happens in cases where the child’s parents suffer from epilepsy, schizophrenia, a tendency to neurosis, and other psycho-emotional pathologies. The child of such parents is at risk. The most poorly studied factor is chromosomal abnormalities, incorrect DNA structure, which can cause not only encephalopathy, but also Down's disease and other congenital pathologies.
Causes
The reasons for the development of this condition can be varied:
- burdened hereditary history or closely related relationships;
- congenital and acquired developmental anomalies;
- genetic diseases;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- skull fractures, concussions and contusions;
- inflammatory diseases of the brain and its membranes (meningitis, encephalitis, arachnoiditis);
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- complicated course of pregnancy and childbirth (hypoxia, prematurity, intrauterine infection, amniotic fluid embolism);
- jaundice of newborns;
- acute and transient cerebrovascular accidents;
- significant increase in intracranial pressure;
- the effects of radiation, toxic substances (including alcohol, drugs, psychotropic drugs) on the body of the child and mother during pregnancy and childbirth.
Prevention
To avoid the development of EC in childhood, parents are advised to plan the birth of their baby in advance. Before pregnancy, it is necessary to be examined for the presence of infectious diseases, cure all chronic ailments, and also undergo a course of compensation for folic acid deficiency, which has a positive effect on brain formation in the early stages of fetal development.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother should give up smoking, as well as the use of drugs and alcohol. During a flu epidemic, a woman should avoid contact with patients (a similar virus can infect the blood vessels of the placenta, causing rapid aging or oxygen starvation of the fetus). Gynecologists advise young mothers to attend courses in order to behave correctly during childbirth. This significantly reduces the likelihood of hypoxia and birth trauma in the child.
To prevent the occurrence of an acquired type of disease, patients must visit a therapist annually, pass a general laboratory minimum, get rid of acute and chronic diseases on time and completely, and not self-medicate.