Causes
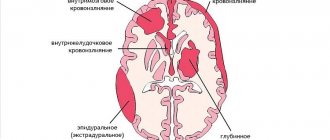
Deterioration of the blood supply to neurons occurs due to vascular dysfunction. In certain areas of the brain there is a lack of oxygen and useful components. Initially, groups of cells die, then individual fragments of the brain. Initially, the work of the damaged areas is performed by neighboring zones, but without treatment this relationship is lost.
The causes of the disorder are determined by its form:
- Harmful protein compounds accumulate on the walls of veins and arteries, and the lumen becomes smaller. Hyposkia appears and the brain works worse. The disease occurs as a result of problems with nutrition, the level of cholesterol in the blood increases.
- Venous appears as a result of compression of the vessels through which blood leaves the head. Due to toxic poisoning of brain tissue, inflammation begins. The likelihood of this form occurring in patients increases if there are changes in blood pressure.
- The hypertensive form is characterized by an acute course with an increase in blood pressure. The risk group includes patients with glomerulonephritis, kidney problems, and Cushing's disorder.
Encephalopathy of the 2nd degree can develop with the help of VSD, tobacco and alcohol abuse, problems with blood composition, toxin poisoning and osteochondrosis. DEP belongs to a separate category. Often atherosclerotic and hypertensive forms occur simultaneously.
This type of disease develops more rapidly in older people.
Degrees of post-traumatic encephalopathy
According to the severity of this pathology in clinical neurology, three degrees are distinguished.
- 1st degree of post-traumatic encephalopathy - there are morphological changes in the brain that are detected only during instrumental examination. Clinical symptoms are minimal.
- 2nd degree – changes in the morphology of brain tissue, neurological symptoms are weak and variable in nature.
- The 3rd degree of post-traumatic encephalopathy is characterized by pronounced neurological clinical manifestations - dementia, problems in self-care, coordination problems and mental changes.
Stages of the disease
Stages of dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
- Organic transformations of the nervous system are mild, but symptoms are already arising. Signs of disorders are sometimes confused with the clinical picture of several lesions of the central nervous system. Often these are fatigue, deterioration of concentration and memory, tinnitus, migraines, sleep problems, nervousness, and apathy.
- A progressive disease has more pronounced symptoms. The deterioration of the nervous system is obvious. The patient manages to take care of himself without assistance. Doctors often try to distinguish between the first and second degrees. The disorder is diagnosed if symptoms persist for 6 months.
- Time for irreversible serious transformations. It is difficult for the patient to take care of himself, he behaves inappropriately, and there is a threat to the health and life of him and those around him. The patient is assigned disability status; treatment does not relieve symptoms, but helps prolong life.
The duration of the illness, individual characteristics and the nature of the assistance provided depend on the stage of the disease.
Neonatal encephalopathy
Separately, it should be said about post-traumatic encephalopathy of newborns. It occurs during fetal asphyxia during childbirth, during rapid labor, during various brain injuries to the fetus during the passage of the birth canal and surgical interventions.
Mild encephalopathy in a child is characterized by a syndrome of increased excitability: restlessness, irritability, tearfulness, hypo- or hypertonic states.
Moderate severity is expressed in one or more neurological symptoms: convulsive or hydrocephalic symptoms, hypertension and movement disorders, impaired reflex activity and depression of the nervous system. The state of hypotonicity is replaced by hypertonicity of the muscular system, strabismus and marbling of the skin are noted, and the large fontanel is swollen. It should be noted that with encephalopathy a complex of conditions is assessed. Isolated symptoms may occur in neurologically healthy infants. Severe stages of the pathology are characterized by a precomatose state or coma.
The tasks of neonatologists include diagnosing pathology, relieving the symptoms of encephalopathy in a child and early drug therapy, including a complex of restorative and developmental procedures - massages, electrophoresis, swimming, gymnastics for infants.
Symptoms
The disease does not have the same symptoms. Many signs at the first stage are the same as in other types of pathologies. Therefore, it is not easy to make a forecast.
Let's list the symptoms:
- Nervous disorders at stage 2. On the 1st they do not appear.
- Memory problems.
- Apathy, lethargy.
- My head hurts.
- Poor concentration.
- It's difficult to remember a lot of information.
- Nausea, dizzy.
It should be borne in mind that symptoms begin in the evening after a long day or difficult exercise. If the duration of such symptoms corresponds to 6 months. This means stage 2 of the disease is developing. The therapeutic method is determined after diagnosis.
When to see a doctor
Even when the patient seems to have fully recovered from the injury, weeks and sometimes months later alarming signs of the development of encephalopathy may appear. Namely:
- Headaches that do not go away after taking analgesics.
- Uncontrollable mood swings (emotional lability).
- Dizziness, especially during physical activity.
- Twitching of the pupils (nystagmus).
- Intermittent sleep or insomnia that cannot be corrected with sleeping pills.
- Depression and attention disorders. Deterioration of memory and intellectual activity.
- Epileptic seizures.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made after studying the symptoms. The same diagnostics are performed to determine the cause of circulatory problems in the nervous system.
For this we use:
- Blood test to study atherosclerosis.
- Assessment of the condition of the fundus veins.
- Duplex scanning.
- MRI.
- Angiography.
- For hypertension, a blood urea test is performed.
- ECG, ultrasound of the heart.
Indications for assigning a group and mandatory examinations
ITU pass if:
- the pathology progresses rapidly;
- certain types of activities and working conditions are contraindicated;
- against the background of repeated strokes (acute cerebrovascular accidents), it is impossible to perform work manipulations.
Before passing the commission, a person undergoes examinations:
- ECG;
- X-ray of the skull and cervical spine;
- CT scan of head tissue;
- rheoencephalogram;
- Dopplerography of the arteries and veins of the brain;
- examination by a therapist, ophthalmologist, psychiatrist;
- tests for glucose, blood lipids and cholesterol.
The commission is provided with data from all examinations and medical reports.
Treatment
This pathology is eliminated in the same way as similar diseases. It is necessary to use complex methods to achieve the best effect. Several examinations are performed to diagnose the nervous system and determine the size of inflammatory foci:
- Positron emission tomography.
- Electroencephalography.
- MRI.
- CT.
- X-ray.
- Blood analysis.
Based on the results of the examinations, it becomes clear how large an area of the brain is affected and how severely the disorder develops. You need to find out how long the treatment will last and the degree of disability the patient will receive.
In addition to eliminating brain disease, a comprehensive approach to symptom management is needed. This examination is performed by neurologists, cardiologists, and therapists.
The list of treatment procedures includes:
- Blood stops circulating in the head. Nootropic drugs are often used in combination with normalizers.
- Medicines that reduce the number of platelets, thin the blood.
- Tablets and injections to eliminate hypertension.
- Treatment of lipid-lowering effect.
The fight against such pathology implies a list of directions for relieving the symptoms of the disorder and factors that provoke structural changes in the brain. In the modern world, this problem is very significant.
The goal of therapy for grade 2 encephalopathy is to eliminate acute vascular pathologies in the brain and change the development of the disease that caused DEP. It is necessary to restore blood circulation to the head and performance. Therapy of the disease involves repeated drug treatment due to problems with diagnosis in the initial stages. The main treatment is prescribed when stage 2 is detected. If you follow the advice of doctors correctly, the courses make it possible to restore the functionality of the patient’s body.
The following medications are prescribed:
- Lisinopril stabilizes blood pressure, blood flow, and reduces the likelihood of stroke and ischemic head injuries. Capropril is prescribed for kidney disease, diabetics, patients with hypertension and heart failure. For all patients, specialists select a personal course of treatment with such drugs.
- When patients complain of diabetes, asthma, and problems with conduction in the heart, doctors recommend anaprilin, pindolol and other drugs from this group.
- The administration of diltiazem, infedipine, verapamil allows you to stabilize heart rhythms, get rid of vascular spasms, stimulate blood circulation in the head, and reduce blood pressure.
- When using hypothiazine, furosemide and other drugs, blood pressure is reduced by eliminating residual fluid from the body.
Therapy is aimed at treating atherosclerosis. Medicines are used by doctors in situations where diet and exercise therapy do not help. For this purpose, medications from the fibrate group, which include nicotinic acid or fish oil, can be used.
Relief of stage 2 DEP involves the prescription of vasodilators such as trental, cinnarizine, Cavinton, and other drugs. The list of drugs to combat such a disease necessarily includes substances to improve metabolism, which have a beneficial effect on the ability to concentrate and remember information, and intellectual abilities. These medications include neuroprotectors and nootropics.
Since venous thrombosis is one of the causes of the disease, many patients must undergo courses of treatment with anticoagulants and antiaggregants.
Treatment of the symptoms of the disorder is mandatory. Its main task is to eliminate depression and emotional background. To eliminate motor functions, massage procedures and exercises are prescribed.
Preventive measures
Doctors have developed 3 types of preventive measures to avoid disability due to cerebral encephalopathy.
Primary measures . They provide for taking into account the initial risk factors for the appearance of vascular diseases, and the correct treatment of patients with NPCI (initial manifestations of cerebrovascular insufficiency). Completion of disease therapy.
Secondary level . Detection of early pathology and treatment of cerebral encephalopathy, especially at an early stage. Elimination of causes that provoke the development of the disease. Quarterly clinical examination to examine and monitor the patient’s health status. For patients who have suffered a stroke, complete rehabilitation.
Tertiary prevention measures . Timely examination for group 3 and appropriate employment. Carrying out other measures for the purpose of social protection of the patient.
To reduce the risk of disease, you should avoid head injuries and various types of poisoning - alcohol, toxic substances, infectious.
Regular and medical examinations will help you avoid an unpleasant situation. The slightest deviations in health cannot be ignored, especially if they relate to brain functions.
How to treat without drugs?
The patient must strictly adhere to:
- Diet.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Normalize your own weight.
- Get more physical activity.
Elimination of such a disease involves surgical intervention. The procedure is performed when 70% of the blood supply to the head is damaged.
Fill a liter jar with dried clover, add grass so that the mixture does not reach 5 cm from the top. The container is filled with alcohol, the mixture is infused for 2 weeks in a dark place. After this, strain the contents, consume 1 teaspoon 3 times a day. It is advisable to drink it with cold water. It is better to use such remedies on the recommendation of a doctor.
Complementary therapy
The doctor may prescribe physiotherapy to the patient - laser and reflexology. Physical therapy, massage and regular exposure to fresh air are an important aspect of the positive dynamics of the disease.
In addition, it is important to stop smoking and drinking alcohol and switch to a healthy diet. Mental exercises such as solving crosswords and logic puzzles have a positive effect on the brain.
Surgery for this pathology is carried out only when the additional damage to brain tissue during surgery outweighs the possible consequences of non-intervention. For post-traumatic pathologies, it is carried out if it is necessary to restore blood circulation in the brain.
Stage 2 disability
The 3rd category of disability is assigned to patients with encephalopathy who are able to perform basic activities at home or at work with difficulty. Living with such a disease is possible without regular monitoring by doctors or relatives. Each individual situation requires personal consideration.
The second category is assigned to patients with other disorders other than cephalgic syndrome. Due to memory problems and limb tremors, they cannot maintain their ability to work. Patients can take care of themselves.
Prohibited types of work
If the patient is diagnosed with encephalopathy, there are contraindications for work:
- in a hot shop;
- associated with significant neuropsychic and physical stress;
- at night time;
- in conditions associated with the influence of toxic substances;
- with the likelihood of stressful situations;
- requiring precise coordination of movements;
- associated with long walking.
ICD 10
Post-traumatic encephalopathy is most often coded T90.5 as a consequence of intracranial damage. Additionally, G93.8 (other specified brain pathologies) is also used. The diagnosis must indicate the damage and its type. For example, according to ICD 10, post-traumatic encephalopathy can be caused by a bruise of varying severity, diffuse axonal damage, and so on. The diagnosis also indicates the date, and the syndromic part describes the manifestations. It must be said that a concussion does not provoke consequences. In this case, post-traumatic encephalopathy can only be described in the presence of necessarily documented multiple concussions. It can manifest itself as the only or leading syndrome. In this case, according to the ICD, post-traumatic encephalopathy is coded under G91.
The first signs of pathology
Memory suffers even in the first stage of damage. The person notices difficulties with retaining information and reproducing it in a timely manner.
Both long- and short-term memory deteriorates. If signs persist longer than 2 to 3 weeks after injury, additional examination is necessary.
Poor attention is often attributed to fatigue, absent-mindedness, or considered a character trait. The actions of a person with organic brain lesions appear inconsistent and often meaningless. It becomes difficult to concentrate on doing one thing, which manifests itself in increased excitability and restlessness.
Problems with thinking or impaired cognitive function occur with a predominance of excitation and inhibition of the nervous system. Signs include not only lethargy and the inability to quickly switch to another topic in a conversation. The appearance of excessive gesticulation, spontaneous and obsessive responses to questions, and strange ideas are also neurological disorders if they did not appear previously before the traumatic event.
After suffering a traumatic brain injury, a person becomes inhibited, lethargic, weakly expresses personal opinions, indifferent to what is happening and apathetic, loses interest in close people and favorite activities.