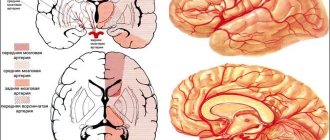
Types of circulatory disorders
In medicine, there are two types of stroke. Each of them has its own causes and characteristic features.
The ischemic type occurs due to the closure of the lumen of the vessels by a thrombus or blood clots. As a result, a certain area of the brain ceases to receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and microelements supplied through the bloodstream. This entails dysfunction and death of tissue cells.
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to rupture of blood vessels in the brain. The result is a large amount of blood, which negatively affects the functioning of the nerve fibers. This provokes their dysfunction.
As a result of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, tissue cell death and impaired blood circulation to the brain are observed. Against the backdrop of ongoing changes, systems and organs cease to function normally.
Consequences of a stroke
Impaired blood flow can affect either a small part of the brain or a large part of it. But regardless of how serious the violations were, a stroke is accompanied by the following complications:
- Impaired coordination of movements and motor skills. They are observed not only during neurological tests. The symptoms are also noticeable in everyday life. It is difficult for a person to hold small objects or open the front door with a key the first time.
- Paralysis of one side of the body, which is opposite to the affected hemisphere of the brain. The patient's limbs and facial muscles also fail. These signs can be expressed to varying degrees, depending on the volume of the affected areas.
- Neuropathy. Patients cease to distinguish taste, smell and temperature.
- Visual impairment. Patients often complain of a narrowing of the field of view, double vision and decreased visual acuity.
- Mental disorders. Most often, after a stroke, patients experience a depressive state. Mood changes quickly, nervousness, anxiety and aggressiveness appear.
- Aphasia. This is a speech disorder, expressed in difficulty perceiving the words of the interlocutor and difficulty in conversation. A person may not always be able to express themselves clearly or absorb large amounts of information.
- Violation of urodynamic functions. There is difficulty urinating and defecating. In some cases, fecal and urinary incontinence occurs.
- Disability. Quite often it becomes one of the consequences of a stroke in which a fairly large area of the brain was affected or in the absence of timely medical care.
A stroke can also be fatal. Many patients who have suffered a mini-stroke have a question about whether it is possible to drive a car while undergoing a rehabilitation course. The ability to drive is determined by a special commission based on the results of examination, testing and medical indicators. The decision is made 3-6 months after the attack.
Medical and social examination ->
b) limitation of life activity (complete or partial loss by a citizen of the ability or ability to carry out self-service, move independently, navigate, communicate, control one’s behavior, study or engage in work); In my case, due to a stroke, restriction of work activity (prohibition of bending, heavy lifting, heavy physical activity). In rare cases, severe dizziness makes it impossible to move independently. Also, due to constant headaches, I have a decrease in the ability to concentrate, memory, and attentiveness, which interferes with normal work activity.
The prospects for establishing disability for ANY disease depend on the DEGREE OF its SEVERITY. It is not possible to assess the severity of the disease based on one word (“stroke”). There is an article on the website that describes in detail the criteria for establishing specific disability groups depending on the severity of a given pathology. If you have time and desire, you can familiarize yourself with it. Medical and social examination and disability in stroke
27 Jul 2021 jurist7sib 73
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Sample power of attorney for receiving documents from individual entrepreneurs
- How to receive an inheritance after 6 months
- What benefits are there for the Chernobyl certificate?
- For Medical Services for Civil Servants on Maternity Leave in 2021
Driving tests
A large number of patients after a stroke get behind the wheel of personal vehicles without undergoing special tests and examinations. It is quite difficult for them to immediately give up the habit of moving freely and quickly around the city. But at the same time, few people think about the safety of themselves and the people around them when driving.
In order to determine whether the driver's skills have been lost, a person must pass a special test. It is performed on the road in a car with an instructor or using a computer simulator. Disadvantages of this test include high cost and long test completion time. All tasks take from 30 to 45 minutes to complete.
Why is it not allowed to travel?
During the rehabilitation period after a stroke, patients are strictly prohibited from driving. This is due to the fact that it is not uncommon for a person to be stressed on the road and can cause a repeat attack. In addition, after a hemorrhagic stroke, restoring brain function is much more difficult.
The patient is allowed to drive a car after a mild attack no earlier than 3 months later.
But not many patients are aware of the possible consequences of driving a car immediately after a stroke. The attending physician should talk about the presence of danger. During a trip, a person experiences many different emotions and feelings. Most often these are panic or stress conditions and overexcitement. They contribute to an increase in blood pressure, which causes hemorrhage in the brain. As a result, an emergency situation may arise on the road.
In addition, after a stroke, patients experience slurred speech and difficulty in assimilating information. This may also cause a conflict situation with police on the road.
You can drive a car after an attack, but not earlier than three months later. Such a restriction is necessary in order to protect not only the driver himself but also the people around him.
Possible problems
Even after successful rehabilitation, the patient may be unable to drive a car. A number of serious problems can prevent this:
Lack of clarity of thinking.
It is difficult to assess the situation on the road.
Untimely reaction and inhibition of actions.
These factors adversely affect driving behavior. The patient poses a risk to other road users and can be seriously injured. Severe deterioration of the visual field and cognitive impairment after a stroke are categorical contraindications for driving.
In 70% of cases, after a stroke, cognitive impairment occurs (the functioning of complex brain functions, for example, memory, attention, orientation, decreases). It is they that cause concern among specialists, since it is not possible to determine with a sufficient degree of certainty the impact of these disorders on the ability to drive a car.
When should you not drive after a stroke?
After a stroke, a general ban on driving is imposed for a period of 3-6 months. Next, the medical commission, guided by the degree of damage and severity of the disease, after studying all the complications that have developed, will make a decision on the possibility of driving. For example, if the field of view decreases by more than 20 degrees, the medical commission will not give permission to drive a car.
As a result of a stroke, the human psyche often suffers. There may be sudden mood swings, depression, and the inability to adequately assess the situation and make quick and correct decisions. Moreover, almost all drugs used to correct mental problems are contraindicated when driving a car.
Complications such as partial paralysis or muscle spasticity are also a complete contraindication to driving.
Sometimes epilepsy develops after blood circulation in the brain is disrupted. In this case, it is impossible to drive the car.
Can I work as a driver in passenger transport with disability group 3?
In accordance with Article 23 of the Law “On Road Safety”, medical support for road safety consists of mandatory medical examination and re-examination of driver candidates and vehicle drivers. The purpose of compulsory medical examination and re-examination is to identify medical contraindications or restrictions for driving activities among vehicle drivers and driver candidates.
In accordance with Art. Art. 25, 27 of Federal Law N 196-FZ, the right to drive a vehicle is granted to citizens who have reached a certain age, after appropriate training, passing qualifying exams, in the absence of medical contraindications to driving and is confirmed by a driver’s license.
After a heart attack
After a heart attack, a person recovers from one to several months, it all depends on the severity of the disease, age and concomitant diseases. Of course, after a heart attack you need to avoid unnecessary stress, and driving is a stressful situation, especially in busy traffic. You can get behind the wheel only after a doctor’s conclusion that there are no contraindications to driving. And experts also say that a person should not have fear. If it is present, it is better not to sit down and save yourself from such stress.
Consequences
The consequences of any type of stroke can be either mild or very dire. Mild consequences of a stroke include: blurred vision (decreased visual acuity or double vision), partial paralysis of the face or limbs, deterioration of motor functions and the appearance of nervousness and anxiety. More severe consequences of a stroke include: speech impairment and the ability to perceive information, the development of serious mental disorders, complete paralysis and disability.
For quite a long time, people who have suffered a stroke have to return to their normal lives. Many have to learn to walk, count and write again. It takes much longer to return to complex work activities, such as work or driving.
Stroke and driving
Quite often, patients whose place of work is located far from home depend on transport. Therefore, doctors are often asked whether it is possible to drive a car after a stroke?
The patient may develop serious complications, the presence of which makes it impossible to drive. Under no circumstances should you drive a car if you have disabilities such as epilepsy or partial dysfunction of the limbs after a stroke. In Russia, driving is prohibited for epileptics.
However, it is worth understanding that patients who are lucky enough to avoid the serious consequences of a stroke can still experience serious problems on the road.
What problems can a person encounter:
- Difficulty in assessing the traffic situation.
This manifests itself in the inability to estimate the approximate speed of other cars and the distance between them. Difficulty arises in rearranging from row to row.
- Difficulty braking.
It is difficult for a person who has suffered a stroke to determine the distance between his car and someone else's. Therefore, collisions often occur near pedestrian crossings.
- Difficulty in distinguishing road signs.
The reason for this is deterioration of vision, a decrease in its acuity. The patient may simply fail to see a sign or traffic light, which leads to traffic accidents.
However, if a patient after a stroke is determined and confident that he is able to return to driving, then he will have to undergo a long and thorough medical examination, and then a rehabilitation course.
Testing as a chance to return to a full life
After the ban on driving a car has expired, doctors decide whether the patient can drive after a stroke, based on the conclusions of an ophthalmologist, psychiatrist and the results of special tests.
Testing is carried out on an outpatient basis and takes the patient only 15 minutes and tells with 90% accuracy whether he can go on the road after the recovery period.
Passing the test includes:
- Ability to recognize road signs.
The patient is asked what this or that sign means, what action on the road needs to be performed in relation to this sign. You must score at least 9 points out of 12.
- Orientation task.
Evaluates visual acuity, the ability to soberly assess the distance from one’s own to another car, and the time required to brake. Minimum 25 points out of 32.
- Ability to plan your own route.
For example, the standard route from home to work or the grocery store. This evaluates the patient's complex thinking and attentiveness. The passage takes no more than 90 seconds.
Unfortunately, based on the test results, only 10% of patients can get their driver's license back. This is due to the fact that usually people who have suffered a stroke make 2-3 times more mistakes on the road than healthy drivers. Patients return to driving more often after a microstroke, less often after a hemorrhagic stroke. The reason is the smaller affected area.
Before getting behind the wheel, the patient should undergo a rehabilitation course for the sake of his own comfort and the safety of those around him.
Attending physicians of various specializations come to the rescue:
- Ophthalmologist
Checks vision and, if necessary, writes a prescription for glasses.
- Speech therapist
Corrects speech defects using a set of exercises.
- Physiotherapist
Restores the muscle frame and muscle tone through massage and a set of physical exercises.
- Psychologist
Consults patients who experience anxiety and loss of strength.
Rehabilitation is important because it reduces the likelihood of a stroke recurrence, which can catch a person driving a car on the road.
Patients who return to riding usually report that it is a long and difficult process. At first, it is impossible to concentrate on anything other than the road, since switching attention to, for example, turn signals, takes the car in different directions. According to subjective feelings, after a stroke a driver has only 20-30% of his previous skills, most skills are reset to zero, and he has to learn everything all over again.
Experts advise at first to drive only on roads where there is no active traffic, preferably on country roads and at low speeds. Hold the steering wheel with both hands and under no circumstances be distracted by conversations or what is on the sides of the road.