Author's rating
Author of the article
Shoshina Vera Nikolaevna
Therapist, education: Northern Medical University. Work experience 10 years.
Articles written
218
The lack of oxygen in the human body in a matter of seconds sometimes causes irreparable harm. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) sometimes sounds like a terrible death sentence for both children and adults. Let's figure out what kind of disease this is, its symptoms and how dangerous hypoxic-ischemic brain damage is at any age.
Features of the pathology
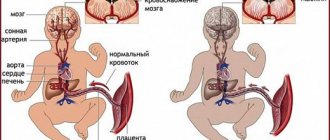
Oxygen deficiency inevitably affects the functioning of the body. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in newborns occurs often: both in full-term and premature babies. 10% of infants who experience it are subsequently diagnosed with cerebral palsy. That is why the expectant mother should spend more time in the fresh air and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations in order to reduce the risk of hypoxia to a minimum.
In adults, injuries or existing serious illnesses are a common cause of pathology. If help is not provided in a timely manner during an attack of suffocation, there is a serious risk of death or disability. The severity of the pathology also plays an important role; the higher it is, the less chance a person has of returning to a full life.
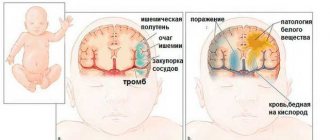
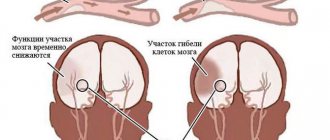
When oxygen starvation occurs in the most important part of the central nervous system, this leads to a deficiency of this substance in brain cells, which slows down blood flow and all metabolic processes. With such a lack of nutrition, brain neurons in some parts of the organ begin to die, leading to neurological disorders.
The process is accelerated by cerebral edema, which also occurs due to a disruption in blood circulation. The pressure increases, and cells begin to die faster. The faster the process, the greater the chance that the damage will be irreversible.
How to avoid getting sick
A serious approach to pregnancy planning and a thorough examination of the mother during pregnancy is a guarantee of a successful pregnancy and the absence of complications in the newborn baby. Women with chronic diseases such as epilepsy or diabetes should undergo comprehensive testing before conceiving a child. Having achieved compensation for their own illness before conception, every woman has a high chance of bearing and giving birth to an absolutely healthy baby.
Since the cause of pathology in infants is hypoxia in the prenatal period, the duty of every woman is to give up bad habits while bearing a child.
A thorough examination and pregnancy management by a qualified doctor will help you avoid complications during childbirth.
Causes
Hypoxic encephalopathy in adults and children occurs for different reasons. It is important to know them in order to take all measures to prevent it.
In adults
Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy occurs due to a lack of oxygen, which is caused by the following reasons:
- state of suffocation;
- strangulation;
- failure of the respiratory system of any kind;
- drug addiction, overdose;
- pathologies of the circulatory system, leading to its obstruction or rupture;
- cyanide, carbon monoxide - poisoning;
- long stay in a smoky place;
- tracheal injury;
- heart failure;
- diseases leading to paralysis of the muscle tissue of the respiratory system.
Acute hypoxic encephalopathy occurs if oxygen does not enter the body for several minutes. This is a severe course of the pathology, which most often ends in death. Isolated cases have been recorded where people survived, but for them it ended in a severe form of serious mental illness.
In newborns
The cause of this condition in a newly born child may be:
- suffocation during childbirth due to weak labor;
- premature labor or with pathological factors such as umbilical cord prolapse;
- diseases of infectious origin in the mother;
- a number of physical factors from dirty air to radiation.
It is asphyxia in infants that is the most common factor leading to HIE. Doctors identify the following risk factors for its occurrence:
- acute hypotension in a woman in labor;
- underdevelopment of the lungs, which leads to a lack of oxygen in the blood;
- difficulties in the functioning of the heart;
- injury to the fetus due to the mother’s narrow pelvis or due to problems with the umbilical cord;
- difficulties in labor, trauma, stress;
- hypoxia;
- birth hemorrhage;
- negligence of medical personnel;
- placental abruption;
- change in the shape of the fetal skull due to pressure;
- birth trauma, uterine rupture;
- low placenta previa.
WE RECOMMEND WATCHING: Consequences of traumatic brain injuries
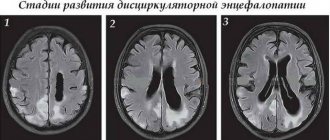
Degrees of severity and characteristic symptoms
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy has 3 degrees of severity, which are characterized by their own manifestations. Using them, doctors often give a preliminary description of brain damage and an approximate prognosis.
Mild degree
With this degree the patient will have:
- the pupil is dilated and the eyelids are wide open;
- lack of concentration;
- impaired coordination of movements, wandering behavior;
- either drowsiness or hyperexcitability was detected;
- high degree of irritability;
- lack of appetite;
- cerebral circulation is impaired.
Average degree
Neurology with it will be more pronounced, since the disturbance in oxygen saturation of the brain is longer lasting:
- the baby has spontaneous cries for no reason;
- the protective and support reflex is either weakened or absent altogether;
- signs of muscle weakness;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure;
- metabolic acidosis of the blood;
- neuralgic attacks;
- failure in the swallowing process.
Severe degree
The damage in such cases is more severe, which manifests itself in:
- convulsions;
- bluish skin;
- loss of consciousness;
- hypertension;
- lack of motor abilities;
- strabismus;
- coma or precoma;
- lack of pupil reaction to light;
- failure of the respiratory process with severe arrhythmia;
- tachycardia.
PEP is a type of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in young children. It is diagnosed both immediately after birth and in the first year of life. PEP develops both in utero, during labor, and in the first 10 days from birth.
It can be of three degrees of severity with characteristic symptoms and occur in an acute form - up to a month, with early restoration of functions - up to 4 months, with late recovery - up to 2 years.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
Hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system is detected immediately after birth. At the first stage, a full examination and diagnosis of reflexes is carried out. If brain damage is suspected, further examination includes the following methods:
- neurosonography - ultrasound examination of brain tissue through the fontanelle, possible only in newborns;
- MRI, CT are the most informative ways to determine the state of the central nervous system;
- electroencephalography – diagnostics of brain activity;
- Dopplerography is a study of blood flow activity.
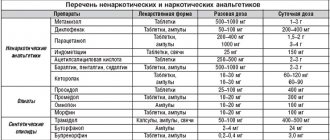
Treatment is selected individually and depends on the stage of the pathology. It is often carried out using conservative methods and involves the use of certain groups of drugs:
- anticonvulsants;
- nootropics – medications to improve blood supply to the brain;
- diuretics to reduce intracranial pressure;
- herbal sedatives (valerian extract) for sleep disorders;
- additional methods according to indications.
During the recovery period, it is useful to attend therapeutic massage sessions and do passive exercises. You may need long-term systematic use of medications to improve cerebral circulation.
Diagnostics
Perinatal ischemia syndrome due to cerebral hypoxia begins to be diagnosed by performing a visual examination of the child. It's the same with adults. Despite all the advances in medicine, a unique test that can accurately identify DIE has not yet been invented. All laboratory techniques are aimed at identifying how badly the brain is damaged and the current state of the whole organism.
What kind of research will be done depends on the symptoms and how they developed. To decipher the tests, there are special biomarkers that give a complete picture of the degree of HIE. The patient's blood is needed for the study.
Neuroimaging is carried out using:
- neurosonography and/or MRI, a tomograph showing internal brain damage and changes in it;
- Doppler ultrasound, recording the functioning of cerebral blood flow;
- electroneuromyograph to determine the sensitivity of fibers of the periphery of the nervous system.
Additional can be used:
- electroencephalograph to detect developmental delay at an early stage and whether there is epilepsy;
- video monitoring to study the motor activity of children.
If necessary, the victim is examined by an ophthalmologist to determine the condition of the optic nerves and fundus of the eye, as well as the presence of genetic diseases in this area.
Treatment and care
Victims must receive special care, and for children who have suffered HIE, it is based on control over:
- room temperature - no more than 25 degrees;
- his comfortable position, so tight swaddling is prohibited;
- so that the light is soft and subdued;
- silence;
- feeding, which should be with skin-to-skin contact and according to the baby’s needs;
- breathing, in the event of a failure in which a special apparatus is connected.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: What is cephalalgia of the brain
Therapy is carried out:
- Surgically, to restore and improve blood circulation in the brain. Most often, an endovascular technique is used for these purposes, which does not violate the integrity of the tissue.
- Medication, choosing drugs depending on how severe the degree of damage is and its clinical picture.
- On anticonvulsants, which stop seizures. Usually this is Phenobarbital, the dosage of which is selected individually. The intravenous method is the fastest. But the drug itself is contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity, severe hypoxic and hypercaptic respiratory failure, problems with the kidneys and liver, and during pregnancy. Lorazepam can be used; it has a similar effect and list of contraindications.
- On cardiovascular drugs to increase systemic vascular resistance and myocardial contractile function, resulting in increased cardiac output. All drugs in this group affect the kidneys, and in case of overdose, side effects are difficult to predict. The most commonly used are Dopamine and Dobutamine.
Forms of pathology
Depending on the degree of damage to the nervous system, there are three degrees of severity of the disease in infants:
- light;
- average;
- severe encephalopathy.
The mild form of the disease is characterized by sleep disturbances, problems falling asleep and waking up, mild restlessness and twitching of the chin. The child has increased reflex activity. The baby is restless, often screams for no reason and sleeps poorly. This form is characterized by an unreasonable increase in motor activity, with a simultaneous decrease in swallowing and sucking reflexes. The disease is successfully treated in the first few weeks after birth and does not leave any negative consequences in the future.
With moderate hypoxic encephalopathy, the following symptoms are observed:
- weakness of natural congenital reflexes;
- neurological disorders of a local nature;
- weakening of body muscles;
- restlessness, frequent screaming for no reason.
Neurological disorders with moderate severity of the disease are characterized by strabismus, ptosis, and weakening of the eyelid.
A severe form of hypoxic encephalopathy in infants is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- frequent convulsive conditions of a paroxysmal nature;
- complete absence of reflexes characteristic of newborns;
- critically low blood pressure;
- weak pulse;
- complete lack of muscle tone.
A severe form of pathology may be accompanied by disruption of various internal organs.
Further observation
Patients are discharged from the hospital only after completing a full course of physical therapy and a comprehensive assessment of neuropsychic development. Most often, after discharge, patients do not require specific care, but regular examinations in the clinic are mandatory, especially for children.
If the illness was severe, the child will be observed in a special center, where he will be assisted by a neuropsychological development doctor.
Treatment for seizures depends on central nervous system symptoms and test results. They are prescribed only with a slight deviation from the norm or even within its limits. Phenobarbital is removed gradually, but it is usually taken after discharge for at least 3 months.
Forecast and consequences
In adults, the prognosis depends on the degree of brain damage by pathology. The most common consequences of perinatal HIE are:
- delay in child development;
- brain dysfunction in terms of attention, focus on learning;
- unstable operation of the body's internal systems;
- epileptic seizures;
- hydrocephalus;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
There is no need to think that this is a death sentence; even disorders in the central nervous system are corrected, ensuring a normal life for patients. A third of people with this disorder recover completely.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment is prescribed depending on the degree of pathology. The cause of mild encephalopathy is a violation of cerebral circulation, so all symptoms disappear safely when blood circulation is normalized. The cause of moderate disease is tissue swelling and a subsequent increase in intracranial pressure.
Treatment of moderate and severe disease is based on the following medications:
- anticonvulsants;
- medications to stimulate the cardiovascular system;
- decongestants.
Drug treatment includes a large list of drugs and is selected individually for each case of the disease in newborns.
Immediately after birth, the baby is placed in an incubator. For babies with this pathology, tight swaddling, loud sounds and bright light are contraindicated. The baby must be kept at a temperature not lower than 250C. In most cases, a ventilation system is installed for newborns.
The child is kept in the hospital for a long time. The baby's health requires careful monitoring during at least the first two weeks of life. In the future, the decision to extend hospital treatment is made by the doctor, depending on the severity of the patient’s brain damage.
The purpose of inpatient treatment is:
- saturation of tissues with oxygen;
- normalization of respiratory function;
- relieving swelling of brain tissue;
- normalization of intracranial pressure.
Subsequently, after the acute symptoms have been relieved, the child is prescribed a course of physiotherapeutic procedures to normalize all metabolic processes of the brain.
After discharge from the hospital, treatment continues at home with mandatory examination by a doctor every three to four days. Since seizures often develop with encephalopathy, taking anticonvulsants can last up to six months, depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Home treatment largely depends on how the baby develops. If there are no developmental delays, and convulsive seizures do not recur, a regular examination by a neurologist is enough for the child, without additional treatment at home.
With extensive damage to the central nervous system, treatment continues for a long time and is adjusted depending on the patient’s condition.