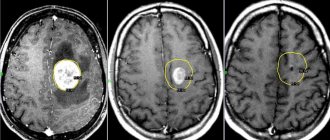
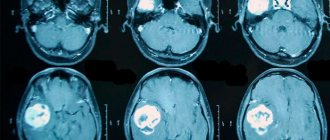
Brain tumors are difficult to diagnose. They are characterized by late symptoms, especially if the tumor is localized in less critical parts of the brain, where by the time the diagnosis is made it reaches a large size. Headache and dizziness may be the first symptoms of the disease. To diagnose brain tumors, the Yusupov Hospital uses the latest neuroimaging techniques. The patient is examined using equipment from leading global manufacturers. All cases of brain tumors are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category.
The development of a tumor often leads to subtle changes in the patient's physical condition, personality, or coordination of movements. If the tumor develops in critical parts of the brain, the following symptoms can help make an early diagnosis:
- convulsions;
- ataxia;
- loss of sensorimotor reactions.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients with headaches and tinnitus, identifying danger signals that may be a manifestation of a brain tumor. How does a headache with a brain tumor hurt? The headache can be dull, occur at night or in the morning, and be located on one side of the head.
The nature of headache with a brain tumor
Headaches with a brain tumor are a symptom that is associated with an increase in intracranial pressure. They have a pressing, bursting or tearing character. Local pain develops as a result of irritation of the vascular walls and cranial nerves.
With a small size of the formation, discomfort is not a characteristic symptom. They develop due to an increase in tumor size. Headaches can have certain characteristics, including:
- intensity;
- localization;
- duration.
Intensity
Headaches due to a brain tumor have a bursting or tearing character, which in severe cases can cause loss of consciousness. Their intensity is similar to migraines. Pain syndrome can also occur during a person’s rest or sleep.
Localization
Pain due to tumors in the brain has a specific localization. This plays a role in diagnosing pathology and prescribing further treatment. Neoplasms may be observed:
- In the frontal part of the head. They are often accompanied by sudden changes in mood, impaired coordination of movements, as well as epileptic seizures. Neoplasms that destroy the structures of the frontal lobe contribute to the loss of conditioned reflexes.
- In the back of the head. The pain syndrome has a tearing character. However, it is eliminated after taking medications.
- In the temporal zone. Most often, pain in this area is noted on both sides. They are accompanied by a sharp increase in intracranial pressure, visual impairment, and epileptic seizures.
- In the parietal part. The pain intensifies when pressed. At the same time, paresthesia is noted, extending to the trunk and upper shoulder girdle. In some cases, seizures may occur.
Duration
Most often, pain in the presence of tumors is noted as independent attacks, the duration and frequency of which may increase over time. They are not removed after taking analgesic drugs.
At night, migraines have a dull, tearing character. In combination with them, rapid fatigue and gastralgic symptoms are noted. Painful sensations that occur in the morning last more than 3 hours. As the tumor grows, attacks of pain become more frequent.
Which doctor should I contact?
The system of modern medical care in public clinics involves an initial visit to a general practitioner, who, after examination and tests, refers the patient to a specialist. If you complain of headaches, see a neurologist. The doctor, after listening to a description of the symptoms, nature, duration of headaches, conducts an examination to identify visual impairment, hearing, and coordination. A visit to an oncologist makes sense only after diagnosis, because a brain tumor can only be determined using special diagnostic methods.
Other symptoms of brain cancer
Clinical signs of the disease indicate the location of the tumor in a specific part of the brain. Features of pathogenic changes determine the symptoms that are noted in the presence of pathological neoplasms:
- chronic weakness, increased fatigue;
- regular drowsiness;
- frequent dizziness;
- impairment of visual and auditory function;
- cognitive disorders;
- psychogenic disorders;
- nausea, vomiting;
- lack of appetite, weight loss;
- loss of voice;
- thinning of the bones of the skull in the area of the crown and temple;
- stiff neck;
- seizures;
- paresis and paralysis.
They also identify signs that indicate a certain type of tumor. With astrocytoma, the patient experiences convulsions in combination with mental disorders; glioma is characterized by breathing and heartbeat disturbances. In the case of oligodendroglioma, patients experience seizures along with loss of visual function.
Under the guise of a migraine
These dangerous diseases are not always accompanied by distinct symptoms. Much depends on the location of the tumor. For example, the frontal lobe of the brain belongs to the so-called “silent” zones, and patients do not feel the presence of even very large tumors there until the tumor reaches a significant size. Often the first symptom of a tumor in the cranial cavity is decreased vision. Often it is ophthalmologists who are the first to guess what the real cause of vision deterioration in patients is.
But more often tumors are located in functionally significant areas of the brain. Even small tumors that arise there lead to very noticeable neurological disorders, such as paresis, paralysis, and speech impairment. Patients may even develop symptomatic epilepsy. But the most common symptom of the disease is headaches. They can focus on a single point or be diffuse - spread throughout the head. The patient may also suffer from nausea (and even vomiting), sleep and memory disturbances.
Tumors in different areas of the brain cause different symptoms. Therefore, the first and necessary stage of diagnosis is an examination of the patient by a neurologist. After analyzing the patient’s complaints, the doctor will be able to direct the search for the causes of the disease in the right direction.
Unfortunately, malignant brain tumors grow very quickly, so neurologists recommend not delaying contacting neurosurgeons. Especially if the patient constantly has a headache.
Distinctive signs of pain with a brain tumor
The nature of the headache associated with brain tumors does not serve as a valid reason for establishing a preliminary diagnosis. Various manifestations of unpleasant sensations can complicate the detection of oncological processes. Pain syndrome, which was caused by the growth of tissue of a pathological neoplasm, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased pain when performing movements and turning the head;
- increased intensity of discomfort during rest and sleep;
- progression of attacks with an increase in their number;
- numbness of the limbs;
- signs of confusion;
- changes in intracranial and blood pressure;
- vomiting that does not bring relief.
Causes of headaches
The causes of pain in the head and the appearance of focal symptoms in brain cancer are often associated with compression of the tissues surrounding the space-occupying lesion. Later, a symptom complex is formed as a result of the spread of cerebral edema and ischemic processes in the area adjacent to the tumor focus. The growth of a space-occupying lesion leads to dislocation (displacement) of brain structures and the appearance of herniation syndrome. The main prerequisites for the formation of pain in the head area and other focal symptoms:
- Mechanical and biochemical effects on the tissues surrounding the tumor focus, with the subsequent development of ischemic processes.
- Compression of nearby vessels supplying parts of the brain.
- Occlusion (blockage) of the vascular lumen by a metastatic embolus (intravascular, unbound substrate).
- Destruction (destruction) of the vessel wall with subsequent hemorrhage.
- Hemorrhage in the area of metastasis.
- Compression of nerves (intracranial, peripheral).
- Displacement (dislocation) of the medulla.
Headache and other focal symptoms of brain cancer appear due to irritation and excessively increased activity of the tissue area that has been compressed. General cerebral signs arise as a consequence of increased intracranial pressure and the formation of cerebral edema.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the cause of pain, doctors use a number of physical, instrumental and laboratory examination methods. The most effective among them are:
- Assessing the degree of impairment of vision, hearing, reflexes and various types of sensitivity. Using this, it is possible to detect functional disorders that were caused by tumor processes.
- Radiography. This diagnostic method is used to detect formations in the skull by obtaining an image from an X-ray machine.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels. This technique allows you to determine the level of displacement of vascular structures, as well as their patency.
- Rheoencephalography, electroencephalography. With their help, extracerebral and intracerebral blood supply is assessed.
- Scanning technique using radioactive isotopes. It allows you to determine the localization of pathogenic processes.
- Computed tomography, MRI. They are used to clarify data on the size, location and stage of development of pathological changes in brain tissue.
- Biopsy. This neurosurgical technique with tissue sampling is used to detect formations of various etiologies.
- Scintigraphy. It makes it possible to establish the presence of a tumor in the brain tissue and determine its size.
- Neurosonography. Ultrasound diagnosis of skull bones in newborns.
The main cause of the pathology
The cavity inside the skull is a closed space. During tumor growth and development:
- intracranial pressure increases,
- the membranes of the brain are compressed,
- the ventricular walls are stretched,
- the trunk of large vessels is compressed,
- pain appears.
The brain itself is insensitive to pain; blood vessels, the membranes of the brain and its other elements react to it. The head tumor grows and compresses these structures, causing pain.
With primary brain tumors, that is, those that form directly in the brain, pain can be the only warning sign about the appearance of pathology, which is what happens in 35%.
Treatment
Several treatment methods are used to treat brain tumors. To begin with, medications are prescribed that can improve cerebral circulation. These include Cavinton, Stugeron and Cinnarizin. Headaches are relieved with Ketanov, Paracetamol and Baralgin. Antitumor drugs are also effectively used, among which Vincrastin and Vinblastine have a pronounced therapeutic effect.
To prevent problems with cerebral vessels, ACE inhibitors are used in combination with calcium channel blockers. In the presence of neoplasms of benign or malignant etiology, it is recommended to use Enalapril, Nifedipine, Amlodipine.
In order to prevent the development of bacterial and viral infections against the background of a decrease in the body's immune defense, antibacterial drugs are used. These include Azithromycin, Ampicillin, Ceftriaxone and Cefuroxime. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also used, including Ibuprofen,
If drug therapy fails, surgical treatment is used. It consists of removing the structures of the neoplasm. Among the main surgical procedures on the brain are:
- Craniotomy. This is one of the most common radical methods of treating pathological processes. It involves removing tumors by creating several holes in the skull, which will allow access to the pathogenic formation.
- Endoscopic method of treatment. To carry it out, special neurosurgical equipment is used, which makes the technique less invasive and safe for the patient’s health.
Surgical therapy for formations of malignant and benign etiology can cause severe complications. The most dangerous among them are:
- relapse of pathology;
- infection of the body;
- sepsis;
- cerebral edema;
- bleeding and hemorrhage;
- violation of vital functions;
- coma.
In some cases, the tumor grows deep into the tissue, as a result of which its removal can harm the patient’s health. In this case, symptomatic treatment is used, which is aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition by inhibiting the division of neoplasm cells.
Chemotherapy is also most often used in the last stages of cancer. It helps reduce the growth rate of the tumor.
Final part
Cancer cells live in the body of any person; their division begins under favorable circumstances. The most important thing is to get help from a qualified healthcare professional in a timely manner. The prognosis of the disease is not the most favorable.
Although oncological abnormalities in brain tissue are quite rare, they are mostly fatal. The main thing to remember is that at the first symptoms you need to contact a specialist, because your life depends on it.