Brain tumors are different from all others. They do not give distant metastases and do not spread beyond the central nervous system. Neoplasms of this localization are not divided into benign and malignant. Instead, they are assigned a grade of malignancy from 1 to 4 based on histological structure.
Our expert in this field:
Sergeev Pyotr Sergeevich
Deputy chief physician for medical work, oncologist, surgeon, chemotherapist, doctor of the highest category, Ph.D.
Call the doctor
There are also no classical stages of brain cancer for most tumors, based on the size of the tumor, the number and location of metastatic foci in the lymph nodes and organs. Survival and treatment methods used are determined primarily by the histological type of tumor. Some types of brain cancer kill most patients within the first year of diagnosis and are never cured. Others have a favorable prognosis, with most patients recovering successfully after surgery or radiation.
What types of brain tumors are there?
Based on the primary site of occurrence , brain tumors are divided into:
- A primary brain tumor is one that arises directly from brain cells, its membranes, or cranial nerves.
- A secondary brain tumor is one that formed in some other organ (for example, the lung) and metastasized through the bloodstream to the brain.
According to histological properties , they are usually named according to the type of cell from which they develop:
- Neuroepithelial tumors – from the brain epithelium (astrocytoma, glioma);
- Meningeal - from the cells of the membranes of the brain (meningioma);
- Tumors of the cranial nerves – neuromas;
- Dysembryogenetic tumors develop due to disruption of the development of the neural tube in the prenatal period.
Are there any features of brain tumors?
Brain tumors are truly special, and the reason for this is the so-called blood-brain barrier (BBB).
The BBB is a physiological barrier between our blood and the cells of the nervous system. It is he who regulates the flow of various substances from our bloodstream into the cerebrospinal fluid and nervous tissue. This barrier protects our brain from microorganisms, toxins and, of course, cancer cells formed in other organs and metastasized to the brain. But it is the BBB that becomes an obstacle in the treatment of primary tumors, since it does not “let through” not only toxins, but also drugs.
Another characteristic of brain tumors is that sometimes benign tumors are as difficult to treat as malignant ones, depending on their size and location in the brain.
In addition, their peculiarity lies in the distribution by stages (more on this below, in the section “Brain cancer, stages” )
What affects survival?
The prognosis for detecting stage 4 brain cancer is based on several important factors:
- Patient's age and gender.
- Type of oncology.
- The size of the tumor, the presence of metastases in other tissues.
- The degree of impairment of nervous functions.
- The presence of certain mutations in the structure of the affected cells.
- Possibility of complete or partial removal of the primary tumor.
- Patient's mood.
In general, the success of treatment is related to the stage of cancer. The sooner you start therapy, the higher the chance of completely getting rid of the disease. However, in the terminal stage of aggressive forms of the disease, especially without proper treatment, the prognosis will always be unfavorable: such patients live no more than a year. With timely and high-quality medical care, it is possible not only to reduce symptoms, but also to extend the patient’s life to 5–10 years while maintaining cognitive and neurological functions.
What are the causes of brain cancer?
Let’s not say anything new; the exact cause of brain cancer, like cancer of other organs, is not fully known. But with all types of cancer, there is a change in the most important macromolecule for humanity - DNA.
DNA is the macromolecule that makes up our genes. Namely, genes control the work of our cells - when to divide and when it is time for them to die.
A tumor is a collection of atypical (“bad”) cells that quickly divide and do not perform any functions.
There are two types of genes in the human body:
- Oncogenes - their activation “stimulates” cells to quickly divide and, as a result, a tumor forms.
- Tumor suppressor genes/antioncogenes are genes that, on the contrary, control cell proliferation, preventing them from dividing randomly.
Cancer occurs when oncogenes turn on and anti-oncogenes turn off.
According to epidemiological and experimental studies, there are several factors that play a significant role in the occurrence of brain tumors:
- Genetic - that is, if a parent has a DNA “breakage” with antioncogenes, then there is a risk of transmitting this DNA to the child;
- Environmental factors, in particular aromatic bicarbonates;
- Viruses;
- Radioactive agents;
- Biological – puberty or aging.
Symptoms
Doctors divide two groups of symptoms:
- focal;
- general cerebral.
Focal symptoms are determined by the location of the tumor. Clinical manifestations include:
- deterioration of sensitivity or mobility of the upper or lower extremities;
- a person’s character changes dramatically, he becomes hot-tempered or overly calm, apathy, increased irritability, and mental disorders occur;
- difficulties and disturbances in the process of urination - either it is difficult to empty the bladder, or incontinence appears.
All types of malignant tumors in the brain are manifested by the following symptoms:
- dizziness, even if the person is in a horizontal position;
- severe headaches, which often appear in the morning and evening, are bursting in nature, become more pronounced when coughing or sneezing, and are usually not relieved with medications;
- the face becomes distorted, there is asymmetry, drooping of the mouth or eyes due to compression of the nerves;
- attacks of nausea or vomiting, regardless of food intake;
- impaired or blurred vision, the appearance of spots before the eyes, in the later stages there is a complete loss of visual functions;
- hearing impairment;
- epilepsy attacks;
- hyperthermia due to damage by atypical cells of the immune system;
- hormonal imbalances;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- disorders in the respiratory system, sense of smell;
- difficulty swallowing;
- impaired perception of light;
- the appearance of sound, auditory or visual hallucinations.
Severe weakness and fatigue often appear, even after performing simple work. It often happens that a person turns to specialists for help already at the stage when irreversible changes occur in the body. This is due to the absence of pronounced symptoms at the first stage of the disease.
For headaches, a person takes painkillers. Meanwhile, the disease continues to develop, and time is lost to fight it. If there is the slightest doubt or suspicion, it is necessary to visit a qualified specialist as soon as possible and undergo all the necessary diagnostic measures.
Brain cancer, stages
As mentioned earlier, one of the peculiarities of these tumors is that they are not divided into stages according to the generally accepted TNM system.
- T (tumor – tumor) – in the case of brain cancer, its size is not as important as its location and what it comes from;
- N (nodus – lymph node) – there are no lymphatic vessels in the brain;
- M (metastasis - metastases) - occur slowly and rarely.
Therefore, they are divided according to the WHO classification proposed in 2007 into four degrees of anaplasia. It is based on a combination of histological, genetic and patient survival data and includes four stages:
- Brain cancer, stage 1 – this includes neoplasms with low proliferative activity (divide slowly), they are treated surgically.
- Brain cancer, stage 2 – tumors are infiltrative in nature (grow into nearby tissues), have a low ability of cells to divide, and often recur.
- Brain cancer, stage 3 - the tumor grows quickly, spreads to nearby tissue, and the tumor cells are very different from normal cells.
- Brain cancer, stage 4 - defined as cytologically malignant, almost always recurs, has an unfavorable prognosis, and widely grows into adjacent brain tissue.
Reasons for appearance
Recently, there has been a steady trend of patients seeking medical help late in the fight against cancer. Insufficiently strict control of regular examinations and patients’ own inattention to their health lead to frequent cases of diagnosing the last stage of cancer.
A number of factors can lead to the development of cancer. The main ones are:
- unfavorable environment;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- diseases with disruption of cell structure;
- the influence of radiation exposure or ultraviolet rays;
- action of carcinogens;
- hereditary predisposition;
- old age (cancer development occurs most often in people over 45 years of age).
Find out the price
Find out the price
Error! Please fill in all required fields
Thank you! We will contact you shortly
✕
What are the symptoms of brain cancer?
Common signs of brain cancer. Any tumor formed in the brain puts pressure on the brain tissue, which causes increased intracranial pressure and contributes to the occurrence of the following symptoms:
- Headache, often of a bursting nature;
- Nausea, vomiting, which provides temporary relief;
- Double vision;
- Dizziness;
- Impaired consciousness;
- Hemiparesis (paralysis of the arm and leg on one side);
- Cramps.
Focal symptoms of brain cancer, depending on location:
- Ataxia (impaired coordination) in the limbs, tremor, nystagmus towards the affected side (cerebellar tumors)
- Violation of statics, muscle hypotonicity (tumors of the cerebellar vermis)
- Hearing impairment, motor coordination, paresis of facial muscles (tumors of the cerebellopontine angle)
- Swallowing disorders, tongue deviations, sensitivity disorders of the pharynx, face (trunk tumors)
Let's look at the symptoms of several common tumors:
Glioblastoma, signs (IV stage) . Glioblastoma is a malignant brain tumor that arises from astrocytes (the supporting cells of the nervous system). Clinical symptoms progress quickly, after 2-4 months general and focal symptoms are mixed, epileptic seizures and psychopathological personality changes are observed.
Sarcoma of the brain , formed from the connective tissue of the brain. Symptoms of brain sarcoma are similar to those of other brain tumors and may include:
- Headache;
- Nausea;
- Impaired consciousness;
- Mental changes;
- Convulsions; Speech disturbances.
Pituitary adenoma - most often develops from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland and is characterized by hormonal disorders that lead to the following symptoms:
- Hypersecretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone - high blood pressure, increased blood glucose levels, stretch marks on the hips, amenorrhea in women, impotence in men, osteoporosis, increased male pattern hair growth.
- Hypersecretion of prolactin – amenorrhea in women, milk secretion in women, infertility in men.
- Hypersecretion of somatotropic hormone - an increase in the size of the limbs and tongue, increased sweating.
Diagnostic methods
Examination of an oncology patient begins with a standard physical examination, assessment of neurological status, collection of anamnesis of the disease and life, and identification of possible risk factors.
Laboratory diagnostics are necessary to identify metabolic and other abnormalities that are typical of brain tumors. To detect them, clinical and biochemical blood tests, a coagulogram are performed, and the hormonal profile is assessed. Additionally, the presence of the main tumor markers in the patient’s blood (AFP, CEA, Ca 19-9) is determined.
The main role in making a diagnosis is played by visualization methods for studying intracranial structures:
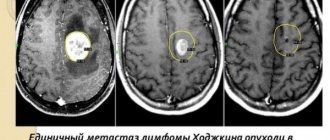
- CT. Computed tomography is the main method of primary diagnosis of brain formations that are capable of accumulating a contrast agent. CT scan reveals foci of varying density, calcifications, necrotic areas and hemorrhages. With metastatic neoplasms, there are multiple foci.
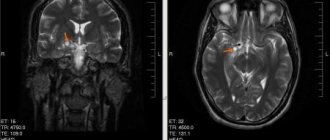
- MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium contrast is considered a more informative and accurate method for diagnosing malignant neoplasms. It is most useful in visualizing posterior fossa tumors that are difficult to diagnose with other methods. MRI more accurately determines the location and extent of the malignant process.
- Echo-EG. Ultrasound diagnostics is used to detect signs of intracranial hypertension and displacement of the midline M-echo. It reveals volumetric processes in the brain, but does not allow them to be differentiated, therefore it is supplemented by tomographic studies.
- PAT. A modern diagnostic method is used to assess the functional activity of brain tissue, early detection of tumor relapses, and determine the degree of its malignancy.
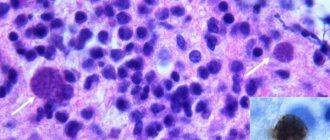
According to indications, a stereotactic biopsy of tumor tissue is performed, which is necessary for histological verification of the malignant process and establishment of an accurate diagnosis according to the WHO classification. It is necessarily carried out in complex diagnostic cases when another method fails to differentiate the neoplasm from a hematoma, granuloma or focus of demyelination. The results of histological diagnosis of biopsy specimens are necessary for a specialist to decide on the feasibility and prognosis of surgical treatment, and the scope of postoperative treatment.
To determine the molecular genetic characteristics of tumor tissue, immunohistochemical studies, PCR, and FISH analysis are performed. During diagnosis, gene mutations are determined (IDH, 1p 19q), which is necessary to determine the prognosis for the patient.
How are brain tumors diagnosed?
- Neurological examinations help determine whether the tumor is affecting brain function.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most common method of imaging almost any brain tumor. MRI signals differ depending on the water, calcium, and fat content of the tumor. The nature of the signal is influenced by the cystic component of the tumor and hemorrhage into the tumor.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan – allows visualization of abnormalities or tumors in the brain. The method can help detect bleeding and enlarged fluid-filled spaces in the brain. In addition, computed tomography allows you to see changes in the bones of the skull. CT can also be used to measure the size of a tumor and in cases where the patient does not have access to an MRI, for example, if a person has a pacemaker for the heart.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) or PET-CT scan - a small amount of radioactive substance is injected into the patient's body. This substance is absorbed by actively dividing cells. Because tumor cells are more likely to actively divide, they absorb more radioactive material. The scanner then detects the substance and creates images.
- A lumbar puncture is a procedure in which a needle is used to remove a sample of cerebrospinal fluid to look for tumor cells, blood, or tumor markers.
- Biopsy + histology. A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope. This is the only definitive way to diagnose a brain tumor.
Assistance to patients in the Turkish center of Anadolu
In Turkey, cancer patients receive special attention. Comfortable rooms, attentive and experienced staff, modern diagnostic methods - all this will help make you feel as comfortable as possible and improve your life. Non-profit medical status allows you to keep prices for the most modern therapy and examination 20-30% lower than in Israel, the USA and European countries.
In accordance with individual indications, patients undergo palliative operations, which significantly reduce pain and relieve stress on vital organs. Specially developed antitumor vaccines and targeted use of chemotherapy and radiation therapy are considered effective.
In medical oncology patients are helped to cope with the problem of the last stage of cancer, both in medical and moral aspects.
The cost and prognosis of treatment for cancer at the last stage are individual in each case: send us a request for a calculation using the feedback form. You can also order a call back on the website or call us (free within the Russian Federation).
The material was prepared in agreement with medical doctors.
Is there a cure for brain cancer?
Treatment for a brain tumor is usually complex and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation and drug therapy.
Main methods of treatment:
Surgery - a small hole is made in the skull and the tumor is removed;
Radiation therapy - this method uses high-energy radiation from an external or internal source to destroy cancer cells, most often after surgery and in conjunction with chemotherapy. Radiation therapy can slow down the division or stop the growth of malignant cells;
Radiosurgery is an approach to radiation therapy that uses many tiny beams of radiation to target a tumor to kill it. Most often it is used if it is impossible to perform an operation;
Chemotherapy - Chemotherapy drugs are used to kill cancer cells after surgery or to relieve symptoms, or in cases where the tumor cannot be removed;
Carmustine implants are a new way of delivering chemotherapy for certain high-grade tumors where implants are implanted in the brain. Carmustine belongs to a class of drugs called alkylating agents. It works by slowing or stopping the growth of cancer cells in the body.
Features of treatment
The most effective method of treating oncology is surgery. But at stage 4 of development, the formation fuses so strongly with the surrounding tissues that it becomes inoperable. Treatment is aimed not so much at reducing the aggressiveness of cancer cells, but at alleviating the patient’s condition. The following therapeutic methods are used for this:
Treatment of malignancy includes the administration of painkillers, such as Morphine.
- The use of potent medications: reducing swelling (“Prednisolone”);
- antiemetics;
- sedatives or tranquilizers;
- anti-inflammatory;
- non-steroidal painkillers or drugs with narcotic substances (“Morphine”).
Brain cancer, prognosis
Survival from brain cancer depends on many factors, and only by studying the patient’s medical history can a doctor form a prognosis. To give an overall picture, below are statistics* on five-year survival rates for patients with brain cancer:
- The 5-year survival rate for people with brain cancer or a central nervous system tumor is almost 36%, and the 10-year survival rate is almost 31%.
- Survival rates decline with age.
- The 5-year survival rate for people under 15 years of age is more than 74%.
- For people aged 15 to 39 years, the 5-year survival rate is about 71%.
- The 5-year survival rate for people age 40 and older is about 21%.
But still, you shouldn’t focus on “dry” statistics; everything happens differently for each of us. Therefore, before drawing any conclusions, consult your doctor on this issue.
*-Statistics adapted from the American Cancer Society, Cancer Facts & Figures 2021, ACS website (January 2021)