But only surgery can prolong the life of a person suffering from a disease such as a brain tumor.
Our consultant is Candidate of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Neurosurgery of the Russian Scientific Center for Surgery of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. B.V.Petrovsky Sergey Vasiliev .
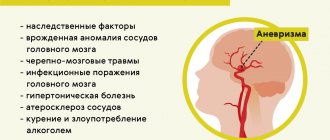
Unfortunately, any neoplasms that arise in the brain pose a serious threat to human life, and therefore can be considered benign or malignant rather conditionally. Even if the cellular composition of the tumor itself, from an oncological point of view, does not inspire concern, its potential harm is very great.
The fact is that any neoplasms that develop in a confined space of the skull lead to an increase in intracranial pressure and sooner or later lead to the death of the patient. In addition, even a benign brain tumor can develop into a malignant tumor over time.
What to look out for in case of brain cancer
A cancerous brain tumor does not metastasize, that is, secondary foci. However, already in the early stages of the development of the process, the patient begins to feel its signs. The following symptoms of trouble should alert you:
- progressive impairment of speech function;
- disturbances in coordination of movements;
- constant fainting;
- chronic headaches. Remember that headaches with a brain tumor are constant. They do not subside after taking analgesics, which are usually found in our home medicine cabinet. This phenomenon should be more alarming than others;
- the occurrence of hallucinations of various types. Most often, a person feels the constant presence of a certain odor.
Surgery: is there an alternative?
Today there are three methods of treating brain tumors. Among them, alas, there is no conservative method, since medications are powerless in the fight against this disease.
The most radical method is surgical. The surgeon performs a craniotomy and removes the tumor. This is the most effective and large-scale method for this disease. The prognosis for surgical treatment of conditionally benign tumors is favorable - the 5-year survival rate of patients reaches 80 percent or more (which in medicine is equivalent to recovery). Unfortunately, with grade 4 tumor malignancy, no more than 5% of patients manage to overcome the five-year mark after surgery. However, for such people, surgery is the only chance to live at least another 3-4 years, since without treatment the tragic ending comes in a few months. Brain surgery is usually very lengthy and complex, and there are contraindications for it. Among them are severe somatic diseases (for example, acute myocardial infarction or diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation).
Tumor localization is another important point. Sometimes tumors develop in a very important area of the brain, access to which is so difficult that it threatens the patient with significant brain damage or even death. In this case, you have to resort to another treatment method - radiation.
The nature of headache during a tumor
Headache during brain tumors is significantly different from others. Not only is it permanent and does not go away after strong enough painkillers. It is oppressive in nature. In some cases it is quite intense. The headache intensifies in the following cases:
- exercise stress;
- sharp bends of the body;
- cough;
- abdominal muscle tension.
The headache is also worse in the morning. This occurs as a result of the fact that huge amounts of fluid accumulate in the brain tissue overnight.
Such pain also has warning signs. Usually they are nausea. In addition to such characteristics as intensity and duration, the patient can also describe his sensations this way:
- the pain seems to “pulsate” in the head”;
- after waking up the sensations are the strongest;
- confusion of consciousness and speech is often noted;
- migraine symptoms are completely absent;
- Sometimes the painful sensation is complemented by dizziness, decreased sensitivity of certain parts of the body, mental disorders, and signs of depression.
Diagnosis in half an hour
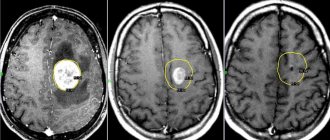
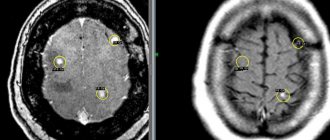
After examination by a neurologist, at the second stage of the examination, hardware methods are used: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). These diagnostic methods are not an alternative, but a mutual complement to each other. MRI is the most informative study in the diagnosis of intracranial space-occupying lesions, and CT is more valuable in acute situations, such as hemorrhage and traumatic brain injury.
Both of these methods are completely painless. During an MRI, the patient is placed on a special table, which then slides inside a cylindrical dome, where an electromagnetic field is created. The patient is only required to remain still for half an hour while the device takes the necessary readings.
With CT, much the same thing happens in a shorter period of time, but instead of a dome, a large ring is used. However, while MRI is an absolutely safe method from the point of view of radiation exposure to the body, the same cannot be said about CT. Therefore, you should not resort to it too often.
MRI can detect not only tumor processes, but also vascular pathologies, so this method is the most preferable when diagnosing any brain pathology (stroke, hydrocephalic syndrome, etc.). Functional MRI is a type of study that identifies functionally significant areas of the brain. It must be carried out before the operation so that it takes place with minimal risk.
A computer study is necessarily supplemented by a biopsy (taking samples to study a tumor). Based on histological features, brain tumors are divided into four grades. The first is the most benign, the last is malignant, the rest occupy an intermediate position.
How to treat meningitis and its accompanying vascular vasculitis?
A common manifestation of a brain tumor is glioblastoma. It does not metastasize outside the central nervous system.
Sometimes isolated cases of pulmonary metastasis are observed. Symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the cancer process.
If the formation is located near the brain cortex, disrupting the functioning of the centers that control speech and movement, signs of the cancer process are felt immediately.
Additional signs of brain cancer include:
- impaired speech and movement coordination;
- fainting;
- vomiting with nausea.
If the cancer process disrupts the functioning of the cortical centers of various analyzers, the pain intensifies. Loss of consciousness is often associated with impaired blood supply.
Therefore, the patient often seeks advice from a doctor when frequent fainting conditions occur. Based on the MRI results, the doctor determines the presence of a tumor.
But if the process occurs in the deep structures of the GM, there are no clear signs of its spread.
First of all, the patient is alarmed by pain in the head, which is not relieved by medications, but is only supplemented by morning vomiting and nausea.
If you observe symptoms of these two ailments, you cannot hesitate. Even if you are afraid that, for unknown reasons, vomiting or circles before your eyes are not a serious reason for calling an ambulance or going to the doctor, then remember: it is better to make yourself paranoid once than to die from an illness that was not paid attention to.
If your suspicions about the presence of meningitis are justified, the doctor will immediately refer you to the neuroinfectious department. There, after passing all the tests, the first stage of treatment will begin - antibiotics. Antibiotic therapy is the most important method of treatment; the drug is prescribed by the attending physician and is selected by him depending on the suspected causative agents of the disease. The time for taking medications is also determined by the doctor.
If there is cerebral edema, diuretics are prescribed, sometimes they are prescribed even when there is no edema, simply for preventive purposes. After outpatient treatment is completed, the patient switches to home treatment. This treatment is also prescribed by a doctor. Usually, due to meningitis, a person is exempted from work and school activities for up to a year.
But with meningitis there are also accompanying ailments, such as vasculitis, which was already discussed earlier. Its treatment is purely individual, it depends on how severely the vessels are affected.
In no case should you self-medicate, since this is not a disease that can be cured with medicinal herbs alone. A drug called Prednisolone is often prescribed.
This is a hormone of synthetic origin, it helps to inhibit the influence of the immune system on the walls of blood vessels, then there is less stress on the vessels and their inflammation weakens slightly. The main thing you should do is consult a doctor and continue to follow his instructions.
Surgical strike
There are several types of radiation surgery. The most modern method is the so-called gamma knife, which is more than 200 highly targeted gamma rays, which, focusing at one point, lead to radiation necrosis (destruction) of pathologically altered cells. This is a very gentle and absolutely painless method. The procedure itself is performed on an outpatient basis. A kind of helmet is put on the patient’s head, and the rays of the device are directed to certain points on it.
The advantage of gamma rays is that they not only do not cause pain to a person, but also do not damage healthy brain tissue. Alas, there are objective limits to this method - only small tumors can be removed using a gamma knife (maximum 3.5 cm in diameter). In addition, relapse (recurrence) of the tumor is common after this procedure. Even if a few tumor cells remain in the brain tissue, they will then begin to divide again and the tumor will grow again. In addition, not all tumors can be removed using a gamma knife - there are also those that do not respond to radiation. For example, for dense tumors this technique is ineffective.
But neurosurgeons have another method in their arsenal - chemotherapy. It is used in the most advanced stages of the tumor, when other treatment methods are no longer effective. The effectiveness of this remedy, unfortunately, is low, but nevertheless, this method helps to slightly prolong the patient’s life. Chemotherapy is also always carried out after surgical removal of malignant tumors - as an additional, auxiliary treatment method that can help prevent further tumor growth. The combination of surgery, radiation and chemotherapy is a mandatory algorithm for the treatment of malignant diseases of the brain today.
Signs indicating a neoplasm
Malignant tumors are classified according to their cellular composition. More than a hundred species are known to medicine, all of them are grouped into 12 groups.
Based on statistics, the most common types of brain cancer are:
- Glioma. Appears directly in the human brain itself. The most common form of the disease: it accounts for 50% of all cases of tumors.
- Meningioma. Malignant changes affect the meninges. The formation is insidious: it develops slowly, almost asymptomatically, and identifying the tumor is quite difficult. In most cases, the disease is discovered by chance. This type of pathological formation accounts for 15% of the total mass of brain cancer.
- Meduloblastoma. The pathology is often diagnosed in children and is highly treatable. In adults, it is much more difficult to cope with a dangerous problem.
- Neuroma. The formation is benign and affects the cranial nerves. It is still better to get rid of the neuroma to prevent complications.
- Adenoma. Affects the patient's hormonal background and growth. Most often, the tumor does not pose a threat to health.
Causes of headaches after chemotherapy
All reasons can be divided into four groups:
- direct damaging effect of cytostatics on brain cells - central neurotoxicity, only 2-3% of all patients suffering from cephalgia;
- the damaging effect of cytostatics on the vascular endothelium and myocardial fibers – cardiotoxicity with a change in blood pressure, no more than 10%;
- activation of infectious agents in nerve cells due to decreased immune defense during leukopenia and neutropenia;
- malnutrition of brain structures with anemia, decreased nutritional status with anorexia and damage to the mucous membranes, lack of microelements due to low intake or large loss.
In other cases, cephalalgia is caused by the peculiarities of the body’s reaction to sleep disturbances, physical and emotional stress, as well as dysfunction of the cervical spine and muscular skeleton, which in the medical literature is referred to as “tension headache.”
Localization
Headaches can be localized in any part of the brain, which also affects the nature and degree of intensity of the symptom.
Whiskey
When a tumor forms in this area, intracranial pressure increases significantly. The pain is localized on both sides simultaneously. Often the pain syndrome is accompanied by hallucinations and epileptic attacks.
If the tumor affects deeper parts, hemianopia may begin to develop, which is characterized by loss of vision in one eye.
Frontal lobes
When the forehead area is affected, pain is also accompanied by epileptic seizures, mood swings and lack of coordination. Against the background of the destruction of conditioned reflexes, the patient is in such a state as if he is performing all the actions for the first time.
Parietal region
If pathology develops in the postvisceral gyrus, the severity of headaches will only intensify.
When the upper part of the crown is involved in the oncological process, paresthesia of the arms, muscle atrophy and epilepsy are noted. When the tumor is localized in the lower parts, the patient experiences loss of sensitivity.