Description
With imbecility, children lag behind in physical development, deviations are noticeable externally.
There may be signs of physical malformations: disturbances in the formation of the head, underdevelopment of the limbs, fingers, defects of the face, ears, eyes, hypogenitalism, etc. There may also be neurological symptoms such as paralysis, paresis. Imbeciles understand those around them, they themselves can pronounce individual words and sometimes even short phrases. Speech consists only of verbs and nouns, is tongue-tied and grammatically incorrect. As a rule, speech consists of very short standard phrases, and the vocabulary is limited to several dozen words (sometimes up to 200-300 words). Thinking is concrete and primitive, but consistent, distractions are inaccessible, the stock of information is extremely narrow, there is a sharp underdevelopment of attention, memory, and will. Imbeciles can form ideas, but the formation of concepts, as a higher stage of mental activity, is inaccessible to them or is severely difficult. They have almost no imagination.
Those suffering from imbecility manage to instill basic self-care skills (dressing themselves, taking care of themselves, eating) and simple work skills, mainly through training in imitative actions. With mild and moderate degrees of imbecility, patients can study in a auxiliary school, but they can be taught little: basic counting (within a few units), writing individual words, reading simple texts.
The emotions of imbeciles are more differentiated than those of idiots, they are attached to their family, and react adequately to praise or blame. Imbeciles lack initiative, are inert, very suggestible, easily get lost when the situation changes, need constant supervision and care, and in an unfavorable environment, behavior can be asocial. The interests of imbeciles are extremely primitive and are limited mainly to the satisfaction of physiological needs.
Sexual desire in those suffering from imbecility is usually reduced, but sometimes there is a painfully increased sexual desire along with a lack of restraining moral restrictions.
Based on their behavior, there are two groups of imbeciles: sluggish and apathetic, indifferent to everything except satisfying natural needs (torpid) and lively, active, restless (erectile). By character they are also divided into two groups: maliciously aggressive, stubborn and sociable, good-natured, friendly, flexible.
Symptoms and capabilities of people with imbecility
The imbecile's thinking is direct, concrete, without understanding abstract things (what is this?), and flows slowly. Knowledge is limited exclusively to simple everyday issues. Memory, attention, perception are underdeveloped.
Speech is illiterate, and the vocabulary is poor - the names of the most frequently used things in everyday life.
If mechanical memory is more developed, then the child can master ordinal counting and use it only superficially. Can memorize the multiplication table. The concept of number and the meaning of addition and calculation is absent.
Visual and auditory analysis of information is impaired, so it is difficult for an imbecile to distinguish between letters that are written and sound the same. A person may be able to read mechanically, but he does not understand the meaning of words and sentences.
Imbecile children begin to walk late - about 2-3 years. All movements are poorly coordinated, precise motor skills are not formed. You can teach such children to be neat. Special educational programs can help slowly develop existing abilities and capabilities.
People with moderate mental retardation are often aggressive and angry and show inappropriate reactions. Sometimes they are characterized by an antisocial type of behavior. Imbeciles have simple and direct emotions, they show sympathy and they have a desire to help someone in trouble.
People with this disease are characterized by increased suggestibility and a desire to imitate not always the best examples. There is a feeling of self-esteem: a person is embarrassed about the violation of his physical development, his own awkwardness.
In adulthood, imbeciles are able to work if they need to perform simple practical tasks, with an accurate and understandable construction of the algorithm, under the supervision of managers.
It is almost impossible for an imbecile to live independently; periodic or constant supervision from loved ones is required. Despite this, they are completely mobile and agile, can make social contacts, and maintain a simple and understandable conversation.
Orphans diagnosed with moderate mental retardation, if possible, live in special homes for people with mental and thinking disorders in particular.
Some may be sent to study at a special school. In adulthood, they live in psychoneurological boarding schools. In rare cases, they try to provide for themselves by living separately.
Imbecility causes and symptoms
The causes of imbecility lie in hereditary factors (microcephaly, Down syndrome, intrauterine damage to the fetus, infectious diseases suffered by the mother, rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis), immunological incompatibility of the blood of the fetus and mother, various harmful effects on the fetus, and birth injuries.
In those suffering from imbecility, motor skills are poorly developed, movements are angular and uncoordinated. Small, precise, manual motor acts are inaccessible to them. Their gait is often stiff, awkward, and hunched over.
The face of imbeciles has no facial expression, it is frozen, dull, and the blinking of the eyes is very rare. Many patients have pronounced congenital stigmas (protruding ears, attached lobes, defective bite, rough structure of the facial skull, microcephalic or hydrocephalic skull). Those suffering from imbecility have focal neurological symptoms. It is difficult for such patients to master the skills of neatness, but they happily take on feasible work, are proud of their successes and express displeasure and anger if someone litters in the place they have cleaned. At the same time, patients exhibit poor switchability and extreme lack of independence.
Characteristics of imbecility
The intelligence quotient (IQ) is determined in imbeciles within the range of 20-50. The International Classification of Diseases distinguishes imbecility as pronounced, in which (IQ is 20-35), and moderately expressed, in which (IQ is 35-50).
Those suffering from imbecility understand speech addressed to them well and are able to pronounce short phrases, but their speech is poor and also has inaccuracies. The active dictionary consists of 200-300 words. Patients' thinking is sequential, concrete, primitive, distractions are inaccessible to them, and the supply of information is extremely narrow. Such people are characterized by a sharp underdevelopment of memory, attention, and will.
Characteristics of imbecility include the following signs: lack of initiative, inertia, suggestibility, loss in a new environment. For those suffering from imbecility, it is possible to instill the simplest work skills, teach counting, reading, and writing. Individuals are able to learn how to perform simple counting operations, as well as learn simple work skills and serve themselves independently. They are capable of rewinding threads, cleaning the yard or room, and performing one operation (for example, gluing boxes, washing dishes).
Emotions in patients are more varied than in idiots. They react adequately to reproach and praise and have a strong attachment to their family. Those suffering from imbecility are deprived of any initiative, are inert, suggestible, and easily get lost in a changed environment. Such people constantly need supervision and care, and an unfavorable environment can make imbeciles antisocial. Those suffering from imbecility do not have the ability to make generalizations or abstract thinking.
Degrees of imbecility
With this disease, three degrees of imbecility are noted: severe, moderate, and mild. All of them are expressed in various levels of mental underdevelopment. Assimilation of new material is given to patients with great difficulty. This happens within the framework of specific ideas and without any generalization. Imbeciles are incapable of thinking independently. Adaptation to the world around them is carried out only in a familiar and familiar environment. A slight change in the situation leads the patient to difficult moments, and he constantly needs guidance.
Those suffering from imbecility are very suggestible. Their personal interests are very primitive and boil down mainly to the fulfillment of physiological needs. They often show gluttony and sloppiness in eating. Their sexual behavior is characterized by fluctuations with increased sexual desire and promiscuity.
According to its behavior, oligophrenia in the degree of imbecility is divided into two groups. The first includes living, active, mobile people, and the second includes lethargic and apathetic, indifferent people who do not react to anything. According to character traits, imbeciles are distinguished as friendly, good-natured, flexible, sociable and aggressive, malicious. Those suffering from imbecility cannot live independently; they need constant qualified supervision. To do this, they are sent to special schools and institutions such as occupational therapy workshops.
Imbecility (Moderate mental retardation)
Depending on the severity of mental underdevelopment (the degree of decline in IQ), imbecility is distinguished between moderate (the severity of symptoms is minimal, IQ - 35-50), severe (IQ - 25-34) and deep (learning is almost impossible, IQ - 20-25).
Depending on the main character traits, patients can be good-natured, shy, aggressive and angry. The behavioral reaction to imbecility is also twofold. Some patients are apathetic and indifferent. Others, on the contrary, are highly mobile. The facial expression is not burdened with a facial reaction (a frozen or “doll” face). Characterized by slow blinking of the eyes. Most patients have a rather rough skull structure, often combined with developmental defects (defective bite, hydro- or microcephalic skull, pronounced distance of the ears from the skull).
Imbecility is accompanied by poor coordination and undeveloped motor skills. The movements of such patients are angular and constrained, and their gait is awkward, often stooped. Small manual actions that require precision are impossible. Patients focus mainly on their own needs, often showing gluttony and sexual promiscuity. Appearance is sloppy.
Thinking is quite primitive, generalization is inaccessible. However, such patients think sequentially. Imbecility is characterized by an extremely narrow outlook, lack of attention and will, and underdevelopment of memory. There is no independent thinking; patients think using patterns learned from outside. They perceive speech well, but their own abilities are limited to simple sentences. The vocabulary is scanty: only 200-300 words. At the same time, patients may make inaccuracies in describing something. Although learning is difficult, in a calm, familiar environment such patients can be taught basic counting and reading syllables.
Using the principle of repetition, imbeciles learn the basic rules of self-service and simple labor actions (winding threads, washing dishes, cleaning the room, etc.), but do not show their own initiative and are easily suggestible.
Imbecility is limited to satisfying one's own needs (sleep, nutrition, etc.). Many patients exhibit good hearing. In an unfamiliar environment, they are confused, and their behavior often becomes antisocial. The emotional background is more developed than with idiocy. Imbeciles become strongly attached to people who look after them and treat them well. Patients react particularly warmly to praise; reprimand causes them to react negatively. They experience strong affection (love) for their parents, call them by name, but often do not recognize them and frighten the people they know.
Imbecility causes problems with adaptation in society. Some patients feel depressingly inferior compared to other people. Attraction to work is also problematic; imbeciles work only according to learned patterns, the change of which causes them confusion. Active patients with an aggressive character often commit acts that are dangerous to themselves and society. There is a tendency to run away.
Imbecility treatment
Treatment is focused on proper education, as well as guiding the actions of patients. Doctors prescribe nootropic drugs, antipsychotics, tranquilizers; Classes with a speech therapist or psychoneurologist are recommended, and home training is recommended.
The normal school environment is not suitable for such patients. Children may have speech defects (stuttering, lisp, tongue-tiedness), which require correction. It is possible to teach imbeciles to count, read, and write, but they cannot do complex arithmetic operations.
An antisocial environment has a bad effect on imbeciles; for this reason, patients pose a threat to society. With the development of pathological uncontrollable situations, patients are hospitalized in a psychiatric hospital.
Treatment of imbecility is conventionally divided into specific (causal) and symptomatic. Specific therapy is carried out for phenylketonuria, as well as other enzymopathies. Hypothyroidism is treated with compensatory hormonal therapy (Thyroidin); congenital syphilis, toxoplasmosis is treated with antibiotics, Arsenic preparations, Chloridine; Brain infections in children are treated with antibiotics and sulfa drugs.
The earlier it is started, the more effective treatment is. The importance of corrective therapeutic and pedagogical measures is great.
The prognosis directly depends on the depth of mental retardation. Primary prevention includes medical and genetic counseling. Such consultation is carried out on the territory of medical genetic institutions.
Symptomatic therapy uses drugs that stimulate brain metabolism, these include (Cerebrolysin, Nootropil, Aminalon); B vitamins; psychostimulants (Phenamine, Sidnocarb); dehydrating agents (Lasix, Magnesium Sulfate, Diacarb); drugs with absorbable effect (Potassium Iodide, Biyoquinol); biogenic stimulants. Convulsive syndrome is relieved by systematic use of antiepileptic drugs.
Nature of the pathology
Disturbances in the higher functions of brain activity lead to pathologies in the development of the human personality. A distinctive feature of this congenital disease is the image of an “eternal child”. As a rule, imbeciles master only primitive life skills. Many of the children with this disease easily make contact with others and show different reactions when approached.
Problems associated with pathology of brain activity make it difficult to master complex sciences. This feature can be clearly seen in the example of mathematics. A person suffering from this disease is able to fold only objects that have a certain specificity. Adding or subtracting simple numbers in the head is an impossible task for imbecile children. Also, children with congenital brain diseases have problems with learning to read and write. Even in adulthood, most people only read syllables. The ability to express one's thoughts in writing is usually limited to monosyllabic phrases.
Most patients experience difficulties in mastering social and everyday skills. Many imbeciles cannot dress or eat food on their own. In order to teach a child to perform various actions, they should be repeated over a long time.
The diagnosis of “imbecilism” leaves a peculiar imprint on a person’s appearance. According to statistical data, most patients have a violation of the proportions of head size. It can either significantly exceed or decrease the norm. External signs of imbecility include deformed facial bones, a “petrified” look, earlobes attached to the head and an incorrect bite. Focal neurological lesions lead to problems related to fine motor skills. Most people with imbecility have problems with the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, which is expressed by poor coordination of movements. To assess the extent of the problem, imagine that you cannot cope with such a habitual action as tying your shoelaces.
Imbecility is characterized by a congenital or acquired mental development defect in early childhood, which does not increase throughout life (but can be partially corrected)
In simple terms, this disease is characterized as “freezing” at the age of seven. Parents of people with the problem in question are perceived by the latter as an object of inexhaustible love. Imbeciles start their own family only in isolated cases. As a rule, their social circle is limited only to close relatives and members of rehabilitation groups.
The vocabulary of people with imbelicism is limited to a few hundred simple words that are used only when necessary. In speech, only monosyllabic sentences consisting of several phrases are used. The development of thinking stops at a primitive level, which is reflected in emotional manifestations. Most people with this pathology experience a complete absence of the volitional factor. If usual living conditions change, the patient may experience a feeling of severe fear. Lack of initiative, passivity and a high degree of suggestibility contribute to the high influence of the opinions of others on the behavioral model. Based on the above, we can conclude that throughout his life the patient needs constant supervision and control from relatives.
The patient's horizons have rigid boundaries, and almost never exceed the framework of satisfying simple instincts. Doctors say that many patients do not feel full, which forces them to eat double portions.
A person with this problem should constantly learn basic rules of behavior.
Without parental and medical supervision, imbeciles can become a danger to themselves and those around them. Each holder of this diagnosis experiences difficulties associated with sexual disinhibition, which are expressed in the form of a lack of self-control of sexual desire. Violations in this area can lead to antisocial behavior, harassment of the fair sex and sexual crimes.
What is imbecility in children
Imbecility is a mental retardation of moderate severity, which can be either congenital, for example, Down syndrome, or acquired in the first few years of life. This disorder is characterized by the fact that it does not develop throughout life, but with the right approach to treating and raising such a child, a slight improvement in mental activity can be achieved.
- Etiology
- Varieties
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
In addition to dementia, this disease is accompanied by such signs as clear speech, but a poor vocabulary, and poor learning ability. Memory problems and sexual promiscuity are also observed. Such people can perform basic self-care activities, but will not be able to live independently.
This type of moderate dementia is quite rare in people. In the world, less than half a percent of the total population suffers from imbecility.
People with such a diagnosis are more susceptible to severe changes in the psyche than patients with a mild degree (moronicity) of dementia, but they can express emotions much better than patients with a deep degree (idiocy) of mental development. People with such a defect are prone to being highly suggestible and imitating bad examples, which is why they need constant supervision and discipline. If raised incorrectly, they can be aggressive and harm not only themselves, but also the people around them.
Types of the disease and causes of its occurrence
Imbecility, what is it? When examining this issue, it should be said that the disease in question is divided into four types, which differ in the reasons that provoked the development of the pathology. The hereditary type of the disease is associated with the presence of defective genes received from parents. The intrauterine type of pathology develops against the background of bacterial or viral lesions of the fetus during intrauterine development. There is also a special form of delayed intellectual development, provoked by pathologies in the functioning of the brain or endocrine system.
Along with external signs of underdevelopment of intelligence, primitive speech and underdeveloped learning abilities are observed
In addition, there is a type of imbecilism that is caused by asphyxia, brain hypoxia or birth injuries. This form of pathology can occur against the background of traumatic brain injury or serious infectious diseases in infancy. According to experts, there are many different factors that provoke disruptions in mental development. These factors fall into three categories:
- The first category is internal factors, the list of which includes poor heredity, genetic disorders and chromosomal abnormalities.
- The second category is external factors, among which we should highlight the presence of acute infectious diseases during gestation, or prolonged use of narcotic drugs by the child’s parents. This category of factors also includes traumatic brain injuries received during birth.
- The third category is the combination of the influence of external and internal factors, which significantly increases the risk of developing imbecility.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, pathology occurs during the prenatal period of the child's development. Several factors contribute to this process:
- chromosomal and gene abnormalities (Angelman, Down syndrome);
- hereditary predisposition.
The cause may be an infectious disease suffered by the expectant mother (rubella, syphilis, cytomegalovirus). Also, sometimes pathology can be triggered by a Rh conflict between mother and baby, that is, immunological incompatibility of blood.
Damaging factors leading to the emergence of a pathological process are chemicals (alcohol, drugs) and an increase in the dose of certain radiations (for example, a pregnant woman undergoing X-ray examinations too often).
In addition, a child's imbecility can be caused by a lack of iodine in the mother's body. During the formation of the baby’s nervous system, this microelement plays a special role. Insufficient nutrition or lack of vitamins, as well as micro- and macroelements, increases the risk of developing this disease.
In infancy, imbecility can develop as a result of difficult childbirth, accompanied by injury and asphyxia of the fetus, childhood infections and traumatic brain injuries. Sometimes pathology occurs due to lack of communication with adults. As a rule, this factor, together with poor nutrition (lack of iodine), manifests itself in dysfunctional families. In general, the development of imbecility is provoked both by abnormalities in the child’s nervous system and by the cessation of his intellectual development after birth (social factor).
Severity of pathology
Oligophrenia is divided into three forms of severity, each of which is determined by the degree of mental retardation. Imbecilism, which is a moderate degree of mental retardation, also has several divisions. This pathology is divided into moderate and severe forms. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Moderate imbecility is a condition in which the IQ ranges from thirty-four to forty-eight points. In this condition, there is limited intellectual ability, which is associated with certain situations. People with this form of the disease lack analytical and associative thinking.
The paucity of vocabulary and incorrect construction of sentences forces the patient to use speech skills only in cases of urgent need. The intensity of emotional perception is extremely low. The vast majority of patients experience neurological and psychomotor impairment. Organic lesions of parts of the brain provoke the development of epileptic seizures and symptoms of autism.
With severe imbecilism, IQ scores vary from twenty to thirty-four points. It should be noted that with this form of the disease, neurological symptoms are pronounced. Many patients experience paralysis and significant impairments in psychomotor functions. The degree of personal and intellectual development can be compared with a five-year-old child. The same can be said about vocabulary. People with this form of pathology need constant monitoring and assistance in self-care.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of the clinical picture, assessment of intellectual and psychomotor development
The concept of the definition of imbeciles and statistics of occurrence
The word imbecil is of Latin origin: imbecillus - this was the name in ancient times for weak, sick and non-viable babies, who were quickly disposed of.
Imbecility is a mental illness that arises as a result of a violation of ontogenesis (development of the body at the stages of formation). Imbecility is manifested by underdevelopment, first of all, of intellectual functions and clinically corresponds to moderate and severe mental retardation (according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision).
It should also be noted that not only mental factors are highlighted, but also the appearance of the person himself, his characteristic appearance, and body composition. Delayed physical development, defects of organs and body parts (head, limbs, internal organs) are possible. Thus, from very early childhood, various disorders and developmental features appear. An imbecile, as a rule, has a limited vocabulary, represented by simple individual words. Concrete thinking, no imagination or figurative representation. Imbeciles do not have a wide range of knowledge, but can learn basic reading and arithmetic skills with good teaching.
The diagnosis of oligophrenia is made on the basis of IQ. An IQ score of 31 – 49 corresponds to moderate mental retardation, and 20 – 34 – severe. Mental age stops at 6–9 years for moderate cases, and 3–6 years for severe cases.
The actual number of patients is difficult to calculate within a single region of the country. This depends not only on the detection of the disease and diagnostic criteria, but also on the characteristics of culture, society, and the current education and upbringing system. Thus, the prevalence of mental retardation ranges from 1 to 3% of the total population.
Diagnostic methods and testing
In order to understand who an imbecile is, you should familiarize yourself with the methods of diagnosing this pathology. According to experts, disorders in the field of brain development can be diagnosed at certain stages of pregnancy. The screening technique allows you to determine the pathology within the first few months. Diagnosis of the level of intellectual development is carried out using various tests and the Wechsler scale. According to established standards, the intellectual development coefficient for this disease varies from twenty to sixty points, taking into account the severity of the disease.
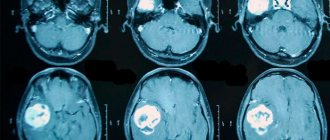
If, as a result of the studies, the patient scores less than fifty-five points, he may be diagnosed with imbecilism. Also, such tests conducted by a neuropsychiatrist help assess intellectual potential. During a diagnostic examination, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient in order to find out the level of development of the speech apparatus, the breadth of interests and social adaptation. The causes of the disease can be determined using procedures such as magnetic resonance and computed tomography. An electroencephalogram can be used as an additional diagnostic method. In cases of suspected vascular abnormalities, angiography is used.
The photos of imbeciles given in the article allow you to clearly see the anomalies in the development of the human body. It should be noted that imbecility has many similarities with other mental illnesses. The pathology in question has the same clinical manifestations as diseases such as dementia, juvenile schizophrenia and epilepsy.
Diagnosis of imbecility
Despite the fact that all the symptoms of imbecility are visible to the naked eye, diagnosis should only be carried out by a qualified specialist. The degree of mental impairment is determined by IQ level. But in addition, the course of pregnancy in the mother of such a child, diseases suffered by both the woman and the child, living conditions and clarification of the time of manifestation of the first symptoms are taken into account.
The main task of diagnosis is to distinguish imbecility from other mental disorders. To do this, a consultation with a child psychotherapist is carried out. When such a doctor and a child communicate, special scales and questionnaires are used, according to which the specialist determines the degree of mental retardation. The doctor evaluates the child’s speech abilities, the child’s level of social adaptation and his attachment to relatives. With such a comprehensive approach, identifying the deep stage is quite easy.
In addition, the small patient will need to undergo a CT and MRI of the brain, which will give a complete picture of its structure and show possible injuries or hemorrhages.
How to treat imbecility?
Treatment methods for imbeciles logically follow from the answer to the question, what is imbecility. Complete recovery of the patient is unattainable; all therapeutic interventions are aimed at reducing the severity of associated symptoms and maximizing socialization. Drug treatment of imbeciles is carried out in the following areas:
- Neurometabolics are drugs that nourish brain tissue.
- Dehydrants are pharmaceutical agents that reduce the number of seizures. For this purpose, diets are also used: salt-free and low-water.
- Tranquilizers for the correction of behavioral deviations.
- General restoratives, including tinctures of medicinal herbs.
- In some cases, antidepressants are indicated.
For a person suffering from a disease such as imbecility, proper care is very important to prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases; three times a day of hospital treatment is indicated throughout the year. Also, families raising imbeciles need to work with a psychologist to improve the adaptation of the ward.
Degrees of mental retardation
Delayed brain development can be expressed in different ways. With a mild degree, patients not only take care of themselves, but also freely carry out everyday activities, for example, going to the store, talking with others on everyday topics. Plus, they can work. A severe degree is characterized by a complete lack of thinking. Oligophrenics are divided into 3 types:
- Morons.
- Imbeciles.
- Idiots.
Moronism is a mild degree of mental retardation, in which patients are quite independent, understand speech addressed to them, and are able to answer simple questions. The intellectual development coefficient of such patients is 50-70%.
Oligophrenia in the degree of imbecility is regarded as an average condition. The intellectual coefficient of patients is 20-50%. Imbeciles are people who are able to understand the simplest appeal to them, serve themselves, and also show their emotions.
A severe degree of oligophrenia is idiocy (IQ less than 20%). These patients require constant care, as they are unable to exist independently. Idiots almost completely lack thinking, they do not understand the meaning of words addressed to them, their loved ones must serve them.