Description
Hypertension syndrome in newborns is one of the most common neurological diseases in children. The disease is an increase in intracranial blood pressure. It can be a symptom of hydrocephalus, where excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the lining of the brain.
There are 2 forms of the disease - acute and chronic. Acute is characterized by a sharp increase in pressure, which can lead to coma or severe brain damage. The chronic form manifests itself in a slight increase in intracranial pressure, which does not pose a particular danger to the child.
Severity
Hypertensive syndrome – ICD code 10, has 3 stages. They are assessed by the level of systolic and diastolic pressure. Deviations from the norm throughout the day are also taken into account. The stages of the syndrome reflect temporary and sequential changes in the body.
| stage | blood pressure indicators | possible violations | |
| Stage 1 blood pressure or moderate hypertension | 65-114 | 140-179 | No disturbances from the central nervous system |
| Stage 2 blood pressure or severe hypertension | 115-124 | 180-209 | There is a focal narrowing of the retinal arteries, the concentration of creatinine in the plasma increases, albeit slightly, and atherosclerotic plaques appear |
| Stage 3 hypertension or very severe hypertension | 125 and above | 210 and above | Heart failure, heart attack, coronary disease, aneurysm dissection, occlusive pathologies appear. |
Development mechanism
Intracranial pressure is the difference between pressure inside the skull and atmospheric pressure. Normally, its values vary from 1.5 to 6 mm Hg. Art. for newborns and from 3 to 7 mm Hg. Art. for children aged 1 year and older. When these indicators increase, increased intracranial pressure is diagnosed.
According to the Monroe-Kelly doctrine, the cranial cavity is an enclosed space filled with fluids. Normally, it is 85% brain matter, 10% cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and 5% blood. If there is more of a substance, hypertension syndrome occurs. Most often this is cerebrospinal fluid. Such changes impede normal blood flow and cause headaches and other unpleasant symptoms of the pathology.
Most patients with this diagnosis are cured within 6 months or 1 year. For some, increased intracranial pressure persists for life. For such patients, it is important to visit a neurologist every six months to monitor the development of pathology and receive recommendations for eliminating symptoms. Consultations also include X-rays of the head and fundus examination to monitor the pathological condition.
Possible manifestations of Graefe's symptom in newborns: why does a baby's eyes bulge?
Often, fathers and mothers complain of some signs characteristic of Graefe's symptom in an infant. It is also called setting sun syndrome. What is this pathology, should we be afraid of it and in what cases? Why can a baby bulge his eyes?
Graefe syndrome in an infant
What is the setting sun sign in newborns?
Graefe's syndrome is often observed in hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
This is a condition in which the ventricles of the brain contain large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid due to increased intracranial pressure.
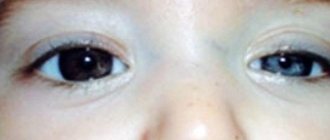
Clinically manifested by the appearance of a white stripe above the iris of the eye. This sign is especially pronounced when the baby looks down or to the side.
Sunset syndrome in children
The positive is that the presence of Graefe's symptom in newborns is not always associated with hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. This disease is rarely detected, although the symptom itself occurs quite often in infants under the age of one year. It is better to consult a doctor in time to prevent negative consequences.
Why does a child stare and stare?
Parents may often notice that the child's eyes are bulging (the reasons why this happens naturally concern them). A child can stare even if he is completely healthy. If this condition appears before 4 months when the lighting changes, there is no need to worry. These may be features of visual focusing that have nothing to do with Graefe's symptom.
Important ! In any case, if some pathology of the peephole is visible, there is no need to panic. Inappropriate fear can only cause harm.
Main manifestations
One of the main signs that Graefe's symptom has in infants is that the newborn stares. Hypertensive -hydrocephalic syndrome may be characterized by other signs, such as:
- Severe strabismus;
- Frequent and profuse regurgitation;
- Convulsions, sudden shaking of the baby in his sleep;
- Low severity of congenital reflexes;
- Decreased muscle tone, arms and legs droop.
Child goggles his eyes
If at least one of the above symptoms is detected, it is necessary to draw the pediatrician’s attention to them.
Why is it dangerous?
Without timely diagnosis and treatment of setting sun syndrome, fecal and urinary incontinence, blindness and deafness, mental and physical retardation, epileptic seizures, coma and cerebral palsy can develop. Death is also possible.
Important ! The sooner you see a doctor, the higher the likelihood that everything will be fine.
A stripe above the iris of a baby
Dr. Komarovsky said that in most cases there is no cause for concern. Everything depends on the results of the examination. If they are normal, then everything is fine. Therefore, you still need to see a doctor for an ultrasound of the brain.
Causes
How long does Graefe syndrome last? Normally, the Grefe symptom goes away on its own about two weeks after the baby is born. In this case, the reason is the immaturity of the nervous system, which still needs to adapt to the new realities of life. If the baby is premature, the symptom of the setting sun in an infant may last longer, since it takes more time to adapt.
Among other things, the reason may be the structural features of the eyeball. Then no medical manipulations are needed. After a while, this feature won't attract as much attention. If the baby has a confirmed diagnosis, parents should contact a neurologist.
Most often the syndrome is caused by the following reasons:
- Diseases of women in the prenatal period;
- The rate of labor is too high or low;
- Complications in the prenatal period and during childbirth;
- Prematurity of the fetus or, conversely, postmaturity;
- Hereditary factors;
- Increased thyroid function – hyperthyroidism.
Diagnosis of the symptom
The main diagnostic method is neurosonography (in simple words, ultrasound examination of the brain). As a result of the examination, it may be discovered that the baby has dilated ventricles of the brain. In most cases, this is followed by a diagnosis of hypertension syndrome, which is translated into simple language as “increased intracranial pressure.”
Protruding eyes may not always indicate this. It may also be that the examination shows that everything is normal, but there are signs of a disorder. Then the doctor prescribes additional examinations or says that there is no need to worry.
The doctor needs to compare the results of the NSG with a specific child. If the examination does not reveal any pathology, but the baby is restless and does not feel well, then he needs medical attention.
What does a doctor do
The actions taken by the doctor depend entirely on the symptoms present and the rate of development of the disease. If the baby’s only symptom is bulging eyes, but the NSG does not reveal a terrible diagnosis, then it is enough to simply regularly show the baby to a neurologist, as well as carry out therapeutic exercises, massage and relaxing baths.
If hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is detected, then at the initial stage the following outpatient measures are sufficient:
- Diuretics that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Nootropics are a group of drugs that improve brain nutrition.
- Sedatives that relax the baby's nervous system.
If the rate of development of the disease is high, it is necessary to admit the newborn to a neurosurgical hospital. This requires the installation of a shunt system that does not allow cerebrospinal fluid to remain in the head. It redirects it to the atrium or abdominal cavity.
Important! There is currently no alternative to this method, despite the large number of complications of this operation.
In addition, endoscopic operations can be performed, which show less effectiveness, but also minimize the likelihood of complications. True, in this case you will still have to carry out bypass surgery, albeit a little later.
Prevention and prognosis
If Graefe's symptom is caused by hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, then the prognosis can vary from conditionally optimistic to pessimistic.
Possible complications
The list of complications of the disease without treatment was given above. The operation itself can also lead to negative consequences. Even if this does not happen, it is necessary to regularly show the child to a neurosurgeon, ophthalmologist and pediatric neurologist. The child is granted disability.
At any moment, the shunt system may stop performing its function. Therefore, repeat surgery may be required. It is also possible that the body may become infected due to poor quality treatment.
None of these points is an argument for refusing medical intervention. This is the only way to raise a child to be adapted.
Causes
Hypertension syndrome in infants can occur due to a number of the following reasons:
- complications during pregnancy;
- premature labor;
- mechanical injuries during childbirth;
- child development abnormalities;
- hypoxia (lack of air), which persists for more than 10 hours;
- traumatic brain injuries and cerebral hemorrhages that occur during intrauterine development;
- illnesses suffered during pregnancy.
It is important to monitor your health during pregnancy in order to avoid possible complications.
Causes that cause the syndrome
The appearance of additional fluid or tissue that exceeds the space of the skull and compresses the brain.
Neoplasms, bleeding into the brain, impaired movement of cerebrospinal fluid, all kinds of trauma, infectious, inflammatory diseases, vascular damage to the brain, hypoxia, infection of the fetus in the womb, trauma at birth.
Most cases of hypertension syndrome in children and adults occur due to the occurrence of malignant or benign brain tumors, cysts, hematomas, abscesses, disturbances in the development of the circulatory system and large vasodilation, which leads to increased pressure and compression of the brain matter in the head.
An increase in intracranial pressure leads to cerebral edema as a result of stroke, meningitis, bruise, damage by toxic substances, or oxygen deficiency. Heavy flow of blood through the veins with damage to the vessels of the brain, pathologies of the vascular bed, defects in the bones of the spine leads to the accumulation of blood in the brain, which leads to a slow increase in pressure.
Doctors identify a number of causes for the syndrome:
- hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome can be caused by tumor processes in the brain;
- hematomas;
- hypotonicity of blood vessels;
- intracranial hemorrhages;
- various neuroinfections (meningitis, encephalitis);
- traumatic brain injuries;
- pathologies acquired at birth;
- heredity.
Thus, all causes can be divided into congenital and acquired.
Congenital causes of hypertension syndrome in adults are:
- complicated pregnancy and childbirth (gestational pyelonephritis, pregnancy diabetes, increased intracranial pressure, rapid and protracted labor, threatened miscarriage);
- brain hypoxia (bradycardia, fetal hypoxia and intrauterine developmental delay);
- prematurity (birth before 34-36 weeks) and late birth (42 weeks or more);
- subarachnoid hemorrhages (head injuries during childbirth);
- intrauterine infections (cytomegalovirus infection, Eppstein-Barr virus, toxoplasmosis and others);
- congenital brain defects (absence of a large part of the brain, formed hemispheres, presence of cysts, too small head size, abnormalities of the skull, brain stem);
- long waterless period (more than 12 hours).
Acquired causes include:
- hematomas, tumors, abscesses, cysts;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the brain;
- traumatic brain injuries with the presence of fragments of skull bones in the brain;
- spontaneous causeless increases in blood pressure;
- infections;
- strokes and their consequences;
- endocrinological problems.
Clinical manifestations of the syndrome
A mild form of hypertension syndrome may have no manifestations, since children's cranial bones are characterized by increased elasticity, and the fontanelles can expand, which will significantly reduce the pressure. In 90% of cases when a child was diagnosed with “mild hypertension syndrome,” a detailed study does not confirm it. This form of the disease does not pose a danger to the child. The acute form is characterized by the following symptoms:
- protrusion of the fontanel;
- increase in head volume;
- frequent regurgitation during feeding, refusal to eat;
- lethargy;
- frequent crying for no apparent reason;
- tremors or cramps of the limbs;
- swelling of the eyeballs.
Older children (from 2 years old) may have the following complaints:
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- headaches, especially after waking up;
- memory problems;
- inability to turn your head without pain;
- photophobia.
These signs of hypertension syndrome require contacting a doctor to determine further steps to treat the pathology.
Hypertension syndrome Dr. Komarovsky
Babies are often diagnosed with hydrocephalic syndrome. In fact, hydrocephalic syndrome in infants is not such a common occurrence. What kind of pathology is this, and what does it threaten? What are its features?
Subsequent examination may not confirm hydrocephalic syndrome in a child. Even if the diagnosis is confirmed, do not be alarmed. The main thing is to have the information and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Hydrocephalic syndrome in adults has its own characteristics. It is provoked not by congenital, but by acquired pathologies of brain nutrition.
Peculiarities
All signs of hydrocephalic syndrome are associated with the fact that an excessive amount of cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the head. It should be there, but the volume is important. When there is an excess, cerebrospinal fluid begins to compress brain tissue, causing disruption of their functioning.
Fluid in the brain accumulates during development in the womb. Normally, before the birth of a child, its amount decreases. If this does not happen, the baby may lag behind in development and will suffer from high intracranial pressure.
Parents should not panic if such a diagnosis is confirmed. We'll fix everything. Correction is possible, especially if the baby is not yet six months old. The main thing is not to delay treatment and strictly follow all recommendations.
Hypertension syndrome in newborns can provoke an increase in intracranial pressure, but this is not an independent diagnosis. This is a symptom. He appears and then retreats for a while. Such jumps can be caused by emotional stress, physical activity and even food intake. In this case, there is no need to treat ICP. It is dangerous only in advanced hydrocephalus.
It is important to determine the origin of HGS in each specific case. For correction, massage is used in combination with drug treatment (do not confuse it with the mentioned syndrome).
Development mechanism
Hypertension syndrome develops differently in adults, newborns and children. In the womb, the child grows quickly, and the system that feeds the brain rapidly develops. At first, it feeds only through blood, then, as it develops, cerebrospinal fluid also joins. By the end of intrauterine development, not only blood, but also spinal nutrition should be formed.
Each of us in the sixth month of development in the womb had quite a lot of fluid in the head. This is due to the fact that the ventricles of the fetal brain are wider. Then they should narrow and return to normal before birth. Then the cerebrospinal fluid completely leaves the head.
If this does not happen or the process has slowed down, a diagnosis of “hypertensive syndrome in infants” is made.
Do not confuse hypertensive hydrocephalic syndrome with hydrocephalus. These are two different diagnoses. The latter has more serious consequences and develops differently.
Kinds
HHS can develop not only in infants. It may appear in:
- newborns;
- children;
- adults.
Causes
There may be several reasons for this pathology in newborns. Most often this is:
- infections;
- complications during pregnancy;
- brain damage;
- prematurity;
- abnormalities of brain development;
- long stay without water (12 hours or more);
- chronic diseases (mothers);
- trauma during childbirth.
The diagnosis of “hypertensive hydrocephalic syndrome” is usually made only in the countries of the former USSR. Russia is no exception. In the West, it is considered a manifestation of certain brain pathologies.
During pregnancy, it is important to take all tests and monitor general blood counts. An analysis for toxoplasmosis will help prevent a crisis and identify the problem in time.
Acquired reasons:
- hematoma, abscess, tumor, brain cysts;
- foreign bodies;
- bone fragments that entered the brain during a skull fracture;
- intracranial hypertension;
- infections;
- metabolic disorders;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- disorders after a stroke.
The listed reasons may indirectly affect the drainage of fluid from the brain area. The disease itself manifests itself in different ways - from mild to severe. Symptoms become especially pronounced if the disease is not treated.
Toxoplasmosis can provoke not only hydrocephalic syndrome. It leads to serious disorders of the central nervous system. Manifestations will not keep you waiting. The most dangerous thing is encephalopathy. This is a pathological condition of the brain in which nerve cells die and dystrophic changes occur. Brain functions are seriously impaired.
Hypoxia, prematurity (deep), and infections can disrupt the normal development of the fetus.
Childbirth itself is also extremely dangerous for the baby. Although this is a natural process, it often leads to complications and injuries. Childbirth can cause hemorrhages, injuries, and hypoxia.
An external open or closed fracture or dislocation may even occur. All these reasons can provoke a serious imbalance between the process of production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. But it is he, along with blood, that nourishes the brain.
It is important to sub-compensate for loads.
Sometimes after birth the baby has a residual syndrome. These are changes in brain tissue and functions due to mechanical trauma.
Symptoms
It is very difficult to determine visually whether these are symptoms of the syndrome or behavioral characteristics of the baby. Pathology manifests itself in different ways. The nature of the manifestations depends on the form, degree of the disease, and its cause. However, there are still signs that may be symptoms of HGS:
- irritability;
- anxiety;
- the child has poor sleep;
- frequent and prolonged cry of the baby;
- lethargy;
- low activity;
- drowsiness.
The severity of symptoms depends on the genesis of the disease. Many of them are the result of hypertension. Children with HGS may experience bulging of the eyes, Graeffe's sign (a noticeable white stripe forms between the upper eyelid and the pupil).
With severe development, the upper eyelid may half cover the eye (the “setting sun” symptom). Such children may develop strabismus and throw their heads back. Muscle tone can be either decreased or abnormally increased.
This is especially noticeable in the leg muscles. The child may walk on tiptoes. Such symptoms should alert you. You need to immediately show the child to the pediatrician, and if necessary, he will refer you to a pediatric neurologist.
Therapy must be comprehensive.
In children with this syndrome, reflexes (walking, crawling, grasping) are reduced. Such movement disorders often accompany HGS. Hypertensive abnormalities are often observed.
The listed symptoms also occur with other pathologies, for example, with perinatal encephalopathy (PEP). It often results from prolonged intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen deficiency).
PEP becomes the result of disruption of intrauterine development processes. The child can recover, but long-term developmental activities are needed.
It is important to exclude other diseases. With PEP, it is strictly forbidden to prescribe diuretics. They can cause heart problems and interfere with neuro-reflex processes. But for HGS and hypertension they are indicated.
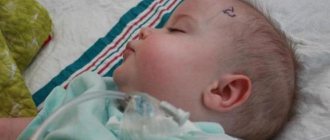
A mandatory symptom of HGS is pathological changes in the size of the baby’s head circumference. She's growing too fast. In a month, 1.5 cm or more may increase. At the same time, the seams of the skull may swell, and the shape of the head itself changes.
Some people may have a naturally large head. This is a genetic feature, not a symptom of pathology. This is why it is important to do an ultrasound and not guess based on tactile and visual examination. If one of the parents has a large head, then the baby’s large head is not a pathology.
HGS does not manifest itself in newborns. In older children, HGS is often associated with infection or trauma. Characteristic symptoms:
- I often have a headache (the pain is throbbing, bursting or aching, more often happens in the morning). Localization – forehead, temples, brow ridges;
- nausea, vomiting;
- the child has difficulty lowering his head or raising his eyes;
- dizziness;
- may see double and consciousness may be impaired;
- Sometimes there are convulsions and even coma.
During a painful attack, the child may turn pale, be lethargic, and feel general weakness. He is bothered by a loud sound and the light seems bright.
Diagnostic features
Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is very insidious. It is not easy to diagnose, especially at an early stage. Only a pediatric neurologist can make the correct diagnosis. He will determine the degree of pathology, its causes, changes in the tissue structure of the brain.
Moreover, it is based on head ultrasound data. As they say, it is impossible to make such a diagnosis by eye, although many pediatricians are guilty of this.
At the first signs of nervousness, poor sleep, or suspicion of increased intracranial pressure, doctors rush to announce the diagnosis of “hydrocephalic syndrome.”
By the way, in 95% of cases such an intuitive diagnosis is not confirmed again. It often turns out that this is not a disease, but the behavioral characteristics of a particular child. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the disease often has a moderate manifestation.
Even instrumental methods do not always help in making a diagnosis. If we are talking about a baby, it is important to monitor the dynamics of the increase in head circumference and check reflexes.
The following methods are also used:
- the condition of the fundus vessels is analyzed;
- neurosonography is performed;
- sometimes a puncture is made in the lumbar region to analyze the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid (this method is considered the most reliable);
- CT scan;
- nuclear magnetic resonance.
If the diagnosis is confirmed
If ultrasound and neurosonography confirm HGS, you will need to:
- treat the baby with medication;
- visit a massage therapist regularly;
- postpone routine vaccinations for a while.
The healing power of massage should not be underestimated. A competent massage therapist can work miracles. It is indispensable in the treatment of HGS. Replacement therapy is also important. It compensates for the insufficient output of cerebrospinal fluid. It is important to treat not the symptoms, for example, high intracranial pressure, muscle tone disorders, poor sleep, but the cause. Specific treatment methods should be selected by a neurologist - pediatric or adult.
Treatment
A neurologist selects the correct treatment regimen. In severe cases, the assistance of a neurosurgeon may be required. An ophthalmologist is often involved. He analyzes how full the vessels of the fundus are, whether they are spasming, etc. Such patients are treated in neurological departments or centers.
Treating a newborn
Traditional methods will not help here. Unqualified treatment can lead to disastrous consequences. Babies up to 6 months are treated on an outpatient basis. The following activities will be required:
- Treatment with diacarb. This is a diuretic. It reduces the production of cerebrospinal fluid. Enhances fluid removal.
- Using nootropics. These drugs stimulate blood supply to the brain (Actovegin, Piracetam, Asparkam).
- Treatment with sedatives (Tazepam, Diazepam).
- A professional massage is a must.
We treat older children and adults
When selecting methods and means of therapy, the doctor must take into account the specific cause of the syndrome. If it is a neuroinfection, treatment with antibiotics or antiviral drugs will be required. Injuries often require the help of a surgeon.
Prognosis, complications
Complications can develop at any age:
- deafness;
- blindness;
- developmental delay;
- paralysis;
- coma;
- epilepsy;
- fontanelle disorders;
- fecal and urinary incontinence;
- mortality.
The younger the child who gets sick, the better the prognosis. The pathology is most easily tolerated by children under 6 months. Their condition can quickly stabilize. Blood pressure, even if it fluctuates, quickly returns to normal.
For older children, the prognosis will be relatively favorable. It will be affected by the reasons, timeliness of treatment, and its adequacy.
conclusions
Hydrocephalic syndrome requires serious attention. Treatment should not be delayed. Remember that it depends on the parents how healthy and developed the child will be!
Source: vsepromozg.ru
Diagnosis of the disease
Hypertension syndrome in young children, especially newborns, cannot be determined based on the patient’s complaints. Therefore, diagnostic measures are carried out to identify the disease:
- X-ray of the skull.
- Echoencephalography is an ultrasound examination of the brain.
- Rheoencephalography is a study of the vascular system of the brain by passing a weak high-frequency electric current through it.
- Computed tomography is a method of examining internal organs using x-rays.
- Angiography is a study of the condition of blood vessels.
- Lumbar puncture, which measures the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Examination by an ophthalmologist who examines the fundus of the eye to detect swelling of the optic disc.
- Examination at birth, during which it is difficult not to notice the syndrome - this is facilitated by the baby’s enlarged head.
- Neurosonography is an examination that is carried out through open fontanelles using an ultrasound diagnostic device. It determines the presence of the syndrome and obstacles to the normal outflow of fluid. This diagnostic method is used in the first years of a child’s life, while the fontanelles have not yet closed, then the method becomes useless and is replaced by radiography.
The results of the diagnostics are assessed by the treating neurologist. Research data helps prescribe the correct therapy in accordance with the form of the identified pathology.
Symptoms and signs that accompany the syndrome
The symptoms of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome (signs) are as follows:
- headache;
- anxiety, insomnia;
- visual impairment;
- the appearance of a vascular session;
- deafness, loss of consciousness, coma;
- deviations in head size and others.
What is Ekbom syndrome and how to treat restless legs syndrome? What causes the disease and is it possible to help yourself at home? Why is grade 1 dyscirculatory encephalopathy difficult to diagnose and what symptoms and signs indicate the disease.
Drug treatment of the syndrome
Treatment of hypertension syndrome is aimed at improving blood circulation, as well as reducing the production of cerebrospinal fluid, the abundance of which leads to accumulation in the meninges and hydrocephalus. The following drugs are used:
- “Furosemide”, “Veroshpiron”, “Diacarb” increase the movement of cerebrospinal fluid and also remove excess fluid from the body.
- "Eufillin" and "Rigematin" are used to normalize the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid through blood vessels.
- When a secondary infection occurs, antibiotics are used.
- “Nootropil”, “Aminalon”, “Lipocerebrin” accelerate metabolism in nerve cells.
- "Eskuzan" increases vascular tone.
- Tinctures of motherwort, valerian and mint contribute to the overall calming of the child.
- Cavinton and Cinnarizine are used to improve blood circulation.
Most drugs are administered by injection and in the form of syrups and suspensions, since other methods are not suitable for a newborn baby. For older children, it is possible to use drugs in tablets.
Therapy
Hypertensive syndrome detected? Treatment must be carried out necessarily, since the pathology leads to the development of serious changes in the body. Consistently high pressure inside the skull leads to a decrease in mental abilities and disrupts the nervous regulation of the functioning of internal organs. As a result, the condition leads to a stable increase in blood pressure and hormonal changes.
In most cases, diuretics are used to reduce intracranial pressure. These drugs allow you to change the rate of cerebrospinal fluid secretion. Therapeutic activities are carried out in courses. In cases where relapses occur constantly, the drugs are taken on an ongoing basis. If the syndrome is detected at the initial stage or is moderate, you can do without drug treatment by normalizing the drinking regime.
To cure hypertensive syndrome, neurology suggests using manual therapy and osteopathy. What it is?
Osteopathy is an integral part of manual therapy and a fairly young area of alternative medicine. An osteopathic doctor is a palpation specialist who not only helps to get rid of pathology, but can also distinguish with his hands even the slightest changes in muscle, joint and bone mass. When treating the syndrome, an osteopath helps to relieve the venous bed of the head.
The doctor may recommend gymnastic exercises that will reduce intracranial pressure. Fruit juice with glycerin shows good effectiveness. The dosage for dilution is prescribed by the doctor, and the mixture is used several teaspoons per day.
In case of exacerbation of the disease with cerebral edema, hypertonic solutions are used. Urea is used less frequently due to the huge list of side effects.
If the cause of the syndrome is osteochondrosis, massage and physical therapy complexes are prescribed. That is, measures aimed at improving blood circulation.
If the pathology is complicated, surgery may be recommended. The main goal of surgery is to eliminate excess cerebrospinal fluid, which will help reduce blood pressure. Despite the pain of the operation, its effectiveness is very high.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated in cases where the pathology cannot be eliminated with medications. If hypertension syndrome is caused by brain tumors, hematomas or foreign objects, the cause should be immediately eliminated surgically.
It is possible to reduce intracranial pressure using craniotomy (drilling holes in the bones of the skull) or puncture of the ventricles of the brain to remove excess fluid. If the situation is life-threatening, shunting is possible, which quickly removes excess fluid from the brain.
Diagnostic techniques
To diagnose this disease, a comprehensive clinical examination is mandatory. It includes examination by specialists and hardware tests.
Ophthalmologists, neurologists, psychiatrists, and neurosurgeons work with hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
To determine the cause of the disease, hardware tests are carried out such as:
- echoencephalography (EchEG) is a highly accurate diagnosis of brain lesions;
- rheoencephalogram (REG) – study of venous outflow of blood from the vessels of the brain;
- radiography of the skull (SCH) – used for long-term development of the disease in children over 1 year of age;
- nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and computed tomography (CT) - highly accurate determination of areas of disturbance in the dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid, the size of the brain cavities, and so on;
- electroencephalography (EEG) – diagnostics of the level of activity of brain processes using electrical impulses;
- examination of the vessels of the fundus - in order to detect hemorrhage, edema or spasm of blood vessels, congestion;
- neurosonography (NSG) – study of the anatomy of the brain;
- cerebrospinal puncture - to measure cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
Medical recommendations
Hypertensive syndrome requires careful medical supervision throughout the entire duration of treatment. In order to guarantee a positive result, it is important to follow all medical recommendations. The mother of a newborn child should devote a lot of time to establishing the baby’s daily routine - this will significantly contribute to improving the general condition.
It is also important to take long walks outdoors every day. Sometimes special exercises are indicated to improve blood circulation and normalize intracranial pressure. In rare cases, doctors recommend performing a massage for a newborn to relieve the tone of the limbs.
What is hydrocephalic syndrome
Babies are often diagnosed with hydrocephalic syndrome. In fact, hydrocephalic syndrome in infants is not such a common occurrence. What kind of pathology is this, and what does it threaten? What are its features?
Subsequent examination may not confirm hydrocephalic syndrome in a child. Even if the diagnosis is confirmed, do not be alarmed. The main thing is to have the information and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Hydrocephalic syndrome in adults has its own characteristics. It is provoked not by congenital, but by acquired pathologies of brain nutrition.
Prognosis, complications
Complications can develop at any age:
- deafness;
- blindness;
- developmental delay;
- paralysis;
- coma;
- epilepsy;
- fontanelle disorders;
- fecal and urinary incontinence;
- mortality.
The younger the child who gets sick, the better the prognosis. The pathology is most easily tolerated by children under 6 months. Their condition can quickly stabilize. Blood pressure, even if it fluctuates, quickly returns to normal.
For older children, the prognosis will be relatively favorable. It will be affected by the reasons, timeliness of treatment, and its adequacy.
conclusions
Hydrocephalic syndrome requires serious attention. Treatment should not be delayed. Remember that it depends on the parents how healthy and developed the child will be!
Source: https://vsepromozg.ru/teoriya/gidrotcefalnyi-sindrom
Possible consequences of the disease
If a child is not diagnosed with a disease in a timely manner or does not receive full treatment, the following pathologies may develop:
- blindness;
- delayed physical development;
- mental retardation;
- paralysis of limbs;
- epilepsy.
If a mild form of pathology is left untreated, it can return in the form of severe attacks of headaches, especially often in adolescence.
Even after treatment, the child should be observed by a neurologist to monitor the condition and receive recommendations if the condition worsens. A mild form of this disease may in the future lead to the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia, which also requires treatment by a neurologist.
Other symptoms
Patients also experience a number of other symptoms. Namely:
- Nausea, often progressing to vomiting. This symptom most often appears in the morning;
- The patient usually gets very and quickly tired, even if there is practically no physical or intellectual stress. There is increased nervousness;
- Hypertensive syndrome is usually accompanied by vegetative-vascular dystonia. And these are changes in blood pressure, increased heartbeat, increased sweating and frequent fainting;
- As a rule, the patient has blue circles under the eyes. This symptom has nothing to do with lifestyle at all. If you stretch the darkened skin around the eyes, then dilated small vessels are clearly visible;
- Sexual desire is almost completely absent;
- When atmospheric pressure changes, the patient’s condition also worsens, that is, he becomes weather-sensitive;
- In the later stages of the disease, mental disorders are observed, manifested in personality changes and decreased intelligence;
- Brady or tachycardia may also appear in the later stages of the disease.
Attacks in the later stages develop according to the following pattern - at first the patient feels “stunned”, then periodically falls into a stop. In the end, everything can end in a coma.
It should be understood that the described signs of intracranial hypertension are subjective and do not confirm the presence of the disease. A person can only suspect the presence of a certain problem and must consult a doctor, who will make a diagnosis based on the results of diagnostic measures.
Preventive measures
Hypertension syndrome - what is it? Since the pathology is increased intracranial pressure and requires drug and surgical treatment, it can be classified as a serious disease of pediatric neurology. Like any other disease, it is easier to prevent than to treat. In order to do this, a woman who is preparing to become a mother must follow the following recommendations:
- undergo all scheduled consultations with a gynecologist and monitor the development of the child and the state of your health;
- avoid diseases during gestation, especially in the first trimester, when vital organs are formed;
- avoid mechanical injuries to the abdomen, which can cause the onset of a pathological process in the baby;
- during pregnancy, monitor your health, eat large amounts of fortified foods;
- during labor, comply with all the doctor’s requirements and, if necessary, give permission to perform a caesarean section.
Following these tips significantly reduces the risk of increased intracranial pressure in a newborn.
Hypertension syndrome in children is a rather dangerous pathology. Therefore, it is important to diagnose it as early as possible and begin correct treatment of the syndrome.
Increased intracranial pressure in infants
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) or intracranial hypertension in infants is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of a certain neurological pathology in childhood.
Causes of ICP in infants
The causes of ICP can be diseases that are accompanied by:
- increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- the presence of anatomical defects that cause disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- deterioration of its absorption;
- a combination of these factors.
The main cause of ICP in young children is hydrocephalus
, which occurs due to increased production of cerebrospinal fluid and its accumulation in the ventricles and canals of the brain, this is what causes disturbances in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid and its absorption.
In newborns, the congenital form of hydrocephalus is more common, which develops during the prenatal period of fetal development.
Pediatricians and neurologists discover this pathology after childbirth, which makes it possible to prescribe treatment in a timely manner and prevent developmental delays in the baby.
Predisposing and provoking factors for the gradual development of increased intracranial pressure in infants can be:
- genetic and chromosomal diseases that provoke the formation of congenital malformations of the brain;
- intrauterine infection;
- deep prematurity;
- pathology of pregnancy (placental insufficiency, severe somatic diseases of the pregnant woman);
- birth injuries or complications during childbirth or surgical interventions.
The main diseases in which ICP develops:
- birth injuries, with the development of perinatal lesions (encephalopathy) and hydrocephalus of the brain;
- previous meningitis, encephalitis (neuroinfections) in young children;
- diseases with severe metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- brain tumors.
According to statistical data, the frequency of hydrocephalus is quite high and is growing every year, which indicates overdiagnosis and the unfoundedness of a number of criteria for diagnosing ICP.
Signs of ICP in a baby
Signs of ICP in infants that are not typical for babies of other age groups are:
- increase in size and bulging of the large (central) fontanel
; - skull dehiscence
; - bulging of the veins of the skull
with the formation of a venous network on the head; - trembling chin and/or hands
; - frequent regurgitation
(often to the point of vomiting “fountain”); - lethargy, retardation in the physical and psycho-emotional development of the child
; - decreased weight gain
; - anxiety, tearfulness of the baby
- cry (“on one note”), in a monotonous voice; - sleep disorders
.
ICP symptoms in infants
Additional symptoms of ICP, depending on the severity and progression of the pathological process in the infant, are:
- significant and progressive increase in head circumference;
- lack of pulsation of the fontanelles;
- symptom of the “setting sun” (when the baby’s eyes look down and the lower part of the iris is covered, a wide strip of sclera is visible from above);
- convulsions;
- increased muscle tone.
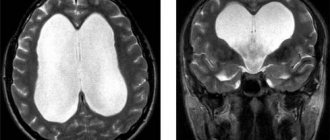
Hydrocephalus in infants
Hydrocephalus
in most cases, this is
a congenital pathology, which is accompanied by active production of cerebrospinal fluid, or a violation of its reabsorption
due to intrauterine infections, chromosomal and genetic defects or the consequence of serious diseases, as well as after neurosurgical interventions.
With hydrocephalic syndrome, an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid expands and puts pressure on the ventricles of the brain.
Premature infants have a high risk of severe intracranial hemorrhage during childbirth and/or the development of hydrocephalus due to incomplete differentiation of brain structures.
At the same time, there is a rapid increase in the size of the baby’s head, an increase and bulging of the large fontanel with divergence of the sutures of the skull.
Types and severity of hydrocephalus in infants
Depending on the cause, type and severity of hydrocephalus, different symptoms and consequences are noted.
Symptoms of this disease appear in the first months of a child's life.
The main symptom is a rapid increase in head size -
with an increase in head circumference by 6-7 centimeters per month
necessary:
- monitor its growth monthly;
- conduct further instrumental diagnostics - NSG (neurosonography) or ultrasound of brain structures through the large fontanel.
In compensated form
all symptoms are expressed moderately, the physical and mental development of the baby does not suffer, and treatment is carried out conservatively - with medications that activate the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and reduce its production.
In severe cases, surgical (neurosurgical) intervention is required - shunting. Less commonly, ICP in infants is a symptom of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the brain (neuroinfections) - encephalitis and meningitis.
Infection of a child can occur in utero, if there is a focus of herpetic, chlamydial or other infection in the mother (herpetic meningitis is most common).
Also, these serious diseases can occur when infections in a baby become generalized due to purulent skin diseases, umbilical wounds, pneumonia with a significant decrease in the immune reactivity of the baby’s body.
Methods for diagnosing ICP in infants
The main methods for diagnosing ICP in infants are based on the presence of clinical symptoms and identifying indirect signs of intracranial hydrocephalus.
If any of the main symptoms of ICP occur, you must contact your local pediatrician, who will then prescribe (if necessary) further examination:
- examination by a pediatric neurologist
, who determines the condition of the fontanel, assesses muscle tone and measures the child’s head circumference over time; - examination
of the fundus by an ophthalmologist; - neurosonography
; - computer or magnetic resonance imaging
with a closed large fontanel.
Neurosonography for diagnosing ICP
NSG (ultrasound of the brain)
is prescribed for infants, since this study can only be carried out with an open large fontanel, which can transmit ultrasonic waves.
With this method of examining the brain, the size of the ventricles is assessed, and their enlargement is a sign of intracranial hypertension and is repeated after a certain period of time.
As well as the progression of clinical symptoms:
- significant monthly increase in head size;
- formation of a venous network;
- dehiscence of cranial sutures with the addition of clinical symptoms (frequent regurgitation, restlessness, chin tremor, progressive lethargy, adynamia of the baby, weight loss).
Examination by an ophthalmologist
The presence of increased ICP in children can also be determined by examining the fundus of the eye by an ophthalmologist.
Indirect signs of the presence of intracranial hypertension are:
- swelling of the optic discs;
- dilation of fundus veins.
Computed or nuclear magnetic tomography
The most accurate methods to clarify the diagnosis are computed tomography or magnetic nuclear tomography. These techniques are considered quite expensive, and the child must be in a state of complete rest, so various types of anesthesia are used.
Tomography is not used often, only in cases of serious suspicion of severe forms of intracranial pathology.
Echoencephalography with increased ICP in infants
The encephalography method (Echo-EG) is now widely used in our country, although it is quite outdated and cannot serve as a reliable sign of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, and this study is extremely difficult to conduct in young children.
ICP in infants treatment
Intracranial hydrocephalus
, which has a benign course in most cases, goes away on its own with adequate comprehensive conservative treatment prescribed by a neurologist.
Therapy consists of prescribing:
- medicines (diuretics and vascular drugs, neuroprotectors and vitamins);
- physiotherapeutic treatment courses;
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- swimming.
It is important to know that only a complex of treatment procedures will be effective and will help to significantly slow down the progression of increased ICP and improve the child’s general condition.
Subsequently, constant monitoring and courses of drug therapy and other conservative methods lead to a complete cure of the child.
An important factor is timely seeking medical help and dynamic observation by specialists - if treatment is not carried out on time, the baby will not be able to develop normally, which will lead to severe impairments in the child’s physical and mental development.
And if this pathological condition is severe and left untreated, it can lead to disability and the development of persistent neurological disorders - cerebral palsy.
In case of severe (decompensated) hydrocephalus, conservative treatment does not give positive results, especially with organic disorders (adhesions, additional vessels, malformations of the meninges).
The main method of treating a child with severe hydrocephalus
is considered a surgical intervention - brain shunting, when, when installing a special shunt (temporary or lifelong), excess fluid is removed from the canals and the ventricle of the brain.