What is psychosis?
It has four main symptoms:
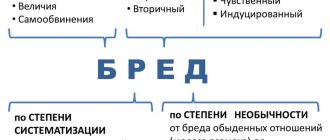
- Hallucinations
. A person who is hallucinating may see, hear, or feel things that do not exist. - Brad
. A person is confident that he is right when in fact he is not. With delusions of grandeur, for example, the patient may believe that he is a very significant person. Paranoid delusions make people fear that someone is trying to harm them or that they themselves have done something terrible. - Confusion and outrage
. A person speaks quickly and incoherently or forgets what he was thinking and talking about. - Lack of self-criticism
. When a person lacks understanding, he does not notice his unusual behavior.
The nature of the symptoms depends on the situation.
What is bipolar disorder?
Bipolar disorder refers to severe mania or depression, along with psychotic symptoms and hallucinations. Symptoms usually correspond to the patient's mood. If a person is in a manic phase, then he believes that he has special powers. This type of psychosis can lead to careless or dangerous behavior.
If bipolar psychosis occurs during a low period, a person may believe that someone is trying to harm them, or that they themselves have done something wrong. These beliefs can cause feelings of extreme anger, sadness, or fear.
Differences between bipolar psychosis and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is another brain disorder that involves a dissociative state. Both disorders can disrupt a person's life and ability to maintain relationships or work.
Bipolar disorder usually lasts for short periods of time. A person experiencing bipolar psychosis is likely to return to a lucid state. A person with schizophrenia is unable to return to normal.
Bipolar disorder is difficult to diagnose, especially in children and adolescents. A psychiatrist must confirm that the behavior is not related to stress, which is common in adolescence. However, if children and teens experience severe mood swings, they should see a doctor.
Types of Mood Disorders
All types of affective disorders are described in the international classifier under the ICD 10 code, episodes F30-39. According to the classifier, types are defined as follows:
- F30 manic episode, diagnosed only in the case of a one-time manifestation of the disease; if repeated, doctors establish the fact of bipolar disorder;
- F31 bipolar mental disorder, characterized by recurrent occurrences;
- F32 depressive episode, accompanied by a decrease in activity, the presence of a depressed mood, increased fatigue, decreased appetite, insomnia, decreased self-confidence and self-esteem. It can be mild, pronounced and severe.
- F33 recurrent depressive disorder is defined by the presence of recurrent episodes of depression. There are no mood swings, with the change from mania to euphoria. The onset of the disease is possible at any age. Including in childhood. With a manic episode, especially if it recurs, it is classified as bipolar disorder.
- F34 persistent mood disorders that last for years, often throughout life, but are not severe enough to be classified as a mild depressive episode or a hippomanic episode.
- F38 Other mood disorders that do not fall into the types listed.
- F39 NOS (affective psychosis).
The diagnosis is made in a clinical setting. Accurate diagnosis is carried out only by a qualified psychotherapist or psychologist.
Diagnosis of bipolar disorder
(c) channelingerik
To be diagnosed with bipolar disorder, a person must have some or all of these symptoms. Psychosis can be difficult to diagnose as it can be confused with depression, anxiety and other mental disorders.
Another factor that makes diagnosis difficult is that people with bipolar disorder often do not realize that their actions are unusual. They think that their problems come from the people around them. Since a person feels well during the manic phase, he does not see the need to seek help.
If a person experiences severe episodes of depression or mania, they should seek help from a doctor or mental health professional. A person who has attempted suicide or is even contemplating suicide should see a doctor immediately. People with bipolar disorder are often unaware of their symptoms, so family members and friends must encourage the person to see a professional.
Treatment of mood disorders
In medical practice, treatment for affective disorders is developed individually for each patient. It is necessary to take into account the present symptoms and the presence of additional diseases. When developing a program, procedures are carried out to:
- stop the active stage of the disease, if present;
- eliminate the cause of the pathology;
- carry out psychotherapeutic work;
- with the help of social work, increase adaptive abilities.
The composition of an integrated approach to the treatment of all types of syndromes includes:
- use of drug treatment;
- psychotherapy;
- social rehabilitation.
In case of acute exacerbation, suicidal thoughts, hospitalization is recommended. Each type of disease requires separate approaches when developing a course.
Affective mood disorder
Almost everyone has experienced mood swings, often without specific reasons. In some cases, such changes, caused by fatigue or based on pleasant occasions, cease to be only one of the manifestations of the norm. In this situation, they require diagnostics and development of a treatment program.
The cause may be genetic predisposition or external factors. For example, a strong shock caused by the death of a loved one. The reason is joy.
To correct the condition, a personal conversation between a specialist and a doctor is required to establish an accurate diagnosis. Elimination of provoking factors allows the state of affect to be relieved. Treatment uses sedatives and antidepressants.
Affective mental disorder
In such a situation, the patient’s condition becomes pathological and interferes with his normal life activities. Therapy is often lengthy. Requires the use of pharmacological drugs.
As in other situations with this disease, first of all the patient is removed from the acute attack stage. Identification of causes that can become a provoking factor is carried out in consultation with a psychologist. The pathology is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbations and remissions. Supervision by a specialist at any stage and attendance at preventive examinations are required.
Affective spectrum disorders
In most cases, doctors try to eliminate manifestations of affective spectrum disorders in restrictive conditions. Hospitalization is required for acute manifestations. At the initial stage of confronting the pathology, relief drugs are used with combinations of neuroleptics and antipsychotics. The use of anticonvulsants of the Valproate group may be required.
In the presence of psychosomatic symptoms, second-generation antipsychotics are used. Such as Serdolex, Clopixol Acufaz. The second generation of these drugs has fewer side effects. Drug resistance after 4 weeks of use becomes a recommendation for the use of anticonvulsants. Lithium salt is prescribed.
Depressive affective disorder
Directly translated in Latin, depression is called “dejection.” This condition cannot be completely cured today, but it can be corrected and stopped. Therapy helps improve the psychological and physiological state of the patient. Using a combination of psychological and biological treatment. In addition to medicinal drugs, folk recipes are distinguished by a high degree of effectiveness. First of all, herbal soothing teas, yoga. Patients are shown psychotraining courses and soothing baths. Following the rules of a healthy diet and avoiding alcohol plays a positive role.
Organic affective disorder
Antidepressants are used in treatment. They improve emotional well-being and reduce anxiety levels. It is necessary to remove the factors that provoked the condition.
An organic affective state is caused by physiological factors. Such as a long-term illness, withdrawal of certain medications, consequences of traumatic brain injury, postoperative condition.
The prescription of medications is carried out taking into account the medications that the patient is forced to take in accordance with the main diagnosis. In most situations, doctors prefer to focus on the use of psychotherapy, soothing infusions and teas, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Manic affective disorder
The problem for conducting a successful course is often the patient's rejection of the diagnosis. A full examination is carried out to exclude concomitant dementia or schizophrenia. During therapy, sessions with a psychotherapist and prescription of medications are used. Anticonvulsant therapy is recommended.
In case of severe cases, compulsory hospitalization is required. In such a situation, doctors need the support of the patient's relatives.
Emotionally affective disorders
With such a lesion, a maximum change in the perception of the surrounding world occurs. The reaction to the provoking factor becomes excessive. There is a loss of understanding of the surrounding situation, and at the same time the understanding of a person’s actions in the current situation decreases.
The provocateur is prolonged exposure to traumatic events, leading to a pathological reaction of the brain. The patient loses control and does not adequately evaluate the actions taking place. Among the provocateurs are the death of a loved one, a sharp decline in social status and material level, and the occurrence of hormonal imbalance. The therapy uses tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, tranquilizers, and mood stabilizers.
In the absence of positive dynamics, anticonvulsant therapy is prescribed. Psychotherapy sessions are conducted both with the patient himself and with his environment.
Bipolar disorder treatment
Courses of mood stabilizers are used for therapy. Such as Carbamazepine, lithium therapy, valproic acid. Treatment is divided into the stage of removing the patient from the acute stage and further preventive therapy, which can be carried out for life. At this stage, the use of a lithium solution is recommended. When you stop taking it, about half of patients relapse within a few weeks. Complete withdrawal within 5 years leads to relapse in 94% of patients.
This remedy shows a positive effect in 60% of patients with short cycles and up to 20% of patients with long cycles. Additional medications are prescribed. With the high potency of lithium, its positive effect occurs approximately 5 days after the start of treatment. During this period, other medications are used. Constant monitoring of the effect of the drug on the body is required. Treatment should be discontinued if dysarthria, widespread tremor and ataxia appear. Most often, negative symptoms are observed in the elderly and patients with poor health.