What is
This pathology can occur for various reasons. If mononeuritis or polyneuritis appears, the following signs appear:
- changes in skin sensitivity
- pain at the location of the affected nerve;
- decreased muscle tone;
- muscle weakness.
If these signs occur, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Neuritis is inflammation of the nerves, most often associated with infection or hypothermia. With this diagnosis, numbness of the innervated area, pain of varying severity, and muscle weakness are observed.
With neuritis of the cranial nerves there is pain, asymmetry, impaired vision, hearing, and taste. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the pathogen and calming the inflammatory process.
The most common neuritis occurs in the occipital, intercostal, and facial areas.
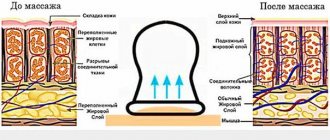
Massage
For neuritis of various etymologies, massage procedures have virtually no contraindications. Thanks to a well-chosen massage technique, you can completely restore the functions of the affected nerve.
Massage for this pathology is necessary for:
- eliminating pain;
- improving blood circulation;
- restoration of PNS functions.
There are three recovery periods for neuritis : early (2-20 days), late (20-60 days) and residual (from 60 days). For each of them there are peculiarities in massage manipulations.
Features of the early period: massage with stroking, rubbing movements, plus hardware massage that provides vibration movements.
Jet underwater massage is widely used , combining both a mechanical effect on the affected tissues and the effect of warm water on them.
The main task of massage during the early recovery period is to create conditions for restoring nerve function.
Features of the late period: massage is carried out taking into account the localization of inflammation - differentially. Weak muscles are massaged intensively, strong muscles are relaxed with stroking and gentle rubbing.
Features of the residual period: the patient is prescribed about 20 massage sessions, the course is repeated after 2-3 months, increasing the number of exercises to train household and professional skills.
as the most effective ways to combat various types of neuritis .
For each specific manifestation of pathology, the basic massage technique is “diluted” with nuances necessary to influence a specific area.
For all neuritis, gentle kneading, pressure, rubbing, and stimulation of acupuncture points are used.
Classification
The disease can be classified according to different criteria.
The division occurs according to:
- location ;
- pathomorphological changes;
- the conditions of its occurrence;
- the number of affected nerves.
By localization they are divided into:
- Optic neuritis The cavity of the eyeball, the back of the orbit or the intracranial area is affected. If you do not go to the clinic in a timely manner, you can completely lose your vision.
- Vegetative. Any area of the human body is affected. Autonomic nerve fibers become inflamed, after which disturbances in blood circulation occur. A different shade of skin appears in the area of inflammation.
- Lesions of the cochlear nerve. Occurs after injuries to the skull, ear or infectious disease. If left untreated, deafness occurs, which later cannot be treated. A common symptom of this pathology is the appearance of noise and ringing in the ears.
- Trigeminal neuralgia, etc.
Peroneal nerve neuritis
Peroneal nerve neuritis is a disease that is an inflammatory process that occurs due to mechanical, chemical or endogenous damage to nerve fibers.
According to pathomorphological changes, neuritis is as follows:
- Axial. Characterized by predominant damage to the axial cylinders.
- Adventitial. During the destruction of the upper outer sheath of the nerve, this type of neuritis occurs.
- Interstitial. Inflammation of the connective tissue structure of the nerve is observed
- Segmental. Individual small sections of nerve fibers along its entire length are affected.
- Rising. This is a process in which the lesion occurs in the distal part of the limb and spreads proximally.
- Parenchymatous. Inflammation of the nervous tissue itself occurs, involving axons and Schwann cells.
- Hypertrophic Gombo neuritis is characterized by segmental disintegration of the myelin sheath in limited areas of the nerve fiber with relative preservation of the axial cylinder; manifests itself in reversible dysfunction of the nerve fiber.
If we take into account the conditions for the occurrence of neuritis, they are divided into:
- Infectious. Appear as a complication after infectious diseases (diphtheria, measles, scarlet fever, rubella). Toxic substances that spread throughout the body quickly give rise to new foci of the inflammatory process.
- Vibrating . If people's professions are associated with constant vibration, then they may suffer from such a disease. Oppression of the hand or foot occurs. In most cases, miners, drillers and construction workers suffer.
- Traumatic. Appear after accidents, bruises, falls, after which bone fractures occur. Another reason is prolonged compression of some part of the body.
- Toxic. The ulnar nerves suffer if heavy metal affects the body. Peroneal nerves, if affected by alcohol. Toxic poisoning can occur in the workplace when working with mercury or zinc.
- Endemic. Appears when there is a lack of nicotinic acid or B vitamins in the body. Frequent victims are patients with diabetes and pregnant women who have toxicosis.
Inflammation of the auditory nerve
Acoustic neuritis occurs due to damage to the organs of sound perception.
If we take into account the number of affected nerves, neuritis is divided into two types:
- Multiple lesions - polyneuritis.
- Single - mononeuritis.
If any of the above processes are diagnosed early, the pathology can be cured.
Review of effective drugs
Let's talk about how to treat a cold trigeminal nerve. In pharmacotherapy, an integrated approach using symptomatic and pathogenetic drugs is used to eliminate neuritis. The most effective in eliminating neuralgia will be:
- "Acyclovir" is an antiviral agent that helps eliminate pathogens at the site of inflammation;
- “Promedol” is an anesthetic drug that affects the functioning of the central nervous system, preventing the processing of impulses coming from affected tissues;
- "Indomethacin" is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that promotes decompression of the affected nerve bundles;
- "Dexamethasone" is a glucocorticosteroid hormone that eliminates inflammation and swelling of tissues;
- "Mydocalm" is a muscle relaxant that inhibits the reflex excitability of nerve cells.
Causes
The frequency of manifestation in the population is 5 confirmed cases for every 100 thousand people. In half of the cases (over 51%), the presence of neuritis in the patient is the first symptom of multiple sclerosis. There are cases where a period of 15 years passed between the onset of neuritis in a person and the subsequent development of multiple sclerosis.
The primary task for neuropathies is to eliminate the physical impact; currently, orthoses are successfully used for immobilization in the damaged area.
To relieve pain, analgesics and NSAIDs are traditionally used in a short course; when the pain syndrome becomes persistent chronic pain, drugs aimed at relieving neuropathic pain are required: anticonvulsants, antidepressants.For tunnel neuropathies, a blockade with an anesthetic and hormone in the area of infringement is successfully used.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
The disease can occur due to external or internal reasons.
With internal causes, various diseases affect inflammation of the nerves. With external ones, the action comes from the environment.
These include:
- infectious diseases (influenza, scarlet fever, measles, herpes, polyarthritis, rubella, etc.);
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- various stages of obesity;
- osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia;
- disorders ;
- thyrotoxic goiter;
- poisoning (alcohol, drugs, mercury, zinc, drugs, etc.);
- lack of B vitamins
- various injuries (fractures, dislocations, wounds, unskilled injection, poorly performed surgery, etc.);
- last trimester of pregnancy (associated with excessive stress on the spine);
- hypothermia.
Regardless of what caused the inflammation of the nerve, only a highly qualified specialist should treat the disease.
Symptoms
The first attack of pain can be triggered by elementary things that no person can do without: laughter, smiling, articulation, brushing teeth, eating, frostbite on the face. Pain appears in one half of the face. At first, the painful attacks are short-lived. They end, just as they begin, abruptly. Over time, pain occurs more frequently and lasts longer. Often the pain begins to originate in the jaw and can be confused with toothache. Then the painful sensations move to the area of the cheek, ear, and forehead. There is lacrimation, paresis of the facial muscle, and the face becomes asymmetrical. After the attack, a period of remission occurs, which lasts several minutes. During remission there is no pain.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease will vary depending on the nerve affected. Common signs include:
- numbness of the affected area;
- feeling of goosebumps and tingling;
- poor sensitivity;
- pain while working or staying in one position for a long time;
- weakness and lethargy in the muscles (if left untreated, atrophy will occur);
- poor motor activity;
- poor functioning of the glands of the skin and organs.
Swelling and discoloration of the skin where inflammation is localized may occur.
| Vegetative | It can appear in any area of the body. Usually blood flow is disrupted and skin color changes in the inflamed area |
| Optic nerve | Partial and then complete loss of vision |
| Cochlear nerve | Ringing and noise in the ears, partial or complete deafness |
| Trigeminal neuralgia | Sudden, rapid shooting pains. Most often - in the face area |
Determination of neurites by their location in the body
Most often it happens:
- Neuritis in the forearm (radial, ulnar and median). There is impaired mobility in the hand. It is difficult to bend your arm and move the phalanges of your fingers. My hand goes numb.
- Femoral neuritis. The knee and hip joints bend poorly. There is poor sensitivity on the front surface of the thigh below and inside the side of the shin. Muscle mass decreases in size and weakens.
- Peroneal neuritis. There is lameness due to the pain of standing on the heels. There is also shuffling and stumbling. When walking, a person lifts his feet strongly upward when he brings them forward.
- Facial neuritis. The affected part of the face immobilizes and relaxes. There is asymmetry. The eye cannot close, the forehead does not wrinkle. Pain behind the ear may occur, and half of the lips lose mobility.
| Symptom at the beginning | Pain behind the ear |
| Face | Asymmetry is noticeable - the corner of the mouth is skewed towards the healthy side |
| Nasolabial fold | Smoothed out |
| Eyelids | Doesn't close completely |
| Facial muscles | Weakened. The patient cannot smile, frown, raise his eyebrows, etc. |
How to determine neuritis of the facial nerve
You can notice the disease immediately, since the signs of neuritis are very specific.
Folk remedies at home
Let's figure out whether and how it is possible to cure nerve inflammation using unconventional methods. Among the antineuritis recipes in the public pharmacy, the leading ones are those containing beekeeping products.
This is, indeed, a centuries-tested medicine, however, it should also be used after consultation with a neurologist as part of complex therapy.
Propolis-honey mustard plasters
Ingredients (take in equal proportions):
- honey;
- vegetable oil;
- propolis solution 20%.
Preparation:
- Mix all ingredients.
- Apply the mixture to regular medical mustard plaster.
To treat an inflamed facial nerve, apply it through gauze to the sore spot to avoid getting burned.
Honey and onion compress
Ingredients:
- honey - 1 tbsp. spoon;
- onion – 1 pc. (take a large onion);
- white of one egg.
Preparation:
- Beat the whites into a strong foam.
- Melt the honey, squeeze the juice out of the onion and add it all to the protein.
- Spread the resulting mass onto natural fabric.
- Apply to the sore spot.
Royal jelly
Milk is used in its pure form for inflammation of the peripheral nerve . Take 5 mg orally 3 times a day for three weeks.
Some herbs and plants have proven themselves well as a medicine against neuritis. We offer recipes from the most accessible of them.
Plantain infusion
Ingredients:
- plantain leaves – 30 g;
- boiling water - 2 cups.
Preparation:
- Pour boiling water over plantain.
- Let it brew overnight.
- Soak gauze with liquid and apply to the inflamed area.
You can simply grind fresh leaves into a pulp and apply to the affected area.
Garlic-lemon-honey mixture
Ingredients:
- garlic – 5 heads;
- lemon – 5 pcs.;
- honey – 0.5 kg.
Preparation:
- Grind honey and garlic in a meat grinder.
- Add honey.
- Infuse for a week.
Take a tablespoon 2-3 times a day before meals . For inflammation of the facial nerve, you can use the mixture as a compress.
When preparing medicines from garlic, you must strictly adhere to the dosage.
Diagnostics
With signs of an inflamed nerve, the patient is sent to see a neurologist. The doctor conducts an examination and functional tests. They determine movement disorders.
If a person has radial neuritis, then:
- when the hands are on the table surface with palms up, the thumb is not moved to the side;
- if the patient is in an upright position, with his arms down along his body, he is not able to turn the hand with the palm forward and move the thumb.
When a patient has median neuritis, then:
- impaired flexion of the hand and fingers in the interphalangeal joints,
- impaired sensitivity on the lateral surface of the palm and 1-4 fingers;
- It is not possible to make a contrast between the little finger and the thumb.
For ulnar neuritis:
- the patient is unable to spread the phalanges of the fingers when the palms are on the table surface;
- deformation of the hand like a “bird’s paw” as a result of paralysis and atrophy of the small muscles of the hand;
- pain and decreased sensitivity on the 5th and 4th fingers.
The patient may be referred by a doctor for a CT or MRI.
Electroneurography is used to measure the speed of transmission of a nerve impulse through peripheral nerve fibers. Using this technique, it is possible to identify pathology, discover where it is localized, and at what stage it is.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Electromyography is done to evaluate the bioelectrical activity of muscle tissue. This makes it possible to determine the functional state of the nerves and understand how far everything has gone.
Evoked potentials are a study of the bioelectrical activity of nerves. Neurologists use this method to study how the autonomic nervous system functions and evaluate the visual and auditory nerves.
Advantages of treating facial neuralgia in our clinic
- “Tibet” – clinical base of the Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov of the Ministry of Health of Russia (Sechenov University)
- Treatment in “Tibet” is carried out by more than 30 doctors with higher medical education
, who are fluent in the methods of oriental medicine. Our specialists - The Tibet Clinic has been operating for 10 years
. During this time, more than 5,500 patients underwent successful treatment with us. - The effectiveness of our methods is confirmed by facts. Positive results in the treatment of facial neuralgia are achieved in 95-98% of cases
. - Tibet has a unique treatment quality control system
. - Clinic “Tibet” is a laureate of the prestigious European award “Aurora Beauty&Health”, winner in the category “Best Clinic of Oriental Medicine”.
More details
Treatment
After a complete examination of the patient has been carried out, the causes of the disease and its degree have been determined, it is necessary to eliminate all the factors that provoked this pathology. This is done so as not to aggravate the situation and cause complications.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
The result and effectiveness of treatment depends on age, type of disease and therapy. All medications and physiotherapeutic procedures are used only after prescription by the attending physician:
- Bacterial mononeuritis and polyneuritis are treated with antibiotics and sulfonamides.
- Viral.
- Traumatic - immobilization of the fracture, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are used. At the same time, you should take vitamins and drugs that improve neuromuscular transmission.
- Vascular – treated using vascular agents.
If the neurosurgeon decides that surgery is inevitable, then surgery is performed. During it, the compressed nerve is released. Plastic surgery or stitching is done, so the functionality of the damaged area is restored.
Medicines for neuritis are usually anti-inflammatory. Physiotherapy, normalization of water-salt balance, and intake of vitamin complexes are required.
Anticonvulsants and antidepressants are prescribed if inflammation occurs in the area of the glossopharyngeal or trigeminal nerve, or the nature of the pain is neuropathic in nature.
Physiotherapy refers to the use of:
- ultrasound;
- pulse current;
- exposure to high-frequency currents;
- electrophoresis.
Inflammation of the optic nerve
Optic neuritis is accompanied by visual impairment.
All of the above procedures can restore functionality to the damaged nerve.
If there are no contraindications, then massage therapy and exercise therapy are advisable. If recovery does not occur for a long time, then inductophoresis procedures, chamber hydrogalvanic sessions, mud and radon baths may be prescribed.
Top effective remedies for drug treatment of symptoms of inflammation of the sciatic nerve
Sciatica neuritis or sciatica is an inflammation of the nerve, which is an important element of the sacral nerve plexus. It ensures the normal functioning of the pelvic organs and lower extremities.
Any pathology of the sciatic nerve leads to disruption of the lower motor system.
In this article we will talk about the symptoms of inflammation of the sciatic nerve and the drug treatment of such neuritis: what injections to give, what tablets to take, we will give the names of the drugs.
Signs and manifestations of neuritis
Sciatic nerve neuritis manifests itself in different ways:
- severe and sharp pain (lumbago),
- discomfort in the lower back,
- heavy legs,
- fatigue in the lower back,
- motor dysfunction,
- loss of sensation in the legs,
- tingling (pins and needles) and burning in the extremities,
- numbness.
Symptoms of sciatica vary in severity and location , can affect only one side of the body and can be paroxysmal or alternating.
Sometimes the pain is so excruciating that it literally paralyzes the patient, depriving him of the ability to walk and even move.
Often, inflammation of the sciatic nerve leads to partial atrophy of some muscles. In this case, the pain syndrome will not be as pronounced, but the person will feel numbness in some areas of the body.
When is drug therapy possible?
Already the first signs of sciatica require medical intervention . Its goal is to relieve pain and stop inflammation. However, medication therapy is possible only after examination and determination of the cause of sciatica.
Drug treatment is possible if the nerve is inflamed due to:
- hypothermia,
- overvoltage,
- pinched nerve.
After taking medications, the pain is dulled, and after a few days of therapy, noticeable relief occurs.
When is it impossible?
If the pain is not relieved by medications and lasts for 3-4 weeks, then the cause of neuralgia is much more serious than just inflammation.
Drug treatment will not help with:
- paralyzing sciatica,
- too severe and prolonged pain,
- intervertebral disc herniation,
- dysfunctions of the bladder and intestines,
- spinal stenosis.
In all of these cases, surgical intervention is indicated.
Find out about other ways to treat sciatica: gymnastics, massage, folk recipes.
Tablets and injections for sciatica: list of drugs
How to treat inflammation of the sciatic nerve, what medications to take, what injections and IVs to give for sciatica? Drugs for the treatment of sciatica are aimed not only at eliminating pain and inflammation, but also at restoring the nerve.
Treatment can be either oral or injectable - the drugs are available in both tablets and ampoules.
But injections are preferable here, because they begin to act faster than tablets and do not burden the digestive organs and excretory system.
Anti-inflammatory
With sciatica, the first thing you need to do is stop the inflammation, since as it decreases, the debilitating pain in the lower part also disappears.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for this:
- Meloxicam,
- Diclofenac,
- Ketorolac,
- Lornoxicam,
- Indomethacin,
- Ketoprofen.
Painkillers
Acute attacks of neuralgia are treated with the following drugs:
- Ketarol,
- Baralgin,
- Pentalgin,
- Tempalgin.
Hormonal medications
Corticosteroid hormonal drugs are prescribed in extreme cases - during the acute period of an attack of sciatica , as well as when the patient has severe swelling in the lumbosacral region.
Hormonal drugs suppress the inflammatory process. The most popular in this area are:
- Hydrocortisone,
- Prednisolone,
- Dexamethasone.
Antidepressants
Sciatica is a disease of a nervous nature and the slightest anxiety can aggravate it. During this period, patients are prescribed antidepressants that relieve nervousness and anxiety.
Antidepressants are prescribed individually and sold by prescription.
Opioids for leg pain
Opioids are powerful drugs that are highly addictive . They relieve any pain, even the most severe, and are prescribed when other means do not help.
Among them are less toxic drugs:
- Morphine,
- Codeine,
- Oxymorphine,
- Hydrocon.
These drugs are only suitable for use in hospital settings.
Muscle relaxants
These drugs are needed to relieve muscle tension, which eliminates pinching , thereby relieving pain, restoring mobility and sensitivity of the limbs:
- This is sirdalud
- Tizanidine,
- Tizalud,
- Tizanil,
- Tolperisone,
- Mydocalm,
- Tolisor.
Botulinum toxin, what is it prescribed for?
Botulinum toxin is used for muscle spasms . This substance relaxes and relieves nervous tension, which greatly alleviates the patient’s condition.
The use of blockade for sciatica of the lower extremities
What other injections are given for inflammation of the sciatic nerve?
If none of the drugs has brought adequate relief from neuritis, and the patient is suffering from unbearable pain, then he is prescribed novocaine or ultracoin blockade.
It will block nerve impulses, relieve inflammation and nervous excitement. The solution is injected into the sciatic nerve bundles in the lumbar region , but this is done in the most extreme cases.
What vitamins are needed?
For sciatica, B vitamins are needed: B1, B6 and B12 . They are prescribed both orally and by injection. Vitamins in intramuscular injections for sciatica are preferable, but more painful.
Vitamins reduce pain, nourish and regenerate nerve fibers, restore sensitivity and motor activity, and stimulate the body's defenses.
The best vitamin complexes are recognized as:
- Combilipen,
- Binavit,
- Neurobion,
- Unigamma.
The duration of treatment for sciatica with vitamins b1, b6, b12 and the course of taking them is prescribed in the instructions for the drugs, but intramuscular injections are given for about 10 days, twice.
How to treat with ointments?
Not only tablets, but also ointments help relieve pain and relieve inflammation:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of local action .
They soothe pain and relieve acute syndrome due to the enzymatic activity of the components. These include: Amelotex, Diclofenac, Nise, Butadione and Voltaren, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen. These ointments are quite aggressive and are prescribed for a period of no more than 5 days. - Analgesic, warming, irritating and blood circulation improving agents - “Finalgon”, “Capsicam”, “Viprosal”, “Apizartron”, “Betanicomylon”. These ointments relieve swelling and also distract from pain.
- Ointments that stimulate the regeneration of cartilage tissue - chondoprotectors . These include “Chondroxid” and “Chondroitin”, “Sofia”, “Teraflex-M”. They relieve pain and eliminate the cause of the disease, and also restore articular cartilage, improve mobility and reduce swelling of the joints, and also prevent the destruction of connective tissue with the help of the active natural component chondroitin sulfate. These drugs are non-toxic and can be used for a long time - more than two months.
Candles
If for some reason the patient cannot take medications orally or by injection, he is prescribed rectal suppositories. They act faster and more effectively than tablets.
Most often, patients are prescribed suppositories:
- Voltaren,
- Diclofenac,
- Indomethacin,
- Diclovit.
Consequences and complications
If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, complications may arise in the form of motor disorders, paralysis, and complete muscle atrophy.
Rational treatment will help to avoid serious consequences and quickly return to a full life. In most cases, after quality treatment by a specialist, complete recovery and recovery occurs.
| Pathology | Probability, % |
| Optic atrophy | 63 |
| Partial blindness | 22 |
| Complete blindness | 15 |
What pathologies does optic neuritis lead to?
Prevention
Following a number of preventive recommendations will help prevent the development of neuritis:
- preventing hypothermia of the body;
- timely treatment of diseases;
- hygiene and safety rules
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- refusal of uncontrolled use of medications .
In addition, it is necessary to include in the diet foods rich in vitamins, micro- and macroelements.
Forecast
At a young age, neuritis responds well to treatment, since the tissues have a high ability to recover and renew. In older people, if there are concomitant pathologies in the medical history, for example, diabetes mellitus, the consequences may not be as favorable. In the absence of adequate therapeutic measures, the likelihood of contractures and muscle paralysis increases.
Nerve inflammation is a serious disease that requires early treatment. To avoid its occurrence, you should eat well, monitor your health, treat all infectious diseases in a timely manner, harden yourself, and avoid hypothermia. It is impossible to treat neuritis on your own, since without examination the treatment will not be beneficial.