What is schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a progressive disease characterized by gradually increasing personality changes (emotional impoverishment, autism, the appearance of eccentricities and oddities), negative changes (thought disorders, dissociation of mental activity, drop in energy potential), various productive psychopathological manifestations (affective, neurosis-like and psychopathic, delusional, hebephrenic, catatonic, hallucinatory). Constitutional and genetic factors play an important role in the occurrence of schizophrenia More severe forms of schizophrenia occur in men, while less progressive forms occur in women. The earlier the disease begins, the more malignant it becomes. Schizophrenia belongs to a group of mental illnesses ( mental disorders ).
Causes of schizophrenia in men
The exact reasons why schizophrenia occurs have not been established. Meanwhile, there are several assumptions that are made on the basis of many years of observations:
- According to doctors, heredity plays an important role in the appearance of pathology. Thus, many patients with a similar diagnosis in their family had people with strange behavior, a tendency towards alcoholism, and attempts at suicide.
- Symptoms of schizophrenia often appear after a traumatic brain injury.
- Another possible reason that provokes such disorders is frequent stress, overwork, and constant lack of sleep.
- The use of psychotropic substances can also cause disorders.
Symptoms of continuous-current schizophrenia
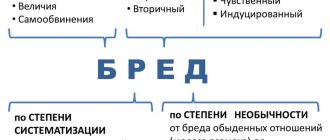
The clinical picture (symptoms) of schizophrenia is characterized mainly by non-psychotic symptoms: phobias, hysterical, senesto-hypochondriacal, depersonalization manifestations, obsession, overvalued ideas. In paranoid schizophrenia, delusions of jealousy, love, and invention predominate. If the process proceeds with greater progression, it is accompanied by hallucinatory-paranoid disorders, phenomena of mental automatism, negative changes and intellectual decline increase.
Diagnostic methods
Only a psychiatrist can make a diagnosis of schizophrenia. In addition, to exclude other mental and neurological diseases, a consultation with a neurologist is necessary.
What studies will specialists prescribe:
- MRI, CT scan of the brain - this examination gives an idea of the pathological processes in the brain tissue
- EEG – this study allows us to judge the functioning of brain areas during periods of rest and activity;
- rheoencephalography of the brain;
- testing to identify predisposition to schizophrenia.
All these studies are secondary in diagnosis. Clinical symptoms are of greatest importance. If signs of depression, apathy, detachment, and indifference are observed for several months, this may become a criterion for making a diagnosis.
In addition, during the examination, the doctor will collect anamnesis and listen to the complaints of the patient and his relatives.
An important factor will be the identification of concomitant diseases, since severe chronic diseases can aggravate the course of schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia should be differentiated from other disorders:
- Schizoaffective disorder.
- Drug use. Drugs can cause mental disorders such as schizophrenia. In this case, a toxicological analysis will help to understand the diagnosis.
- Chronic diseases. Diseases of the internal organs can cause symptoms characteristic of schizophrenia. For example, diseases of the central nervous system, epilepsy, brain tumors, diseases of the endocrine system.
- Bipolar disorder. Distinguishing schizophrenia from manic-depressive state is quite difficult, because hallucinations and delusions can look like an episode of mania, and detachment and isolation can look like an episode of depression.
- Reactive psychosis is a condition that occurs after suffering a severe nervous shock. The symptoms of PTSD are also similar to those of schizophrenia.
Was Gogol schizophrenic?
Attacks of schizophrenia
Various types of attacks develop:
1. Acute delusional (with delusions of jealousy, poisoning, persecution).
2. Hallucinatory.
3. Catatoparanoid.
4. Catatonic.
5. Catatohebephrenic.
6. Syndrome of mental automatism with delusions of physical influence.
7. With a predominance of affective disorders.
8. With a predominance of neurosis-like disorders.
9. With a predominance of psychopathic disorders.
Treatment of schizophrenia
Without treatment for schizophrenia in men, the prognosis for the patient is extremely unfavorable . Therapy for this disease includes symptomatic treatment and correction of the psycho-emotional state.
In most cases, patients can be treated for schizophrenia on an outpatient basis, but in the acute stage, observation in a hospital is recommended.
Aggression in schizophrenia in men . If a man with schizophrenia poses a threat to himself and others, he may be subjected to compulsory treatment.
How to treat schizophrenia in men?
Drug therapy includes the use of psychotic drugs - antipsychotics. The dosage is selected individually depending on the severity of schizophrenia.
With the advent of modern atypical antipsychotics, the risk of severe side effects from drugs has decreased. These drugs have a comprehensive effect on all signs of schizophrenia, reducing the manifestation of both negative and positive symptoms.
Also, modern psychotic drugs restore the patient’s mental activity and restore his ability to work.
The duration of treatment is aimed not only at stopping the acute phase of schizophrenia, but also at preventing relapse in the future.
In addition to antipsychotics, patients may be prescribed antidepressants, drugs that improve brain function. General strengthening therapy is also indicated - taking vitamins.
Social therapy . People suffering from schizophrenia gradually withdraw from society. Therefore, psychotherapy and rehabilitation are so important in the treatment of this disorder. Properly selected social rehabilitation will help a man live with this disease, start a family and work successfully.
Psychotherapy happens:
- - family - it will provide an opportunity to improve family relationships. The patient's relatives need to understand that he is not to blame for his illness. A favorable atmosphere in the family will help cope with severe schizophrenia;
- — individual psychotherapy is necessary for the patient to understand what is happening to him. The correct approach of specialists will teach them how to cope with the symptoms of the disease;
- — group therapy is aimed at the social adaptation of men.
In addition to all of the above, occupational therapy, art therapy, swimming pool, and physiotherapy are of great importance in the treatment of schizophrenia. Under no circumstances should the disease be ignored. Schizophrenia leads to irreversible consequences.
Sexual disorders in schizophrenia
Sexual dysfunction in schizophrenia may clearly reflect personality changes in schizophrenia. Sexual desire disorders are one of the first signs of impending mental breakdown. Among the clinical manifestations of schizophrenia, the increase in autism and alienation is of particular importance. This changes the attitude towards others, narrows personal connections and makes it difficult to establish sexual contacts. Loss of emotionality causes a weakening of sexual desire. Sometimes, as part of an internal personality change or under the influence of unsuccessful attempts in normal sexual life, schizophrenics experience perversions of sexual desire. However, sexual disorders themselves can provoke an exacerbation of schizophrenia, just like any other difficulties in life; stressful situations often lead to the manifestation of the disease in previously mentally healthy people. For example, a young man who has been raised at home since childhood, when he ends up in the army, may have the first attack of schizophrenia in his life, although no doctor would have given him this diagnosis before.
First signs
The first manifestations of schizophrenia in men most often occur early (about 15-18 years), which makes it difficult to identify the pathology. Adolescence is accompanied by a change in character, a sharp change in behavior and increased sensitivity are observed. Against this background, parents do not attach much importance to the changes that are characteristic of mental disorders.
When it comes to adults, changes in behavior and habits are often explained by severe fatigue and depression.
According to doctors, it is still possible to notice the signs characteristic of the latent period of schizophrenia. At this time, men experience the following changes in character and habits:
- Attitude towards loved ones. A person begins to develop emotional coldness towards family, friends, and colleagues. If previously a man was distinguished by a cheerful disposition and sociability, now he avoids people, becomes withdrawn and avoids contact by any means.
- Logical conclusions. When making any decisions (even everyday ones), the patient builds logical diagrams and chains.
- Changes in color preferences. A person begins to choose clothes or objects of a color that was not previously welcomed.
- Changing habits. A man stops taking care of himself and becomes sloppy. He no longer likes his hobby, and the person often withdraws into himself.
- Attitude towards women. A man ceases to have interest in the opposite sex; women often become the reason for his aggression.
Sexual disorders in patients with schizophrenia
Sexual disorders in patients with schizophrenia are varied: men develop erectile dysfunction, ejaculation disorders, decreased brightness of orgasm, decreased sexual desire; women develop a-, hypo-, hyperlibidemia, genitalgia, anorgasmia, as well as menstrual irregularities. Sexual motives are often found in general psychopathological syndromes of schizophrenics: delusions of jealousy, delusions of love, continuous writing of love letters, passion for pornography, unusual sensations in the genital area, as well as in other areas that excite the patient. Patients with schizophrenia are prone to exhibitionism, persistent demonstrative masturbation, and rape.
How does schizophrenia manifest in men?
The peculiarity of the clinical picture in schizophrenia is the alternation of remission and exacerbations.
Question to the expert
What is remission in schizophrenia?
Remission is a period during which the symptoms of schizophrenia weaken or disappear completely.
The period of exacerbations is usually understood as that stage of the course of a chronic disease at which symptoms intensify or new signs of pathology appear. In the case of schizophrenia, it is impossible to talk about a complete cure, since exacerbation is possible even after a ten-year remission. During this period, a person is susceptible to sudden aggression (due to jealousy or mania), hallucinations, delusional states, and attacks of apathy.
Symptoms of schizophrenia in men
Doctors distinguish between 2 types of symptoms of schizophrenia: positive and negative. Positive signs of the disease can be seen by the patient’s relatives and doctors. Negative symptoms include those that are felt only by the patient himself. Such manifestations can be extremely difficult to determine.
Positive symptoms include the following.
- Hallucinations (they can be olfactory, visual, auditory or tactile). Most often, patients hear voices that force them to perform certain actions.
- Thinking disorders. The patient's speech becomes incoherent and illogical. This is explained by the fact that it becomes increasingly difficult for a person to systematize his thoughts and actions.
- Rave. Patients are visited by delusional ideas and delusions of persecution arise. For example, a patient may be completely sure that he is one or another historical figure.
- Movement disorders. Involuntary movements often appear, patients repeat the same word or movement, make grimaces or freeze in one position.
Aggression in schizophrenia in men
One of the characteristic changes accompanying schizophrenia is aggression. The reasons for this behavior in a man can be different:
- Lack of understanding of the changes that occur in consciousness. In other words, a person believes that it is not he himself that is changing, but the world around him.
- Reaction to one's own behavior and committed actions. In a state of delirium, a man can do one or another action that he is not capable of in life.
- Excessive suspicion, mania. A man may develop unreasonable jealousy and resentment.
The manifestation of aggression can be directed at himself or at the people around him. In addition, patients with this diagnosis often take out their anger on pieces of furniture.
The peculiarity of an aggressive state in mental disorders is that a person begins to show great strength. Coping with a patient in a psychiatric ward can be difficult even for several orderlies.
In this state, a person may scream, threaten, wave his arms, rush at his opponent, or grab knives or other dangerous objects.
Men with mental disorders have pathologies in the area of sexual desire, so acts of violence often occur in a state of aggression.
Attempted suicide due to unhappy unrequited love, sensations in the genitals
Patients with schizophrenia have a history of episodes that radically change the entire understanding of the reasons for certain actions. For example, a suicide attempt due to “unhappy love” may be dictated by delusions of sexual incompetence, and not at all by the emotional experiences of a rejected lover. Depression, which supposedly caused a decrease in sexual desire, is actually caused by unpleasant sensations in the genital area, which also turns out to be included in the framework of delusion. Usually, a patient with schizophrenia is brought to a specialist by the conviction of his “sexual impotence.”
Pathogenetic therapy
Based on the postulates of the neurotransmitter theory of the emergence of schizophrenia, the neurotransmitter dopamine is given leading importance in pathogenesis. An increase in its concentration causes delusional and hallucinatory symptoms. To suppress dopamine activity, neuroleptics (antipsychotics) have been created that successfully relieve these symptoms. The varieties of the group are presented in the table.
| Groups | antipsychotics | ||
| Phenothiazine derivatives | Butyrophenone derivatives | Thioxanthene derivatives | Derivatives of other chemical groups |
| Aminazine | Haloperidol | Clopixol | Leponex |
| Tizercin | Droperidol | Truxal | Olanzapine |
| Etaperazine | Fluanxol | Eglonil | |
| Triftazin | Risperpet | ||
| Majeptyl | Quetiapine | ||
| Moditen | Sultopride | ||
| Sonapax | |||
| Neuleptil |
Doses and combinations of drugs, duration of administration, are selected individually.
Drugs of the first three groups, in case of overdose, can cause neuroleptic syndrome - a condition in which the patient becomes inhibited, moves like a robot, obsessive hyperkinesis is observed (flapping arms, muscle twitching), pretentious movements, and severe tremors. At the first symptoms, you must immediately consult a doctor to prevent the syndrome from becoming malignant. Drugs of the fourth group belong to atypical neuroleptics, the syndrome in them is less pronounced and to a lesser extent. To prevent side effects, antikinetic drugs (cyclodol, akineton) are prescribed in parallel with neuroleptics.
Decreased libido, weakened erection in schizophrenia
With sluggish schizophrenia, patients complain of decreased sexual desire, weakened erection, premature ejaculation, and dullness of orgasm. Many of them in childhood intensively engaged in masturbation, which was accompanied by unusual fantasies or proceeded in a perverted form. In youth, there is a sharp cessation of relationships with others and relatives, anger, and unstable mood. Sometimes there are complaints of fluid transfusion in the testicles or lower abdomen, pulsation, and incomprehensible pain. Explanations for what is happening boil down to “blockage” of the vas deferens or urethra, “reproduction of microbes,” or damage from masturbation many years ago.
Initial manifestations
How to recognize schizophrenia in young men? The first symptoms and signs of schizophrenia in men can be noticed as early as adolescence. Parents attribute this to puberty and do not turn to specialists, believing that over time everything will go away on its own.
How is psychosis different from schizophrenia?
However, over time, the course of the disease only worsens. Character and habits change, ordinary hobbies cease to interest. The child becomes overly emotional. Or, on the contrary, completely indifferent to everything that happens.
How to recognize a schizophrenic in a man by his behavior? It is also worth paying attention to sudden dissatisfaction with your appearance. The reasons for dissatisfaction may be completely far-fetched.
Teenagers tend to worry about their appearance. Someone thinks he is ugly, and someone thinks he is fat. Disliking your own appearance can have negative consequences. For example, the desire to lose weight sometimes leads to anorexia.
Hypolybidemia in schizophrenia
Libido often decreases after 20 years. If the patient is not yet married by this age, weakening of erection does not allow starting sexual activity and getting married. In 20% of cases, chronic prostatitis and premature ejaculation develop. Schizophrenics are characterized by a dual approach to sexual problems: on the one hand, there is persistence in receiving specialized help, and on the other, a sluggish justification “I want to be like everyone else.” Decreased libido is associated with constant physical discomfort characteristic of schizophrenia. The mental content of sexual desire is far from reality; it reflects not the usual interaction of the sexes, but rather one’s own peculiar fantasies or delusional experiences. But even this quickly fades over time.
Biological methods
Biological methods effectively relieve acute psychotic states - constant companions of male schizophrenia. The following types of therapy are used:
Insulincomatous - achieving a comatose state of the patient by daily administration of insulin with a gradual increase in dose. The course of treatment is 15–20 lm. A properly carried out procedure allows you to achieve remission for 20–25 years, which is not possible with antipsychotics. But the method has many contraindications and can lead to complications.
Electroconvulsive (ECT) - provoking convulsive seizures by passing an electric current for 0.2–0.4 s. The course consists of 5–7 sessions. The procedure is carried out every other day. ECT is especially effective for catatonic stupor and drug resistance. Complications such as breath-holding, dislocation of the lower jaw, and vertebral fractures limit the use of the method.
Both procedures are performed by specially trained medical personnel, with the written consent of the patient and relatives.
Fantasies on sexual themes
With paroxysmal schizophrenia, sexual disorders may appear only during an exacerbation. However, as the disease worsens, the disorders become irreversible. Sometimes with schizophrenia, especially with its biphasic course, there may be a sharp increase in libido, an increased need for more and more sexual acts, accompanied by a decrease in the brightness of orgasm. Sometimes older women with an exacerbation of the schizophrenic process begin to feel a strong desire and vivid fantasies on sexual topics, which are not accompanied by lumbrication (wetting) of the genitals.
Features of therapy of various forms
Hebephrenic. A frequent form in teenage boys 15 years old and young men. The first signs almost always go unnoticed; absurd behavior, foolishness, and swagger are not written off as “bad upbringing.” The danger of this form lies in the rapid progression of negative symptoms with the collapse of mental functions. Therefore, early diagnosis is especially important for this form. Timely treatment includes antipsychotics, tranquilizers, nootropics. Great importance is attached to psychotherapy and support from loved ones.
Catatonic. In this form, treatment is carried out only in a hospital to prevent complications. During the period of catatonic agitation, benzodiazepine tranquilizers and electroconvulsive therapy are indicated. Antipsychotics are not recommended due to the risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which can be fatal.
For catatonic stupor, mood stabilizers and muscle relaxants are used. In advanced cases, when there is a refusal to eat or sleep, intensive infusion therapy is carried out in the hospital to restore the functioning of the vital systems of the body.
Treatment of the paranoid form is carried out according to the scheme described for the manifestation stage.
Schizophrenia treatment - sexual disorders in schizophrenia, how to treat schizophrenia
Sarklinik (Saratov) provides treatment for sexual disorders , erectile dysfunction, and weakened potency in men, including patients with schizophrenia in Saratov.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required. Photo: Dontcut | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Vibration disease and sexual disorders
Systemic scleroderma and sexual function, treatment in Saratov
Sexual disorders after STIs, STDs, sexually transmitted infections
Manager syndrome, symptoms, treatment in Saratov, Russia
Ejaculation disorders (ejaculation): treatment in Saratov, Russia
Comments ()
Stages of schizophrenia in men
According to most people, schizophrenia is a disease with a severe course throughout its entire course, but this is not entirely true. This pathology is characterized by the development and intensification of symptoms.
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish 3 stages of schizophrenia:
- mastery;
- adaptation and remission;
- degradation.
initial stage
The initial stage (mastery) can develop at different speeds. In some cases, this takes several decades. The list of symptoms includes:
- the appearance of strange fantasies;
- frequent depression, apathy;
- headaches, sleep disorders;
- anxiety, hysteria, manifestation of aggression;
- poor expression of emotions;
- hypochondria, the appearance of phobias and manias;
- sloppiness, unwillingness to take care of oneself;
- reluctance to contact people, excessive suspicion;
- the occurrence of obsessive thoughts and actions.
The person himself is unaware of the disease and regards his thoughts and actions as standard.
This stage is often called the period of discovery, as the patient believes that he has begun to see the hidden meaning of things and events. Only a specialist can identify the presence of pathology.
Last stage
The last stage of schizophrenia is the period of degradation. It is characterized by irreversible, persistent mental defects. In other words, the man’s personality becomes completely destroyed.
The symptoms are:
- complete apathy, autism;
- inability to care for oneself independently;
- the patient's stay in the illusory world;
- delusions and hallucinations;
- signs of dementia;
- the presence of delusional thoughts;
- inability to control your body.
Thus, a patient with the last stage of schizophrenia receives the disability of a mentally ill person.