Acalculia (a + lat. calculo - to count) is presented in the form of a neuropsychological symptom, the peculiarity of which is the loss of the ability to perform arithmetic operations due to lesions of the cerebral cortex.A synonym for acalculia is dyscalculia.
Patients lack the ability to compare numbers, subtract and add them, and solve basic mathematical problems.
In essence, a person’s ability to count is the simultaneous integration of several cognitive skills. The pathology under consideration provokes difficulties in the following areas:
- association of number and its spoken name;
- comparison of numbers with different numerical values;
- registering the meaning of a number in the mind and understanding its essence;
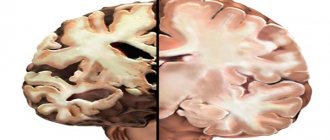
The symptoms of acalculia are often a precursor to dementia, the cause of which is the presence of lesions in the frontal or parietal lobe of the brain.
General characteristics of the violation
The disease is divided into several types, which simplifies the choice of treatment method.
Description
Acalculia and dyscalculia are two different conditions, although they are quite similar in appearance.
In the first case, we are talking about a symptom of the underlying disease, and in the second there is an independent disease. Acalculia was first described by Swedish pathologist F. Henschen. It develops if the part of the brain in which the center responsible for mathematical functions is located is affected. A combination of this condition and sensory aphasia is often observed.
There is also the opposite condition - Savant syndrome, in which a person, on the contrary, has unique, excessively high abilities in mathematics.
Acalculia and dyscalculia: differences
These two disorders, one a symptom and the other an independent pathology, are very similar in external manifestations.
Therefore, without collecting an anamnesis and a general examination, it is not always possible to immediately understand which of them is occurring. In the case of acalculia, treatment will be aimed at eliminating the disease or brain damage that the condition is a manifestation of. Therapy is carried out not only by a speech therapist using exercises, as in the case of dyscalculia, but also by doctors using medications.
Dyscalculia - What kind of disease is this?
What complications can the syndrome cause?
The manifestation of acalculia syndrome significantly inhibits personality development. She becomes poorly trained, because she perceives the material worse. A specialist with this syndrome quickly loses his qualifications. In addition, having such a disease, many feel inferior. This is where mental disorders appear.
Like any disorder caused by abnormalities in the structure of the brain, acalculia is very dangerous, but do not despair. In the vast majority of cases, complete rehabilitation of the patient is possible.
Video for the material
If you see an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Types of acalculia
The condition is classified by the reason it appears and what changes it causes.
So, acalculia can be primary or secondary. With the primary growth, the center responsible for the ability to count is directly affected, and with the secondary, pathological changes occur in various parts of the cerebral cortex, which to one degree or another are involved in the process of perceiving numbers and counting.
Depending on what violations are observed in this condition, four of its varieties are distinguished.
- Optical.
The patient has an exclusively visual impairment in the perception of numbers. This condition is typical when the occipital region of the cerebral cortex is affected. Usually the phenomenon is combined with visual agosia. - Sensory or auditory.
The condition is characterized by the fact that there is a violation in the recognition of speech and sounds. Difficulties usually arise not only with mathematics, but also with general understanding. This pathological condition develops when the superior temporal gyrus is damaged. It is combined with sensory aphasia. - Amnestic.
This type is characterized by impaired auditory-verbal memory. It occurs when the underlying pathology affects the temporal cortex of the cerebral hemispheres. There are also other memory impairments. - Frontal.
Any arithmetic operations are impossible due to a disorder in the organization of purposeful activities. Other manifestations of the underlying disease of apraxia are also noted.
After identifying the cause of the disorder, treatment is prescribed to eliminate the underlying pathology.
Savant syndrome: symptoms and treatment
Acalculia in children
The dysfunction in question is an acquired ailment, manifested in a failure to perform arithmetic operations.
The causes of acalculia in children are damage to brain structures. The ability to count is a fundamental skill, the absence of which significantly complicates life and interferes with obtaining an education and mastering a profession. The dominant place in the formation of counting processes belongs to the parieto-occipital zones and parietal segments of the cortex.
The causes of acalculia are due to damage to the listed brain areas, resulting in disruptions in spatial orientation and understanding of spatial relationships.
Luria determined that the majority of children suffering from the described defect are proficient in ordinal counting, correlating the number of objects, and can count, but they cannot understand the principle of place value or operate with generalized sets. The cardinal symptoms of this pathology are: a breakdown in the understanding of numbers, a disorder in understanding the bit structure of a number, and an understanding of the meaning of signs. Numeracy is the integration of several cognitive skills. An individual suffering from acalculia experiences great difficulties in four areas.
Acalculia syndrome and its manifestations are determined by the location of the abnormal focus. Thus, if the occipito-parietal segments are damaged or if there is a bilateral lesion, primary acalculia can be assumed. If the occipital segment is damaged, the visual image of the number disappears; for the patient it ceases to be a symbol reflecting a certain quantity. An individual recognizes numbers; they are mixed in perception. This especially applies to numbers that are similar in style. If the temporal zones are damaged, failures in mental counting are observed, and in the prefrontal segments, purposeful activity is disrupted, the patient cannot plan counting actions and control their implementation.
Sometimes the dysfunction in question does not completely deprive the child of the ability to perform computational operations. Some young patients retain their addition skills, but subtraction becomes an impossible task for them. The described illness can often be accompanied by sensory aphasia. The degree of impairment in the work of arithmetic operations varies from absolute inability to calculate to errors in counting operations and when manipulating numbers.
Causes
This symptom appears due to damage to the cerebral cortex in its various lobes.
The most common reasons for the appearance of acalculia are:
- cerebrovascular disorder
- such causes include hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, as well as chronic cerebral ischemia, which causes the gradual development of vascular dementia; - open and closed craniocerebral injuries
- if the injury results in a hematoma in the brain, then the risk of developing a counting disorder is quite high. Crushing of the brain substance in certain areas of injury may also occur; and then, if the area of the cortex that is responsible for arithmetic operations is involved, acalculia develops. Depending on the injury, the condition may be reversible or irreversible; - neuroinfections
- in addition to other symptoms of brain damage, these diseases are often accompanied by changes in the ability to count. The most common infections are encephalitis, encephalomyelitis, and meningoencephalitis; - intoxication
- severe poisoning in acute or chronic form, caused by chemicals or disturbances in the functioning of the body, such as hyperglycemia or uremia, lead to damage to various parts of the brain, including those used in calculations. As a result, acalculia of varying severity develops; - neoplasms in the brain
- when present, compression of the brain tissue occurs, which is why it ceases to fully perform its functions. At the moment when the cerebral cortex is damaged in the area responsible for arithmetic abilities, a pathological condition develops; - a disease of the central nervous system of a degenerative nature
- in this case, a violation of counting occurs due to general degeneration of the nervous system and is combined with symptoms such as memory impairment, degradation of thinking, inadequate perception of what is happening around and loss of the ability to independently care for oneself.
Acalculia in a child is usually associated with the fact that there are abnormalities in the development of the brain, which are caused by hypoxia suffered during intrauterine development or during childbirth, as well as infection of the fetus or birth trauma.
Important!
Rarely, hereditary pathologies lead to acalculia.
Symptoms of the problem
Children suffering from dyscalculia are not able to understand what a number is and on what principle the number series is built; they cannot distinguish and remember numbers. They cannot perform operations with numerical values and do not know how to decompose them into terms. It is difficult for them to compare the number of objects, perform simple arithmetic operations and carry out calculations according to the internal plan, that is, to count “in their minds”.
Symptoms of dyscalculia:
- difficulty recognizing and writing numbers;
- inability to tell time and navigate hours, minutes, seconds;
- impaired coordination of fine movements;
- inability to determine the distance traveled or measure the length of a segment;
- difficulty in perceiving the concepts “less” and “more”;
- the impossibility of solving problems without illustrative support;
- difficulties in solving logical problems and performing actions with abstract categories;
- inability to visually determine the number of objects, putting them into groups without counting them one by one.
As soon as relatives discover the above symptoms in a child, you should immediately seek advice from a speech therapist or psychotherapist. The specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis, determine the form of the disorder, identify the causes of its occurrence and develop an effective correction method.
Due to a violation in the processing of visual information, the child can solve examples only if their objective component is present. The child cannot independently imagine what is written in the task conditions. In addition, schoolchildren in primary grades are unable to rationally calculate their free time, which leads to poor academic performance and behavior problems in the future. This aspect is described quite fully in the video below:
Symptoms
Patients with acalculia need specialist help
The disorder does not manifest itself in exactly the same way in patients of different ages. There are also general signs of acalculia.
Signs
Depending on the form of the disorder, the general symptoms also change somewhat. However, for all patients it is still similar in its manifestations and can be assessed for diagnostic purposes.
- With the primary lesion,
there is a loss of understanding of numbers and numerical digits. As a result, for the patient, the difference between numbers that are similar in appearance or sound when pronounced disappears. Quite often the condition is combined with the impossibility of orientation, since the correct concepts of right and left, top and bottom are lost. - The secondary form
is characterized by visual disturbances in which the patient cannot recognize images of numbers. As a result, he is unable to correctly name the numbers he sees, and also gets confused when writing them. Auditory perception and mental arithmetic are preserved. Quite often, the conditions are combined with the inability to recognize letters, objects in images, and people’s faces. - With sensory impairments,
there is a lack of perception of sounds, which makes counting by ear impossible. In the frontal form of the disease, the ability to sequence mathematical operations is lost, which also leads to the inability to count. Solving even elementary problems turns out to be extremely difficult.
Acalculia in adolescents and schoolchildren
In children, due to congenital abnormalities in the structure of the brain, the problem arises early.
It is not difficult to notice it, since the patient’s mathematical development lags behind. The child is not capable of mastering numbers at the same level as his peers. In younger schoolchildren, the disorder becomes especially noticeable. Diagnosis is carried out using a comprehensive examination.
Examples
The most common phenomenon in childhood is the inability to remember numbers and learn to relate them to written symbols.
For this reason, the impression of severe mental retardation may be created. Such children also cannot correctly determine the time, depending on the form of pathology, auditorily or visually.
Acalculia in adults
In adults, the condition develops after brain damage.
As a result, the counting abilities that were previously available are lost. When disorders in the structure of the brain are congenital, they pass into adulthood from childhood if therapy does not bring results.
Parkinson's disease - what is this disease?
Classification
It is customary to distinguish two types of acalculia according to the mechanism of occurrence: primary and secondary. Primary appears as a result of the appearance of certain violations in the area responsible for the score.
The secondary form of pathology appears due to damage to other areas involved in arithmetic operations. This type is divided into 4 subspecies:
- optical – people have impairments in number recognition;
- auditory – there are problems with the sound perception of numbers;
- amnestic – disorders affect auditory-verbal memory;
- frontal - a person cannot perform any arithmetic operations.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment is possible
Treatment depends on the causes of acalculia.
Treatment, correction
Treatment is carried out using medications to improve brain health. Depending on the cause of the disorder, these include antibiotics, antipsychotics, and drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain and reduce the risk of organ swelling. Classes in a complex of rehabilitation measures are also required.
How to get rid of it?
Classes and exercises for each patient are selected individually. These include arithmetic exercises, sessions with a speech therapist and a course of psychotherapy.
Prevention
Since acalculia is only a symptom of the underlying disease, prevention of the condition comes down to reducing the risk of brain injuries and diseases.
If there are factors predisposing to brain damage, it is necessary to regularly visit a doctor for preventive purposes.
Treatment
Acalculia is treatable, but to completely eliminate the symptoms, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the pathology, the disease that caused the disorders. A different situation arises with dyscalculia. Since this disease is not acquired, but congenital, treatment involves only correction and preventive measures.
Treatment methods for acalculia will depend on the patient's age and the severity of the disease. If an adult is sick, therapy will be carried out with specialists using various computer programs. The patient is gradually brought to awareness of the concept of number. After this, learning mathematical operations begins, from simple to more complex.
For children, treatment is based on play. Most often, pictures with numbers are used for this. The child is visually taught to distinguish numbers.
Correction of dyscalculia should be carried out by a speech therapist. If necessary, a psychologist and a neurologist can be involved in working with the patient. Special techniques are being developed for correction. Classes can take place in any place comfortable for the child. The technique consists of a whole set of game exercises that teach counting. Also, classes should be aimed at developing the child’s speech, thinking, and visual abilities.
To eliminate dyscalculia, it is very important to develop competent and coherent speech. Correction should be based on expanding the child’s vocabulary while simultaneously learning mathematical terms. at the very beginning, an understanding of more, less, the name of geometric figures, and the characteristics of an object should be introduced.
The next stage introduces teaching ordinal counting and the use of numbers in speech. The child is taught to compare numbers, objects, their quantity, and quality characteristics. The child forms a connection between a number and its visual expression in writing. Both fine motor skills and thinking develop immediately.
As soon as stable achievements in counting are achieved, the teacher moves on to simple arithmetic operations. The goal is to show the child the logic of the solution.
The main thing about acalculia
The condition is a symptom, not the disease itself.
It can occur at any age and requires comprehensive treatment. The older the patient, the lower the likelihood of a favorable prognosis. Acalculia manifests itself in various counting disorders depending on which areas of the brain are affected. Correction is also prescribed based on what caused the disorder and what part of the brain is affected.
Have you encountered acalculia in your loved ones? Write in the comments how your treatment is going.
Elizarova Lilia · Mar 12, 2019
Acalculia and dyscalculia
At school age, approximately 5% of children suffer from dyscalculia, which is manifested in the inability to perform any calculation operations, the inability to distinguish numbers and a lack of understanding of counting.
Acalculia syndrome arises with adequate mental formation as a result of some illness or injury. Dyscalculia is, first of all, characterized by the inability to master arithmetic, and acalculia is characterized by a disorder of counting operations.
Acalculia is an acquired brain defect in which the ability to perform simple arithmetic operations is lost. Dyscalculia, in turn, is characterized by a loss of ability to teach a child mathematical operations. Often this problem is accompanied by an inability to recognize letters. Often, acalculia is accompanied by mental dysfunction, as a result of which in adults certain segments of the brain responsible for counting and number operations are damaged.
Acalculia, what is it and what are its causes? Below are the main types of acalculia and their causes.
Primary acalculia is found as a result of damage to the occipital-parietal-temporal segments of the cortex. With this type of illness, he has difficulty performing simple mathematical operations, does not understand the structure of numbers, and often confuses the arithmetic sign.
Against the background of mental dysfunction, secondary acalculia may arise. With this variation of the disease, the subject may confuse the numbers due to their similarity in spelling. There may also be failures in mental account operations. Such subjects are not able to correctly perform a counting operation. Individuals suffering from the disorder under analysis cannot be classified as mentally retarded. Such individuals find it difficult to count money or remember numbers.
The formation of acalculia is observed due to violations of various cognitive processes.
Types of acalculia are distinguished depending on the affected cognitive function.
The verbal variety of the disease is revealed in the inability to verbally designate mathematical concepts. The patient can successfully perform mathematical operations, but cannot verbally name numbers, symbols, or indicate the number of objects.
The apraxic variation of the disease is expressed in the inability to count objects. The individual cannot count objects and determine quantitative characteristics.
The operational type of acalculia is the loss of the ability to perform mathematical operations.
The graphic variety of the described disorder is found in the inability to write down mathematical signs and notations, as well as to correctly draw geometric figures.
Dyslexic acalculia consists of the loss of the ability to read mathematical symbols and formulate quantitative terms.
Dyscalculia occurs at an early age. It is expressed in the inability of children to learn mathematical operations. Their brain does not perceive this information. This problem is congenital and is present throughout life. Often this defect occurs due to a genetic predisposition. The result is, since the crumbs are not able to count, determine the right or left side, time, they have difficulty recognizing geometric shapes and letters.
Among the common signs of dyscalculia are the following: inability to perform some calculation operations, problems with recognizing numbers (for example, one is similar to seven), difficulties in basic calculations due to the inability to identify a symbol or sign, or explain a mathematical operation.
Prevention methods
Precautionary measures to prevent dyscalculia can be carried out in early preschool childhood. First of all, the most complete correction of existing neurological pathologies should be carried out. At an early age, you can start learning basic mathematics in a playful way.
Parents should clearly demonstrate to their child how to count objects, shapes and perform basic mathematical tasks, for example, while swimming, you can ask your child to count blue balls or catch three red balls with a net. When teaching a child to count, it is necessary to carefully pronounce the names of numbers, and then arithmetic operations. You can show the number of objects to the child on your fingers or using small toys and objects. Gradually, you need to teach your child to correlate the number of objects with a specific number.
To prevent a child from developing operational dyscalculia, he must be taught the rules of counting and the order of mathematical operations. To prevent verbal and lexical problems, it is necessary to ask the child to say the name of the numbers when counting, and when looking at various figures and other objects - their color and shape. Parents should monitor the correct use of certain symbols and, if their child makes mistakes, calmly correct them, without using harsh punishments.
To prevent the occurrence of dyscalculia in graphic form, it is necessary to pay special attention to the development of the child’s visual memory, fine motor skills, coordination of movements through finger and outdoor games, collecting cut pictures, cubes, puzzles, playing with small parts of the construction set, stringing beads on a cord, identifying them shape and color. The productive activities of children are very effective in this regard - modeling, drawing, appliqué, making crafts, origami.
Moms and dads must pay attention to the development of thinking and memory in the child, and then, in the future, the occurrence of dyscalculia can be avoided.