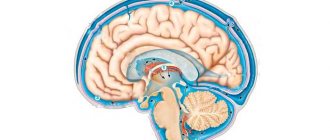
Statistical data
Diagnosing SCN is quite difficult, since the main symptoms are similar to pathologies such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's syndrome (rigid form). Moreover, it is extremely rare.
The disease was first described in 1964. Today it is most widespread abroad. Most often it occurs after 60 years of age, regardless of gender.
Classification
Forms of the disease depending on the course:
- acute – symptoms manifest themselves clearly;
- chronic – characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation.
Types based on functionality:
- obstructive;
- hypersecretory;
- communicative;
- hyporesorptive.
Classification according to development dynamics:
- passive form;
- active form.
According to the location of the lesion:
- internal (excess cerebrospinal fluid is found inside the ventricles of the brain);
- external (excess fluid is in the skull);
- general (combined).
By etiology of origin:
- idiopathic (primary) – there are no visible causes;
- symptomatic (secondary) – is a sign or complication of an existing pathology.
Causes
The main reason for the development of the syndrome is an imbalance of cerebrospinal fluid resorption and secretion. Because of this, liquor dynamics (proper circulation of cerebrospinal fluid) is disrupted. In the adult population, impaired glucose tolerance is observed.
The following causes and factors can provoke normal pressure hydrocephalus:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- internal bleeding in the brain;
- cranial purulent inflammatory processes;
- intracranial formations;
- perinatal damage to the brain and its membranes;
- consequences after brain surgery;
- abnormal development of the ventricles of the brain (usually atresia of the Sylvian aqueduct);
- tumor oncological neoplasms;
- meningitis;
- cyst, cerebral aneurysm;
- atrophy of areas of the brain;
- disorders in the central nervous system during intrauterine development.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus of the brain: symptoms, causes, treatment and prognosis
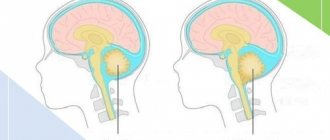
Normal pressure hydrocephalus, or Hakim-Adams syndrome, is a disease characterized by a combination of dementia, pelvic disorders and gait disturbances with pronounced dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain. The set of symptoms was called the “Hakim-Adams triad”, named after the researchers who first described the pathology.
In this case, the cerebral cortex is not damaged or atrophy is mild. Normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure is maintained.
According to research, the disease is accompanied by dementia in 0.4-6% of cases. The variability of observations is due to the lack of uniform criteria for diagnosing the syndrome.
Types of disease
Pathology can develop in acute or chronic form.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus can be primary, occurring without apparent external causes, and secondary, or symptomatic, developing in cases of brain damage with impaired cerebrospinal fluid circulation. The ratio between the varieties of the disease is 1:1.
The pathology most often occurs in adults and the elderly, but cases of the disease have also been described in children.
Reasons for the development of normal pressure hydrocephalus:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- disorders of the development of the brain and its membranes in the perinatal period;
- cerebral hemorrhages
- tumors and aneurysms of cerebral vessels;
- atresia of the Sylvian aqueduct;
- meningitis and other infectious diseases;
- surgical intervention.
Factors influencing predisposition to the disease are:
- elderly age,
- high blood pressure,
- disturbances in the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid,
- congenital features of the anatomical structure.
In 30-50% of cases, it is not possible to identify the cause of normal pressure hydrocephalus in patients. Observations are being conducted to determine the relationship between the frequency of the disease and genetic predisposition.
Complications
The main problems that arise after surgery are: subdural hematoma (2-17%), infection (3-6%), seizures (3-11%), incorrect placement of the shunt (21%). Liqueur hypotension syndrome may also occur, manifesting itself in the form of headaches when changing body position. Complications usually occur during the first year after surgery.
The risk of infection is reduced when the shunt is impregnated with antibiotics.
The mortality rate of patients is about 2% and, according to experts, occurs as a result of concomitant diseases.
Symptoms
When the disease was first described by neurosurgeons Adams R. and Hakim S., the main symptoms were made public, which were later called the “triad.”
Hakim-Adams syndrome is characterized by a latent course, so it is almost impossible to detect primary signs. This leads to late diagnosis, which complicates the treatment process.
Disturbed gait
This is the very first sign that is detected in patients with Hakim-Adams syndrome. Develops against the background of ataxia and brain damage in the frontal lobe. The gait has features:
- Small steps, magnetism (a feeling that the feet are sticking to the floor), impaired balance, difficulty turning around, shuffling, wide leg spacing when walking.
- As the disease progresses, the patient develops uncertainty and fear, so his steps become even smaller.
- Instability and a decrease in the height of steps develop, which is why a person cannot climb stairs.
- If the patient wants to turn in the other direction, he has to prepare for this for a long time, marking time in one place.
- In a lying or sitting position, the lower limbs perform certain manipulations in a stereotypical manner (reminiscent of steps).
Dementia
This is a dysfunction of brain structures in which the following abnormalities develop:
- Memory is significantly impaired, the speed of mental reactions slows down.
- The patient develops a depressive and apathetic state, after which all desire disappears.
- After some time (in each case differently), a person adapts to what is happening, beginning to agree with everyone.
- At the same time, he becomes disoriented in space, events and time. If you take him to another (nearby and previously familiar) street, he will not be able to find his way back. If you ask what time it is, the patient will not answer.
- In some representatives, cognitive disorders transform into mental disorders, against which manic tendencies and hallucinations appear. As a result, the personality is completely suppressed.
- In some cases, the normal psyche is transformed into a frontal one. Namely, the patient does not accept criticism, makes vulgar jokes, and has fun for no reason.
- In severe cases, drowsiness, stupor, and akinetic mutism are noted. These manifestations are dangerous for human life.
- The ability to chronologically sequence is impaired. For example, instead of putting a T-shirt on a naked torso first, the patient puts on a jacket and then a T-shirt.
The cause of dementia lies in the lack of functionality of the frontal lobes. This impoverishes commissural and associative connections, the corpus callosum.
Inability to hold urine
The patient has a frequent urge to urinate in the initial stages of the development of Hakim-Adams syndrome. Over time, a person ceases to control the urge and does not notice how urine is released.
Other symptoms
Other signs that are present in Hakim-Adams syndrome:
- impaired fine motor skills;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- fecal incontinence;
- noise in ears.
In Hakim-Adams disease, the lower extremities are predominantly affected; the arms function normally. This is due to the close location of the brain structures that are responsible for the movement of the legs to the lateral ventricles.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus. Hakim-Adams syndrome
The disease was first described in 1965 by S. Hakim and R. D. Adams. [13]. It is a variant of open hydrocephalus. This disease is characterized by slow expansion of the ventricular system with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. This leads to the development of a triad of symptoms (Hakim-Adams triad). These include walking impairment, dementia and urinary incontinence. [1].
Epidemiology. There are different data on this matter in the literature. The disease usually affects older people. The diagnosis is made in 0.41% of the population over 65 years of age, 0.4-6% in patients with dementia and 15% with walking impairment [1]. D. Jaraj et al.
(2014) noted that normal pressure hydrocephalus occurs in 0.2% of cases aged 70–79 years and in 5.9% of cases aged 80 years and older. However, the authors are of the opinion that the real figures are much higher. It is noteworthy that cases of diagnosing this disease even in childhood have been described.
The prevalence is similar between men and women. [2].
Etiology. There are primary and secondary normotensive hydrocephalus. In the first case, it is not possible to identify the causes of the disease. Such patients account for between half [1, 2] and one third [3] of cases. Secondary hydrocephalus is a consequence of subarachnoid hemorrhage (30J), meningitis (15%), traumatic brain injury (10%), neurosurgical operations [3].
Pathogenesis. The disease is based on the formation of an imbalance between the secretion and resorption of cerebrospinal fluid, a violation of liquor dynamics. As a result, the volume of the liquor space increases and the volume of brain tissue decreases [2].
This leads to irreversible ischemic and degenerative white and gray matter of the brain. In this case, the predominance of the frontal nature of neurological disorders is characteristic.
It is believed that this is due to the predominant expansion of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles, which leads to compression of the deep parts of the frontal lobes, anterior parts of the corpus callosum, motor pathways connecting the cortex with the lower extremities, disconnection of the basal ganglia from the frontal cortex, dysfunction of the frontal lobes, and impaired sensorimotor integration . [1]. In some cases, there is a decrease in blood flow to the brain. [2].
Clinical picture. The clinical picture of the disease is characterized by the gradual development of the classic triad of symptoms (gait impairment, dementia and urinary incontinence) over several months or years [1, 3]. However, after a traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage, symptoms may appear in the first days and weeks. [1].
Walking disturbances usually appear as the first signs of the disease. The gait slows down, then becomes unsteady, and falls are possible. Next, apraxia of walking manifests itself (uncertainty when standing and walking, difficulty starting movement).
At the same time, lying and sitting, the patient easily imitates walking movements, but in an upright position this is instantly lost. Strength in the limbs is not impaired. [1]. Postural tremor and akinetic-rigid syndrome (the “freezing” phenomenon) may be detected.
This brings the disease closer to the rigid form of Parkinson's disease (this diagnosis is often made initially). However, upon examination, muscle rigidity is not detected. Sometimes pseudobulbar syndrome occurs. [2].
Cognitive impairments are characterized by a frontal-subcortical nature and usually develop against the background of already existing motor manifestations. [1]. Loss of short-term and long-term memory and disorientation in time appear. Patients have difficulty explaining their medical history.
Problems arise in planning, concentration, abstract thinking, and semantic memory impairment. The emotional side becomes impoverished, apathy and complacency appear. The phenomena of agnosia (impairment of various types of perception: visual, auditory, tactile) are not uncommon.
The speed of mental processes and psychomotor reactions slows down. The degree of cognitive impairment varies. [2].
Dysfunction of the pelvic organs is detected in the early stages with active questioning - frequent urination and nocturia. Next comes urgency and then urinary incontinence. With the progression of cognitive impairment, patients lose their criticism of this problem and treat it indifferently. [12].
Diagnostics. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a triad of symptoms with dilatation of the ventricular system with a normal level of intracranial pressure.
Clinical and radiological criteria:
1) the presence of a complete or incomplete Hakim-Adams triad (gait disturbance, cognitive impairment, impaired control over the function of the pelvic organs, primarily urination)
2) the presence of a characteristic X-ray picture of NTG, which includes a combination of the following signs:
- expansion of the ventricles of the [brain] brain: Evans index more than 0.3 (30%) and expansion of the temporal horns of the lateral ventricles more than 2 mm (for reference: the Evans ventricular-hemispheric index is the ratio of the distance between the most distant points of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles to the largest internal skull diameter)
- disproportionate expansion of subarachnoid spaces (DESH symptom): expansion of the cisterns of the skull base, lateral fissures of the brain in combination with compression of the interhemispheric fissure and parasagittal subarachnoid spaces in the parietal region [2].
The diagnosis also involves performing a lumbar puncture to determine the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid. CSF pressure remains normal in this disease [1, 2].
In addition, a TAP-TEST is carried out. It is also called the Miller-Fisher test, lumbar test, or spinal test. It is carried out as follows: a lumbar puncture is performed to remove 30-50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid. Before and after the test, a video recording of the gait is performed.
The test is considered positive if, after evacuation of the cerebrospinal fluid, a significant improvement in gait or other symptoms is noted. A positive test confirms the diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus. It has not yet been finally decided when and how to evaluate the results of this test. Basically, the assessment is made after 1 day.
For normal pressure hydrocephalus, gait and cognitive function are temporarily improved after this procedure. However, K. Kang et al. (2013) described a patient who had no response after 1 day, but improved after 7 days. [2]. The degree of improvement in the patient's condition after the test coincides with the effect of bypass surgery.
Even a short-term decrease in the manifestations of at least one of the symptoms of the disease is considered a favorable prognostic sign. [1].
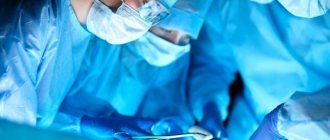
Treatment. The main treatment method for these patients is shunt surgery with the application of a ventriculoperitoneal, ventriculoatrial or lumboperitoneal shunt. Positive results are observed in 60% [4] -66% [1] -75% [2] of patients.
The prognosis of surgical intervention worsens as the disease progresses. [1].
It is preferable to use valve-regulated systems with an anti-siphon device and systems with a programmable variable pressure valve with the smallest possible design step of changing the opening pressure. [2].
It is important to note that according to some authors, even in the absence of a positive effect from the tap test, bypass operations had a significant positive result. [4, 5, 6].
In the postoperative period, comprehensive rehabilitation treatment is necessary.
Bibliography:
- Diseases of the nervous system: A guide for doctors: In 2 volumes – T. 1/Ed. N. N. Yakhno, D. R. Shtulman. – 2nd ed. , processed and additional – M.: Medicine, 2001.
- https://laesus-de-liro.livejournal.com/285115. html
- Gusev E. N., Nikiforov A. S. Neurological symptoms, syndromes and diseases. – M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2006.
- Moretti J. -L. “Assessment of alterations in cerebrospinal fluid kinetics. ” /In: Radionuclide Imaging of the Brain. Ed. by B.L. Holman. -New York etc.: Churchill Livingstone, 1985. -P. 185-223
- Adams RD, Fisher CM, Hakim S. et al. “Symptomatic occult hydrocephalus with “normal” cerebrospinal fluid pressure: a treatable syndrome.” //N. Engl. J. Med. -1965. -Vol. 273. -P. 117-126
- Ketonen LM, Berg MJ Clinical Neuroradiology. 100 Maxims. -London etc: Arnold, 1997
Source: https://volynka.ru/Diseases/Details/642
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the doctor pays attention to the presence of a symptomatic triad. The following are instrumental diagnostic methods:
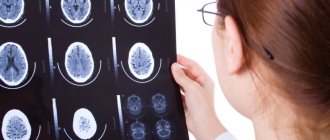
- Magnetic resonance imaging. The level of cerebrospinal fluid outflow and the structure of the Sylvian aqueduct are assessed. The lateral ventricles and anterior horns are studied. In a pathological condition, they are increased in size, the sulcus and gyri are thinned and atrophied. However, no changes are observed in the cerebral cortex.
- Examination of the fundus is an integral part of the examination. The syndrome is characterized by congestion and swelling of the discs in the optic nerves.
- Craniogram, that is, an x-ray of the skull. With a protracted course of Hakim-Adams disease, osteoporosis is detected in the bony part of the skull, deformation of the sella turcica, and thinning of the anterior edge in the foramen magnum. Upon closer examination, it appears as if fingers are pressed into the skull.
- CT angiography. The level of blood supply and the presence of a sinus are considered.
After the basic research methods, the doctor conducts testing:
- Lumbar puncture. CSF pressure is determined. Normally it should be a maximum of 200 mm of water. Art.
- Monitoring intracranial pressure. It is carried out along with a method such as polysomnography. The syndrome reveals a coincidence of high intracranial pressure during REM sleep with regression during wakefulness.
Additionally, other tests, surveys, etc. can be carried out, which will reveal increased sensitivity to the psyche of a frontal nature.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus – Hakim-Adams syndrome | diet-and-treatment.rf
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH, Hakim-Adams syndrome) is a syndrome characterized by a combination of dementia, walking disorders and urinary incontinence with pronounced dilatation of the ventricular system and normal CSF pressure. The prevalence of NTG is low, it is detected in 1-5% of patients with dementia.
IGT as an independent disease was first described by S. Hakim and RD Adams. In 1965, they published articles on "symptomatic occult chronic hydrocephalus of adults with normal fundus", or "hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure".
The authors paid special attention to the possible reversibility of the clinical manifestations of this syndrome with adequate treatment.
Causes of normal pressure hydrocephalus The development of the disease is based on an imbalance between the secretion and resorption of CSF, as well as a violation of liquor dynamics. IGT in adults can be induced for various reasons:
- bleeding in the brain,
- TBI,
- purulent-inflammatory process in the cranial cavity,
- perinatal damage to the brain and meninges,
- volumetric intracranial formations,
- abnormalities of brain development (the most common cause is atresia of the Sylvian aqueduct),
- undergone brain surgery.
In approximately 40-60% of cases, the history of patients with Hakim-Adams syndrome does not indicate any clear cause underlying the development of the disease (so-called idiopathic IGT).
Clinical manifestations of Hakim-Adams syndrome
IGT is characterized by the gradual development of the Hakim-Adams triad - dementia, walking disorders and urinary incontinence. In most cases, walking impairment is the first symptom, followed by dementia and later pelvic disorders. Fluctuation in the severity of symptoms is possible, but this is not typical for IGT.
The main complaint of patients with dacha pathology at an appointment with a neurologist is dizziness, which they describe as a feeling of instability when moving or making sudden turns of the body. In this case, the basis of dizziness is postural instability and dysbasia. characteristic of the disease.
Gait disorders include elements of gait apraxia in the form of a shuffling gait with short steps on widely spaced legs and loss of balance control. With normal pressure hydrocephalus, there are no changes in arm movements when walking, which distinguishes it from Parkinson's disease.
In the early stages, with minimal support, changes in gait in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus may be minor.
As the disease progresses, the height of the step decreases, it becomes difficult for patients to lift their feet off the ground, difficulties arise in initiating the act of walking, turns are made in several stages. Falls are common and postural instability may occur.
It is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with Parkinson's disease and other extrapyramidal disorders. In this case, patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus can imitate the movements of the legs that they should make when walking, lying down or sitting.
In idiopathic normotensive hydrocephalus, there is a relationship between the presence of arterial hypertension and the severity of clinical symptoms, especially gait disturbances. Muscle tone in the legs, as a rule, is increased according to the plastic or countercontinence type.
In more severe cases of normal pressure hydrocephalus, spasticity, hyperreflexia occur in the lower extremities, and pathological foot signs are detected.
The presence of symptoms predominantly in the legs with this pathology may be due to the fact that the motor pathways connecting the cerebral cortex with the lower extremities are located more medially, near the walls of the lateral ventricles, and the pathways going to the upper extremities are more lateral. Changes in gait in patients may also be due to disconnection of the basal ganglia from the frontal regions, dysfunction of the frontal cortex, and impaired sensorimotor integration.
Another important manifestation of Hakim-Adams syndrome is dementia. Patients are characterized by disorientation more in time than in place. It is often difficult for patients to tell the story of their illness.
Some may develop hallucinations, mania, depression. A characteristic symptom of normal pressure hydrocephalus is also the development of emotional dullness.
In general, cognitive impairment is manifested by a decrease in memory, a slowdown in the speed of mental processes and psychomotor reactions, a decrease in the ability to use acquired knowledge, and apathy, which is associated with dysfunction of the anterior parts of the brain and is characteristic of the so-called subcortical dementia.
Cognitive impairment in IGT is not the dominant syndrome, especially at the onset of the disease, when gnosis and other cortical functions are, as a rule, not impaired. Unlike Alzheimer's disease, memory impairment in normal pressure hydrocephalus is not as pronounced and is caused by an ocular decrease in the functional integration of the frontal lobes.
Severe dementia in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus implies either an irreparable morphological defect (due to TBI, stroke, etc.) or the presence of concomitant Alzheimer's disease or vascular dementia. To identify cognitive disorders, especially in the early stages of the disease, neuropsychological methods sensitive to frontal disorders are used.
The frontal nature of cognitive disorders in normal pressure hydrocephalus may be due to the predominant expansion of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles, accompanied by more significant dysfunction of the deep parts of the frontal lobes and the anterior parts of the corpus callosum.
Unlike Alzheimer's disease, the cognitive defect in normal pressure hydrocephalus develops more quickly - within 3-12 months. The severity of cognitive impairment may decrease after administration of 20-50 ml of CSF (tap-test).
It is believed that the basis of cognitive disorders in normal pressure hydrocephalus is compression of the brain capillaries by increased intraparenchymal pressure, especially since positron emission tomography data reveals a diffuse decrease in metabolism in both the cortical and subcortical regions.
Already in the early stages, with active, targeted questioning, it is possible to identify patient complaints of frequent urination and nocturia. As the disease progresses, urgency and periodic urinary incontinence occur.
Patients stop feeling the urge to urinate and are indifferent to the fact of involuntary urination, which is typical for the frontal type of pelvic disorders.
Fecal incontinence is rare and usually occurs in patients at an advanced stage of the disease.
Results of additional examinations
It is important to note that during ophthalmoscopy, patients do not have congestion in the fundus. According to EEG, with normal pressure hydrocephalus, nonspecific changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain are detected, characterized by a predominance of slow frequency characteristics.
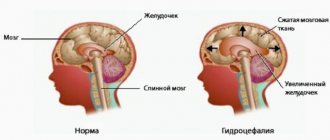
The results of CT and MRI make it possible to detect sharply dilated ventricles of the brain, while the cortical grooves remain within normal limits or are slightly dilated. Using these techniques, other causes of hydrocephalus can be excluded.
The detection of small ischemic foci or areas of leukoaraiosis does not contradict the diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus, since a combination of Hakim-Adams syndrome and cerebrovascular insufficiency is possible.
In normal pressure hydrocephalus, the 111 ventricle, temporal and frontal horns of the lateral ventricles are especially significantly enlarged, which leads to the appearance of a characteristic “butterfly” shape of the ventricular system on axial sections. The expansion of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles in normal pressure hydrocephalus reaches 30% or more of the diameter of the skull.
Surgical treatment of IGT syndrome
The basis of treatment is shunting operations of ventriculoperitoneal and lumboperitoneal shunting, in which a positive effect is achieved in 60% of patients. In advanced stages of the disease, when there are already irreversible changes in the brain, the prognosis for surgical treatment worsens. In some patients, among whom there was no
significant improvement after lumbar puncture, bypass surgery may also be effective. Complications after ventriculoperitoneal shunting in 30-40% of patients:
Source: https://xn——6kcpfdaaudd7a2a6d7d.xn--p1ai/normotenzivnaa-gidrocefalia-sindrom-hakima-adamsa/
Treatment
The choice of treatment method is based on the stage of severity of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies and complications. Most often, surgery is required. Drug therapy is used only in cases of early diagnosis, as well as to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Conservative methods
The effectiveness of drug treatment has not been scientifically proven, but many specialists prescribe medications that the patient must take before surgery. These are the following:
- Diacarb based on the substance acetazolamide.
- Digoxin (cardiac glycoside).
A puncture is required to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, which eliminates the triad of symptoms. The procedure must be carried out multiple times, as it has a temporary effect. To avoid this, surgery is prescribed.
Surgery
The only technique used in surgery for Hakim-Adams syndrome is bypass surgery. During the operation, a shunt is installed, which is impregnated with special antibacterial drugs to avoid infection.
The effectiveness of surgical intervention reaches an average of 60-70%. The patient gets rid of problems with urination, mental disorders and gait. Recovery does not occur immediately, but gradually. Full results are seen in approximately 10-12 months. It is after this period that it is necessary to undergo a control examination, which includes monitoring on a computed tomograph.
To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is necessary to fully complete a rehabilitation course in a hospital setting. And also strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. Rehabilitation is carried out by rehabilitation doctors.
What is Hakim-Adams syndrome? Its types, symptoms, treatment methods
13.02.2019
Hakim-Adams syndrome refers to a neurological disease in which the ventricular system in the brain dilates, against which intracranial pressure does not increase, and cerebrospinal fluid does not circulate normally. The abbreviation is SHA. Another name is normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Statistical data
Diagnosing SCN is quite difficult, since the main symptoms are similar to pathologies such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's syndrome (rigid form). Moreover, it is extremely rare.
The disease was first described in 1964. Today it is most widespread abroad. Most often it occurs after 60 years of age, regardless of gender.
Classification
Forms of the disease depending on the course:
- acute – symptoms manifest themselves clearly;
- chronic – characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation.
Types based on functionality:
- obstructive;
- hypersecretory;
- communicative;
- hyporesorptive.
Classification according to development dynamics:
- passive form;
- active form.
According to the location of the lesion:
- internal (excess cerebrospinal fluid is found inside the ventricles of the brain);
- external (excess fluid is in the skull);
- general (combined).
By etiology of origin:
- idiopathic (primary) – there are no visible causes;
- symptomatic (secondary) – is a sign or complication of an existing pathology.
Causes
The main reason for the development of the syndrome is an imbalance of cerebrospinal fluid resorption and secretion. Because of this, liquor dynamics (proper circulation of cerebrospinal fluid) is disrupted. In the adult population, impaired glucose tolerance is observed.
The following causes and factors can provoke normal pressure hydrocephalus:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- internal bleeding in the brain;
- cranial purulent inflammatory processes;
- intracranial formations;
- perinatal damage to the brain and its membranes;
- consequences after brain surgery;
- abnormal development of the ventricles of the brain (usually atresia of the Sylvian aqueduct);
- tumor oncological neoplasms;
- meningitis;
- cyst, cerebral aneurysm;
- atrophy of areas of the brain;
- disorders in the central nervous system during intrauterine development.
Symptoms
When the disease was first described by neurosurgeons Adams R. and Hakim S., the main symptoms were made public, which were later called the “triad.”
Hakim-Adams syndrome is characterized by a latent course, so it is almost impossible to detect primary signs. This leads to late diagnosis, which complicates the treatment process.
Disturbed gait
This is the very first sign that is detected in patients with Hakim-Adams syndrome. Develops against the background of ataxia and brain damage in the frontal lobe. The gait has features:
- Small steps, magnetism (a feeling that the feet are sticking to the floor), impaired balance, difficulty turning around, shuffling, wide leg spacing when walking.
- As the disease progresses, the patient develops uncertainty and fear, so his steps become even smaller.
- Instability and a decrease in the height of steps develop, which is why a person cannot climb stairs.
- If the patient wants to turn in the other direction, he has to prepare for this for a long time, marking time in one place.
- In a lying or sitting position, the lower limbs perform certain manipulations in a stereotypical manner (reminiscent of steps).
Dementia
This is a dysfunction of brain structures in which the following abnormalities develop:
- Memory is significantly impaired, the speed of mental reactions slows down.
- The patient develops a depressive and apathetic state, after which all desire disappears.
- After some time (in each case differently), a person adapts to what is happening, beginning to agree with everyone.
- At the same time, he becomes disoriented in space, events and time. If you take him to another (nearby and previously familiar) street, he will not be able to find his way back. If you ask what time it is, the patient will not answer.
- In some representatives, cognitive disorders transform into mental disorders, against which manic tendencies and hallucinations appear. As a result, the personality is completely suppressed.
- In some cases, the normal psyche is transformed into a frontal one. Namely, the patient does not accept criticism, makes vulgar jokes, and has fun for no reason.
- In severe cases, drowsiness, stupor, and akinetic mutism are noted. These manifestations are dangerous for human life.
- The ability to chronologically sequence is impaired. For example, instead of putting a T-shirt on a naked torso first, the patient puts on a jacket and then a T-shirt.
The cause of dementia lies in the lack of functionality of the frontal lobes. This impoverishes commissural and associative connections, the corpus callosum.
Inability to hold urine
The patient has a frequent urge to urinate in the initial stages of the development of Hakim-Adams syndrome. Over time, a person ceases to control the urge and does not notice how urine is released.
Other symptoms
Other signs that are present in Hakim-Adams syndrome:
- impaired fine motor skills;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- fecal incontinence;
- noise in ears.
In Hakim-Adams disease, the lower extremities are predominantly affected; the arms function normally. This is due to the close location of the brain structures that are responsible for the movement of the legs to the lateral ventricles.
Which doctor is treating you?
Since Hakim-Adams syndrome is a neurological disease, a neurologist is involved in the treatment. If necessary, consultations with other specialists may be necessary.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the doctor pays attention to the presence of a symptomatic triad. The following are instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging. The level of cerebrospinal fluid outflow and the structure of the Sylvian aqueduct are assessed. The lateral ventricles and anterior horns are studied. In a pathological condition, they are increased in size, the sulcus and gyri are thinned and atrophied. However, no changes are observed in the cerebral cortex.
- Examination of the fundus is an integral part of the examination. The syndrome is characterized by congestion and swelling of the discs in the optic nerves.
- Craniogram, that is, an x-ray of the skull. With a protracted course of Hakim-Adams disease, osteoporosis is detected in the bony part of the skull, deformation of the sella turcica, and thinning of the anterior edge in the foramen magnum. Upon closer examination, it appears as if fingers are pressed into the skull.
- CT angiography. The level of blood supply and the presence of a sinus are considered.
After the basic research methods, the doctor conducts testing:
- Lumbar puncture. CSF pressure is determined. Normally it should be a maximum of 200 mm of water. Art.
- Monitoring intracranial pressure. It is carried out along with a method such as polysomnography. The syndrome reveals a coincidence of high intracranial pressure during REM sleep with regression during wakefulness.
Additionally, other tests, surveys, etc. can be carried out, which will reveal increased sensitivity to the psyche of a frontal nature.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method is based on the stage of severity of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies and complications. Most often, surgery is required. Drug therapy is used only in cases of early diagnosis, as well as to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Conservative methods
The effectiveness of drug treatment has not been scientifically proven, but many specialists prescribe medications that the patient must take before surgery. These are the following:
- Diacarb based on the substance acetazolamide.
- Digoxin (cardiac glycoside).
A puncture is required to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, which eliminates the triad of symptoms. The procedure must be carried out multiple times, as it has a temporary effect. To avoid this, surgery is prescribed.
Surgery
The only technique used in surgery for Hakim-Adams syndrome is bypass surgery. During the operation, a shunt is installed, which is impregnated with special antibacterial drugs to avoid infection.
The effectiveness of surgical intervention reaches an average of 60-70%. The patient gets rid of problems with urination, mental disorders and gait.
Recovery does not occur immediately, but gradually. Full results are seen in approximately 10-12 months.
It is after this period that it is necessary to undergo a control examination, which includes monitoring on a computed tomograph.
To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is necessary to fully complete a rehabilitation course in a hospital setting. And also strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. Rehabilitation is carried out by rehabilitation doctors.
Forecast
It is known that with normal pressure hydrocephalus, symptoms do not appear immediately and resemble many other pathologies.
It is also noted that sick people cannot, due to mental disorders, sensibly assess their own condition and behavior. This is precisely what prevents people from going to the clinic when the very first “bells” are detected.
Therefore, relatives and friends should especially carefully monitor the condition of their elderly relatives.
The prognosis largely depends on the neglect. If bypass surgery is performed at an earlier stage, the operation significantly prolongs life and improves its quality (death is observed in only 2%). In the later stages, it is difficult to completely get rid of the pathology even after surgery.
Complications and consequences
The main complication of the syndrome is disability and death. If we talk about the consequences after shunt surgery, they are mainly associated with the diseases that the patient has, but not with the operation itself or the shunt used.
After surgery, the following complications may occur:
- subdural hematoma;
- hypotension of the cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid pressure is too low);
- epilepsy;
- adhesion of the ventricles of the brain;
- infection.
Prevention
To avoid developing normal pressure hydrocephalus in old age, people must adhere to certain preventive rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle (eliminate bad habits);
- avoid head injuries;
- control blood pressure;
- If you have frequent headaches, consult a specialist;
- promptly treat infectious pathologies;
- conduct active mental activity (solve crosswords, etc.);
- After operations, follow all medical recommendations.
Preventive measures after surgery (bypass surgery), which are followed throughout the rest of your life:
- be sure to wear a warm hat in cold weather;
- avoid exposure to strong winds;
- in the summer, use panama hats and scarves;
- do not overcool;
- prevent infection;
- visit your doctor once a year and undergo an appropriate examination.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (video story)
We present to your attention a video from which you will learn about Hakim-Adams syndrome, the prevalence of the disease, characteristic symptoms and diagnostic methods:
Hakim-Adams syndrome is considered the most dangerous and complex disease, so you should follow the rules of prevention and pay attention to the signs. Shunting is an effective technique, but you need to know that over time the effect of the shunt decreases, so periodic changes in the pressure value at which the valve opens are required.
Source: https://telemedicina.one/nevrologiya-i-psihologiya/sindrom-hakima-adamsa.html
Forecast
It is known that with normal pressure hydrocephalus, symptoms do not appear immediately and resemble many other pathologies. It is also noted that sick people cannot, due to mental disorders, sensibly assess their own condition and behavior. This is precisely what prevents people from going to the clinic when the very first “bells” are detected. Therefore, relatives and friends should especially carefully monitor the condition of their elderly relatives.
The prognosis largely depends on the neglect. If bypass surgery is performed at an earlier stage, the operation significantly prolongs life and improves its quality (death is observed in only 2%). In the later stages, it is difficult to completely get rid of the pathology even after surgery.
Complications and consequences
The main complication of the syndrome is disability and death. If we talk about the consequences after shunt surgery, they are mainly associated with the diseases that the patient has, but not with the operation itself or the shunt used.
After surgery, the following complications may occur:
- subdural hematoma;
- hypotension of the cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid pressure is too low);
- epilepsy;
- adhesion of the ventricles of the brain;
- infection.
Surgical treatment of IGT syndrome
The basis of treatment is shunting operations of ventriculoperitoneal and lumboperitoneal shunting, in which a positive effect is achieved in 60% of patients. In advanced stages of the disease, when there are already irreversible changes in the brain, the prognosis for surgical treatment worsens. In some patients who did not experience significant improvement after lumbar puncture, bypass surgery may also be effective. Complications after ventriculoperitoneal shunting in 30-40% of patients:
- subdural hematomas;
- liquor hypotension syndrome.
Mortality after ventriculoperitoneal shunting is about 6-7%. To prevent complications, individual selection of a shunt is recommended.
Prevention
To avoid developing normal pressure hydrocephalus in old age, people must adhere to certain preventive rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle (eliminate bad habits);
- avoid head injuries;
- control blood pressure;
- If you have frequent headaches, consult a specialist;
- promptly treat infectious pathologies;
- conduct active mental activity (solve crosswords, etc.);
- After operations, follow all medical recommendations.
Preventive measures after surgery (bypass surgery), which are followed throughout the rest of your life:
- be sure to wear a warm hat in cold weather;
- avoid exposure to strong winds;
- in the summer, use panama hats and scarves;
- do not overcool;
- prevent infection;
- visit your doctor once a year and undergo an appropriate examination.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (video story)
We present to your attention a video from which you will learn about Hakim-Adams syndrome, the prevalence of the disease, characteristic symptoms and diagnostic methods:
Hakim-Adams syndrome is considered the most dangerous and complex disease, so you should follow the rules of prevention and pay attention to the signs. Shunting is an effective technique, but you need to know that over time the effect of the shunt decreases, so periodic changes in the pressure value at which the valve opens are required.