Depending on the type of necrosis, a specific type of treatment is prescribed. Necrosis of the coagulation or dry type is formed in a certain element of the body or in an organ, without spreading to other parts of the body. With dry necrosis, dead tissue slowly dries out. This creates a line of demarcation that separates healthy tissue from infected tissue. There are cases when necrotic tissue decreases in size. This process is called mummification.
Crown in the head: SARS-CoV-2 can cause brain necrosis
Russian scientists warn that the pathogen that causes Wuhan pneumonia is capable of penetrating the blood-brain barrier and directly destroying brain tissue.
Descriptions of clinical cases have already appeared in which COVID-19 caused necrotizing encephalopathy in those infected - a critical lesion of the main organ of the central nervous system. However, coronavirus can cause neurological complications without damaging the lungs at all.
Brain dysfunction is indicated, in particular, by a symptom such as loss of smell. The pathogen can also have a negative effect on the cardiovascular system.
Attack on the brain
Some patients with COVID-19 develop serious brain damage, doctors warn.
In addition to the high temperature, fever, cough and difficulty breathing that traditionally accompany coronavirus pneumonia, some infected people experience mental changes caused by neurological disorders.
Professor of the Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, head of research in the field of molecular virology and oncology Andrei Kozlov told Izvestia that influenza and herpes viruses can lead to the death of entire areas of the brain. A similar picture is observed with the new coronavirus.
— Several articles noted that some patients did not have pulmonary dysfunction, but experienced absent-mindedness or epileptic symptoms. Together with the previously noted loss of taste and smell, such symptoms may indicate infection of brain tissue by coronavirus, the expert believes.
At the end of March, doctors from Detroit described a case of necrotizing encephalopathy in an employee of one of the American airlines. A woman in her 50s was hospitalized with a fever and cough. In addition, she experienced confusion.
Doctors conducted a series of tests for influenza, chicken pox and West Nile fever, but all of them were negative. A swab taken from the nasopharynx confirmed the diagnosis of COVID-19. However, due to symptoms atypical for coronavirus, it was decided to undergo a CT and MRI scan for the woman.
The resulting images showed focal lesions in various areas of the brain, in particular, the temporal lobes, whose functions are associated with the perception, analysis and synthesis of speech, as well as the ability to sense tastes and smells, were damaged.
Doctors diagnosed the patient with acute necrotizing encephalopathy, a rare disease that develops against the background of viral infections, most often influenza.
Cytokine storm
Encephalopathy (dystrophic damage to brain tissue) can develop due to the fact that the cells of the immune system of a person infected with coronavirus begin to actively release cytokines into the blood.
This class of substances includes about a hundred complex proteins involved in many immune and inflammatory processes in the human body, Nikolai Karpov, an employee of the Institute of Biology of Tyumen State University, told Izvestia.
The increase in the concentration of such proteins is called a “cytokine storm.”
“In excess, these substances can damage the walls of blood vessels and cause hemorrhages in the brain, which leads to the development of certain neurological symptoms (depending on the affected area),” the expert said. “It is also possible that the virus can penetrate the blood-brain barrier directly into the brain tissue.
According to the scientist, not only coronavirus, but also influenza, as well as other acute respiratory viral infections, can cause encephalopathy, but this complication is rare. In general, science knows dozens of viral diseases, which in a certain percentage of cases cause neurological complications.
For example, viruses of tick-borne encephalitis, measles, herpes types 1 and 2 and West Nile fever, almost all alphaviruses, including the Karelian fever virus (an acute infection, the carriers of which are considered to be Culex mosquitoes) can have a negative effect on the brain.
- “Izvestia”) and many others.
Double punch
Scientists note that COVID-19 is indeed capable of attacking the entire body, not just the lungs.
This pathogen especially often negatively affects the cardiovascular system, Mehman Mamedov, an expert at the National Health League, told Izvestia.
According to him, coronavirus infection can cause acute complications in various organs and systems, including the brain, and also affect the course of chronic diseases, causing adverse outcomes.
— So far, cases of direct effects on the brain are rarely recorded and this cannot be called a common cause of death. But respiratory failure is recorded in every second patient.
In every third person, the situation is aggravated by a combination of respiratory and heart failure, and in 10% of cases, death is caused by heart failure,” the expert said.
“Thus, complications of cardiovascular diseases occupy the second place among the causes of mortality in those infected with coronavirus infection.
As for the effect on the brain, this is still a rather rare symptom that still needs to be studied.
“Perhaps the virus really affects the brain,” emphasized Sergei Netesov, head of the laboratory of biotechnology and virology at Novosibirsk State University, corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, in a conversation with Izvestia. — Accurate confirmation of this will be provided by the results of high-quality clinical observations of experienced and attentive doctors who are now actively involved in the treatment of hundreds of patients infected with COVID-19.
As Izvestia previously wrote, a new type of coronavirus is also capable of disrupting the process of normal hematopoiesis. Based on this, Italian scientists proposed measuring the level of platelets in the blood of patients to predict severe forms of the disease.
Source: https://iz.ru/997173/mariia-nediuk/korona-v-golove-sars-cov-2-sposoben-vyzyvat-nekroz-mozga
Symptoms
Initial signs of atrophy affecting the tissues and structures of the brain usually appear in people over 45 years of age. Pathology is more often diagnosed in female patients. Characteristic symptoms:
- Changing personality type. Apathy, indifference, narrowing of interests.
- Psycho-emotional disorder. Mood swings, depression, increased irritability.
- Impaired memory function.
- Reducing vocabulary.
- Motor dysfunction, impaired coordination of movements and fine motor skills.
- Deterioration of mental activity.
- Decreased performance.
- Epileptic seizures.
The body's regenerative reactions weaken. Reflexes are depressed. Symptoms become brighter and more expressive. Atrophic changes are manifested by Parkinson's and Alzheimer's syndrome. The following signs indicate a specific affected area:
- Medulla. Deviations in the functioning of the respiratory, digestive, and cardiovascular systems. Defense reflexes are suppressed.
- Cerebellum. Weakness of skeletal muscles, malfunctions of the musculoskeletal system.
- Midbrain. Inhibited or absent reactions to external stimuli.
- Diencephalon. Pathological deviations in the functioning of the thermoregulation system, disruption of the hemostatic and metabolic systems.
- Frontal lobes. Secrecy, aggression, demonstrative behavior.
Signs such as impulsiveness, previously unusual rudeness, increased sexuality, decreased self-control, and apathy indicate malfunctions in the functioning of the main organ of the central nervous system.
Is it possible to survive brain death?
The death of a person is an action that has taken place. However, dying itself is a long and systemic process, which includes the failure of all organs and tissues of the body and the inability to restore their vital functions.
At the moment, in medicine there are several separate and unequal concepts. Doctors around the world distinguish between clinical, biological and brain death:
Possible reasons
Brain death can occur for various reasons, but the pathophysiological processes are approximately the same. Brain death occurs due to persistent circulatory disorders, oxygen starvation, and stagnation of metabolic products. Diseases that lead to organ death can be varied: trauma, inflammatory diseases, heart disease, multiple organ failure and many others.
After cardiac arrest, the brain does not die immediately . This depends on many criteria: the general condition of the patient, concomitant diseases, the age of the patient, the disease that caused this condition, the ambient temperature.
Irreversible tissue necrosis begins after 3 minutes, but in young healthy people this process is slower. At low air temperatures, the brain dies more slowly.
If after 3 minutes or more the patient responds to resuscitation measures and returns to life, no one can predict the consequences; perhaps some neurons have died, and this will significantly affect the patient’s life in the future.
Signs
Criteria for brain death:
- Persistent lack of consciousness;
- Lack of response to addressing the patient, tactile sensitivity, stroking, pinching the skin;
- Lack of eye movement;
- Cardiac arrest, straight line on ECG;
Brain death is not immediately diagnosed.
If all of the above signs are present, the patient is observed in a hospital setting for an average of 12 hours; if during this time the patient does not react in any way to external stimuli and has no reflexes of the brain stem structures, biological death is declared.
If the cause of the disease is suspected of poisoning, the patient is observed for 24 hours. If death occurs as a result of a traumatic brain injury, the patient can be observed for less time, only 6 hours; this decision is made by the neurosurgeon who provided assistance from the onset of the disease.
In addition to the subjective ones (which are determined by the doctor at his own discretion based on protocols and his personal experience), there are also objective criteria for brain death.
When a patient has been sick for a long time and relatives understand that sooner or later he will die anyway, this is one thing, but how to explain and prove that a person has died and should be disconnected from life support devices if the irreparable happened suddenly?
Diagnostics
To diagnose brain death in a hospital setting, some instrumental research methods are used.
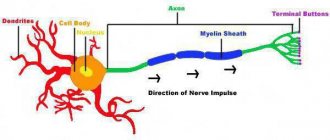
Neurons in the human brain are very sensitive to lack of oxygen and, in its absence, die within a few minutes . On the electroencephalogram of such a person, only the so-called zero line will be detected, since there is no brain activity.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U-YlOW8ri9Y
Electroencephalography is a type of instrumental study of the activity of the nervous system, in particular the brain, which records biocurrents in the brain and reproduces them on paper in the form of specific curves.
A contrast study of cerebral vessels is also a sign of brain death and is included in the diagnostic research protocol.
However, due to its financial component and the need for special equipment, it is not always carried out.
A person is injected with a contrast agent and, using a series of x-rays, its distribution with the bloodstream through the vessels of the brain is observed. With brain death, there is no blood circulation, which indicates the onset of neuronal necrosis.
When performing apneic oxygenation, the patient is disconnected from the ventilator and observed for the appearance of spontaneous independent respiratory movements. The monitor monitors the increase in carbon dioxide in the blood.
It is known that it is the increase in CO2 that stimulates respiration, therefore, when the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood increases by 20 mm. Hg Art.
above the initial level, and spontaneous breathing does not resume within 8-10 minutes, we can reliably say that brain death has occurred.
However, when an ambulance team discovers an injured person, doctors cannot absolutely say that the patient has died long ago and does not need assistance.
Often such victims are diagnosed with clinical death, and with correct and timely resuscitation (artificial ventilation, closed cardiac massage), they can be brought back to life without significant health consequences.
Resuscitation measures are not carried out only if, at the time of discovery of the victim, signs of necrosis - cadaveric spots - are clearly visible on the skin.
Preparing relatives for disconnection from life support devices
When all diagnostic studies have been completed and brain death has been proven, the patient’s relatives decide to disconnect him from life-sustaining devices; they should be warned about the possible occurrence of the Lazarus symptom. After being disconnected from the ventilator, a person may experience muscle contractions, and he may turn his head, bend his limbs, or arch in bed. Relatives should be prepared for this.
Consequences
It is possible to survive diagnosed brain death, but the consequences of brain tissue necrosis are dire.
A person will never be able to return to a full life; as a rule, he lives only on supportive medications and medical equipment.
There are cases in the literature when a person returns to life and even becomes a socially active member of society, but in these cases clinical death is mistaken for brain death, the consequences of which are less sad.
The consequences of clinical death are reversible. With properly performed cardiopulmonary resuscitation, necrotic changes in the body do not have time to occur, and accordingly, organ functions can be completely restored.
That is why it is very important for every person to know and be proficient in resuscitation techniques. Timely implementation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (artificial ventilation using the mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose method and closed cardiac massage) can save the life and health of those around you.
When an emergency occurs, the body redistributes blood circulation, as a result of which the vital organs receive a maximum of blood rich in oxygen and nutrients; if the people with the victim keep him alive until paramedics arrive, this will significantly increase his chances of survival and reduce the consequences of oxygen deprivation and necrosis.
Rate this article:
Total: 192
4.44 192
Source: https://mozgius.ru/zdorovie/vliyanie/smert-mozga.html
Diagnostics and differential diagnostics
Cerebral arthrosis is a disease for which diagnosis may require a detailed history of the patient.
The medical history is studied and the patient is interviewed about his living conditions and well-being.
But to make an accurate diagnosis, professionals send the patient to undergo the following diagnostic tests:
- CT head;
- diffuse optical tomography;
- MEG (measurement and visualization of magnetic fields);
- two-photon or single-photon emission tomography;
- MRI of the head.
And also in rare cases, differential diagnosis is possible. Having a patient's medical history, using a specially created computer program, a diagnosis can be made by exclusion. Based on the facts and symptoms that appear in the patient, the computer reduces the range of all possible diseases to one.
If it is impossible to carry out a complete diagnosis, a partial differential diagnosis can be made.
Radiation necrosis of the brain
Unfortunately, the resource of human health is exhaustible, and one of the most vulnerable areas is the head. The brain is susceptible to various diseases, the worst of which can manifest themselves in the form of tumors, both benign and malignant.
The main treatment method for such pathologies is radiation therapy. But it often leads to a problem such as radiation necrosis of the brain - Due to the effect of radiation on the tumor, adjacent tissues die.
A little about brain tumors
A tumor is a zone in which cells that have undergone pathological changes during their development are concentrated. In the case of the brain, a tumor can form both directly on the substance and around it. Such neoplasms are characterized by the development and subsequent destruction of healthy cells around them.
Tumors are divided into two types: malignant and benign. The first is characterized by rapid development, as well as the creation of a direct danger to human health and life. Benign neoplasms develop more slowly and are less aggressive.
There are two main groups of tumors: primary and metastatic. The primary tumor can be either malignant or benign, and originates from brain tissue.
A metastatic neoplasm can be exclusively malignant, since it is always an element of a tumor of a different localization that has penetrated the structure of the brain.
That is, metastases are a derivative of the development of any malignant tumor.
Due to their specificity, malignant tumors are subject to detailed medical examination. They are classified according to degrees and stages, which are determined by the following criteria:
- rate of cancer cell development;
- the presence of tissue areas susceptible to necrosis (death);
- volume of blood supply to the tumor;
- the ability and rate of spread of malignant elements to other (healthy) tissues;
- the level of similarity of abnormal cells to normal ones.
Today, modern medicine does not know the answer to the question of where the primary neoplasm comes from, or more precisely, why this happens.
The most accessible explanation is genetic predisposition and environmental factors, including poor quality food and poor ecology.
Sometimes the consequences of radiation, including those of a therapeutic nature, which could have been suffered in childhood, are cited as the cause of a brain tumor.
Among the symptoms that the disease manifests itself, the first to be listed are:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- visual and auditory dysfunction;
- convulsions;
- changes in behavior;
- memory impairment, etc.
How are brain tumors treated?
The method of treating a tumor is determined depending on its size, nature and other clinical factors. The main types of treatment include:
- chemotherapy;
- surgical intervention;
- radiation therapy;
- combined techniques.
If the tumor causes a complication in the form of a critical increase in intracranial pressure, a decision is made on surgical intervention by direct resection of the tumor.
Recently, the efforts of doctors treating brain tumors have been aimed not only at direct effects on the lesion itself, but also at protecting neighboring tissues from radiation. Radiation therapy can be used in the case of those formations on which radiation has a positive effect.
This method of treatment usually continues for several weeks, and in the case of the presence of several pathogenic foci, a decision may be made to irradiate the entire area of the head. One of the negative aspects of such irradiation quite often is radiation necrosis of the brain.
Surgical intervention by resection occurs in the case of primary tumors, which are removed during surgery. Chemotherapy can be used as an independent treatment, and is often used in combination with radiation therapy. Along with this, the effectiveness of radiotherapy can be increased by prescribing radiosensitizing drugs.
Possible complications
The main side effect of such an effective method as radiation can be radiation necrosis of the brain. This can happen due to damage to healthy cells and tissues during treatment. This problem is accompanied by convulsions and severe headaches, and in some cases the death of the patient may occur.
Radiation necrosis of the brain can develop over six months to several years. Today's statistics indicate a decreasing trend in cases of necrosis, the reason for which is new advances in the medical field.
Complications after radiation therapy include tumor recurrence and various neurological disorders.
When treating children with radiation, disturbances may occur in various parts of the brain, including the pituitary gland, which directly affects their subsequent development.
Therefore, today's goal is to replace radiotherapy in cases of childhood tumors with treatment with chemotherapy drugs.
conclusions
In our article, we briefly touched on the types of existing tumors, their classifications and possible causes. We also reviewed the main methods of treating benign and malignant neoplasms.
As with any other serious illness, radical treatments have their own risks, complications and consequences. In the article we discussed radiation necrosis of the brain, what it is and what signs such a problem can manifest in.
In the light of progressively developing medicine, there is hope that from year to year not only the number of precedents with side effects after treatment, but the number of cases of the disease themselves will decrease.
Source: https://vgoloveboli.net/luchevoj-nekroz-golovnogo-mozga.html
Classification
According to the international classification, atrophic lesions are divided according to the severity of the disease and the location of the pathological changes.
Each stage of the disease has special symptoms.
Atrophic diseases of the brain of the 1st degree or subatrophy of the brain are characterized by minor changes in the behavior of the patient and quickly progress to the next stage. At this stage, early diagnosis is extremely important, since the disease can be temporarily stopped and how long the patient lives will depend on the effectiveness of treatment.
Stage 2 of the development of atrophic changes is manifested in a deterioration in the patient’s communication skills, he becomes irritable and unrestrained, and the tone of speech changes.
Patients with degree 3 atrophy become uncontrollable, psychosis appears, and the morality of the patient is lost.
The last, 4th stage of the disease, is characterized by a complete lack of understanding of reality by the patient; he stops responding to external stimuli.
Further development leads to complete destruction; vital systems begin to fail. At this stage, hospitalization of the patient in a psychiatric hospital is highly advisable, as it becomes difficult to control him.
Classification according to the location of the affected cells:
- Cortical atrophy most often develops in older people and lasts as long as a person lives, affecting the frontal lobes;
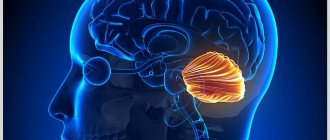
- Diffuse atrophy of the brain is accompanied by impaired blood supply, atherosclerosis, hypertension and decreased mental abilities. Stage 1 of this form of the disease most often develops in the cerebellum, and then affects other parts of the brain;
- Multiple system atrophy develops as a result of mutations and gene disorders during pregnancy. In this form of the disease, not only the brain is affected, but also other vital systems. Life expectancy directly depends on the degree of mutation of the entire organism and its viability;
- Local brain atrophy of the 1st degree appears as a result of mechanical lesions, strokes, focal infections and parasitic inclusions. Symptoms depend on which part is damaged;
- The subcortical or subcortical form of the disease is an intermediate condition in which the centers responsible for speech and thought processes are damaged.
Treatment of radiation necrosis of the brain
Atrophic changes occurring in the brain look like a compensatory increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid against the background of a decrease in the proportion of neurons (brain parenchyma).
The condition resembles hydrocephalus with the difference that it does not reflect a focal loss of tissue volume, but progressive pathological changes in them. Grade 1 atrophy occurring in the brain is characterized by the absence of pronounced symptoms.
A person may experience headaches, be depressed, emotionally unstable, become irritable and tearful. Copes with the usual tasks of professional activity and lives a full life.
Neurological symptoms are more pronounced - motor dysfunction, movement coordination disorder. Pathological processes lead to inevitable and irreversible dementia. The third degree is accompanied by death - necrosis of areas of gray and white matter from which the brain is built.
- incoherent, uninformed speech;
- loss of professional skills;
- loss of orientation within space and time period;
- loss of self-service skills.
The number of complaints about poor health decreases as the destructive processes of cortical atrophy increase. This is an alarming signal indicating a deterioration in the adequate perception of one’s own physical and mental state.
Exodus
A problem such as tissue necrosis can have several logical conclusions.
The first is the resorption of necrotic tissue, after which its complete restoration occurs. An example is the healing of small areas of necrosis in the liver or skin.
When considering necrosis, stages, types, and the consequences of this disease as a whole, you need to pay attention to the fact that sometimes the process of cell death ends in resorption with the formation of a scar. This may be a scar on the skin after exposure to thermal or chemical factors, as well as a mark on the tissue of the heart, especially when a myocardial infarction has been suffered.
In some cases, the resorption process may result in the formation of a cyst. This often occurs in the brain after an ischemic stroke that took the form of a heart attack.
Another possible outcome of necrosis is rejection by mutilation or desquamation. In the first case, we mean the process of rejection of organs or their parts. An example is the loss of toes due to gangrene. The intestinal epithelium or epidermal cells that have died can be exfoliated.
The significance of the consequences of tissue necrosis for the body is determined based on the functional characteristics of the dying parts. Necrosis of the heart muscle can lead to the most severe complications.
Regardless of the type of damage, the necrotic focus is a source of intoxication, to which the organs respond by developing an inflammatory process (sequestration) in order to protect healthy areas from the harmful effects of toxins.
The absence of a protective reaction indicates suppressed immune reactivity or high virulence of the causative agent of necrosis.
An unfavorable outcome is characterized by purulent melting of damaged cells, complications of which are sepsis and bleeding.
Necrotic changes in vital organs (kidney cortex, pancreas, spleen, brain) can lead to death.
With a favorable outcome, the dead cells melt under the influence of enzymes and the dead areas are replaced with an interstitial substance, which can occur in the following directions:
- organization - the place of necrotic tissue is replaced by connective tissue with the formation of scars;
- ossification - the dead area is replaced by bone tissue;
- encapsulation – a connecting capsule is formed around the necrotic lesion;
- mutilation - external parts of the body are rejected, self-amputation of dead areas occurs;
- petrification - calcification of areas that have undergone necrosis (replacement with calcium salts).
Causes of the disease
Understanding the topic of what atrophy that occurs in the brain is, it should be noted that this is always a secondary diagnosis that develops against the background of long-term damaging effects on the central nervous system. Doctors name several reasons why brain cells die:
- Genetic predisposition. The most important factor.
- Intoxication of the body, repeated with high frequency, associated with the use of alcoholic beverages and drugs.
- Injuries to the skull and soft tissues inside the skull.
- Insufficient blood supply to tissues, cerebral ischemia.
- Chronic anemia – insufficient oxygen supply. The condition occurs as a result of low concentrations of hemoglobin protein and red blood cells in the blood, which deliver oxygen to the tissues.
- Infections that affect the nervous system - polio, meningitis, Kuru disease, leptospirosis, brain tissue abscess.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system - ischemia of the heart muscle, heart failure, atherosclerotic vascular pathologies.
- Decortication due to coma.
- Intracranial pressure. It is often the cause of cerebellar atrophy in newborns.
- Large tumors that compress surrounding tissues and interfere with normal blood supply to parts of the brain.
- Cerebrovascular disease is destructive changes in the vessels located in the brain.
If a person avoids mental activity, the risk of developing atrophic diseases occurring in the brain increases. Among the factors that increase the likelihood of the death of neurons located in the brain are smoking, low mental stress, chronic arterial hypertension, hydrocephalus, and long-term use of drugs that constrict blood vessels.
At this stage, medicine is unable to answer the question of why the destruction of neurons begins, however, it has been found that the predisposition to the disease is inherited, and birth injuries and intrauterine diseases also contribute to its formation. Experts share congenital and acquired causes for the development of this disease.
Congenital causes:
- genetic predisposition;
- intrauterine infectious diseases;
- genetic mutations.
One of the genetic diseases that affects the cerebral cortex is Pick's disease. Most often it develops in middle-aged people and is expressed in the gradual damage of neurons in the frontal and temporal lobes. The disease develops rapidly and leads to death within 5-6 years.
Infection of the fetus during pregnancy also leads to the destruction of various organs, including the brain. For example, infection with toxoplasmosis in the early stages of pregnancy leads to damage to the nervous system of the fetus, which often does not survive or is born with congenital abnormalities and mental retardation.
Acquired causes include:
- drinking large amounts of alcohol and smoking lead to cerebral vascular spasm and, as a result, oxygen starvation, which leads to an insufficient supply of nutrients to the cells of the white matter of the brain, and then their death;
- infectious diseases that affect nerve cells (for example, meningitis, rabies, polio);
- injuries, concussions and mechanical damage;
- a severe form of renal failure leads to general intoxication of the body, as a result of which all metabolic processes are disrupted;
- external hydrocephalus, expressed in an increase in the subarachnoid space and ventricles, leads to atrophic processes;
- chronic ischemia causes vascular damage and leads to insufficient supply of neural connections with nutrients;
- atherosclerosis is expressed in a narrowing of the lumen of veins and arteries, and as a result, an increase in intracranial pressure and the risk of stroke.
Atrophy of the cerebral cortex can be caused by insufficient intellectual and physical activity, lack of a balanced diet and poor lifestyle.
The main factor in the development of the disease is a genetic predisposition to the disease, but various injuries and other provoking factors can accelerate and provoke the death of brain neurons. Atrophic changes affect different areas of the cortex and subcortical substance, however, with all manifestations of the disease, the same clinical picture is observed.
Atrophy of the frontal lobes of the brain can develop during intrauterine maturation or prolonged labor due to prolonged oxygen starvation, which causes necrotic processes in the cerebral cortex. Such children most often die in the womb or are born with obvious abnormalities.
The death of brain cells can also be triggered by mutations at the gene level as a result of exposure to certain harmful substances on the body of a pregnant woman and prolonged intoxication of the fetus, and sometimes it is simply a chromosomal malfunction.
Source: https://PosPsy.ru/patologii-i-otkloneniya/nekroz-mozga-2.html
How to stop or slow down cell death
In order to stop the disease, it is necessary to eliminate its causes. In most cases, this is very difficult to do, especially considering the fact that nerve cells are not restored - this is impossible.
If cell death was diagnosed at the initial stage, then it is possible to stop it or at least minimize the consequences for the brain with the help of vitamin complexes that strengthen cells and antioxidants that block the oxidation process. This treatment is aimed only at eliminating symptoms. Atrophy itself cannot be treated with modern drugs.
If we talk about the patient’s lifestyle, then all responsibility now falls on the shoulders of loved ones. They must provide the person with constant care. The patient needs to be surrounded with care, ensure comfort and absence of stressful situations.
The patient should not be spared from homework; on the contrary, it would be better if he went about his usual activities. As for inpatient treatment, this will only worsen the situation. When focusing on the problem, the patient worries more, which leads to the progression of cell death.
A calm and stable environment without changes can slow down the development of the disease, and in the best case, stop it. In addition, you can use antidepressants or tranquilizers, thereby avoiding outbursts of aggression.
Brain necrosis symptoms
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Necrosis of brain tumors usually occurs as a result of exposure of the tumor itself to radiation therapy, which is necessary to destroy it.
What to expect from brain tumor necrosis? If radiation therapy treatment is successful, then it is possible that some living brain tissue will still remain.
This is not yet a reason for joy, since in such cases patients regularly suffer from very severe headaches. In addition, they also experience very frequent convulsive conditions. You can still live with this.
In the worst case, this pathology can cause death of the patient.
Most often, this disease makes itself felt only half a year after radiation therapy. In very rare cases, this pathology develops in a cancer patient after several years. If the patient feels normal, then after a certain period of time it is still possible to get rid of necrosis.
This can only be done through surgery, which is why patients with severe cancer cannot undergo such operations. There are also situations when surgical intervention is simply necessary, since without it the patient’s general condition cannot be improved in any way.
In general, cases are actually different.
Why does necrosis still occur during radiation therapy? The fact is that this treatment method has a destructive effect on the blood-brain barrier. As a result, a fairly large amount of fluid begins to accumulate in the brain area, which prevents blood from flowing normally into this area. Since there is not enough oxygen, tissue necrosis begins.
Pashkov M.K. Content Project Coordinator.
Brain death
- a condition when the death of the brain occurs, while with the help of resuscitation measures the function of the heart, blood circulation and respiratory activity are artificially maintained, creating the appearance of life.
Currently, “brain death” is understood as a pathological condition associated with total necrosis of the brain, as well as the first cervical segments of the spinal cord, while maintaining cardiac activity and gas exchange, ensured by continuous artificial ventilation.
Brain death can be due to many reasons, including brain injury, intoxication, and swelling of the brain due to other causes.
Necrosis of the first cervical segments is caused by cessation of blood circulation through the vertebral artery system.
The actual synonym for brain death is the concept of “exorbitant coma,” the treatment of which is meaningless. A patient who is declared brain dead is actually a “living corpse.” In the practice of pathologists, the term “respiratory brain” is sometimes used. The condition must be distinguished from a chronic vegetative state.
What is atrophy that occurs in the brain
Atrophic changes occurring in the brain look like a compensatory increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid against the background of a decrease in the proportion of neurons (brain parenchyma).
The condition resembles hydrocephalus with the difference that it does not reflect a focal loss of tissue volume, but progressive pathological changes in them. Grade 1 atrophy occurring in the brain is characterized by the absence of pronounced symptoms.
A person may experience headaches, be depressed, emotionally unstable, become irritable and tearful. Copes with the usual tasks of professional activity and lives a full life.
Neurological symptoms are more pronounced - motor dysfunction, movement coordination disorder. Pathological processes lead to inevitable and irreversible dementia. The third degree is accompanied by death - necrosis of areas of gray and white matter from which the brain is built.
- incoherent, uninformed speech;
- loss of professional skills;
- loss of orientation within space and time period;
- loss of self-service skills.
The number of complaints about poor health decreases as the destructive processes of cortical atrophy increase. This is an alarming signal indicating a deterioration in the adequate perception of one’s own physical and mental state.
Types of pathology
The generalized form of cerebral atrophy involves multiple areas of nerve cells in the brain tissue. Diffuse brain atrophy is the uniform death of neurons in all areas of the brain structures. It develops as a result of arterial hypertension, which is characterized by damage to small vessels located in each part of the brain.
The initial symptoms of diffuse atrophy resemble dysfunction of the cerebellum. The progressive course leads to a rapid increase in symptoms, which makes it possible to differentiate the pathology at later stages. Unlike the cortical type, with diffuse atrophy the symptoms of damage to the controlling, dominant hemisphere are clearly expressed. With cortical subatrophy occurring in the brain, destruction and tissue destruction are only just beginning.
Subatrophy, which occurs in the brain, is a condition that precedes the stage of neuronal death. The mechanism of the disease has already been launched, destructive processes have begun, but the body independently compensates for the violations that have arisen. Subatrophic changes are accompanied by mild symptoms. Bihemispheric cortical atrophy occurs in the tissues of both hemispheres. Manifested by Alzheimer's syndrome.
Organic damage to the structures of the brain matter, which develops against the background of constant exposure to ethanol, is called toxic encephalopathy. Affects all parts of the brain. The cortical layers and cerebellum are especially sensitive to the negative effects of alcohol. Often leads to cranial nerve palsy. The frontal lobes are responsible for behavior, intelligence, emotions and moral qualities - properties that characterize a conscious personality.
Developing pathology causes atrophic changes in tissues and is one of the main causes of dementia. Dementia, as a consequence of alcoholism, is diagnosed in 10-30% of patients who abuse alcoholic beverages. A person becomes infantile and loses the ability for abstract logical thinking.
Covers multiple areas - the cerebellum, basal ganglia, spinal cord. If we understand in detail the topic of what atrophic degenerative changes are that affect the brain in a multisystem form, it is worth noting the progressive course, cerebellar ataxia (motor dysfunction) and autonomic failure syndrome.
Cortical atrophy is expressed by the death of neurons located in cortical structures in the frontal lobe. The frontal lobes are responsible for speech function, emotional behavior, determine personal characteristics, regulate human motor activity - planning and execution of voluntary movements. Cortical atrophy occurring in the brain negatively affects these abilities.
Atrophy of the cortex and frontal areas of the brain is predominantly associated with age-related destructive changes in tissues. Signs indicating cortical atrophy are behavioral disturbances and loss of intellectual abilities. With cerebral atrophy of the 1st degree cortical type, the patient is characterized by unmotivated actions that do not comply with generally accepted ethical standards.
A person cannot explain the reasons or assess the consequences of his actions. A characteristic sign that indicates atrophy affecting the frontal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres is regressive changes and personality degradation. Cognitive abilities decrease, the ability to think, remember, and concentrate is lost.
The cerebellum is the department responsible for motor coordination. Destructive changes are manifested by malfunctions of the musculoskeletal system, imbalance, disorders of swallowing functions and eye control. The tone of the skeletal muscle corset decreases. It is difficult for a person to keep his head straight. Enuresis is often observed.
How to keep neurons safe and sound
All preventive measures consist of treating and preventing diseases that contribute to the death of cerebral cells. According to statistics, this phenomenon is quite often observed in people with diseases of the nervous system. From this we can conclude that it is necessary to think positively and lead a healthy and active lifestyle. It has been scientifically proven that positive people live longer and do not have such health problems.
The main “friend” of dementia, especially in old age, is vascular atherosclerosis. Its appearance adds to the death of cells and atrophy of the cortex, which is fraught with functional disorders of other vital organs.
In order to prevent “friends from reuniting”, it is necessary:
- to live an active lifestyle;
- balance your diet so as not to gain excess weight;
- give up nicotine and alcohol products;
- strengthen the immune system;
- avoid stressful situations and worry less;
- control blood sugar levels.
You should also reduce your cholesterol intake and increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet. Such nutritional trends bring the body’s condition back to normal.
Clinical manifestations
Oxygen starvation of the brain has fairly typical symptoms:
- Headache
- Impaired concentration
- Loss of coordination
During the development of hypoxia, oxygen starvation undergoes several phases:
-excitation phase - the victim experiences a state of euphoria, a surge of energy, and the inability to control his movements. The skin is either too pale or red, sweat appears.
-inhibition phase – nausea, vomiting, blurred vision and possible loss of consciousness come to the fore.