Cerebral palsy has a hyperkinetic form - a disease in which the nervous system is affected, muscle tone is impaired, and speech disorders are observed. At birth, babies have a number of reflexes that should disappear as they grow older (up to about 2 months). But, if the child begins to hold his head later than expected, does not roll over, does not follow objects well, or inactively sucks the breast, the alarm should be sounded. Such a child may develop cerebral palsy (CP).
What is cerebral palsy?
Cerebral palsy is a chronic disease. It combines a whole range of manifestations associated with motor dysfunction. Most often develops during intrauterine development of the fetus.
Cerebral palsy is non-progressive in nature. This means that the disease does not spread within the body, but specifically damages individual areas of the brain. As a result, it becomes difficult for the child to monitor the coordination of movements.
There are 3 stages of the pathological process:
- early;
- initial chronic-residual;
- final residual.
The first stage lasts about 4 months. It is characterized by: increased heart rate, periods of respiratory distress, nystagmus, and convulsive syndrome. Movement disorders are difficult to discern.
The next stage lasts from the fifth month of a child’s life to 4 years. During this period, persistent muscle hypertonicity arises. The late residual stage is characterized by the consolidation of motor disorders, the formation of contractures against the background of muscle atrophy.
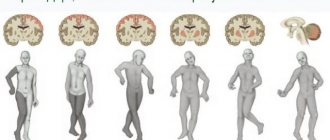
A child with cerebral palsy. Classification of various forms and types of cerebral palsy and their characteristics
Signs of cerebral palsy are a number of symptoms that indicate functional disorders against the background of structural and morphological damage to the brain. In this case, the violations concern specifically defined functions for which the area of the brain that has undergone pathological changes is responsible.
Cerebral palsy is always accompanied by certain disorders of the human motor sphere, which are not progressive in nature. This means that a child with cerebral palsy experiences difficulties with a certain category of movements, coordination, and orientation in space.
The form and nature of the disorders are directly related to the area of the brain whose neurons were damaged.
Classification of forms of cerebral palsy
Depending on the main cause of cerebral palsy and the location of the brain tissue disorder, several forms of the disease are distinguished based on a number of signs:
- Spastic diplegia is the most common and common form of cerebral palsy. With this type of disease, there is bilateral impairment of muscle function, with the legs, arms and face to a lesser extent being more affected. This form is characterized by skeletal deformities and pathological changes in the joints. Spastic diplegia most often results from the birth of a child with significant prematurity. The disease is often accompanied by a sharp decrease in the motor function of all four limbs, sometimes with partial or complete paralysis (tetraplegia). Against the background of pathology of the cranial nerves, disturbances in speech, auditory and visual functions may develop. With this form of cerebral palsy, if there are no serious impairments in intellectual development and significant impairments in the motor function of the hands, children have the highest chance of social adaptation and self-care.
- Double hemiplegia is one of the most complex and severe forms of cerebral palsy; its development is most often caused by chronic fetal hypoxia during gestation or early infancy (birth trauma). With this form, disorders such as spastic paralysis of all limbs, severe deformities of the torso, and stiffness of the joints develop, which begin to appear at a very early age. Against the background of motor dysfunctions, in approximately half of the diagnosed cases there are serious mental development disorders - cognitive (poor memory, lack of ability to cognition, lack of ability to understand the surrounding world), speech, visual, auditory disorders, pathological changes in the facial muscles, weak swallowing, sucking, chewing reflexes. Often children with this form of the disease suffer from epilepsy. The prognosis for such patients is disappointing; pathologies of motor functions in combination with impaired mental development lead to an inability to self-care.
- The hyperkinetic form is most often caused by hemolytic disease of the newborn, which is caused by an immunological conflict regarding the Rh factor or blood group of the mother and child. In severe forms of the disease, the newborn becomes intoxicated with antibodies from the mother's blood directed against the child's red blood cells. The disease is characterized by excessive motor reactions of muscles, which are caused by impaired muscle tone. Skeletal deformities in this form of the disease are absent or mild. Children experience various types of hyperkinesis - involuntary movements from slow worm-like to fast intermittent, spasms of the facial muscles, cramps of the limbs. Muscle tone can be variable from lethargy and weakness at rest to hypertonicity when moving. Often, with this form of cerebral palsy, hearing impairment and pathologies of motor function of the eyes are observed. Intellectually, such children can develop within normal limits; only the verbal function of communication is impaired with severe dysarthria (impaired pronunciation, speech breathing, articulation, tempo-rhythmic organization of speech).
- The atonic-astatic form is most often a consequence of birth trauma, chronic hypoxia and fetal development abnormalities during pregnancy. In most cases, this form of the disease is caused by damage to the tissue of the cerebellum, sometimes to the cerebral cortex in the frontal region. Children with this form of cerebral palsy are characterized by symptoms such as very low muscle tone, inconsistency of movements, poor coordination, and poor ability to maintain balance when walking. Sometimes speech disorders and intellectual pathologies of varying severity are also observed - from mental retardation to severe forms of mental retardation.
- The hemiplegic form is caused by a hematoma or hemorrhage with damage to one of the hemispheres of the brain, against which unilateral damage to the limbs develops. Hemiparesis (muscle weakening or partial paralysis) of the limbs of the right or left side may be accompanied by spasms and convulsions. In most cases, the motor function of the hand is more impaired. Depending on the degree of damage to the cerebral hemisphere, pathologies of speech function and mental retardation may also be observed.
Diagnosis of the condition
By 12 months of age, a normally developing child can already do a lot. He turns over, sits down, stands up on his legs, tries to walk, pronounces individual words. The baby responds to his name, reacts emotionally to the world around him, and communicates.
Of course, each baby has an individual pace of development. One child can walk with his own legs or start talking earlier, another later. However, CNS pathologies usually appear in aggregate.
Parents should be wary if, at the age of 1 year and older:
- does not crawl and does not try to walk (some children do one thing: either crawl for a long time, or immediately walk);
- cannot stand independently without support;
- does not speak individual short words (“mom”, “dad”, “woof”, etc.);
- does not try to find a toy hidden in front of his eyes, does not reach for flashy things that interest him;
- the baby’s limbs on one side of the body are more active than on the other;
- The child has seizures.
READ MORE: Classification of retinal detachment By the age of one year, a baby with cerebral palsy usually has all the signs of the disease: non-progressive motor impairment, uncoordinated movements, developmental delay. Diagnostic methods are usually used to confirm the diagnosis, exclude diseases with a similar clinical picture, and clarify the form of the disease. However, making an accurate diagnosis of a baby can be difficult.
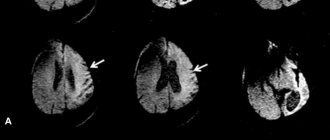
The child is examined by a neurologist who will prescribe an MRI - magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. The purpose of this procedure is to identify affected areas of the brain. In addition, MRI helps to determine the presence of changes in the substance of the cortex and subcortex of the brain, as well as to determine their type. This could be, for example, a decrease in white matter density.
The disease is diagnosed based on the identified characteristic signs. Conditioned reflexes and muscle tone are checked, and an MRI of the brain is also taken. If there is a suspicion of brain damage, an EEG and ultrasound are performed.
A timely diagnosis is very important for a young patient. It is important to recognize the disorder. Children should be examined in the maternity hospital; doctors pay special attention to children:
- With light weight.
- Those born prematurely.
- Having defects and developmental anomalies.
- With a diagnosis of newborn jaundice.
- Born as a result of difficult and prolonged labor.
- With infectious diseases.
Cerebral palsy is diagnosed by a neurologist, but he may additionally prescribe other tests to clarify the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of cerebral palsy covers the following stages of analysis:
- Ultrasound of the brain;
- CT and MRI;
- Electroencephalogram.
The main goal of treatment for cerebral palsy is to eliminate malfunctions in the motor system, speech barriers, and correct mental development. Treatment is selected individually, taking into account all the characteristics of each individual organism, because there is no universal treatment today. Methods that accompany positive results:
- physiotherapy;
- medications that normalize muscle tone;
- massage.
The following methods are also effective:
- Voight method;
- Atlant pneumatic suit;
- load suits;
- classes with a speech therapist;
- walkers, bicycles and other exercise equipment.
If the methods do not produce changes, a surgical operation is performed, plastic surgery of the muscle structure and tendons is performed, and the tissues are given the correct shape. In this way, contractures and damaged areas are removed and the spinal cord is stimulated.
Analyzing cerebral palsy, the causes of which can be different, it can be noted that a very effective non-traditional method is animal-assisted therapy - treatment using positive emotions from communication with animals (horses and dolphins).
Cerebral palsy is difficult to treat and the later the diagnosis is made, the less chance there is for recovery and correction of disorders. The most favorable range for complex treatment and correction is considered to be the age period from one month to three years, and it is very important to make a diagnosis and begin treatment in this period.
Treatment of cerebral palsy is a long process. The treatment method is developed by a group of doctors working together. The group includes a pediatric neurologist, a physical therapy doctor, an orthopedic doctor, a speech pathologist, a teacher-educator and a psychologist. When drawing up the methodology, the child’s age, form and severity of the disease are taken into account. Each child with cerebral palsy requires an individual approach.
The main complex of rehabilitation treatment for cerebral palsy consists of three components.
- Medical rehabilitation, which includes the prescription of medications, physical therapy and massage, the use of special therapeutic-load suits and pneumatic suits, physiotherapy, orthopedic and surgical treatment, treatment using orthoses - devices that help make correct movements in the joints.
- Adaptations in the social environment. Teaches children to navigate, adapt and behave adequately in society.
- Psychological, pedagogical and speech therapy correction, which consists of classes with a psychologist, teacher, speech therapist, occupational therapy, training in simple skills and activities with the family.
Among the methods of medical rehabilitation, kinesiotherapy or movement therapy, medications and physical therapy are most often used.
Kinesiotherapy
This is a method of correcting movement disorders and reducing or eliminating the consequences of a sedentary lifestyle.
Source: https://TherapyaDushi.ru/bolezni-i-narusheniya/spastiko-giperkineticheskaya.html
Main reasons
Any type of pathology is a consequence of malnutrition of the brain of the fetus or newborn. The causes of hyperkinetic cerebral palsy are hidden in defects in the subcortical parts of the brain, more precisely, in the striopallidal system.
The following pathologies during pregnancy can lead to the disease:
- infectious lesion (syphilis, toxoplasmosis, etc.);
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- prolonged toxicosis;
- Rhesus conflict;
- early placental abruption;
- diseases not related to pregnancy in the mother (diabetes, heart defects, hypothyroidism).
Directly during childbirth, cerebral palsy can be provoked by:
- long waterless period;
- birth injury;
- protracted/premature/rapid labor.
In the postpartum period, the cause of cerebral palsy may be asphyxia of the newborn due to suffocation by the umbilical cord or the entry of amniotic fluid into the lungs.
Hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) - causes, symptoms, treatment, prognosis
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a serious and unpredictable disease.
It can develop in the first trimester of pregnancy, or it can occur after childbirth, as a result of birth trauma or hypoxia. The hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy (CP) occurs in 25% of cases. A feature of this form of cerebral palsy is a predominant violation of muscle tone with a slight impairment of the child’s mental development.
The hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy differs from other forms by the presence of involuntary movements or hyperkinesis. Hyperkinesis can manifest itself in various parts of the body, but most often it affects the toes, hands, muscles of the face and neck.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist !
- Health to you and your loved ones!
With this form of cerebral palsy, children do not develop bone defects and contractures (limitation of joint mobility), but children are prone to subluxation of small joints of the hands. Due to the lack of precise coordination, targeted grasping may be impaired, which makes such patients quite vulnerable in everyday life.
The prognosis for the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy depends on the severity of the disease, concomitant pathology, timeliness, adequacy and continuity of treatment and rehabilitation. Cerebral palsy is incurable, but with proper treatment and recovery it is possible to compensate developmental defects as much as possible.
In the absence of seizures, the disease has no tendency to develop. With mild and moderate forms, as well as adequate treatment and rehabilitation, children with the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy can move independently from the age of 5-6 years.
Despite the terrible diagnosis, with this form of cerebral palsy, the mental development of children suffers much less than their physical development. This allows children with mild and moderate forms of cerebral palsy to master the general educational program at school and receive secondary specialized and higher education.
Causes
Any form of cerebral palsy occurs due to malnutrition of the fetal or newborn brain. The hyperkinetic form occurs due to defects in the subcortical parts of the brain, namely the striopallidal system.
The following pregnancy pathologies can lead to the development of cerebral palsy in the fetus:
- infections (syphilis, papillomavirus infection, toxoplasmosis, etc.);
- fetoplacental insufficiency (fetal nutritional disorders, including hypoxia caused by defects in the mother’s placenta);
- severe and prolonged toxicosis;
- early placental abruption;
- Rhesus conflict;
- maternal diseases not related to pregnancy: heart defects, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, etc.
During childbirth, a risk factor leading to or contributing to the development of cerebral palsy may be:
- long waterless period;
- prolonged, premature or rapid labor;
- birth injury.
In the postpartum period, the main risk factors for the occurrence of cerebral palsy are asphyxia of the newborn (suffocation due to the entry of amniotic fluid into the lungs or suffocation by the umbilical cord).
One of the central causes of damage to the subcortical parts of the brain is bilirubin encephalopathy, which occurs as a complication after jaundice in full-term and premature infants. This jaundice occurs when there is a Rh conflict between mother and fetus.
Careful and correct management of pregnancy, monitoring the vital signs of the mother and fetus, allowing timely identification of conditions dangerous to the fetus and preventing the occurrence of hypoxia, is the best prevention of cerebral palsy.
Equally important are the choice of the optimal method of delivery and competent management of labor and the postpartum period and monitoring the vital signs of the newborn.
Symptoms of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy
Symptoms of hyperkinetic paralysis include:
- Variable muscle tone, muscle dystonia, intermittent spasms, hyperkinesis.
- Violent involuntary movements that occur during nervous excitement or excitement and are absent during sleep. The movements of such children are excessive, clumsy, and sweeping.
- Swallowing disorders and speech disorders. The speech of such children is slurred and slow; in 30-50% of cases, sensorineural hearing loss may develop.
- To a lesser extent, autonomic disorders and lability of the emotional system are manifested.
| Severe forms of hyperkinetic paralysis | They are expressed in involuntary movements already in the first months of life, however, in most young patients moderate hyperkinesis appears at the beginning of the second year of life and is of a descending nature: from the root of the tongue, the face of the neck to the torso and distal limbs. |
| Mild forms of paralysis | Manifested by quick, unexpected spasms of the upper half of the body. Severe forms of paralysis are characterized by slow, increasing hyperkinesis of the arms and legs. Rest and sleep help relieve spasms, and on the contrary, stress intensifies and increases hyperkinesis. |
Changes in muscle tone are characteristic in the first years of life of a child with a hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy. In newborns with cerebral palsy syndrome, as a rule, muscle tone is reduced during the first month of life.
By the second month, dystonic attacks may appear with a sharp increase in muscle tone. Tendon reflexes may be normal or increased.
Speech disorders are manifested by delayed speech development, insufficient articulation and slow speech rate.
Recovery and rehabilitation
Cerebral palsy is an incurable pathology and absolute recovery cannot be achieved with it. With timely, comprehensive and continuous treatment and rehabilitation, it is possible to achieve compensation for neurological deficits, avoid or reduce skeletal deformities and contractures, including in the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy.
It should be remembered that until the age of 5, a child is actively developing his psyche and intellect and learning skills. Also, up to 4-5 years of age, motor disorders and contractures are formed and consolidated in all types of cerebral palsy. Therefore, treatment and rehabilitation measures in early childhood bring the greatest effect, and also allow you to instill in the child basic handling skills in everyday life.
Treatment of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the child’s disease. When drawing up a treatment program, the severity of brain damage, concomitant pathologies, the presence of seizures, epileptic seizures, etc. are taken into account.
Treatment of cerebral palsy involves not only drug therapy, but also medical rehabilitation, speech correction and psycho-pedagogical correction, restorative therapy and rehabilitation.
For drug therapy, a number of drugs are used aimed at:
- normalization of muscle tone, reduction of hyperkinesis;
- anticonvulsants;
- neurotrophic drugs and nootropics for correction of the nervous system and emotional background;
- means for increasing the metabolism of the nervous system;
- B vitamins.
Massage, physical therapy (physical therapy) and physiotherapy are of utmost importance in the treatment of muscle spasms. To correct defects in the muscular and skeletal skeleton, means are used that compensate for impairments in cerebral palsy: special shoes, crutches, strollers, etc.
More progressive methods of treating cerebral palsy include mechanotherapy, which uses various training devices and suits to develop the necessary motor pattern and reduce tension or provide muscle stretching.
Speech therapy and psycho-pedagogical correction consists of classes with a defectologist, psychologist, elimination of speech defects, and work with the patient’s family. Social adaptation of young patients with cerebral palsy is carried out, they are taught communication skills, the ability to learn and acquire a profession.
Animal therapy and rehabilitation through sports provide a good restorative effect. Animal therapy is treatment through communication with animals. Horses and dolphins are used for these purposes.
Read here how to provide first aid for epilepsy.
You will find a description of status epilepticus in another article.
Source: https://nerv.hvatit-bolet.ru/giperkineticheskaja-forma-dcp.html
Characteristic manifestations and disorders
The main symptom of the disorder is instability of muscle tone. It can be normal, decreased or increased. If spastic symptoms appear against the background of paralysis, the disease is diagnosed as a spastic-hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy.
The usual movements of children with this diagnosis are disrupted: they look awkward and a little sweeping. It is this form that is characterized by the appearance of hyperkinesis - involuntary contraction of facial muscles, legs and arms.
There are several types of hyperkinesis:
- athetosis;
- chorea;
- choreoathetosis;
- torsion dystonia.
They can occur singly or in combination. Often, disorders of the musculoskeletal system are combined with hearing and speech disorders.
In children with the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy, joint deformation and contractures do not occur. However, subluxations can occur in the area of small joints of the upper limbs. Another characteristic sign is a violation of the grip of small objects. Difficulties also arise with other movements that require concentration.
There are different degrees of severity of the pathology. With the mild version, defects in the musculoskeletal system are almost invisible. Such children can attend general education institutions and cope without outside help. However, they may experience involuntary and sharp muscle spasms, spreading mainly in the upper torso area. Such symptoms intensify after stress and during depression.
For severe hyperkinetic forms of cerebral palsy, the following conditions are symptoms:
- involuntary muscle movements appear in the first months of life;
- in the second year of life, moderate hyperkinesis of a descending nature occurs;
- contractions of the muscles of the upper and lower extremities are of an increasing nature.
Children with moderate and severe pathology require constant comprehensive care.
Hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy: symptoms, causes and proper recovery
According to medical statistics, the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy occurs in approximately 25% of cases.
This is a special form of cerebral palsy in which the child experiences involuntary muscle contractions called hyperkinesis.
Among the most characteristic signs of this pathology are lesions of the central nervous system, muscle tone disorders, and certain speech disorders.
Characteristic manifestations and disorders
The most important sign of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy is the instability of muscle tone, which can be normal, decreased or, conversely, increased.
If spastic symptoms appear against the background of hyperkinetic activity, then the disease is diagnosed as a spastic-hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy.
Spastic-hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy
Normal movements in children suffering from hyperkinetic cerebral palsy are disrupted - they often look awkward and somewhat sweeping.
This form of pathology, unlike other forms, is characterized by the appearance of hyperkinesis - that is, involuntary contractions of the muscles of facial muscles, as well as the upper and lower extremities.
There are several types of hyperkinesis:
- athetosis;
- chorea;
- choreoathetosis;
- torsion dystonia.
These manifestations can occur either individually or in combination. Quite often, disorders of the musculoskeletal system in a child develop in combination with speech and hearing disorders.
Despite the fact that children suffering from the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy do not develop joint deformities and contractures, in most cases, they may develop subluxations in the area of small joints of the hands.
A characteristic manifestation of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy is a violation of the targeted grasp of certain objects, as well as significant difficulties in other movements that require maximum concentration.
Among other signs of this form of pathology, emotional lability (that is, mood instability), as well as all kinds of autonomic disorders, should be highlighted.
Compared to all other forms of cerebral palsy in children, in this case, brain activity is practically not affected.
There are different degrees of severity of this pathology. With a mild degree, defects of the musculoskeletal system are presented minimally.
Such children can go to regular educational institutions and have absolutely no need for outside help. In contrast, children with moderate and severe degrees of this pathology must be constantly under the constant supervision of caring relatives.
Manifestations characteristic of a mild degree of hyperkinetic cerebral palsy include rapid and unexpected involuntary muscle spasms, mainly in the upper torso. As a rule, spasms intensify during stress and depression, and decrease and become less frequent during sleep and a state of calm.
The severe form of hyperkinetic cerebral palsy is characterized by the following manifestations:
- involuntary movements that begin in the first months of the baby’s life;
- in the second year of life - moderate hyperkinesis of a descending nature, which starts from the root of the tongue, face and neck, and ends in the torso, as well as the distal parts of the child’s limbs;
- hyperkinesis of the arms and legs, which are rather slow and increasing in nature.
Methods of correction and restoration
Unfortunately, cerebral palsy in any form belongs to the category of pathologies that cannot be completely cured. However, there are highly effective correction methods that, when properly selected and prescribed, contribute to a significant improvement in the child’s health.
Therapy for the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy completely depends on the individual characteristics of the baby and the nature of the course of the disease.
At the stage of drawing up the most optimal recovery program, many factors are taken into account, which include:
- degree of brain damage;
- frequency and nature of convulsive spasms;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies;
- the presence of epilepsy attacks, their nature and frequency.
In order for the treatment of hyperkinetic cerebral palsy to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to approach this issue comprehensively.
The therapeutic course must include the following important components:
- drug treatment;
- medical rehabilitation;
- correction of speech abilities;
- pedagogical correction;
- restorative procedures.
Treatment and rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy must be carried out as early as possible in childhood. The ideal period for this is up to 4-5 years of age, until the motor disorders characteristic of cerebral palsy are fully formed.
The following methods are widely used in the treatment of this pathology:
- therapeutic massage and physical education;
- taking muscle relaxants;
- laser therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- hippotherapy is a highly effective comprehensive method of rehabilitation through horse riding;
- swimming.
A competent combination of these methods allows you to achieve great success in treatment.
Educational video for parents of a child with cerebral palsy - techniques of restorative gymnastics and endemic massage:
The hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy requires competent, timely diagnosis, as well as comprehensive treatment that combines the most effective medications, physiotherapy and sports methods. It is also very important to provide the child with a positive emotional background.
Source: https://neuro-logia.ru/zabolevaniya/detskij-cerebralnyj-paralich/giperkineticheskaya-forma.html
Reasons for the development of cerebral palsy
The reasons for the development of cerebral palsy are varied. It is customary to distinguish prenatal, perinatal and postnatal unfavorable factors related to its origin. In practice, most often there are combinations of such factors acting at different stages of development.
Prenatal factors. Typically, there are 3 groups of these factors: the state of health of the mother; deviations during pregnancy; factors that interfere with fetal development.
If the cardiovascular system is damaged, the mother may develop metabolic acidosis, causing oxygen deficiency in the fetus, which, in turn, is complicated by asphyxia during childbirth.
Intrauterine infection plays an unfavorable role in the development of cerebral palsy, especially the rubella virus. The clinical manifestation of pathology in congenital rubella may be the occurrence of spastic paresis.
Perinatal factors. These factors include: asphyxia during childbirth; birth injury.
Postnatal factors. At the postnatal stage, the following causes of deviations are identified: trauma; infections; intoxication; oxygen deficiency; neoplasms and other acquired abnormalities in the brain.
Structural changes in the brain in children with cerebral palsy are divided into 2 groups:
• nonspecific changes in the cells themselves;
• changes associated with impaired brain development, i.e. with dysontogenesis.
There is a connection between the severity of the cerebral cortex disorder and the clinical manifestations of movement disorders. Pathological changes in the brain in children with various forms of cerebral palsy were identified by computed tomography in 68% of cases.
Forms of cerebral palsy
More than twenty classifications of cerebral palsy have been proposed in the world literature. They are based on etiological signs, the nature of clinical manifestations, and pathogenetic features.
In domestic clinical practice, the classification most often used is K. A. Semyonova’s classification, developed in 1968, which includes the author’s own data and elements of D. S.’s classification.
Futera and M. B. Duker [1].
Source: https://yazdorov.win/nevralgiya/giperkineticheskaya-forma-dtsp-simptomy-prichiny-i-gramotnoe-vosstanovlenie.html
Methods of correction and restoration
It is not possible to completely overcome the disease. However, there are various techniques through which it is possible to correct the child’s behavior and movements. They are selected by the attending physician, taking into account the characteristics of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy and the individual characteristics of the little patient.
To ensure the most effective therapy, it is recommended to use an integrated approach. It involves the use of the following techniques:
- medical rehabilitation;
- drug treatment;
- speech correction;
- restorative procedures;
- help from teachers.
Each method will be discussed in detail later in the article.
Drug therapy
It is recommended to start rehabilitation from an early age. It is better to start treating the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy at the age of 4-5 years. At this time, motor disturbances characteristic of the pathology are minimal.
Drug therapy includes taking muscle relaxants to eliminate muscle spasms and anticonvulsants to relieve the severity of symptoms. To correct the emotional background of the child and the functioning of the central nervous system, the help of neurotrophic medications is required.
Through properly prescribed drug therapy, it is possible to normalize muscle tone and reduce hyperkinesis. To speed up the recovery period and improve the effects of drugs, it is additionally recommended to take B vitamins.
Other treatments
For various disorders against the background of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy, the use of means that provide their compensation is recommended. We are talking about strollers, uprights, crutches, and special shoes. At later stages, progressive methods are used, involving the introduction of suits and training apparatus. With their help, it is possible to compensate for stress and develop motor skills.
If necessary, speech therapy and psycho-pedagogical correction is prescribed. The work of a speech pathologist is usually aimed at reducing the severity of speech defects. The psychologist collaborates not only with the child, but also with his parents to ensure the most comfortable environment in the family. The child is taught to communicate with peers.
Massage is widely used for cerebral palsy. The procedures help improve blood circulation and metabolism. To obtain maximum effectiveness, sessions should be carried out by a qualified specialist.
Physical therapy is also useful for children with cerebral palsy. Exercises are selected individually. Almost all young patients are recommended to swim. Physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect.
Features of hippotherapy for cerebral palsy
The listed therapeutic measures help reduce muscle hypertension, but they are not capable of teaching the child new skills. Therefore, today hippotherapy is widely used in the treatment of synkinesias in the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy.
Contact between a child and a horse stimulates the functioning of his subcortical areas of the brain, allows him to learn complex movements and improve speech skills. During exercise, muscle hypertonicity and the severity of hyperkinesis decrease.
While riding, the rider begins to involuntarily repeat all the movements of the horse, learns to maintain balance and work with both legs at the same time. In addition, the habit of falling on the affected side disappears, and fine motor skills develop. In just a few sessions, emotional tension normalizes against the background of a feeling of inferiority in society.
Even long sessions of hippotherapy practically do not bother children. Each time they gain new skills, experience and impressions. Fresh air has a beneficial effect on the condition of the whole body.
Spastic diplegia
Characteristic features:
- muscles of the lower and upper extremities are toned;
- the lower extremities are more affected;
- hands are more active and coordinated.
Diplegia is a very common type of cerebral palsy, its symptoms to a certain extent appear in newborns. Intelligence is not affected, the child can be successfully trained.
Despite this, exceptions are still possible; there are individual cases where intellectual development is below normal. Minor deviations in mental or speech development may be observed.
Spastic diplegia occurs most often in premature babies, but the main cause is hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain and liquefaction of nervous tissue. The part of the brain responsible for motor activity is affected.
Prognosis for recovery
The prognosis for the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy is largely determined by the severity of the pathology, the presence of concomitant health problems, and adequate and timely treatment. The disease cannot be completely overcome. However, with a competent approach and rehabilitation, developmental defects can be compensated as much as possible.
In the absence of seizures, the disease practically does not progress. Children can move independently from the age of 5-6 years with a mild or moderate severity of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy. Their mental development suffers less than physical development. Therefore, in most cases, they master the school curriculum and receive secondary or higher education.
Source: fb.ru