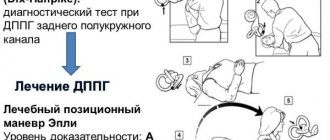
In most cases, treatment for postural vertigo is not necessary. The disease does not cause serious damage to organ systems.
The term "orthostasis" comes from the Greek and means "upright". Orthostatic hypotension is a form of arterial hypotension. Phobic orthostatic hypotension, in addition to attacks of dizziness, accelerates the heartbeat, causes weakness and nausea . In medicine, orthostatic hypotension is divided into 5 types: Shy-Drager syndrome (ICD-10 code: G90.3), drug-induced, hypovolemic, idiopathic, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (ICD-10 code: I49.8).
Anxiety and its causes
Healthy people often feel anxious when exposed to many external factors. Anxiety during an exam, when family problems arise, an unexpected change in your usual lifestyle, or troubles at work can cause psychological stress and will quickly disappear once the difficult situation is resolved. However, there is a psychotype of people who are in a constant state of anxiety, regardless of external influences, or who react much more strongly to ordinary everyday troubles, falling into nervousness.
If you believe scientists, then such a symptom is inherited at the genetic level and can subsequently be clearly expressed in the case of improperly constructed intra-family relationships. In addition, psychologists argue that inflated self-esteem, which runs counter to a person’s real capabilities, is often the first step that creates anxiety. The sooner a person realizes the impending danger and begins effective treatment, the easier and faster the disease can be dealt with.
Causes
The term “hypotension” literally means “low blood pressure,” but orthostatic hypotension is a sharp decrease in blood pressure after a change in body position in space. Changing position causes blood to flow from the head to the feet. In response to this process, the heart rate accelerates and blood vessels constrict, leading to a rapid increase in blood pressure.
Redistribution of blood when body position changes
Within a short time, the body can return blood to the head. However, if this reaction occurs too slowly, cerebral hypoperfusion occurs.
It is not orthostatic hypotension that is life-threatening, but the resulting injury caused by loss of consciousness.
Often, with age, the ability to normal orthostatic reaction is partially lost. But some diseases are also considered a risk factor for the development of orthostatic syndrome . These include primarily diabetes mellitus and diseases of the nervous system .
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
Another possible cause of orthostatic dysregulation is the use of certain medications. Most often, orthostatic hypotension is caused by vasodilators - drugs that dilate blood vessels.
Blood pressure can also be reduced by diuretics, cytostatics, antiparkinsonian drugs and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Some tranquilizers, tricyclic antidepressants, opiates, psychostimulants, insulin, muscle relaxants, alcohol and cannabinoids such as marijuana are triggers for the disease.
Rarer causes include heart failure, congenital heart defects, hypothyroidism, and mental disorders (phobias, trauma, or depression).
Diseases that can lead to anxiety
Many doctors encountered in their patients the manifestation of an unmotivated feeling of anxiety, which defied logic and did not give patients the opportunity to lead a full life. Often the root cause was the following diseases:
- Disruption of the normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Difficult menopause in women.
- Loss of sexual desire in men.
- Some infectious diseases.
- Pre-infarction condition.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
- A sharp increase in blood sugar levels.
- Most mental illnesses are accompanied by feelings of anxiety.
- People with schizophrenia often become more restless during periods of exacerbation.
- With neuroses, feelings of anxiety can grow like an avalanche.
- Patients with alcohol or drug addiction, as well as those suffering from “non-chemical addictions” (shopaholism, gambling addiction, Internet addiction) experience a pronounced feeling of anxiety during withdrawal symptoms.
Many people in an anxious state complain of the appearance of hallucinations, partial or complete loss of sleep, their mood inexorably deteriorates, aggressiveness and irritability appear, often unrelated to the events taking place around the person.
Anamnesis
Phobic postural dizziness is characterized by the following symptoms (Brandt and Dieterich, 1986; Huppert et al., 1995; Brandt, 1996):
Lack of objective signs of imbalance with complaints of dizziness and unsteadiness while standing and walking.
Feeling of dizziness as a feeling of derealization and instability, expressed in varying degrees, paroxysmal fear of falling (without falling as such) & sometimes short-term swaying.
The occurrence of attacks in certain situations, including those that provoke other phobias (for example, in crowded places (shops, restaurants), on a bridge, while driving, in an empty room).
A gradual increase in the number of situations that provoke dizziness and an increasing desire to avoid them. During or immediately after attacks, patients note anxiety and autonomic disorders (which are often reported only after leading questions); most also experience attacks of dizziness without anxiety.
Reducing dizziness under the influence of small doses of alcohol or during sports.
The development of psychogenic vertigo due to an organic disease of the vestibular system, such as vestibular neuronitis, benign positional vertigo (Huppert et al., 1995), or mental trauma (Kapfhammer et al., 1997).
The occurrence of phobic postural dizziness in people prone to obsessive states and placing increased demands on themselves. Combination of dizziness with reactive depression.
Which doctor will help you cope with anxiety?
Whatever the reasons for the appearance and development of a phobia, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible so that the disease does not get out of control and lead to serious consequences. If anxiety does not go away within several days, and you cannot determine the cause of the condition, do not delay visiting the doctor. Treatment will be much more effective if the specialist has sufficient practical experience and good specialized medical education. If necessary, take all the tests and undergo a full examination, this will help you get a more complete picture and make treatment more productive and faster.
If necessary, the therapist can refer the patient for consultation to specialists. An endocrinologist or neurologist, cardiologist or psychotherapist will be able to conduct a full examination and identify the root cause of anxiety. Often, effective treatment of chronic diseases automatically leads to a change in psychosomatic state. If no chronic diseases are identified, and the person complains of hallucinations and an anxious decline in mood, it is necessary to seek help from a psychiatrist. If feelings of anxiety lead to loss of consciousness or strange tremors appear in the limbs, a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed. If the symptoms grow like an avalanche and are accompanied by pronounced pain, convulsions, and sudden surges in pressure, it is better to call a doctor at home. Remember that anxiety often leads people to commit suicide because their mental state becomes unbearable.
Phobic disorders
Common symptoms of phobic disorders are intense acute fear when confronted with the object of the phobia, avoidance, anticipatory anxiety, and awareness of the irrationality of one's own fear. Fear upon contact with an object provokes some narrowing of consciousness and is usually accompanied by violent vegetative reactions. A patient with a phobic disorder completely focuses on the frightening object, to one degree or another ceases to monitor the environment and partially loses control over his own behavior. Increased breathing, increased sweating, dizziness, weakness in the legs, palpitations and other vegetative symptoms are possible.
The first encounters with the object of a phobic disorder provoke a panic attack. Subsequently, the fear worsens, exhausts the patient, and interferes with his normal existence. In an effort to eliminate unpleasant sensations and make life more acceptable, a patient with a phobic disorder begins to avoid frightening situations. Subsequently, avoidance is reinforced and becomes a habitual pattern of behavior. Panic attacks stop, but the reason for their cessation is not the disappearance of the phobic disorder, but the lack of contact with the object.
Anticipation anxiety is manifested by fear when imagining a frightening object or realizing the need to get into a situation of contact with this object. Erased vegetative reactions arise, thoughts appear about intolerance to such a situation; a patient suffering from a phobic disorder plans actions to prevent contact. For example, a patient with agoraphobia, if necessary to visit a large shopping center, thinks through alternative options (visiting small stores selling similar goods); a patient with claustrophobia, before visiting an office located on the upper floors of a building, finds out whether there are stairs in this building that can be used instead elevator, etc.
Patients with phobic disorders are aware of the irrationality of their own fears, but ordinary rational arguments (their own and those of others) do not influence the perception of a frightening object or situation. Some patients, forced to regularly be in frightening situations, begin to take alcohol or sedatives. With phobic disorders, the risk of developing alcoholism, dependence on tranquilizers and other drugs increases. Debilitating fear and restrictions in social, professional and personal life often provoke depression. In addition, phobic disorders are often combined with generalized anxiety disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Diagnostics
In medical practice, the Shellong test is used to diagnose postural hypotension. During the test, the patient lies on a couch for 5-10 minutes while their blood pressure and heart rate are measured. He should then quickly stand up and remain standing for 5-10 minutes. During this period, pulse and blood pressure are monitored.
With a sharp change in body position in patients with orthostatic hypotension, blood pressure sharply decreases.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is also necessary to exclude other possible causes of dizziness.
Symptoms
Orthostatic dysregulation is characterized by nonspecific symptoms. As a rule, they appear after a sudden change in body position . If a person lies down for a longer period of time, symptoms may be even worse.
Common symptoms of orthostatic hypotension:
- Feeling cold.
- Nausea.
- Pallor.
- Excessive sweating.
- Inner restlessness.
In addition, tachycardia, a feeling of fear, dizziness, headache, a feeling of unsteadiness while walking, tinnitus, spots before the eyes and a feeling of emptiness in the head are often observed.
Due to symptoms, the patient is forced to sit or lie down. In this case, symptoms usually disappear quickly. In some situations, brief fainting is also possible, which can lead to injury.
Treatment and therapy
Treatment of orthostatic dysregulation should be carried out without the use of medications . Only in severe cases can the patient take alpha-adrenergic agonists.
To counteract the hypotension that usually occurs in the morning, it is recommended to do exercises that improve blood circulation in the lower extremities. Thus, venous return can be stimulated by activation of the lower leg muscles even in the supine position.
Before getting out of bed, you need to sit for at least 2 minutes.
It is also recommended to reduce the room temperature, since cold also increases venous return.
In some cases, strong coffee may help reduce symptoms of postural hypotension.
In most cases, treatment for postural vertigo is not necessary. The disease does not cause serious damage to organ systems.