Symptoms
Nausea, tinnitus and dizziness are accompanied by a number of symptoms that cause causes of even more unpleasant conditions. The noise can appear at any time of the day and be of different types. If we turn to medical terminology, it would be more correct to say not tinnitus, but tinnitus. It can be periodic, constant, sharp or muted.
Discomfort in the ears also manifests itself as congestion. During the day, when a person is at work, tinnitus is not felt as much. It brings severe discomfort at night. Constant noise and ringing make it difficult to relax and sleep. Prolonged discomfort can lead to decreased hearing of the patient.
Along with tinnitus, sudden dizziness occurs, disorienting the person. Against this background, weakness, headache, and irritability appear.
Why do my ears get stuffy and my head hurt?
Everyone has experienced such an unpleasant sensation as pain in the head. However, when such symptoms are accompanied by congestion in the ears, the condition should not be ignored. It indicates that dangerous malfunctions are occurring within the body. To answer the question of whether your ear can cause a headache, you need to consult with a specialist and immediately determine the provoking factor of the pathology.
Initially, the cause of unpleasant symptoms may be localized in the head and ears. It is possible to establish the origin of the pathological process using auxiliary signs. The main reasons include:
- High blood pressure. It is the most dangerous condition. In addition to pain inside the head and congestion in the ears, the following symptoms are noted: “spots” in the eyes, the appearance of nausea that develops into a gag reflex, painful pulsation in the temples, discomfort in the heart. When such signs occur with a certain consistency, you should not delay visiting a specialist.
- Colds and infections. With ARVI, the head may hurt, as well as the muscles of the limbs. In addition, nasal congestion is observed. Due to a runny nose, the lungs and brain do not receive enough oxygen, and blood circulation may suffer.
- Acute form of sinusitis. The mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus swells as a result of the penetration of a viral infection. Breathing through the nose will be significantly difficult. The body will experience a lack of oxygen, which leads to blocked ears and pain in the head. In addition, discomfort may affect the area near the eyes. Slight tilting of the head immediately increases the pain.
- Inflammation in the ears. Infections from the nose can penetrate deep into the membrane and cause diseases in the middle ear: acute and chronic forms of otitis (congestion in the ears, severe pain, dizziness with otitis and hyperthermia), mastoiditis (a consequence of otitis), labyrinthitis (inflammatory phenomena in the inner ear) . The disease is associated with noise in the ear and discharge of purulent contents.
- Neuroma. Benign neoplasm on the auditory nerve. Often observed in women. In addition to congestion in the ears, there is a headache with otitis media, the patient feels nauseous, and dizziness appears. There is also a disruption in the functioning of the masticatory muscles.
- Sulfur plug. The presence of wax in the ear is important. It is designed to trap pathogenic microflora that can enter the ear canal, and also helps to remove foreign elements from the outside. In addition, sulfur is involved in creating a moist environment for the membrane. If there is excessive accumulation of sulfur, the plug can reach the membrane. In such a situation, pain in the head, congestion in the ears and a gag reflex occur.
- Ear injury. Most often observed: damage to the outer ear due to a blow or fall, penetration of foreign elements into the ear canal, ear burns due to exposure to alkali or acid, frostbite or barotrauma.
You might be interested in the article - Why do ears get stuffy when you have a runny nose and what to do about it?
There are quite a lot of factors that lead to headaches and stuffy ears with otitis media. It is quite difficult to install them yourself. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
Inflammation in the ears.
Possible causes of discomfort
Causes of the condition accompanied by noise and dizziness:
- Ringing in the ears, headaches and nausea accompanied by vomiting are symptoms of hypertension. In addition to the listed symptoms, the main one is high blood pressure.
- Atherosclerosis is characterized by the formation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels that slow down blood flow, which negatively affects the body. This is where the constant noise and ringing in the ears arises. Atherosclerosis is diagnosed not only in grandparents, as they began to believe. This disease is also detected in young people.
- Concussions and other traumatic brain injuries of varying severity may be accompanied by dizziness and noise.
- Loud noise can occur with tumors in the head or subsequent development of neurosis.
- Noise and a symptom of vertigo after rising from a sitting or lying position are caused by compression of blood vessels due to osteochondrosis. Pronounced symptoms include nausea, blurred vision and blurred gait. The human brain does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which leads to unpleasant symptoms.
- The appearance of noise, nausea, suffocation, dizziness and a feeling of weakness are noted with vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Hearing impairment in the form of ringing and noise manifests itself with sulfur plugs. This problem is easy to get rid of, which quickly eliminates the symptoms.
- Tinnitus in the case of Meniere's disease occurs because fluid accumulates in the ear. The hearing organ is compressed and hearing deteriorates.
- The vestibular apparatus is an organ whose disturbances lead to dizziness, nausea, noise, and possible vomiting.
- Vascular crisis is characterized by nausea and weakness, as well as tinnitus.
These are not all the causes of unpleasant symptoms. Blocked ears, weakness, sometimes nausea, dizziness with chronic otitis media and infectious diseases, depressive disorder.
The presented symptoms in rare cases are a consequence of taking medications. If the dose is exceeded or personal intolerance to the drug, these symptoms may occur. These symptoms are similar to side effects caused by drugs.
Possible causes of dizziness
It is not difficult for a specialist to establish the provoking factor that causes dizziness and headaches during otitis media. In certain situations, an ENT doctor determines the cause of why headaches appear in children and adults, without conducting specific diagnostics. The cause may be indicated by the location of the unpleasant sensations and their nature.
Dizziness during otitis media in adults and children is in all cases associated with the labyrinth of the inner ear, which acts as a vestibular controller. The information that is read from the labyrinth is considered basic and necessary for the brain to properly coordinate the simplest movements.
When the head hurts due to otitis media , dizziness is observed that does not go away for a long time, this can be associated with:
- labyrinthitis (inflammatory process in the inner ear);
- changes in pressure in the ear cavity due to a violation of the integrity of the membrane;
- chronic form of otitis media (due to fluid accumulating inside it);
- various pathological processes in the middle ear, which cause changes in pressure on the labyrinth.
As a result, the patient:
- unable, probably, to coordinate movements;
- he feels dizzy;
- he is unable to make precise movements with his hands;
- feels various unpleasant sensations: nausea, anxiety, panic.
Dizziness with otitis is a dangerous sign, indicating inflammation in the middle or inner ear. In addition, it is a symptom of a large number of diseases that do not depend on the disease in question:
- Vestibular neuritis.
- Head trauma.
- Vascular pathologies in the brain.
- Shingles.
- Meniere's disease.
- New growths inside the ear.
- Diseases of a neurological nature.
The main symptomatic difference between such pathologies and otitis media is that they, predominantly, do not provoke hearing loss and pain in the ears.
Labyrinthitis.
Methods for detecting the disease
If symptoms do not go away for a long time, you should consult a doctor to prescribe treatment. To prescribe an effective method, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease.
Diagnosis occurs through the following methods:
- First of all, the patient is sent for an X-ray of the skull and neck, which excludes or confirms the presence of a foreign body in the ear canal.
- To determine a person’s hearing level, he is asked to undergo audiometry. This method tests sensitivity to sounds familiar to the patient.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed for suspected tumors in the head.
- Otoscopy is a common diagnostic method that involves examining the inner ear using a special instrument.
A system consisting of a number of diagnostic methods will allow you to exclude possible diseases and make a correct diagnosis.
How to treat dizziness due to ear infection
Internal otitis is called inflammation of the inner ear area (labyrinth).
The labyrinth itself consists of three semicircular canals, the function of which is to control balance. In most cases, inflammation of the inner ear is caused by a viral, less often bacterial, background. Internal otitis media cannot appear on its own.
Most often it occurs as a result of complications of chronic or acute otitis, as well as against the background of a severe general infectious disease (for example, tuberculosis).
In addition, a common cause of the disease is inflammation of the upper respiratory tract - flu, colds. Trauma is also a cause of otitis media of the inner ear.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of internal otitis are:
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- ear pain;
- hearing loss.
As for dizziness, this symptom can be a sign of many diseases. In the case of internal otitis, dizziness appears after 1-2 weeks of bacterial infection. During this time, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through the bloodstream into the cavity of the inner ear, causing an inflammatory process there.
It is worth noting that severe attacks of dizziness may be accompanied by symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. From the outside, this course of the disease strongly resembles “sea sickness.” As a rule, dizziness goes away after a few days or weeks. But, if there are sudden movements of the head, dizziness may return again.
In addition to the main signs, the following symptoms are distinguished:
- imbalance;
- fever - this symptom is characteristic of any inflammatory processes;
- eye twitching;
- The purulent form of internal otitis is characterized by persistent hearing loss, leading to its complete loss.
Infection can enter the inner ear in a variety of ways. With a favorable course of the disease, the exudate (inflammatory fluid) resolves. In case of complications, fluid (pus) accumulates, which subsequently leads to complete loss of hearing.
Dizziness with internal otitis
Diagnostics
If the above symptoms and characteristic complaints of the patient are present, an examination is performed, which includes a clinical blood test. Also, to find out the true cause of dizziness, special tests are performed.
If the doctor cannot fully determine the cause of dizziness, the following studies are carried out:
- Electronystagmography - this study records the movement of the eyeballs. The movement is recorded by electrodes. Dizziness, which is caused by otitis media of the inner ear, causes a certain type of movement of the eyeballs. Dizziness caused by another cause is characterized by different types of movement.
- MRI, CT - computed tomography, as well as magnetic resonance imaging allows you to visualize the brain and make visible any of its pathologies (for example, tumors, strokes, etc.).
- Hearing test - this research method is carried out in order to identify the presence of any hearing abnormalities.
- Response Test - This test examines the auditory parts of the brainstem to determine whether the auditory nerve, which runs to the brain from the inner ear, is functioning normally. If this test reveals hearing loss, Meniere's disease is confirmed.
- metry - determined subjectively using audiometry. how well a person hears. The study includes behavioral testing as well as behavioral tone audiometry.
The doctor conducts an examination
Treatment
In most cases, the symptoms of otitis media of the inner ear go away on their own. In cases where labyrinthitis was caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. In cases of viral infection, antibiotics are not prescribed.
It is worth noting that drug treatment of internal otitis is similar to the treatment prescribed when Meniere's disease is detected. This kind of treatment can be called symptomatic - aimed at reducing the manifestation of the disease.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- antiemetics - these medications are aimed at eliminating symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. These include phenegran, cerucal, compazine.
- Antihistamines are also prescribed to reduce dizziness, vomiting, and nausea. These are drugs such as suprastin, diazolin, diphenhydramine, etc.
- Steroids are prescribed to reduce the inflammatory process. These drugs include methylprednisolone.
- Sedatives - to reduce vomiting, nausea, and various types of anxiety. These include drugs such as lorazepam, diazepam.
Scopolamine is also used in practice - a special patch form that is glued behind the ear. The drug is also aimed at reducing nausea and vomiting. Used for internal otitis, Meniere's disease.
But not always even the most adequate and timely treatment can completely eliminate a symptom such as dizziness. This happens with bacterial inflammation. But over time, the dizziness goes away completely and no longer bothers the patient.
In some cases, the patient is prescribed surgery, simultaneously on the labyrinth and on the middle ear. The operation is prescribed for a purulent form of labyrinthitis with an intracranial complication.
#8801; 2 November Category: Symptoms and causes
Headaches and dizziness with otitis media
Headache and so-called dizziness are subjective sensations that arise as an interpretation of certain nerve impulses. The function of transmitting impulses from parts of the body and sensory organs to the brain is performed by the nervous system, which is a collection of nerve cells united into long nerve fibers.
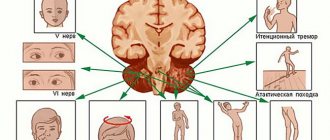
Each main nerve pathway, branching into smaller ones, innervates several areas. Signals from the ear region are transmitted by several cranial nerves:
An inflammatory or any other pathological process excites impulses in the nervous system, which are transmitted to the brain and interpreted as pain.
Why does otitis media cause headaches?
Due to the branched structure of the nervous system, headaches can occur during inflammatory processes in any part of the face and head. Dental disease and sinusitis are classic examples, in which the source of the disease is located in one place, and the pain is transferred (or “radiated”) to neighboring areas. The same is true for ear pain.
When a headache occurs due to otitis media, this is related to the pathological process on the average (due to the close location to the main nerves) and, less often, in the outer ear.
The inner part of the ear is located in close proximity to the brain: pain during otitis of the labyrinth and cochlea is always headache-related and is constant and strong.
This “erroneous” method of innervation of the body is justified and makes it possible to signal the degree of threat to life long before the moment when the inflammatory process moves to the brain.
Otitis headaches are caused by numerous symptoms:
- Inflammation of the labyrinth
- Presence of pus or fluid in the middle ear cavity
- Loss of eardrum integrity
- Chronic otitis of the external ear
- Boils in the ear canal
Symptoms of a headache in acute otitis media:
- Pain sensations are characterized as constant with periodic intensification, “waves”
- The pain is localized in the ear area and radiates to the frontotemporal lobe.
- Accompanied by fever.
- The nature of the pain is aching, sluggish.
- Localization of pain - the entire half of the head with an unhealthy ear.
If complications arise. such as mastoiditis or labyrinthitis:
- The headache becomes extremely strong and intense.
- The pain may spread to the occipital region and other parts of the head.
- The pain symptom is accompanied by high temperature. dizziness.
Thus, headache is a standard symptom of otitis media that occurs due to the location of inflammation in the head.
Why does otitis media make you feel dizzy?
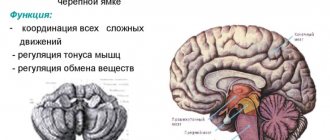
Dizziness syndrome with otitis media is always associated with the labyrinth of the inner ear, which serves as the vestibular controller of the body.
This is a unique human organ, which was created by evolution with pinpoint precision so that the brain always has an adequate idea of the position of the body in space.
The data read from the labyrinth is basic and necessary for the correct coordination of even the most basic movements by the brain.
The vestibular apparatus is a complex of three semicircular canals located in three different planes and several so-called “sacs”.
Inside these cavities of the labyrinth there is a liquid in which dense membranous formations with endolymph inside float.
Regardless of the position of the body and the nature of motor activity, the fluid system in the channels, like water in a closed bottle, always follows the force of gravity. Sensitive hair receptors capture information about the slightest movement occurring in the semicircular canals.
This is the most complex system, honed over millions of years of evolution. All information is transmitted in real time from the inner ear to the brain, where it is analyzed every second and compared with the movements performed. Based on the analysis, the brain corrects movements, making them accurate and targeted.
When you feel dizzy with otitis media, this may be due to:
- with labyrinthitis #8212; inflammation of the inner ear;
- c change in pressure in the tympanic cavity as a result of the eardrum losing its integrity;
- with chronic otitis media #8212; due to the liquid accumulating in it;
- with any disease of the middle ear. causing a change in pressure on the labyrinth.
In all of the following diseases, sensory information is distorted:
- From the labyrinth, the brain receives incorrect data about the movement of fluid in the semicircular canals.
- The brain, receiving mismatched information from the right and left labyrinths, is unable to reduce it to one denominator, correctly analyze it and give commands.
- feels dizzy
- unable to coordinate movements correctly,
- cannot perform precise manual manipulations,
- feels a complex of unpleasant sensations: nausea, anxiety, panic.
Dizziness with otitis media is a serious symptom that may indicate not only inflammation of the middle or inner ear, but can be a symptom of many other diseases independent of otitis media:
- Vestibular neuritis
- Head injuries (skull fractures, labyrinthine concussions)
- Vascular diseases of the brain
- Shingles
- Meniere's disease
- Syphilis
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Multiple sclerosis
- Tumors in the ear
- Neurological diseases
The main symptomatic difference between these diseases and otitis media is that they usually do not cause hearing loss or ear pain.
Source: https://aptekacheboksary.ru/vospalenie/kak-lechit-golovokruzhenie-pri-vospalenii-uha/
Troubleshooting
You can get rid of unpleasant symptoms only through a competent approach to treatment. Self-medication does not always lead to a positive effect. Even if the symptoms are eliminated, it is worth maintaining the condition by taking preventive actions.
Medication approach
Once the root cause of the disease is identified, treatment can begin. The disease should be treated by addressing its root cause. If the cause of nausea or tinnitus is high blood pressure, medications that cleanse blood vessels are prescribed. The same applies to atherosclerosis that torments a grandmother or a young person.
Patient's atherosclerosis
The lack of oxygen in the brain is solved with the help of nootropic substances. If the cause of the symptoms is an inflammatory process in the body, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are used. Treatment of osteochondrosis involves not only medications, injections, but also exercises. There are cases when traditional medicine is powerless, then they resort to surgical intervention. A neoplasm is a serious illness that also requires surgery.
Conventional analgesics can eliminate dizziness and tinnitus. In addition to them, they take Clonazepam and Gabapentin.
A number of effective drugs include Tanakan. This remedy is used for various brain injuries and high blood pressure. Its purpose is to improve blood circulation in the human brain. No less effective are Trental and Vasobral. The first drug is prescribed for circulatory disorders and otosclerosis. The second remedy also improves blood flow and affects the receptors of the central nervous system.
In addition to those listed, there are others that eliminate discomfort. The use of any drug requires consultation with a specialist.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is used in combination with drug treatment. Folk remedies are not used as an independent type of treatment when it comes to serious diseases.
Alternative medicine offers many recipes to eliminate painful symptoms. The use of these methods should be discussed with your doctor. Some herbs are powerful allergens, so self-medication for some individuals may result in the appearance of new symptoms and allergies. Each case requires an individual approach.
Popular folk remedies are onion juice, dill water, and viburnum decoction. Depending on the case, a separate method is used.
Steamed viburnum is prescribed if dizziness, nausea, and ringing in the ears are a consequence of high blood pressure. Brewed dried dill helps improve blood circulation. To achieve maximum effect, you should drink dill water for two months, 100 ml daily three times before meals.
Propolis tincture is considered an effective remedy. Place tampons soaked in a solution of tincture and oil into the ears overnight. The number of procedures required to relieve symptoms is at least 8-12.
Onion juice with cumin is considered a remedy for pain and discomfort in the ears. To prepare the juice, a hole is made in the onion for the cumin, then baked. After baking, squeeze out the juice and drop two drops into the ear.
Diagnostics
Such an unpleasant condition as tinnitus, ringing, and constant dizziness causes people a lot of discomfort, depriving them of a normal life. These symptoms signal problems with other body systems. They will not disappear on their own; proper treatment is necessary, so you should consult with specialists. Today, otoneurologists deal with this problem, but doctors with such a narrow specialization are not always available in the clinic. Then you should contact an otolaryngologist and neurologist to determine the cause of dizziness, ringing and tinnitus. These specialists will help prescribe adequate treatment.
Doctors usually prescribe the following types of diagnostics:
Ultrasound examination of arteries
This diagnostic method will allow you to see the reason that is preventing normal blood access to the brain.
CT and MRI
Using these techniques, tissue of the brain or inner ear is examined to identify inflammatory processes.
Study of auditory nerve functions
With its help, otolaryngological diseases and the causes of ringing and tinnitus are identified.
Preventive actions
If you feel a positive result, you should not abandon treatment. The duration of therapy will help consolidate the results. The duration of use of medications and folk remedies depends on the severity of the disease. If we are talking about wax plugs, you can fix the problem quickly. And osteochondrosis and its consequences will disappear after restoration of the damaged vertebrae.
It will be possible to eliminate the problems after changing your lifestyle and diet. If you are overweight, you should get rid of it, as well as give up bad habits and introduce physical exercise into your life.
Diagnostic methods
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor prescribes treatment.
So, you are convinced that symptoms such as stuffy ears and dizziness have numerous causes. This makes diagnosing the disease very difficult, but there are a number of tests that can help you narrow down your search. The simplest of them are:
- collecting anamnesis to determine previous inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs or taking new medications;
- blood pressure measurement;
- conducting coordination tests;
- taking a general blood test;
- consultation with a neurologist.
When conducting a more detailed examination, X-rays of all parts of the spine, CT or MRI of the brain are used. These methods allow you to determine the cause of dizziness and correct them.
Stuffy rooms
Very often, numbness of the head occurs in stuffy and enclosed spaces. Thus, students can easily lose consciousness in lecture halls. To avoid this, you need to try to switch your attention and think about pleasant things. There are cases when you start to feel sick in the minibus and feel pressure on your head. In such a situation, you need to get off at the nearest stop or simply move forward so that the road can be seen.
We looked at why the ears become blocked and the head feels dizzy. But that is not all.
Recommendations
When a person has stuffy ears, dizziness, or pain in the back of the head, these symptoms may be evidence of a wide range of diseases. To avoid negative consequences, you need to spend more time in the fresh air, adhere to an active lifestyle and proper nutrition, and establish a daily routine.
It is necessary to limit the amount of salt in your diet, as well as foods that contain fat. Your bedroom and work area should be constantly ventilated. If the activity is related to a computer, then you need to do eye exercises and eat foods that contain magnesium. As a rule, many people experience stuffy ears and dizziness. The reasons must be determined by a doctor.
What causes the described symptoms?
Internal otitis is called inflammation of the inner ear area (labyrinth). The labyrinth itself consists of three semicircular canals, the function of which is to control balance. In most cases, inflammation of the inner ear is caused by a viral, less often bacterial, background.
If you constantly have stuffy ears and feel dizzy, you should definitely consult a therapist. After all, such deviations may indicate serious diseases that need to be treated urgently.