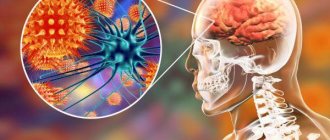
Causes of cephalalgia
Often headaches occur as a result of chronic fatigue. They are less common in cases of serious pathologies. Cephalgia can be observed in the presence of a number of factors, including:
- spasm or dilation of the lumen of cerebral vessels;
- intoxication of the meninges with toxins and various chemicals;
- increased blood or intracranial pressure;
- diseases of the cervical spine;
- viral and bacterial diseases with a characteristic increase in body temperature;
- diseases of the bones of the skull, eyes, ears;
- overstrain of muscle fibers;
- metabolic disorders;
- frequent stress, depression, emotional stress;
- dehydration;
- heat and sunstroke;
- skull injuries;
- stroke;
- anemia.
Among the provoking factors, the most common are high blood pressure, trigeminal neuralgia, diabetes mellitus, insomnia, and increased meteosensitivity. In addition, bad habits can lead to cephalgia of the brain, including smoking tobacco products and frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Other types of headaches
Cephalgia syndrome is very common today. There are also the following types:
- Liquorodynamic headache (appears with increased intracranial pressure). At the same time, unpleasant sensations fill your head.
- Infectious-toxic. It is characterized by a weakening of the body's defenses, which allows pathogens to enter the human body.
- Neuralgic. In this case, the attacks have a short duration.
- Angiodystonic. Its cause is considered to be increased blood pressure and late toxicosis during pregnancy. This pathological condition manifests itself as nausea, changes in consciousness, and swelling of the face.
- Chronic. The reason for its appearance is constant stress, persistent nervous tension, and hormonal imbalance. If treatment for this pathological condition is not started, the headache can last for quite a long time. The nature of the unpleasant sensations is oppressive. We must try to prevent the appearance of just this form of development of the disease.
- Persistent. In this case, the discomfort lasts for a very long time, and it is almost impossible to relieve it with analgesics.
- Persistent. Most often it is provoked by depression, but it can also indicate other diseases.
Neurologist and immunologist Kirill Aleksandrovich Shlyapnikov will help us consider the most common manifestations of cephalalgia:
- Cluster. This type of headache is very persistent and severe. Most often it occurs in men. Its peculiarity is that the discomfort spreads to only one half of the skull. In addition to intense discomfort, the patient’s eyes turn red, the pupil narrows, and the eyelid droops slightly.
- Sexy. The fact is that pain appears at the moment of orgasm, which, however, is not their cause.
- Cephalgia of mixed origin. It should be noted that headaches of any one type are extremely rare. For example, vascular cephalgia is directly related to tension headaches. Pathologies of mixed origin occur in 90% of patients.
How does it manifest itself?
Clinical manifestations of cephalalgia of the brain depend on the cause of development. The main symptoms of this condition are:
- acute human reaction to external stimuli;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased irritability and excitability;
- pupil dilation.
In addition, there are a number of symptoms, in the presence of which you should contact a specialized specialist. Among them it is worth highlighting:
- sudden onset of pain, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, psycho-emotional disturbances, and mood swings;
- increased feeling of discomfort during coughing;
- stiff neck;
- increased body temperature above 38°C;
- loss of speech, confusion;
- cephalalgia has a pulsating nature with irradiation in the forehead and eyes;
- a unilateral manifestation of the pathology is possible.
Causes of cephalgic syndrome
Taking into account that cephalalgia of the brain is a secondary syndrome that is quite common, it is impossible to determine the causes independently. In this case, it is imperative to consult a specialist in order to stop the development of the disease causing headaches as early as possible.
Today, there are many known diseases that are accompanied by pain in the brain.
Among such pathologies are infectious, oncological, bad habits, failure of the daily routine, inflammatory diseases and biochemical metabolic disorders. In children, the main reason is the incorrect daily routine.
Since there are many causes, diagnosing the disease is very difficult. Therefore, it is often impossible to say why a headache occurs.
Sometimes cephalalgia can be caused by several pathologies at once. The lifeline in this matter is related symptoms, which often appear a little later.
Basically, pain is caused by several factors:
- leading an unhealthy lifestyle;
- hereditary factor;
- neuralgic and vascular diseases.
According to the latest research data, we can conclude that the hereditary factor plays a very important role in the occurrence of pain in the brain. This is especially reflected in the state of a child’s fragile body.
Often, the reasons for the development of cephalgic syndrome are:
- bad habits;
- passive lifestyle;
- circadian rhythm disorder;
- starvation;
- lack of fresh air;
- long periods of time in front of the computer.
In addition, vascular dysfunction may contribute to the occurrence of headaches. In some cases, this pathology can cause a stroke.
It is important to remember that cephalgia is a sign of the development of quite dangerous disorders that can be fatal.
Classification
Cephalgia of the brain is divided into several types, depending on the etiology of the disorders. Among the main types of pathology, doctors distinguish the following forms of pathology:
- vascular;
- vasomotor;
- tension headache;
- liquorodynamic;
- neurological;
- infectious-toxic.
Vascular
This type of cephalgia is observed with constant spasms or dilation of cerebral vessels. Patients compare the vascular form of the pathology with rhythmic hammer blows to the head with limited localization. The feeling of discomfort is accompanied by characteristic pulsation and synchronous compression. This form of pathology is observed with migraines, physical fatigue, emotional stress, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
As a result, there is a disruption in the supply of oxygen to brain tissue, which leads to the development of hypoxia. Patients complain of pressing and bursting headaches, dizziness, and clouding of consciousness. The skin of the face and neck turns pale, and there is a pulsating noise in the ears.
Vasomotor
The vasomotor type of cephalgia is in most cases associated with muscle strain. The pain syndrome may be mild or moderate in intensity. Patients feel a feeling of tightness in the head, stiffness of the neck muscles, tightness of the neck and pressure in the forehead. In most cases, these symptoms are observed on both sides at once. This type of pathology is caused by stress, as well as depressive and neurotic conditions.
Tension headache
This type of cephalalgia occurs during severe physical or emotional stress. Headaches are accompanied by a feeling of compression of the skull. They can also pulsate and radiate into nearby structures.
Liquorodynamic
A change in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid can contribute to the development of pain. This type of pathology develops in the presence of a number of factors, including:
- hydrocephalus;
- cysts;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- failure of venous outflow;
- disruption of the structure of the meninges.
Neuralgic
This form of cephalgia is a response of inflamed nerve structures to the action of irritating factors. Patients complain of intense cutting pain that is limited in localization. In addition, patients experience lumbago in the ears, eye sockets and jaws while moving, coughing, chewing food or in a static position.
Infectious-toxic
Unpleasant sensations in this case are characterized by progressive intensity. At first, the pain is localized in one place, but over time it spreads to all parts of the head. The infectious-toxic form of the pathology develops due to many factors, including:
- poisoning;
- infectious diseases of viral or bacterial etiology.
When to sound the alarm
If you or someone close to you has cephalgic syndrome, which is regular and does not go away after rest, you should think about the fact that it may be caused by a dangerous disease. Here are the symptoms that should seriously alert you:
- the feeling of pain in the head occurs unexpectedly and increases quickly. At the same time, nausea and vomiting appear. The patient experiences confusion. This may indicate a hemorrhagic stroke;
- if the pain intensifies during sneezing or coughing, this may indicate cerebral edema;
- when, as a result of injury to the skull and brain, pain does not go away for a very long time and becomes more intense - this is a likely sign of intracranial hemorrhage;
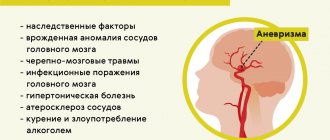
- unbearable, excruciating pain of a point nature, which appeared suddenly, may be a sign of a ruptured aneurysm;
- when fever and increased tone of the neck muscles are added to the main symptom - this is one of the specific manifestations of inflammation of the brain as a result of infection;
- We are talking about a stroke if, simultaneously with a constant headache, memory impairment, clouding of reason, partial loss of vision and hearing are observed. The patient suffers from imbalance, decreased sensitivity of the limbs;
- if severe attacks of pain occur regularly, but are localized exclusively in the area of one temple, then this may be a dangerous pathology - temporal arteritis. The consequence of this disease can be blindness or impaired blood supply to the brain;
- throbbing pain in the eye and frontal area, along with inflammation of the inner surface of the eyelids, may indicate the onset of a serious illness - acute glaucoma.
Diagnostics
If you have cephalgia of the brain, you first need to seek help from a therapist. To begin with, he will collect complaints and anamnesis of diseases, after which he will begin a subjective examination. In order to confirm the clinical diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods, among which the most effective are:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- clinical urine analysis;
- measurement of pulse, temperature, blood pressure;
- X-ray diagnostics of the cervical spine;
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- electrocardiography;
- encephalography;
- spinal tap.
In addition, advisory opinions from other specialists may be required. For this purpose, the patient is referred to an appointment with a neurologist, surgeon, oncologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, orthopedist, ophthalmologist, and psychotherapist.
Helpful information
Pathologies in which cephalgia of the brain is one of the main signs can occur according to one scenario. Therefore, it is not recommended to diagnose yourself. Improperly administered therapy can worsen a person’s condition and lead to the development of complications.
Treatment
The main directions in the treatment of cephalgia are the elimination of the underlying disease, which entailed pathology, stabilization of vascular tone, as well as symptomatic therapy. The main method of eliminating headaches is the use of medications.
The most effective medications for cephalalgia are medications that improve blood circulation in the brain. Among them are Stugeron, Cinnarizine, Cavinton. It is also recommended to use drugs that improve the transmission of nerve impulses through synapses. These include Neuromidin, Milgamma, Prozerin. In addition, it is possible to use nootropic drugs Nootropil and Piracetam.
In order to eliminate viral and bacterial lesions, antibiotics Ampicillin, Ceftriaxone, Azithromycin, Cefuroxime are prescribed. Corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to combat inflammatory processes. In the case of cephalgia, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone are used.
Helpful information
To obtain an additional therapeutic effect of drug therapy and normalize the patient’s condition, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures.
For cephalgia, electrophoresis is most often used. It is also possible to use:
- water and mud procedures;
- therapeutic exercises;
- acupuncture;
- magnetic therapy.
Prevention
To prevent the development of cephalgia, it is recommended to follow a set of rules aimed at the etiological factors of the pathology. These include:
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- balanced diet;
- avoiding stressful situations and heavy physical activity;
- spending free time outdoors;
- good sleep;
- timely treatment of concomitant pathologies;
- rejection of bad habits.
If headaches occur, you should immediately consult an experienced specialist. A timely diagnosis allows you to prescribe the most effective treatment tactics, which will prevent the progression of the pathology and maintain the patient’s health.