Despite the benign nature of the neoplasm, it can pose a threat to human health and life.
Cerebral hemangioma is found mainly in adult patients, more often in men.
The tumor can be diagnosed in any area of the brain, but is more often found in the brain stem, cerebellum or spinal cord.
Causes
Scientists currently cannot name the exact causes of the disease. However, experts identify some possible factors for the development of cerebral hemangioma in adult patients:
- hereditary disorders, genetic predisposition to diseases of the vascular system;
- arterial hypertension and increased intracranial pressure;
- extensive, serious traumatic brain injuries of the head;
- long-term exposure to large doses of radiation on the body. The risk increases in patients who are exposed to ionizing radiation. And also to radiation caused by the influence of an atomic bomb, man-made disasters with the formation of radioactive radiation. Factors such as radiation from mobile phones, electromagnetic fields of power lines remain unproven;
- exposure to chemical or carcinogenic substances. There is a risk of developing brain hemangioma among employees working in enterprises whose specific activity is the production or use of chemicals;
- constant nervous tension, severe stressful situations;
- wrong lifestyle. This includes both low physical activity and the use of alcoholic beverages, drugs, and nicotine.
Relationship between location and clinical manifestations
The presence of a malformation may not be noticed as long as it is small and does not affect adjacent tissues and brain structures. But in the future, when the size of the hemangioma increases, it will put pressure on the healthy tissues of the very section where it is located, which will certainly manifest itself with certain symptoms.
For example, a tumor in:
- The temporal lobe causes hearing loss and dizziness.
- The occipital part negatively affects visual acuity and causes hallucinations.
- The frontal lobe is characterized by disturbances in sleep, motor skills, speech, memory, and vision.
- The cerebellum leads to problems related to coordination of movements.
With hemangiomas formed in the deep tissues of the brain, patients often experience a buzzing in the ears. They often complain of sudden attacks of aching cephalgia.
Pathology is more often detected in young people with complaints of specific symptoms. In adult patients, hemangioma is detected during an examination of the head or the entire body associated with a preventive examination, since at this age the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Interestingly, clinical manifestations in men are more pronounced than in women. Often, in the weaker half of humanity, anxiety symptoms are more pronounced when carrying a child.
Symptoms
Often in adults, cerebral hemangioma occurs unnoticed over a fairly long period of time. Often a patient learns about his problem by chance during an examination. However, there are common symptoms of cerebral hemangioma in adults that make you think about the existence of the disease. These include:
- regular headaches of varying duration, disturbing for unknown reasons;
- violation of movement coordination;
- vision problems, weakened sense of taste, hearing, decreased sense of smell;
- constant dizziness, vomiting, nausea;
- fainting conditions;
- epileptic seizures;
- convulsions;
- intellectual disability;
- impaired memory, concentration;
- muscle weakness.
Brain hemangioma is divided into 2 types:
- Sluggish (torpid). Sluggish hemangioma is characterized by headaches, cramps, nervous disorders and insomnia. Convulsions occur against the background of a headache and can manifest themselves both locally and in several places at once.
- Prone to bleeding (hemorrhagic). A symptom of the hemorrhagic type of hemangioma is high blood pressure.
Signs of hemangioma
Hemangiomas do not manifest themselves in any way, and there are no characteristic symptoms. Such formations are detected during MRI or. Hemangiomas are classified into: torpid, hemorrhagic .
Hemorrhagic refers to a small collection of blood vessels. Arterial hypertension is considered the main symptom of such disorders. The torpid variety is large in size and is supplied with blood from nearby arteries. With such hematomas, convulsions, migraines, sleep problems, and nervousness occur.
Convulsions in torpid hemangiomas differ in localization. Neoplasms are accompanied by headache, the patient loses consciousness. Doctors often confuse this set of symptoms with malignant neoplasms. Therefore, if symptoms occur, you should contact a neurologist.
Sometimes an arm or leg is temporarily paralyzed, muscle weakness appears, dizziness, loss of consciousness, vision loss, hearing deteriorates, and problems with speech function often arise.
Additional classification
There is an additional classification, taking into account the type of vessels that form them:
- Capillary (telangiectasia) is the most common brain tumor that is localized to the skin. Hemangioma of cerebral vessels in children and adults rises above the skin, but does not affect the epidermis, so bleeding occurs extremely rarely. The structure of a capillary neoplasm is a network of densely intertwined capillaries. Their walls can grow together and turn into a lump of vascular tissue.
- Venous hemangioma of the brain - a neoplasm puts pressure on the brain, causing the appearance of neurological disorders. If it appears in the crown area, symptoms may be noted that correspond to the capabilities of this area. The patient has a headache, fever, coordination is impaired, it is difficult for him to recognize symbols and signs, and there is also a disorder of touch. Due to its structure, venous hemangioma is considered the most dangerous - there is a risk of vein rupture and hemorrhage.
- Arteriovenous (mixed) hemangioma is usually localized in the internal organs. But with a superficial location, it can take the form of tortuous and branched arteries, veins and bundles, which are located under atrophied, altered skin and its fiber. In most cases, the tumor is located in the neck or head.
- Cavernous hemangioma of the brain - neoplasms of this type feed large arterial vessels. Most often they are localized in the skin. This type of tumor is the rarest. Cavernous hemangioma of the brain spreads quite quickly. With internal localization, parenchymal structures with a rich vascular network are affected.
The question often arises: why are small cavernous hemangiomas of the brain dangerous in adults? They are dangerous due to the possibility of extensive bleeding.
Causes and development of the disease
This benign neoplasm looks like a tangle of choroid plexuses filled with blood. Similar growths occur on the skin of newborns and appear as red, slightly swollen spots. Brain hemangioma looks the same, but it is much more dangerous than skin pathologies in infants.
The formation of hemangioma is influenced by many reasons. Its occurrence is associated with a disruption in the formation of the circulatory system in utero, as a result of which more vascular tissue is formed than necessary. That is why this growth is also called vascular hyperplasia.
There are a number of provoking factors leading to the development of the pathological process:
- Viral and infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
- The harmful effects of toxic substances (alcohol, taking certain medications, drugs).
- Environmental pollution.
- Bad heredity.
- Pathological course of pregnancy.
Hemangioma of cerebral vessels can be not only congenital. The risk of developing tumors in vascular tissues increases in people exposed to ultraviolet radiation, living in constant stress, or having experienced a head injury. In 12.5% of victims, vascular malformations provoke hemorrhage in the brain (stroke).
Of the many types of hemangiomas, based on the structure of the choroid plexus, the following are distinguished:
- Arterial , which is a plexus of arteries.
- Capillary , in which intertwined capillaries disrupt blood flow.
- Venous , which is a plexus of veins or a bundle of vascular extensions.
- Cavernous , in which pathological plexuses with septa are formed from once healthy blood vessels. Compared to other tumors, this type of growth is considered particularly dangerous. A tumor with thinned septa and impaired blood circulation threatens to rupture the growth at any moment.
Diagnostics
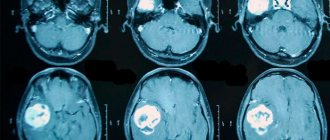
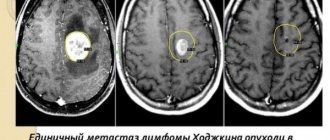
Brain hemangioma is detected only by computer technology; it is impossible to make such a diagnosis using other methods.
Contrast angiography was in great demand until recently, but since the method was dangerous for patients, it is now practically not used. How is angiography performed? A special contrast is injected into the patient's vascular system and then an X-ray of the brain is taken.
Superselective angiography - this method is more gentle for patients, it is less dangerous for the body. It is often prescribed to detect pathology in the vascular system. This diagnosis is carried out using this method: a special contrast is injected into a certain part of the brain where the hemangioma may presumably be located.
Computed tomography or CT is a safer method, as it does not violate the integrity of the tissue. This is a diagnostic method that uses X-rays of the brain. Special X-rays are produced in a tube and affect areas of the brain from different angles. The sensors receive data that is scanned layer by layer, the data is instantly processed and output to a computer. Therefore, the doctor immediately sees a detailed picture, detailed data of the entire brain.
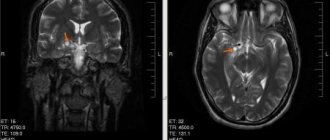
Magnetic resonance imaging is a 100% effective examination. During diagnosis, it reveals hemangiomas of various sizes, from very small to large. And up to 98% detects the type of hemangioma. Also, basic computer diagnostics are supplemented by general analyzes and additional studies. This is a general blood test, biochemical analysis, ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels.
Hemangioma
Signs
There are several types of hemangiomas.
A simple (capillary) hemangioma is located on the surface of the skin and is a red or purple-bluish spot that turns pale when pressed, but quickly restores color. Its surface can be smooth or bumpy. The spot may be flush with the skin or slightly raised above it. As the child grows, the hemangioma may increase in size. Cavernous hemangioma is located under the skin and looks like a round tumor-like formation. The skin over this formation is unchanged or bluish. When pressed, the cavernous hemangioma decreases in size for some time, and the skin over it, if it is colored, turns pale. This occurs due to the outflow of blood from the formation. However, soon the blood flows back, the color and size of the hemangioma become the same.
Cavernous hemangioma can be combined with a simple one, in this case they speak of a combined hemangioma. This tumor has cutaneous and subcutaneous parts.
There is also a mixed hemangioma, it consists of tumor cells of blood vessels and other tissues. Its appearance depends on what tissues it is formed from.
Hemangioma can form not only on the skin. It often develops on internal organs - liver, spine, kidney. Liver hemangioma may be asymptomatic. However, if the tumor is large, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting and pain in the right hypochondrium.
A small hemangioma of the spine is also painless. However, when it increases, the patient complains of pain in the spine.
Small renal hemangiomas do not cause any discomfort and are discovered by chance during an examination. And as the tumor grows, the patient’s temperature rises, weakness appears, and performance decreases. The patient loses weight, blood and protein appear in the urine. In addition, there is pain in the lower back, radiating to the groin.
Description
Hemangioma is a common benign tumor in children. Moreover, if previously it was diagnosed in one child out of 100, now many more children are born suffering from this pathology. Why this tumor appears is not known exactly, but there are several hypotheses. First and foremost: it’s about the child’s hormonal characteristics. The second is that infectious diseases that the mother suffered in the first weeks of pregnancy, when the child’s vascular system was developing, are to blame. In addition, it is known that hemangiomas are found more often in premature babies than in those born at term. Poor ecology is often blamed for the increase in the number of hematomas.
Hemangioma can form on any part of the body - on the face, neck, chest, torso, arms and legs. A tumor that appears on the skin can grow inward, affecting other organs and even disrupting their functioning. Thus, a hemangioma located near the ear can grow into the eardrum, and as a result, hearing can deteriorate or even disappear completely.
Unlike most tumors, hemangioma does not metastasize. However, relapses of this tumor occur quite often.
During this disease there are three stages:
- active growth stage (from birth to 6-8 months);
- growth cessation stage (from 6-8 to 12-18 months);
- reverse development (up to 5-7 years).
True, in most cases, the hemangioma does not develop back, and it must be removed if necessary.
Spinal hemangioma occurs when vascular tissue cells divide incorrectly. Most often this occurs in women 20-30 years old. This pathology is found in approximately 10% of patients seeking examination of the spine. 75% of hemangiomas are localized in the thoracic spine. Most often, only one vertebra is affected; it happens that the disease affects 2-5 vertebrae, but damage to 6 or more vertebrae is extremely rare.
According to their structure, spinal hematomas are divided into:
- capillary, consisting of a tangle of thin-walled blood vessels separated by fatty or fibrous tissue;
- cavernous, consisting of several interconnected thin-walled cavities;
- mixed, consisting of vessels and cavities.
These hemangiomas can be located in the vertebral body, less often in its arches or processes. In almost 90% of cases, the tumors are non-aggressive and asymptomatic. If they are also small in size, then they do not pose any threat to the patient and treatment is not required. However, in 10% of cases, the tumor not only grows quickly, it also destroys the bone tissue of the vertebra, disrupting its density. Because of this, even with a small load - when running, jumping, the vertebra may not withstand it and break. In this case, there is a danger of compression of the nerves and the development of paralysis of the legs or urinary disorders.
Massage is contraindicated for those suffering from vertebral hemangioma.
Renal hemangioma is most often found in older people. Women suffer from this pathology twice as often as men. The tumor can form as a result of a growth spurt in early childhood or adolescence, or it can also form as a complication of certain chronic kidney diseases.
Kidney hemangioma is also found in children. It usually occurs due to any infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy. In addition, the cause of tumor development can be bad habits, for example, smoking, decreased maternal immunity, and radiation exposure. In newborns it is detected in the first month of life, but in 7% of them it disappears as the child grows.
Liver hemangioma is found in 7% of people, and in women it is detected six times more often than in men. It can be congenital, but there are also cases of acquired hemangiomas. Typically, capillary (small, 2-3 cm in diameter, consisting of small cavities) and cavernous (large, up to 20 cm in diameter, heterogeneous, consisting of small cavities, often united into larger ones) hemangiomas are formed in the liver. Many doctors believe that estrogen promotes tumor growth in the liver, so before planning a pregnancy, a woman suffering from liver hemangioma should consult a doctor.
Despite the fact that liver hemangioma is a benign tumor, those suffering from this disease should take it seriously, since if the tumor ruptures, massive bleeding can begin, which can be fatal. Therefore, if you experience severe abdominal pain, as well as abdominal injuries, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
Cutaneous hemangiomas are detected by simple examination. This usually happens immediately after birth or, less often, in the first two to three months of the child. An ultrasound examination is also performed to determine the volume of the tumor, its structure and the characteristics of its location. For extensive or deep hemangioma, angiography is performed.
To diagnose renal hemangioma, radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are used. A general urine test is also required.
Magnetic resonance or computed tomography is required to identify spinal hemangioma.
Liver hemangioma is usually detected by ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. Liver scintigraphy is also performed to confirm the diagnosis. A biopsy of the tumor cannot be done, as there is a risk of bleeding. Diagnosis of liver hemangioma takes three months. This is necessary to understand whether the tumor is growing and whether it will cause trouble for the patient after some time.
Treatment
Small hemangiomas located on the body do not require treatment. However, if the hemangioma is large or located on the face, it is better to remove it. Small, pinpoint hemangiomas are removed by electrothermocoagulation, but after this manipulation, patients are often left with cosmetic defects.
For small cavernous hemangiomas on the face, sclerosis of the tumor with alcohol is used. For combined hemangiomas, the skin part is first removed using cryotherapy, then the subcutaneous part is sclerosed.
Nowadays, hemangiomas are often removed with a laser. This method is good because it leaves no cosmetic defects, and the treatment does not take very long.
Small non-aggressive capillary hemangioma of the spine does not require treatment. In other cases, the tumor can be treated in several ways. Irradiation of a tumor with X-rays leads to a decrease in its size, and later to its death. Another method of getting rid of spinal hemangioma is embolization (clogging its vessels); due to malnutrition, the tumor dies. In some cases, ethyl alcohol is injected into the vessels leading to the tumor. The vessels stick together (sclerosis), blood and nutrients do not reach the tumor, and the tumor dies. Using the method of puncture vertebroplasty (injection of bone cement into the cavity of a destroyed vertebra), you can not only get rid of the hemangioma, but also strengthen the destroyed vertebra.
For small size (up to 3 cm) renal hemangiomas, treatment is not required, but monitoring of the tumor is necessary. For large tumors, surgery is required. Either just the hemangioma or, if necessary, the entire kidney is removed. After surgery, constant monitoring of the patient is required. In most cases, renal hemangioma does not recur.
If the liver hemangioma is less than 5 cm in diameter, no treatment is required. However, in this case, periodic examination of the patient is necessary so as not to miss the moment when the tumor begins to grow. However, if the hemangioma compresses neighboring organs, grows rapidly, and causes discomfort to the patient, it is necessary to remove it. The tumor must be removed before pregnancy and before hormonal therapy. Currently, the endovideoscopic method is used to remove liver hemangioma. Surgeons make several small incisions, insert probes with lights, a video camera and instruments through them, and remove the tumor.
However, liver hemangioma is not removed if it affects large blood vessels, if there are large liver hematomas, or with cirrhosis. In these cases, the hemangioma is sclerosed.
© Dr. Peter
Treatment
Under the influence of external factors, a tumor formed by the tissues of blood vessels in the structure of the brain can occur. A hemangioma looks like a red-blue node, the size of which can reach 2 cm. It contains tangled blood vessels with voids and clotted blood.
A mass in the head is very rare and difficult to remove. Most often, the tumor forms in females; in males it usually occurs less frequently, after 25 years. Hemangioma can be located in any part of the brain, but it is usually found in the cerebral hemispheres. They also occur on the surface of the skin, but they are not as dangerous as brain formations.
The danger lies primarily in hemorrhage, which can lead to a stroke. If left untreated, its progression will lead to death.
Diagnostic methods
It is impossible to determine a hematoma without examination. To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors need to know the signs of the disease. When there is a suspicion of an accumulation of blood vessels in the head, the following procedures are performed:
- Angiography involves the use of a contrast agent in the vessels.
- MRI or CT. Such techniques are among the most accurate and harmless to people.
- Superselective angiography. Contrast liquid is injected pointwise into the site of formation of a cluster of blood vessels.
With the help of modern diagnostic methods, the size, structural components and localization of the tumor change. Normal therapeutic procedures can be performed without difficulty.
Effective ways
There are several ways. Each of them contains certain means and the required sequence.
Doctors begin treatment of any disease and malformations based on three factors:
- location of the disease;
- size of the malformation;
- presence of possible hemorrhages.
Therefore, before getting rid of a nodular tumor, they undergo a consultation, after which individual treatment is prescribed.
Surgical removal
For a small nodular formation, which is not located near the main part of the brain and is not so deep, removal occurs through open access surgery. To avoid any difficulties during the operation, it is performed after a hemorrhage that has occurred recently.
Hemangioma forms in different parts of the brain and skin. In the brain it can be located both on its surface and deep in it. If the tumor is located far from the surface of the skull, then any operations against it are very dangerous for the patient’s life. In this case, they try to avoid surgical intervention, because this can affect the functioning of certain brain structures.
Possible complications
Hemangioma is a benign neoplasm, but despite this, it causes severe consequences. First of all, it leads to cerebral hemorrhage, which causes various complications. When enough blood accumulates, convulsive and epileptic seizures occur.
Bleeding caused by a hemangioma in the brain can be fatal in severe cases.
In case of timely diagnosis, the formation does not pose a danger to the patient and is successfully treated. That is why experts recommend regular preventive examinations and, if unpleasant symptoms occur, consult a doctor.
Endovascular surgery
If the hemangioma is located in the deep tissues of the brain, endovascular surgery is used. With this type of intervention, a catheter is inserted into the problem area through the cerebral artery using radiographic instruments and a guide. In this way, an embolus is delivered to the brain, which can cause blockage of blood vessels.
After this, the patient is repeatedly subjected to an additional series of angiographic images. In this way, doctors can verify how successful the operation was. This method of combating brain hemangioma is one of the most advanced of all other treatment methods.
Radiosurgery
Another method of treating cerebral hemangioma is radiosurgery. In this case, all existing vascular clusters stick together due to the effect of radiation on them. This process gradually leads to the death of malformations. The most important advantage of this type of surgery is that the integrity of the brain tissue is not damaged in any way and there is no use of surgical knives. The accuracy of this method is maximum; the operation has virtually no side effects. The only disadvantage of radiosurgery is the long treatment period.
With such a disease, you need to get diagnosed in time so that there are no bad consequences.
Diagnosis of brain hemangioma
Diagnosis of brain hemangioma abroad is carried out within 3-4 working days. During this time, doctors carry out all the necessary diagnostic measures, establish a diagnosis and determine a treatment regimen.
Diagnosis of brain hemangioma begins with a consultation with a neurologist or neurosurgeon. At the first meeting, the doctor carefully interviews the patient, examines him, conducts a neurological examination, studies medical documents, after which he refers the patient for examinations.
It is noteworthy that most foreign clinics offer unique services. This is when you can get advice from a qualified doctor without visiting a clinic. All you need is to send scanned copies of medical documents related to your diagnosis to the foreign clinic. Over the course of several days, a foreign specialist studies the documents, after which he contacts the patient via video link and announces his conclusion. The doctor may agree with this conclusion and treatment, adjust the diagnosis, refer to insufficient research, or completely refute the previously made diagnosis. In many foreign clinics, the patient can then count on a free first in-person consultation (if he decides to undergo treatment in this hospital).
Among the diagnostic measures carried out if a brain hemangioma is suspected, the following must be indicated:
- MRI of the brain
- allows you to identify a tumor, its shape and size. - CT scan
is performed using a contrast agent. The study makes it possible to clarify the location and size of the tumor, as well as assess its potential impact on nearby brain structures. - Other studies
(at the discretion of doctors).
After the examination, an expert group of doctors gathers to establish a diagnosis and determine treatment tactics for the disease.
Prognosis and prevention
For timely detection of cerebral hemangioma, it is necessary to regularly conduct examinations: angiography, magnetic resonance and computed tomography. When the disease is diagnosed early, doctors often remove the tumor without damaging the tissue, especially if the tumor is located on the surface of the brain. If a tumor is detected in deeper layers, more complex operations are required, which can lead to negative consequences.
The prognosis for cerebral hemangioma in adults is quite favorable. Since it is not a malignant tumor, in about a quarter of patients it does not affect a full lifestyle and does not manifest itself in any way. But complications are also possible that can cause serious damage to the patient. To avoid cerebral hemorrhages, you need to avoid any mechanical damage to the head, psychological stress, as well as sudden changes in blood pressure.
To prevent the appearance of a tumor, doctors recommend leading a healthy lifestyle: spending more time in the fresh air, playing sports and not abusing alcohol. If any symptoms of brain hemangioma are detected in children and adults, you should immediately contact an oncologist for further treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Neoplasms formed from blood vessels are dangerous because they show almost nothing about themselves. Usually the patient is informed that a hemangioma has been discovered in his brain only during a random examination. But there are still a number of general signs indicating the presence of pathological growth. These include:
- Attacks of cephalgia localized in one area of the head.
- Frequent increases in blood pressure.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Mental instability.
- Convulsive activity.
- Decreased memory, concentration, performance.
Hemangioma can be located in the brain in a variety of areas, but most often it is found in the cerebral hemispheres. In some cases, growth is detected in the cerebellum and spinal cord.