Vegetative-vascular dystonia is known for having many symptoms. Many people are interested in how VSD and vision are interconnected? Some sufferers begin to notice blurred vision or strange effects during attacks and panic attacks. Can a person really go blind if timely measures are not taken to treat vegetative dystonia? These questions concern everyone who is faced with a problem. And not without reason - after all, the visual organs play a vital role in our lives.
Let's consider how vision and VSD are interconnected, what symptoms there are, what to do, how to treat the eyes if deterioration is observed.
The main causes of visual impairment in VSD
Neurocircular dystonia (aka VSD) is a somatoform disorder associated with a violation of the nervous regulation of organs and tissues. The autonomic system regulates almost all life processes in our body - breathing, heartbeat, digestion, metabolism, and the like. In a healthy state, we do not notice the occurrence of all these processes in ourselves.
But under the influence of certain factors, the autonomic nervous system malfunctions, and the person begins to experience multiple symptoms.
This dysfunction may well affect the functioning of parts of the body responsible for vision: the retina, optic nerves, blood vessels located around the eyes, etc.
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, the tone of blood vessels changes and blood circulation is disrupted. As a result of dysfunction, visual acuity deteriorates. Pathology usually develops gradually. But there are cases when, during an attack (crisis of VSD), a person experiences severe visual impairment. In rare situations, temporary vision loss may occur.
Most often, people note blurred vision during VSD, distortion of objects, blurriness, and defocus.
Important!
Under the mask of VSD, other serious diseases may be hidden, especially those related to the endocrine system. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment! All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is not a reason for self-diagnosis or self-medication.
There is a completely logical explanation for this phenomenon. With VSD, muscle tone also decreases. The disorder can affect the functioning of the smooth muscles of the iris. In addition, the structure of the organs of vision contains muscles that regulate the degree of curvature of the lens, which refracts light. Deterioration in the nutrition of muscle tissue due to impaired blood circulation weakens them. There are hypotonicity and hypertonicity of muscles, which can be observed with dystonia. Both of these conditions contribute to distorted visual perception.
Therefore, if there is a tendency to VSD or its chronic course, it is necessary to identify the causes of the disease. Only after this can effective control methods be found that will help prevent blindness.
Vision problems occur sporadically, unexpectedly. Doctors explain the connection between vision and vegetative-vascular dystonia in different ways. Some say that the reason is a failure of the autonomic system; they are sure that this is directly related to the organ itself. Still others believe that the reason is poor blood circulation and surges in blood pressure. And they are all right in their own way. But not everyone sees the root cause. After all, VSD, changes in blood pressure, hypo- or hypertonicity of muscles and blood vessels are not a disease, but a consequence.
Causes of dark circles under the eyes due to VSD
Circles under the eyes With VSD also occur due to disruption of the blood vessels. Of course, except for those cases when they are caused by somatic diseases.
Deteriorated, disrupted functioning of blood vessels leads to insufficient nutrition of certain organs. The eyes and surrounding tissues are no exception.
It is the insufficient supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen through the blood that leads to the appearance of dark circles around the eyes and redness of the eyelids. Weakened vascular tone can cause increased fragility. This leads to bleeding in the eyes when under strain, such as reading for a long time or sitting at a computer monitor.
During the acute course of vegetative-vascular dystonia, spasms of small vessels can cause pain, pain in the eyes, visual disturbances, and headaches. The skin around the eyes becomes pale and bluish.
Loss and decrease in vision due to neurosis
For advertising purposes:
One of the main causes of neurosis is the short-term or long-term effect of a psychotraumatic factor. The influence of mental trauma can manifest itself both at the psychopathological level and at the neurosomatic level. One of the manifestations of such a disorder as neurosis is visual impairment, that is, a disorder of the sensitivity of the senses against the background of emotional stress.
Difference from optic neuritis
Optic neuritis is an inflammatory disease that results from otitis media or, for example, injury. And ocular neurosis occurs due to a stressful factor that a person cannot cope with.
A different clinical picture is characteristic of ocular neurosis. Symptoms and causes differ from optic neuritis.
How does ocular neurosis occur?
Psychogenic visual impairment involves a narrowing of the field of vision.
A characteristic feature of the disorder is that the patient complains that his vision has deteriorated, he does not see surrounding objects, but at the same time he retains spatial orientation.
With complete blindness, patients do not bump into sharp corners or objects. When such a person begins to be examined, the result is that his reaction to light is preserved.
Optic nerve neurosis disorder begins quickly, at one moment, and is always preceded by a conflict or traumatic situation. A person’s eyes express his inner desire “not to see the problem”, he is “disgusted to look at it” and more.
In most cases, amorosis and concentric narrowing of vision are characteristic of hysterical neurosis. In other forms of neurosis, asthenopia and photopsia may occur.
Neurosis and subsequent visual impairment most often develop acutely in women. Persons prone to neurotic disorders have a greater predisposition to psychogenic blindness. In most cases, optic nerve neurosis is not limited to; other neurological manifestations are added to the symptoms. This may include a lump in the throat or difficulty breathing.
The behavior of such patients is also interesting. Although neurosis is characterized by panic attacks, they do not have the severe anxiety that is inherent in people who suddenly lose the ability to see. Experts describe such patients as indifferent to the symptom; they tolerate vision loss quite tolerantly.
An ophthalmologist, when examining such patients, does not find any reason for the sudden loss of vision. The patient still has nystagmus, and all EEG and visual evoked potentials do not show any changes. Thus, sudden blindness indicates neurosis of the optic nerve.
Causes of neurotic visual impairment
Why does a person lose the ability to see when in a frustrating situation? The eyes look at everything that happens in the world. If reality is frightening and causes fear, then irresistible horror makes you want to close your eyelids and not see what is happening. That is, a traumatic situation makes one’s vision darken.
Although in modern practice, a disorder of the optic nerve due to a psychotraumatic situation is not so common, such cases do occur. Psychogenic disorder often occurs in children, especially if the child is in a chronic traumatic situation that will not end.
Case Study
Boy M., 10 years old, did not want to study music, but his parents forced him to attend piano lessons. In addition, the music teacher often scolded him for his poor results and lack of preparation for lessons. The boy was active and had difficulty sitting in one place.
The child's stress accumulated, the boy began to complain that he could not distinguish objects, and there was darkness in his eyes. The parents took the child to an ophthalmologist, but the examination showed no abnormalities. The doctor noticed that the boy sees letters well, but does not see symbols similar to musical notes at all.
After a conversation with a psychotherapist, it turned out that the child has a complex complex that does not allow him to listen to musical phrases. Music lessons caused severe trauma to the boy, as a result he developed neurosis, the main symptom of which was a psychogenic decrease in vision.
Who is susceptible to optic nerve neurosis?
Disorders of the senses, including vision, occur after severe stress. Neurosis always occurs after severe trauma, so poor vision is the desire not to see someone or something. For example, a person is subject to ridicule in a team, so decreased vision is an opportunity to save oneself from suffering and not come to a job that one does not like.
: neurotic optic nerve syndrome can also manifest itself in a person’s words. In conflict situations, people often say: “get out of my sight”, “so that my eyes don’t see you”, “it’s sickening to see you”, “it’s scary to look at everything” and others.
Factors provoking visual impairment in VSD
There are three main factors that cause physiological disorders in the visual organs. Above, we looked at why vision at the physical level deteriorates with VSD. Now let’s figure out what exactly provokes disruptions in the body and leads to dysfunction of all processes.
- Distorted perception of reality (brain disorders ). People suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia are prone to increased anxiety, fears, hypochondria, and obsessive thoughts. When a sufferer is constantly fixated on his mental “horror stories,” negative thoughts become entrenched at the subconscious level. The lesions that process them spread throughout the cerebral hemisphere and affect the visual center. As a result, there is a violation of the transformation of information received from the eyes. The brain simply cannot compare what you see in your fantasies and what is outside (in reality). The pictures are too different and the brain, coming into a kind of stupor, cuts off vision for a while, because in its opinion, your internal pictures are more real.
- Anxiety and panic attacks. The cause of visual impairment in VSD is constant tension caused by fears and stress. When a person is nervous, worried, worried and experiences severe attacks of fear, his whole body becomes stiff. Muscles tense, blood vessels constrict, blood circulation slows down. It’s not for nothing that there is an expression “the blood in your veins froze with fear.” This leads to the consequences described in the chapter above - insufficient tissue nutrition and disruption of metabolic processes in the organs of vision.
- Lack of nutrients. With VSD, the entire body suffers . Nutrients begin to be absorbed worse. In a stressful state, it is impossible to produce some valuable elements that our body supplies itself with on its own. The eyes begin to lack essential substances. This is also one of the causes of visual impairment in vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Interesting to know!
The simplest visual acuity test. Look at the sky at night and find the Big Dipper. And if in the handle of the ladle, near the middle star, you clearly see a small star, then your eyes have normal sharpness. This method of testing vision was adopted by the ancient Arabs.
Darkening in the eyes
This symptom in the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia can be easily explained. The fact is that this disease almost always leads to an increase or decrease in blood pressure. This condition causes dizziness or loss of consciousness in people diagnosed with this condition.
Quite often, darkening of the eyes precedes loss of consciousness. This condition is typical for people suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia. To cope with this problem, you need to consult a doctor. A specialist will be able to train you to identify such symptoms and deal with them in a timely manner.
What to do
If your vision has decreased, you should never panic. Such problems are not always associated with eye conditions.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia worsen in spring and autumn, as well as when the weather changes.
What is an attack of VSD and how you can get rid of it - read here.
Quite often in such a situation, the reason lies in the influence of other factors. If a diagnosis has already been made and a tendency to such attacks has been discovered, you need to remember that they do not appear out of the blue.
Despite the fact that the darkening in the eyes that accompanies vegetative-vascular dystonia does not cause pain, it can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life.
There are also hidden risks, the consequences of which may appear after a long time. The fact is that poor vision may indicate that an insufficient amount of nutrients is reaching the brain.
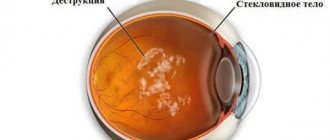
With VSD, both vision and other body functions are disrupted from time to time. Separately, it is necessary to mention the ripples, since this visual defect appears often and is usually preceded by a sharp loss of the ability to see anything around for some time.
It all starts with overwork or exacerbation of a chronic illness. First, a ripple appears; its intensity is not necessarily the same in both eyes. A person stops seeing small objects, and the text in front of him blurs into an illegible blur.
Then floaters appear in the eyes, ripples intensify, and flashes of light begin to appear. The surrounding space looks blurry and unreal, and even large objects lose their outline. Gradually the ripples turn into flickering, the space around becomes unrecognizable.
During such an attack, you cannot continue to do any work - neither at home nor outside its walls. It is dangerous to drive a car or operate a power tool. Medicines do not help, for your peace of mind the only thing you can do is take a validol tablet.
It is important to understand that this is normal with VSD. There is no need to go to the hospital, an MRI will not detect a tumor, and the ophthalmologist will not find any terrible eye diseases. The essence of the problem comes down to the fact that with vegetative dystonia and panic disorder, due to an increase in fear hormones in the blood, the blood vessels serving the visual organs suddenly narrow.
Each person has individual manifestations of VSD, and vision problems are included in the main list of symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia. If there were no such problems before, but now ripples in the eyes have been added to other symptoms, this may indicate a weakening of the body. You need to tell your doctor (psychiatrist or neurologist) about this; you may need to increase the dosage of medications or change the drug.
What to do
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia worsen in spring and autumn, as well as when the weather changes.
What is an attack of VSD and how you can get rid of it - read here.
Symptoms
VSD has one feature - its course has no specific signs and has extensive symptoms. Nervous system failure manifests itself differently in each person. This also applies to visual dysfunctions - there is no clear clinical picture here, everything is very individual.
The most common symptoms of vision problems that patients with VSD complain about:
- If a person suddenly changes body position, flashes of light and darkening may appear. Sometimes this is accompanied by loss of balance and noise in the temples.
- During panic attacks or severe nervous excitement, vision seems to float, blur, and become unclear.
- When the patient is very tired, spots appear in the eyes, especially if the person concentrates on an object for a long time and then suddenly changes the position of his gaze.
- The image may be distorted, the contours of objects change, and a person will perceive straight lines as broken.
- In some cases, painful sensations in the eyeballs may occur, especially with prolonged strain. Pain can be triggered by various factors, such as a flash of light, touching the eyes, or due to blinking.
- The sufferer sometimes blurs the background, the object on which the gaze is concentrated. A person sees clearly, but everything around this object becomes cloudy.
- It is sometimes difficult for the patient to focus on one object for a long time, gradually the gaze weakens and defocus occurs.
How consciousness influences the perception of the world
It could be conflicts in the family or difficult tasks at work, when vision shows the world around you as unattractive and even cloudy. At such moments, the turned on TV is not absorbed by the brain, the contours of the images are unclear, and the words on the screen do not reach consciousness.
The culprit is other thoughts that are spinning in the head and concentrating the brain on itself. For a healthy body, such occasional moments are considered normal. But in a person with dystonia, when the nervous system is unbalanced, the brain constantly focuses on internal troubles, having difficulty processing information from the outside.
Diagnostics
Visual impairment in VSD is not associated with organic diseases. But in any case, a person experiencing any symptoms needs to undergo a diagnostic examination.
The initial examination of the visual organs includes:
- consultation and examination by an ophthalmologist.
- Consultation with a neurologist;
- checking visual reflexes;
- computer vision diagnostics;
- blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound and MRI if there is a suspicion of compression of nerves and vessels in the spine or other disorders.
Interesting facts about vision:
- Fact 1
- Fact 2
- Fact 3
The eyes process about 36,000 pieces of information every hour.
The eyes use about 65 percent of the brain's resources. This is more than any other part of the body.
The wriggling particles that appear in your eyes are called floaters. These are shadows cast on the retina by tiny filaments of protein inside the eye.
What treatment is prescribed?
The patient must visit an ophthalmologist.
Visual impairment with VSD requires immediate medical attention. You should consult with a therapist and ophthalmologist and undergo the prescribed examination. Only after a diagnosis is made, comprehensive treatment is prescribed. If vision deterioration occurs due to hypo- or hypertension, medications are used to normalize blood pressure.
If a patient has a vegetative disorder, neurotropic and psychotropic drugs are prescribed. This allows you to quickly get rid of fear and anxiety. An ophthalmologist prescribes medications that normalize blood circulation in the organs of vision. The course of therapy is selected individually. Attempts at self-medication will lead to aggravation of the patient's condition.
How to treat visual impairment with VSD
For VSD with visual impairment, complex therapy is used. It is useless to treat just one thing. Moreover, any symptom of dystonia is only the result of a complex disorder that has a cause. And as you know, in 90% of cases the cause of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia is psychological problems or physical fatigue.
To eliminate vision problems with VSD, the following treatment methods are prescribed:
Drug therapy
To relieve symptoms and correct physical condition, the doctor may prescribe medications from the following groups:
- Tranquilizers to relieve anxiety.
- Sedatives, to suppress excitement of the nervous system.
- Nootropics – improve blood circulation, supply the brain with oxygen, and have a positive effect on cognitive functions.
- Vitamins to strengthen blood vessels, the nervous system and the body as a whole.
The dosage and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor. Self-administration of medications is prohibited. If the drug does not help, the doctor cancels it and replaces it with another.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatments provide more effective results, especially when combined with the other two.
These include:
- Massage.
- Manual therapy.
- Acupuncture.
- Hydrotherapy.
- Exercise therapy.
Any type of physical therapy should also be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the patient’s history and current condition.
Psychotherapy
Although psychotherapy is often put in last place or excluded altogether, it is the key in the treatment of VSD, visual impairment and imbalance of other organs. For successful recovery, the patient needs to balance his psycho-emotional background and learn to react differently to irritating factors.
There are often cases when internal problems, psychological trauma and conflicts become the cause of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia and anxiety disorder.
For example, a person is tired of working at a certain job and everything there irritates him terribly. But he is afraid of being left without income or condemnation from his loved ones. A serious conflict occurs inside, which the unfortunate person tries to suppress. Even if you manage to drown out the suffering for a while, it doesn’t go away. Internal tension negatively affects the nervous system, gradually depleting it. At some point, the body cannot stand it and a crisis of VSD occurs.
The problem is that often such causes of illness are unconscious or strongly suppressed. A person begins to treat symptoms without understanding the true cause. Recovery is slow or there is no improvement at all.
Psychotherapy allows you to identify such psychological problems and resolve them. This significantly speeds up recovery and often the patient manages to improve his health even without medication.
Online appointment with a doctor in any city in Russia
Treatment and prevention
Treatment of visual disorders associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia is carried out in conjunction with the elimination of other symptoms of VSD, as well as its causes.
In most cases, special treatment for floaters and other symptoms may not be necessary. Measures that are more preventative than therapeutic often help:
- Maintaining a daily routine;
- active lifestyle;
- transition to a balanced, balanced diet;
- strengthening the immune system;
- eliminating reasons for worries and worries (if possible);
- changing your attitude towards life;
- reducing time watching TV, working at the computer, reducing other eye strain;
- regular eye exercises;
- stopping drinking alcohol and smoking;
- spending a long time in the fresh air;
- eliminating any overload of the central nervous system.
The body begins to be saturated with oxygen, nutrients, rest and gradually recover. Because of this, the cells responsible for normal vision begin to work more harmoniously. The same applies to vascular cells, nerve cells, etc. If symptoms of eye disorders remain, you need to visit doctors - a therapist, an ophthalmologist, and undergo laboratory tests. It is possible that an examination of the fundus of the eye and the vessels feeding the tissues of the eyes will be carried out.
Based on the totality of complaints and examination results, doctors will give recommendations and prescribe the necessary treatment. Putting the first drops in your eyes just because they helped your neighbor is the worst decision you can make in this case. Remember: self-medication is strictly prohibited!
Optic neuritis
Diseases of the visual system can have serious consequences if you do not consult a doctor in time. One of these pathologies is optic neuritis. Which deprives the patient of the ability to clearly see distant objects, causes pain in the eye area and has other unpleasant symptoms.
Optic neuritis is an inflammatory disease that causes a decrease in visual function. The main symptoms are: pain in the eyes, a sharp decrease in vision, impaired color perception, and the appearance of white spots.
Due to the inflammatory process, the myelin sheath that covers the optic nerve is destroyed, and scar tissue begins to grow in its place.
This phenomenon is called demyelination and, if not treated promptly, can lead to irreversible blindness.
The disease most often affects people aged 20 to 50 years, but the pathology poses an equally serious danger to older people. Due to a weakened immune system, treatment in such patients is more difficult. Therapy includes a combination of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, decongestant, desensitizing and detoxifying agents.
In the international classification of diseases ICD-10
Optic neuritis is coded
H46
.
Causes of optic neuritis
One of the main reasons contributing to the development of optic neuritis is another disease - multiple sclerosis, during which the myelin that covers the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord is destroyed. Therefore, patients diagnosed with neuritis are at risk, because after some time they may develop multiple sclerosis.
Another disease, which is also autoimmune, can contribute to the development of the disease: neuromyelitis optica. The main symptoms include inflammation of the spinal cord and optic nerve.
The main difference from the first disease is that neuromyelitis optica does not affect brain cells. Some diseases that are also classified as autoimmune, such as sarcoidosis and lupus erythematosus, can trigger the development of neuritis.
Not only diseases, but also other factors that directly affect the optic nerve can provoke the development of neuritis.
These include:
- Radiation therapy. It is used in the treatment of a number of severe diseases and can cause the development of optic neuritis.
- A number of infectious diseases occurring in the membranes of the brain, different parts of the eyes or nasopharynx.
- Viral or bacterial diseases (syphilis, measles).
- Severe dental diseases (caries, periodontitis).
- Weakened body due to certain infections (HIV, AIDS, tuberculosis).
- Incorrect treatment of colds.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Blood diseases (gout).
- Previously suffered traumatic brain injuries.
- Taking drugs.
- Alcoholism.
Optic neuritis is classified depending on the cause of infection and the area affected.
From the point of view of the etiological factor, neuritis of an infectious, parainfectious, demyelinating, ischemic, toxic and autoimmune nature is distinguished:
- Parainfectious
- is the result of a viral disease or previous vaccination. - Demyelinating
– the cause of the development of pathology is the destruction of the membrane of neurons. - Ischemic
is the result of impaired blood circulation in the brain. - Toxic
- occurs due to damage to the optic nerve as a result of methyl alcohol poisoning. - Autoimmune
– occurs when the body’s autoimmune functions are disrupted.
If we classify the disease according to the area affected, then neuritis is of two types:
- Intrabulbar neuritis
affects the eye disc and is most often observed in children. The main symptoms are a decrease in field of view and an inability to see objects clearly. - Retrobulbar neuritis
is an inflammatory process that occurs outside the apple of the eye. It may begin due to untimely treatment.
The first signs of the disease may appear unexpectedly. All types of optic neuritis have different clinical symptoms.
The main features that are characteristic of all species include:
- inability to clearly see distant objects or those at a short distance;
- pain in the eye area;
- rapidly progressive vision loss;
- inability to distinguish colors;
- eye sensitivity to light;
- more limited visual field. Objects and areas located in the center or nearby may fall out.
Occasionally, the main symptoms may be accompanied by fever, general weakness and headache.
Symptoms of intrabulbar neuritis
With this type of pathology, clarity of vision gradually begins to be lost, which leads to blindness.
In cases of partial inflammation, vision remains at the same level, but a change in the optic disc is observed, the boundaries become blurred, the vessels dilate, and hemorrhage is possible.
This type of visual neurosis develops within 3-6 weeks, but the first symptoms appear after 2 weeks.
The main symptoms of intrabulbar neuritis:
- unstable color perception;
- blurred boundaries;
- inability to clearly see objects at night;
- development of myopia;
- the appearance of white spots in the visible area, most often in the center;
- hemorrhage in the area of the eye disc.
It has several subtypes (axial, peripheral). The main symptoms of the retrobulbar type appear on the 3rd day of the disease. The acute form is characterized by pain in the eye area and a sharp decrease in vision. Each species has its own characteristic features.
The axial type is characterized by:
- inability to clearly see objects in the distance;
- blindness;
- skomoty;
- painful sensations.
The peripheral variety is different:
- inability to see objects located to the side;
- painful sensations.
The transversal form combines all the symptoms listed earlier.
Diagnosis of optic neuritis
When diagnosing optic neuritis, your doctor will take into account certain factors. But in all cases, to confirm the disease, the patient is examined using an ophthalmoscope. The doctor also checks the patient's reaction to light.
In the future, based on the patient’s complaints, the following diagnostic methods may be prescribed:
- MRI of the brain;
- Ultrasound of the eye;
- blood analysis;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- testing the patient's ability to distinguish colors;
- visual acuity test.
In ordinary cases, diagnosing the disease is not particularly difficult. It is more difficult to diagnose neuritis, which occurs in a mild form without a sharp decrease in vision or the formation of edema. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish pseudoneuritis from a congestive disc.
The first disease is characterized by the preservation of the ability to see and the absence of any symptoms or visible changes. In the initial stages, congestive disc differs from neuritis in the preservation of vision and swelling of the optic disc. The occurrence of even small hemorrhages confirms the diagnosis of neuritis.
The most accurate diagnosis can be made using fluorescein angiography of the fundus. It also helps to distinguish neuritis from a congestive disc.
Treatment of optic neuritis
Treatment of optic neuritis takes place in a hospital setting. Until an accurate diagnosis has been established, therapy is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and infection, immunocorrection and improving metabolism.
After the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics that relieve inflammation. Their purpose is due to the fact that very often neuritis is caused by a bacterial infection.
- To prevent multiple sclerosis, corticosteroids are prescribed intravenously.
- Diuretics. Prescribed, if necessary, to reduce the pressure inside the skull.
- Glucocorticoid drugs - help relieve inflammation.
- Nootropics prevent the development of atrophy of nervous tissue, improving its nutrition.
- Medicines to improve blood circulation.
- Vitamins.
In cases where the patient has increased pressure in the optic nerve sheath, a surgical operation is performed - decompression of the optic nerve sheath. If neuritis is identified as a toxic retrobulbar variety, then antibiotics are stopped.
A separate treatment regimen for neuritis is prescribed for patients with multiple sclerosis and schizophrenia. In addition to general therapy, they are prescribed psychotropic drugs. After the end of treatment, there remains a high probability of relapse, so the patient is registered with an ophthalmologist.
Complications of optic neuritis
Inflammatory diseases of the nervous system can cause irreversible changes in the body. The severity directly depends on the duration of exposure of the disease to the tissue. With a long absence of normal blood circulation, degenerative changes may begin in the nerve fibers. Previous injuries or poisoning contribute to the complete destruction of the tissue.
Possible complications of optic neuritis include:
- Decreased visual acuity or complete loss. A rare but difficult to treat complication.
- Damaged nerves and tissues of the central and peripheral nervous system that cannot be restored. Due to the fact that the complication is irreversible, the negative consequences of the disease can remain for life.
- Tissue atrophy. A large number of scars increases the risk of possible complications.
Dangerous complications from neuritis do not occur often. For many patients, their vision is completely restored after some time. At the same time, in severe cases of the disease, the myelin sheath is destroyed, which is why irreversible consequences occur.