Migraine prevention is as important as its treatment.
Seizures significantly impair the quality of life, and with a hereditary tendency, it is easier to prevent them than to treat them.
There are a number of recommendations that will help, if not cure migraine completely, then at least improve the patient’s condition by reducing the frequency of manifestations of the disease.
The basis of migraine prevention
For effective prevention of migraine attacks, the main thing is mutual trust and joint work between the doctor and the patient.
To do this, the doctor requires a thorough interview and examination, and the patient needs to keep a “migraine diary”, where you need to scrupulously record all the circumstances, even minor ones, accompanying the attack:
Complete information about the individual characteristics of the disease is the key to successful selection of the most effective treatment methods.
- what preceded the headache: food, drinks, medications;
- meteorological conditions: which can provoke an attack, worsen or improve the condition;
- women make notes about menstruation, on what day of the cycle headaches occur, when associated symptoms appear: nausea, irritability, insomnia.
The main goals of migraine prevention are:
- Reduce the intensity, duration and frequency of attacks.
- Normalize the state of the autonomic nervous system in order to increase the body’s susceptibility to treatment of acute conditions.
- Help the patient adapt to life despite the presence of migraine attacks.
Symptoms of migraine with aura and atrial fibrillation
It should be noted that experts distinguish between atrial scotoma as an independent disease and visual impairment that accompanies classic migraine. In the second case, visual symptoms form the so-called migraine aura, after which the end of a migraine attack occurs directly with a severe headache. If atrial scotoma itself is often limited only to visual disturbances, then the aura of classic migraine can be accompanied by other symptoms - general weakness, dizziness, numbness of the limbs, hearing and smell impairment.
The onset of an attack of scintillating scotoma is characterized by the appearance of a large pinpoint spot in the central part of the visual field. Gradually it “grows” and can move. Lighting spots may appear in blind spots.
Some patients note the appearance of ghostly objects on the periphery of the visual field; in others, sparkling images with a certain periodicity are replaced by loss of visual areas. In some cases, a person may become temporarily blind in one or both eyes.
General symptoms characteristic of ocular migraine are as follows:
- the appearance of flickering spots, flashes and glare;
- blurry outlines of objects;
- blurred vision.
In some cases, other symptoms may also occur:
- headache of a pulsating nature, concentrated in one half of the head (this symptom characterizes migraine with aura);
- visual hallucinations;
- dysfunction of the pupil;
- nausea and vomiting;
- the appearance of strabismus;
- drooping upper eyelid.
The symptoms of ocular migraine go away on their own by the time the attack ends. If it is a migraine with a visual aura, then immediately after it the person begins a long attack of headache in one half of the head.
Types of preventative care for migraines
Correcting or eliminating migraine triggers may be an effective way to prevent attacks from occurring.
But most often, a beneficial effect is achieved by a combination of the right lifestyle and non-drug methods aimed at strengthening the health of the cardiovascular and nervous system.
To prevent migraine, they prefer to use non-drug therapy methods, and if it is insufficiently effective or unavailable, medications are prescribed.
Elimination of provoking factors
The most common causes of migraine attacks are sleep disturbances, consumption of caffeine-containing drinks, alcohol, improper eating habits, and poor and unhealthy diet. Therefore, to prevent migraine attacks, it is worth changing your lifestyle:
- minimize the dose of caffeine consumed in drinks, it is advisable to drink no more than two glasses of coffee, cola, strong tea per day;
- give up alcohol or reduce the amount of alcohol in your life to a minimum;
- establish regular nutrition, include healthy foods and vitamins in the diet;
- introduce regular physical activity into your daily routine;
- get a full night's sleep.
other methods
Anticonvulsants are used to prevent migraines. Valproic acid and Topimarate. Antiserotonin drugs help by constricting blood vessels, but have side effects: pain in the back, scarring around the lungs, chest pain and shortness of breath.
Antidepressants
Dox and Imipropine prevent headaches by altering norepinephrine and serotonin.
Side effects:
- increased heart rate;
- vision is blurred;
- problems with urination;
- the mouth is dry;
- problems with stool;
- a person gets fat;
- blood pressure drops.
Antidepressants are contraindicated in people with a tendency to seizures and an enlarged prostate gland. The pressure in the eyes increases.
The following medications are also used for migraines:
- analgesics and other tablets;
- triptans;
- vasoconstrictors and homeopathic;
- painkillers;
- folk remedies.
Antiepileptic substances
Benzonal and Vimpat have a sedative effect, inhibit activating neurons, and activate inhibitory nerve cells.
Contraindicated for pregnant women.
Butoloxin A includes butolinic toxin. Used in cosmetology. . Blocks nerve impulses, the effect is visible after 2 weeks.
Nutritional Supplements and Herbs
Saccharin is replaced by stevia - a sweet herb without side effects. Avoid artificial sweeteners. Lavender soothes irritated nerves. Tryptophan is added to food (there is a lot of it in turkey). Butterbur softens the intensity of the disease, reduces inflammation, and stabilizes blood flow to the brain.
More information about herbal remedies for migraines can be found here.
Non-drug preventive measures
Even the most well-known and advertised non-drug methods may be ineffective in a migraine patient.
A specialist will help you choose the most appropriate remedy or treatment complex, taking into account the individual manifestations of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and contraindications.
Established as a preventive treatment for migraine
- physiotherapy;
- reflexology;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- psychotherapy;
- methods of using biofeedback (exposure to contrasting temperatures, electrical impulses);
- behavioral therapy – training in auto-training, methods of managing emotions, ways to avoid conflicts and stress.
Beta blockers for migraines
Beta blockers are the first choice drugs for the preventive treatment of migraine. Among them, propranolol is the most widely used.
Propranolol (anaprilin, inderal, obzidan). Its advantages include: high efficiency for simple and classic migraine, good tolerability, minimal side effects, possibility of use for a number of concomitant diseases (arterial hypertension, thyrotoxicosis, angina pectoris).
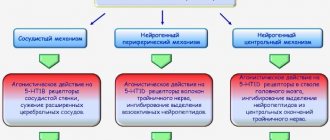
Its antimigraine effect is explained by its effect on pial vessels that have beta-adrenergic receptors. Propranolol prevents spasm of these vessels. It penetrates well through the blood-brain barrier, accumulates in brain tissue and, thus, can block central 5-HT3-serotonin receptors.
The drug also has a clear psychotropic (anxiolytic) effect, and is used to relieve somatic anxiety attacks.
It is contraindicated in chronic obstructive bronchitis, chronic nonspecific lung diseases, bronchial asthma, heart failure, heart block, sinus bradycardia.
Typically, treatment begins with a minimum dose of 40 mg/day in 2-4 divided doses with a gradual increase to 160-240 mg/day.
Many authors believe that propranolol is a relatively safe drug with minimal side effects, of which bradycardia and orthostatic hypotension are possible. The patient should be aware of the absence of increased heart rate during physical activity and refrain from heavy exercise.
The duration of prophylactic treatment with propranolol is 6-14 months. The drug should be discontinued gradually.
In addition to propranolol, you can use long-acting beta-blockers - atenolol at a dose of 100 mg/day, metoprolol - 200 mg/day.
Beta-blockers are especially indicated for the preventive treatment of patients with migraine with concomitant arterial hypertension, sympathoadrenal crises, panic attacks (vegetative migraine).
Medicines to prevent migraine
The first thing that comes to the mind of an ordinary person when thinking about how to prevent a migraine attack is to take a pill. But this approach will not provide a lasting effect.
The goal of drug prevention of migraine is to ensure the strengthening of the vascular and nervous system in the inter-attack period, which means that medications will have to be taken regularly and for quite a long time.
Migraine prevention with medications is carried out in the case of
- frequent - 2 times a week, or prolonged - more than two days of attacks;
- decreased performance and vitality between attacks;
- treatment of acute attacks is difficult, there are side effects and contraindications;
- when the effectiveness of acute pain relief is reduced or the patient is prone to abusing analgesics during this period;
- the patient’s personal desire to treat migraine prophylactically with medications;
- the presence of forms of migraine that can provoke the development of stroke: basilar, hemiplegic migraine, forms with an extended aura,
- previous migraine status or migraine stroke.
Shall we count?
A large-scale study conducted in Russia in 2012 found that among people under 65 years of age, 20% of the population suffers from migraines, that is, approximately 20 million people! Moreover, half of them experience pain more than 15 times a month.
Yes, people don’t die from migraines, but this disease significantly reduces people’s quality of life and places a heavy burden on the economy. Thus, according to the WHO rating, chronic headaches rank sixth in terms of the number of days of disability over a lifetime, far ahead of diseases such as diabetes, HIV and oncology. And it is for this reason that the Russian economy loses 22.8 billion euros annually.
Groups of drugs used in the prevention of migraine
- Beta blockers.
- Calcium antagonists.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antidepressants.
- Anticonvulsants.
Drug prophylaxis is usually initiated with a small dose of a single drug. If the effectiveness is insufficient, it is increased, changed, or combined with other drugs. Recommended to combine
- antidepressant and beta blocker (anticonvulsant, antiserotonin drug, calcium antagonist);
- calcium antagonist and antiserotonin drug.
Preventive medications are continued for up to six months, then they try to gradually stop them.
Diseases and conditions that accompany migraine make adjustments to treatment, as they have contraindications to the use of a number of drugs. Migraine is treated with
- pregnancy - not with medications; in case of urgent need, choose medications that are minimally toxic to the fetus;
- depression - tricyclic antidepressants, beta blockers are contraindicated;
- bronchial asthma, diabetes, mitral valve prolapse - without using beta blockers;
- epilepsy - anticonvulsants, excluding tricyclic antidepressants;
- arterial hypertension - calcium channel blockers, beta blockers;
- Raynaud's disease - calcium channel blockers, excluding beta blockers;
- kidney diseases - exclude NSAIDs, methysergide;
- ischemic stroke in the past - aspirin and NSAIDs.
To avoid deterioration of the general condition and complications, the use of any drug, even well-known ones, must be agreed with the attending physician.
Don't be patient!
Migraine, like any chronic disease, cannot be cured. But you can control it quite successfully. There are two approaches for this.
If migraine rarely bothers you, taking symptomatic medications is enough. Conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (like ibuprofen) or special migraine medications - triptans and ergotamine drugs - can help relieve an attack. Sometimes a combination of these is required. The doctor can also add antiemetic drugs to therapy - they not only relieve nausea, but also help the drugs to be absorbed faster and better, which means they act faster and more effectively. For treatment to give a good result, it is important:
- take the drug in the prescribed dose (in no case spontaneously decreasing or increasing it);
- take the medicine with plenty of water;
- start taking it as soon as possible, it is better from the first minutes of the attack, without waiting until the migraine is in full force.
Pain, I will eat you! What products have pain-relieving properties? Read more
Selected effective means of prevention
Vasobral
Combination drugs also show good effectiveness. For example, Vasobral helps well as a preventive measure for migraines.
This product contains ergot alkaloid and caffeine. The administration of this drug normalizes vascular tone by blocking alpha receptors in the smooth muscles of the artery walls.
Vasobral stimulates dopamine and serotonin receptors of the central nervous system, prevents blood thickening, improves tissue metabolic processes in the brain, and has a psychostimulating and analeptic effect.
Proroksan
Proroxan, which blocks alpha receptors during the transmission of nerve impulses, will help prevent attacks, thereby eliminating vascular spasm.
It also reduces the excitability of diencephalic formations of the brain and normalizes the tone of the sympathoadrenal system.
Botox
A relatively new way to prevent migraines is Botox injections. Research has proven that injection of this drug not only weakens the transmission of pain impulses, but also blocks the release of a number of substances by nerve endings that cause neurogenic inflammation.
These substances, when released into the external environment, cause stagnation of blood in the vessels of the meninges, which increases pain and other unpleasant sensations during migraines. Scientists testify that botulinum therapy significantly reduces the frequency of attacks in 72% of patients.
Botox is used for migraines in case of frequent attacks or in the chronic form of the disease. The specialist performing the medical manipulation must have the necessary certificate for his activities. For treatment, 10-20 injections are given in the forehead, eyebrows, temples, back of the head and nose and neck. Improvement occurs in the first month or two, and the effect lasts about three months.
Botox treatment has a number of advantages:
- the amount of medication taken for headaches is reduced,
- the effect of reducing attacks allows people living far from capital clinics to get rid of the need to visit a clinic for medical care for a long period,
- when planning pregnancy, early administration of botulinum toxin can solve the problem of finding analgesics that are safe for the fetus in the early stages,
- reviews from users of the drug record a pleasant side effect - the disappearance of facial wrinkles in the injection area.
Spigelon
Migraine pain can also be prevented using homeopathic remedies. The most famous is spigelon. During the interictal period, it is prescribed one tablet under the tongue for resorption three times a day.
Spigelon consists of components that have not only an analgesic effect. The drug calms, relieves spasms, helps with insomnia, irritability, depression and dizziness.
Spigelon is used not only for migraines, but also for any headache. If symptoms worsen, it is recommended to dissolve a tablet every 15 minutes, lasting no longer than two hours. Spigelon is contraindicated for children under three years of age, patients with lactose intolerance, or allergic reactions to the components of the drug.
Homeopathic medicines, and in particular, spigelon, at the beginning of treatment can worsen the patient’s general condition. After temporarily stopping taking the pills, once symptoms normalize, you can try resuming therapy. If the side effect reoccurs, your doctor should recommend a replacement.
Vessels have nothing to do with it
Migraine is mistakenly considered by many to be a disease of the blood vessels of the brain. In fact, the blood vessels have nothing to do with it, the problem is in the brain itself. This disease is genetic and hereditary, most often it is transmitted through the female line. However, the migraine gene, the search for which scientists have long been preoccupied with, has not yet been found. And the mechanism of the disease is not completely clear, although it is clear that the cause of painful spasms is the increased activity of the trigeminal nerve nucleus, which sends pain signals to the cerebral cortex.
To diagnose migraine, a neurologist does not need any research at all. If there is no suspicion of secondary headache, then the presence of criteria that are assessed during the examination and interview of the patient is sufficient. Migraine has a special clinical picture.
Question answer
Why do migraines mostly affect women?