Pharmacological properties of the drug Asentra
Antidepressant. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in brain neurons. The uptake of norepinephrine and dopamine by neurons is practically not affected. The drug has no affinity for serotonin, dopamine, histamine, benzodiazepine, GABA, M-cholinergic and adrenergic receptors. When sertraline is taken orally in doses of 50–200 mg once a day for 14 days, the maximum plasma concentration is achieved after 4.5–8.5 hours. The average half-life in young and elderly individuals is 22–36 hours. Binding with blood plasma proteins - 98%, volume of distribution - 20 l/kg. Intensively metabolized during the first passage through the liver. The main metabolite found in the blood plasma (N-desmethylsertraline) is pharmacologically inactive. The half-life of N-desmethylsertraline ranges from 62 to 104 hours. It is excreted primarily in the form of metabolites through the intestines and urine in approximately equal amounts; less than 0.2% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Asentra
Release form, composition and packaging
White film-coated tablets, round, with beveled edges and a notch on one side; on the fracture there is a white rough mass.
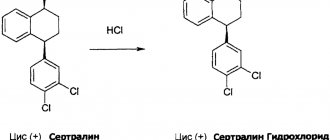
1 tab. sertraline hydrochloride 55.95 mg, which corresponds to the content of sertraline 50 mg.
Excipients: magnesium stearate, hydroxypropylcellulose, sodium starch glycolate, calcium dihydrogen phosphate, microcrystalline cellulose, talc. Shell composition: Opadry 03H28758 (hypromellose, titanium dioxide, talc, propylene glycol).
White film-coated tablets, round, with beveled edges and a notch on one side; on the fracture there is a white rough mass.
1 tab. sertraline hydrochloride 111.9 mg, which corresponds to the content of sertraline 100 mg.
Excipients: magnesium stearate, hydroxypropylcellulose, sodium starch glycolate, calcium dihydrogen phosphate, microcrystalline cellulose, talc. Shell composition: Opadry 03H28758 (hypromellose, titanium dioxide, talc, propylene glycol).
Clinical and pharmacological group: Antidepressant.
pharmachologic effect
Antidepressant. A specific inhibitor of serotonin (5-HT) reuptake in neurons. The metabolism of norepinephrine and dopamine is slightly affected. At therapeutic doses, sertraline blocks the uptake of serotonin into human platelets.
The drug does not have a stimulating, sedative or anticholinergic effect. It has no affinity for serotonin, dopamine, histamine, benzodiazepine, GABA, cholinergic and adrenergic receptors. The antidepressant effect is observed by the end of the second week of regular use of Asentra, while the maximum effect is achieved only after 6 weeks. Unlike tricyclic antidepressants, Asentra does not cause weight gain; in a number of cases its decrease was noted. The drug does not cause mental or physical drug dependence.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After taking the drug orally, sertraline is slowly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, Cmax in blood plasma is reached after 4.5-8.4 hours.
Distribution
Css is established within a week when taken once a day daily. The binding of sertraline to plasma proteins is 98%. Vd >20 l/kg. Sertraline is excreted in breast milk. There is no data on its ability to penetrate the placental barrier.
Metabolism and excretion
Sertraline undergoes intensive biotransformation during the “first pass” through the liver by N-demethylation. The main metabolite, N-desmethylsertraline, is less active compared to the parent compound. Metabolites are excreted in urine and feces in equivalent quantities. About 0.2% of sertraline is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. T1/2 of the drug is 22-36 hours and does not depend on the age or gender of patients. For N-desmethylsertraline T1/2 - 62-104 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
T1/2 and AUC in blood plasma increase with impaired liver function. The pharmacokinetic parameters of sertraline in patients with both mild and moderate renal impairment (CR 20-50 ml/min) and severe renal impairment (CR <20 ml/min) do not change with its continuous use. Sertraline is not eliminated by dialysis.
Indications
- treatment and prevention of depression of various etiologies;
- treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD);
- treatment of panic disorders;
- post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Dosage regimen
For depression and OCD in adults, the average initial dose is 50 mg 1 time / day, in the morning or evening. The daily dose can be gradually increased, no earlier than after a week, from 50 mg to a maximum daily dose of 200 mg.
For panic disorders and PTSD, the initial dose of Asentra is 25 mg 1 time / day, in the morning or evening. After a week, you can increase the dose to 50 mg 1 time / day, and then gradually, no earlier than a week later, increase to a maximum daily dose of 200 mg. The initial dose of Asentra for children aged 6 to 12 years is 25 mg sertraline 1 time / day, in the morning or evening. After a week, you can increase the dose to 50 mg 1 time / day.
For children aged 12 to 17 years, the initial dose is 50 mg 1 time / day in the morning or evening.
If necessary, the daily dose can be gradually, no earlier than after a week, increased from 50 mg to a maximum daily dose of 200 mg. To avoid an overdose, the lower body weight of children compared to adults should be taken into account, and when increasing the dose to more than 50 mg/day, careful monitoring of this category of patients is necessary: at the first signs of an overdose, the drug should be discontinued. A satisfactory therapeutic result is usually achieved within 7 days from the start of treatment. However, to achieve the full therapeutic effect, regular use of the drug is required for 2-4 weeks.
In patients with OCD, it may take 8-12 weeks to achieve good results. The minimum dose that provides a therapeutic effect is subsequently maintained as a maintenance dose. In elderly patients there is no need for special dose selection.
In case of liver dysfunction, the drug should be prescribed with caution.
In case of severe liver dysfunction, the dose of the drug should be reduced or the intervals between doses increased. In patients with impaired renal function, no special adjustment of the dosage regimen is required.
Side effect
- From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: dry mouth, increased sweating, drowsiness, headache, dizziness, tremor, anxiety, agitation, hypomania, mania, insomnia, decreased appetite (rarely increased), up to anorexia, weakness, restlessness .
- From the digestive system: flatulence, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain; rarely (0.8%) with long-term use - an asymptomatic increase in transaminase activity in the blood serum (normalized when the drug is discontinued).
Other: visual disturbances, redness of the skin, ejaculation disorders, decreased libido, weight loss.
- From laboratory parameters: reversible hyponatremia (more often in elderly people, as well as when taking diuretics or a number of other drugs) associated with the syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion. When using the drug in isolated cases, extrapyramidal disorders, dyskinesia, tremor, convulsions, menstrual irregularities, hyperprolactinemia, galactorrhea, and skin rash were noted; occasionally - erythema multiforme. Motor disorders were more often observed in patients with indications of their presence in the anamnesis or with concomitant use of antipsychotic drugs.
When you stop using the drug, withdrawal syndrome rarely occurs. Paresthesia, hypoesthesia, symptoms of depression, hallucinations, aggressive reactions, psychomotor agitation, anxiety or symptoms of psychosis are possible. These manifestations are difficult to differentiate from the symptoms of the underlying disease, and they can occur when using other antidepressants.
Contraindications
- simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors and within 14 days after their discontinuation;
- simultaneous use of tryptophan or fenfluramine;
- unstable epilepsy;
- children under 6 years of age;
- pregnancy;
- lactation (breastfeeding);
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The drug is prescribed with caution for neurological disorders (including mental retardation), manic states, epilepsy, liver and/or renal failure, weight loss, and children over 6 years of age.
Pregnancy and lactation
Adequate and strictly controlled clinical studies on the safety of sertraline during pregnancy have not been conducted. Prescribing the drug is possible only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Women of childbearing age should be advised to use effective contraception during the period of use of the drug. Sertraline is found in breast milk.
If it is necessary to prescribe the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped due to the lack of reliable data on the safety of sertraline use during this period.
Use for liver dysfunction
In case of liver dysfunction, the drug should be prescribed with caution. In case of severe liver dysfunction, the dose of the drug should be reduced or the intervals between doses increased.
Use for renal impairment
In patients with impaired renal function, no special adjustment of the dosage regimen is required.
special instructions
According to clinical studies, the drug sertraline is effective and safe in the treatment of depression in patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction and in patients with unstable angina. Placebo-controlled studies have shown the effectiveness and safety of sertraline in patients with diabetes mellitus. Sertraline is not prescribed together with MAO inhibitors, or within 14 days after stopping treatment with MAO inhibitors; After discontinuation of sertraline, MAO inhibitors are not prescribed for 14 days.
Patients with depression are at risk for suicide attempts. This danger persists until remission develops. Therefore, from the start of treatment until the optimal clinical effect is achieved, constant medical monitoring of the patient should be established.
Currently, there is insufficient experience with the use of sertraline in patients undergoing electroconvulsive therapy. The possible success or risk of this combination treatment has not been studied.
Use of Asentra
Orally 1 time per day in the morning or evening. Depression The usual starting dose is 50 mg sertraline once daily. If necessary, the daily dose can be gradually increased by 50 mg (at intervals of at least 1 week) to a maximum daily dose of 200 mg. Obsessive states The initial dose is 50 mg of sertraline per day. If necessary, the daily dose can be gradually increased by 50 mg (at intervals of at least 1 week) to a maximum daily dose of 200 mg. Children aged 6 to 12 years are prescribed an initial dose of 25 mg 1 time per day. After a week, the dose can be increased to 50 mg of sertraline once a day. Doses in children over 12 years of age are similar to those in adults. Panic states The initial dose is 50 mg of sertraline per day. If necessary, the daily dose can be gradually increased by 50 mg (at intervals of at least 1 week) to a maximum daily dose of 200 mg. It is advisable to take the drug daily, at the same time, with or without food, with water. Tablets should not be crushed or chewed.
Cases of overdose and actions for it
Signs of overdose can trigger the development of serotonin syndrome, which includes:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- increased drowsiness;
- signs of damage to the conduction system;
- psychomotor stimulation;
- profuse diarrhea;
- clonic convulsive contraction of the upper and lower extremities.
Emergency measures to provide medical care:
- restoration of patency of the upper respiratory tract;
- checking heart rate and rhythm followed by monitoring;
- gastric lavage, then enterosorbents are taken.
To date, no specific antidote has been developed for an overdose of antidepressants.
Special instructions for the use of Asentra
If hypersensitivity reactions or severe sleep disturbances occur, stop taking the drug. Patients with depression are at risk (suicidal behavior), therefore, from the start of treatment until clinical effect is achieved, they should be under constant medical supervision. Sertraline is prescribed to patients with impaired liver function with caution. It is possible to reduce the dose or increase the interval between its increases. Sertraline is not recommended for patients with severe liver dysfunction. The safety of the drug during pregnancy and lactation has not been established. Asentra may affect the patient's psychophysical abilities, so the patient's condition must be carefully assessed before allowing the patient to drive or operate potentially dangerous machinery.