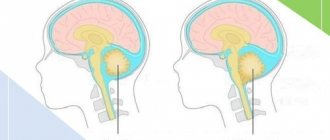
Cysts of the choroid plexus of the brain in the fetus are detected in less than 1% of cases. The possibility of their detection usually occurs between the 16th and 20th week of intrauterine development. As a rule, most of these tumors regress on their own in the third trimester of pregnancy (closer to 28 weeks).
A choroid plexus cyst can be identified during fetal development and usually disappears by the time of birth.
Characteristics
The formation is an isolated cavity filled with clear liquid.
Structure Features:
- They are small in size and tend to dissolve on their own.
- More often they are localized closer to the caudal part of the choroidal glomus.
- It has clear, even contours.
- Does not show any upward trend.
- The presence of signs of malignancy is not typical. Due to the location, it should be differentiated from choroid carcinoma and choroid papilloma.
- There are no clinically significant symptoms. The exception is the development of occlusive hydrocephalus (disruption of the normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and its accumulation in the head). It is extremely rare.
- It is regarded as a stigma of dysembryogenesis (developmental defect). These newborns are at high risk of having chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy 18 - Edwards syndrome).
- The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. Discovered as an incidental finding during screening.
- The pathology does not have serious consequences and does not affect the life and health of the child, therefore it does not require treatment.
- The prognosis is favorable.
Signs of a cyst
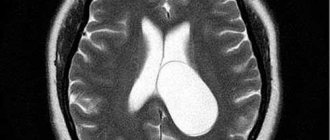
Education may not manifest itself for a long time. It can be detected for the first time 3 months after conception during an ultrasound procedure. Plexus cysts appear on an echogram as contrasting spots with liquid filling. They are small - they may not even reach a millimeter in size.
The following non-specific signs may indicate the presence of a formation:
- Developmental delay. The child may be growing too slowly, gaining weight, not focusing his vision, etc. Only a pediatrician can note developmental disorders.
- Deformed skull. The anatomical regions are subject to the greatest deformation. Weak violations of the form do not indicate the presence of a violation: you need to pay attention to pronounced deviations.
- Frequent, causeless crying of the child, sleep disturbances, anxiety.
It is quite difficult to detect a deviation by external signs, because the baby cannot report the pain he is experiencing. The diagnostic process is also complicated by the fact that the symptoms of the cyst are similar to the manifestations of many other diseases, from head injuries to poisoning and viral diseases.
Origin
The choroid plexuses are derivatives of the pia mater, which are localized in the ventricles of the brain. During embryogenesis at week 4, 3 brain vesicles are formed from the neural tube:
- front;
- average;
- diamond-shaped with internal cavities.
The walls of their cavities are lined with a layer of ependymal cells, and the blisters themselves are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (the contents of the future cyst). Blood vessels grow through the cells of the ependyma (the future pia mater) and ensure its protrusion into the cavity of the brain vesicles, where folds of cells form. The choroid plexuses are formed in the following order:
- 4-5 weeks – network in the fourth ventricle;
- 6-7 weeks – network in the third ventricle;
- Weeks 7-9 – lateral ventricles.
Thus, based on the characteristics of the formation of choroid plexus cysts, we can conclude that they do not belong to typical cystic formations (they are regarded as a congenital malformation).
What's happened
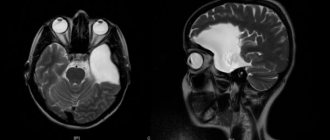
A cyst is a benign neoplasm. Its cavity is filled with a specific liquid (cerebrospinal fluid). Has clear boundaries. The walls are lined with glial, arachnoid or epithelial tissue.
In most cases, the tumor does not have a negative effect on the brain and is not dangerous to the health and life of the baby.
When the cystic sac grows rapidly, resulting in pressure on nearby tissues, cerebral circulation and the functioning of nerve cells are disrupted.
On this topic
- central nervous system
How does a headache with a brain tumor hurt?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2021
The location of the cystic tumor most often becomes the lumen of the choroid plexuses.
During the period 14-22 weeks of pregnancy, the formation of a cyst is normal, since by the time of birth it usually completely resolves.
Causes
The exact reason for the development of a cyst in the prenatal state has not been established, but this is not required, given its harmlessness and ability to disappear after a short period of time.
Conditional factors include:
- Genetic mutations (trisomy 18, trisomy 21). In this case, the cyst is only one of the symptoms of the underlying disease. It is important to understand that it is not the cyst that causes the mutation, but the mutation that causes the formation of pathologies (for example, due to divergence or underdevelopment of the skull bones). These pathologies are identified using karyotyping.
- Intrauterine infections . Of particular importance are the herpes virus and cytomegalovirus. In this case, there is a risk that an ultrasound examination will reveal a cystic formation formed directly in the brain tissue (a choroid plexus cyst is formed only at the stage of formation of the brain vesicles, long before the appearance of clearly differentiated organ tissue, but it is not possible to distinguish between these two types in utero). In this case, the cysts will often be multiple and will be located in the frontal and temporal lobes. The pathogenesis is based on necrosis of nervous tissue. To clarify the nature of the neoplasms, PCR of the baby’s blood after birth (DNA/RNA of the virus) is required.
- Traumatic injuries . They can occur either during fetal development or during childbirth. It is necessary to understand that during screening ultrasounds it is not always possible to view all tissues and structures of the fetus (due to its small diameter, the choroid plexus cyst is not always visible). If a cystic cavity is detected in a child during the neonatal period (usually they do not persist until this time, but there are exceptions), it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with hematomas and other formations.
- As a consequence of ischemic stroke . It occurs extremely rarely and usually against the background of severe oxygen starvation (partial placental abruption, concomitant maternal diseases).
- As a consequence of hemorrhagic stroke (ruptured aneurysm). It is extremely rare.
Only general factors that can presumably cause cystic neoplasms are given.
Prevention
Normal intrauterine development in most cases depends on the lifestyle of the pregnant woman. She needs to avoid many negative factors. They can affect the development of the unborn baby's brain. Smoking and drinking strong alcoholic beverages pose a great danger. These habits cause persistent hypoxia due to insufficient oxygen supply.
Already at an early stage it is necessary to register with a gynecologist and undergo examination by specialized specialists. You need to take care and avoid hypothermia, which can lead to viral infections. If the factors cannot be avoided, careful adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician will be required.
Consequences
Choroid plexus cysts do not have any health consequences. Below are the expected complications of any cystic formation (suppuration, rupture):
- prolonged hypertension in newborns;
- focal symptoms due to compression of brain structures (visual impairment, hearing impairment, sensory or motor disorders);
- partial epileptic seizures.
One of the most dangerous, but extremely rare complications is hydrocephalus. It occurs due to blockage of the cerebral aqueduct by a cystic formation. In this case, shunt surgery and a course of medications to normalize brain function in the postoperative period are indicated. Signs of pathology:
- divergence of the skull bones due to increased intracranial pressure;
- bulging and pulsating fontanelles;
- retardation in mental and physical development due to prolonged ischemia of the cerebral cortex.
Choroid plexus cysts are far from the first and extremely atypical form of formation that leads to the formation of hydrocephalus (there is no clear evidence base).
Therapy for plexus cysts
Treatment is carried out conservatively, that is, without surgical removal of the cyst. The formation may resolve on its own. If this does not happen, medications are prescribed to improve blood circulation.
The most popular children's medicine is Cavinton. It stabilizes blood flow and eliminates formations that may disrupt it.
For preventive purposes, a specialist may prescribe regular testing. Neurosonography or MRI is usually prescribed once a season. Examinations are carried out until the formation disappears.
Surgery is resorted to only in cases where the formation grows too large in size or degenerates. However, there are very few such incidents in medical practice. With constant monitoring by doctors and the use of absorbable medications, the risk of degeneration is very small.
Diagnostics
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Routine ultrasound in the second trimester. It should be noted right away that if a cyst is detected, the uzologist may not tell the expectant mother anything. The diagnosis is considered legitimate only if a cyst is present after 30 weeks. In this case, the diagnosis is included in the chart and after birth the child is indicated for neurosonography (repeated at 3 months, 6 months and a year). If the cyst enlarges or changes in its shape, more complex diagnostic measures are required (differential diagnosis with similar diseases and, if necessary, correction of the diagnosis).
- MRI/CT. Used in cases of questionable diagnosis (signs appear that are atypical for simple choroid plexus cysts).
- Laboratory tests are not carried out (with the exception of PCR), since they are not informative.
Diagnosis of pregnant women is based on critical or sensitive periods of fetal development (the greatest sensitivity to external influences and the greatest risk of developing pathologies, including cystic formations):
| Embryogenesis period | Time | Peculiarities |
| Preimplantation or tubal period | First week of pregnancy | Development of ectopic pregnancy, disruption of division processes and the occurrence of mutations (abnormal mitosis processes) |
| Second period | From 3 to 8 weeks | The initial period of organogenesis, when tissue formation occurs (the formation of the placenta takes 3 months, but begins in this period). It is during this period that the rudiments of the cerebral cortex (bone marrow hematopoiesis) are formed. Beginning of cystic cavity formation |
| Third stage | From 20-24 weeks | This period is associated with the formation of all systems and structures of the body from tissue rudiments (cell differentiation). Approximate time to detect a cystic cavity by ultrasound |
The periods are allocated conditionally, since it is problematic to identify the exact time of formation.
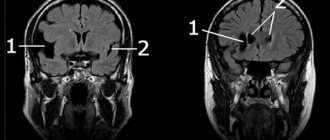
Screening ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy can detect a choroid plexus cyst in the fetus
Providing medical care
As a rule, a vascular cyst does not require any treatment, because The body can deal with it independently and effectively. Even if the size of education remains the same, the child's development will not slow down in any way.
The increased volume and accelerated growth still force doctors to prescribe a course of corrective medications that can speed up the resorption of such a cyst.
Such a specialist is a neurologist. Drug therapy for cysts consists of taking drugs that eliminate liquorodynamic disturbances, help reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid, and improve blood circulation in the brain.
Treatment begins with taking:
- Cinnarizine is a drug that has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system and helps stabilize and even destroy unwanted growths, including cysts;
- Cavintona - prescribed for impaired blood circulation in the brain.
Article on the topic: Aseptic necrosis of the head of the hip joint
The above drugs are well tolerated and do not cause unwanted effects or reactions in the body. But you can start taking medications only after consulting a professional.
There is no methodological treatment for such formations. Doctors recommend repeating the ultrasound examination every 3 months, observing the dynamics of the reduction of the vascular cyst, until it disappears.
If a subependymal cyst is detected, it is necessary to conduct MRI or MR diagnostics 2-3 times a year. The process of formation of cysts of this kind is considered favorable. However, with complications, an increase in pressure in the enlarged cystic cavity is possible.
An arachnoid cyst requires special attention - radical measures. She will no longer be able to disappear on her own. The child will be under constant supervision of a neurologist. If surgical intervention is indicated, it will be performed by shunt surgery, endoscopy or microneurosurgery.
Treatment
Not required in 95-98% of cases. Only monitoring of the child's condition is indicated.
If clinical manifestations occur, medications may be prescribed:
- Antiviral agents – for laboratory-confirmed herpes virus (Acyclovir).
- Drugs that reduce intracranial pressure (diuretics) – if signs of hydrocephalus occur (Spironolactone).
- Anticonvulsants - they are prescribed not only when an epileptic focus has formed in the brain, but also when there is pronounced activity of the neural network (pre-epileptic state).
- Weak sedatives – for increased excitability (Glycine).
- Antioxidant complexes and nootropics - to restore metabolic processes in the brain and normalize blood circulation.
All these groups of drugs are used only to eliminate symptoms.
Symptoms
In most cases, existing cystic cavities that have not resolved on their own do not manifest themselves for a long time.
The only manifestation of damage to brain structures is possible with the later formation of a neoplasm, as well as if the formation of a cyst was provoked by an infectious disease or injury.
As the size increases, compression of the brain tissue occurs. There is also a high production of cerebrospinal fluid. All this leads to increased intracranial pressure, which is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of hydrocephalus.
On this topic
- central nervous system
Everything you need to know about pituitary adenoma
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2021
The process of formation of cystic tumors is characterized by:
- nausea;
- frequent regurgitation;
- vomiting;
- hypotonicity or hypertonicity of the lower and upper extremities;
- squint;
- motor dysfunction;
- convulsions.
In addition, the child experiences severe headaches and increased tearfulness. The newborn begins to sleep poorly, becomes capricious and apathetic.