Euphoria is a joyful, elevated mood that gives the individual a feeling of well-being and contentment, which often does not correspond to objective circumstances. In people in a state of euphoria, an optimistic assessment of the entire surrounding reality predominates, and the opposite state - affect - is inaccessible to them.
Euphoria is combined with an accelerated flow of thoughts, marked by imaginative fantasizing, unproductive but active activity, slowness of mental processes, disinhibition of drives, lethargy, passivity, and lack of motivation.
Elevated mood can occur under the influence of small doses of alcohol, morphine, other psychostimulants and drugs. Oxygen starvation (altitude sickness) and severe somatic diseases can also provoke this feeling. This unhealthy condition can be a manifestation of organic brain damage (progressive paralysis) and can be combined with signs of dementia (oligophrenia).
Causes of euphoria
Medicine considers this condition as an unhealthy manifestation that occurs after toxic brain damage, drug intoxication, etc. A person can get into this state after psychological or physical trauma, but not for long.
Euphoria is a symptom of various mental illnesses and is pronounced in affective disorder and manic syndrome.
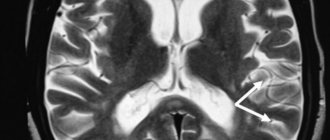
Causes of euphoria: damage to the frontal lobes of the brain (trauma, mental retardation, oxygen deficiency, severe intoxication); mental illness (hyperthymic psychopathy, manic-depressive psychosis); use of psychoactive substances (psychedelics, drugs, alcohol, sleeping pills); terminal conditions (the final stage of tuberculosis - agony or recovery after severe illness).
Euphoria, what does it mean?
Euphoria is a state of a person when he feels most happy, joyful and satisfied (the opposite of apathy). Seeing him in an unreasonably elevated and elevated (inspired) mood, one can diagnose euphoria.
Psychology explains the reasons for the formation of euphoria as follows:
- Use of potent psychotropic substances, strong alcoholic beverages, prohibited substances;
- Special breathing that helps change brain function (think oxygen masks on an airplane);
- With prolonged physical activity, endorphins are released;
- Falling in love, inspiration for the creative process, amusement of consciousness from the successful completion of a task due to pragmatism;
- Various mental illnesses.
Almost all healthy people know what euphoria is. The most common moments when a person is in such an elated mood is the feeling of falling in love for the first time. Let's look at an example.
The girl refuses to date you for a long period of time. You don’t back down, you try in every possible way to win her heart. After a couple of moments, she understands the seriousness of your relationship and begins to communicate with you. In this case, the young man has a feeling of satisfaction, because he was able to get the girl. This state is the most pleasant. The body at this moment is completely relaxed and you don’t think about anything. This is what euphoria is, the meaning of which can be seen in winning situations.
Symptoms
Being a strong emotional state, euphoria manifests itself in the form of positive emotions and is always marked by complacency, elevated mood, a state of bliss, delight, and happiness. A distinctive feature from hyperthymia is low motor activity, inhibition, slowing down of intellectual processes and a complete absence of problems.
In this emotional state, everything around you is seen through rose-colored glasses and there is impenetrable optimism, and tragic life moments are perceived with extreme joy. The feeling of euphoria is marked by altered consciousness, accompanied by a decrease or significant increase in reflex, motor, and mental processes.
This state gives a feeling of supreme happiness, complete satisfaction, which cannot be constantly achieved in natural conditions, since there are always irritants. This state is characterized by a joyful mood; a person in euphoria is absolutely satisfied with everything, serene and calm. Euphoria of happiness manifests itself in a feeling of all-consuming delight and joy.
What it is
“ Euphoria ” literally translated from Greek means “bringing good.”
Common people and medical experts understand this term differently. The first believe that bright positive emotions, sudden all-consuming happiness, delight, the height of bliss are a normal reaction that occurs at certain moments in life for all people, for example, during the period of falling in love.
However, for doctors, such manifestations may indicate the presence of pathology, especially with the sudden onset of high mood for no apparent reason.
Why are experts wary of euphoria? A state in which an absolutely happy person loses self-control and the ability to adequately perceive the people around them and reality is often a sign of an incipient mental illness or is the result of exposure to psychostimulants.
What the word “euphoria” means in clinical psychiatry may seem surprising to the untrained. This designates a form of painfully elevated mood, which is characterized by complacency, serenity and quiet joy without increasing the motor and intellectual activity of a person.
Similar symptoms appear in many mental disorders, in particular those of a manic nature. Prolonged forms of pathological inspiration can not only bring joy to a person, but also cause harm to the body due to severe emotional exhaustion.
Some people confuse the meaning of the words
euphoria and ecstasy . The latter also means the highest degree of delight, however, in a brighter and short-term version. We can say that euphoria is, in psychology, a long and protracted ecstasy or a series of them.
Musical euphoria
This state is achieved when a musical composition is based on a pleasant rhythm and also has repetition of small sections of melodies. With musical euphoria, listeners fall into a trance state and demonstrate a joyful, as well as pathologically complacent mood. Examples include the Beatles. The guys from the Beatles are not only talented musicians who were able to find the key to the hearts of millions of listeners, but also a successful experiment by sociologists in changing consciousness, which has no analogues in history.
Science believes that everything in the world is a number, a sign and a measure. Material bodies are subject to the laws of resonance and vibration. These resonances and vibrations can be harmonic as well as destructive. It follows from this that the popularity of the Beatles was artificially created by American and English sociologists.
Euphoria tendency test.
1. Do you care what they say and think about you?
2. Are you able to motivate people to take action?
3. Do you often feel “mad” energy within yourself that you want to throw out into something positive?
4. Do alcoholic drinks have a relaxing effect on you?
5. Do you often get told that you strive to stand out from the crowd?
6. Is the company of your friends able to provoke a break from everyday life?
7. Do you often come up with ideas rather than look for “stencils”?
8. How often do you say “I don’t care about this, I don’t care about that!” or similar?
9. Do you often demonstrate your intelligence if you understand that people like you?
10. Have you observed your talent as an actor?
11. Did your friends admire you to the point of: applause, uncontrollable laughter, etc.?
12. Do you often find yourself in such a good mood that you forget about all your problems?
If you have any questions, you can write them in the comments. We wish you all the best!
Subscribe to receive new published articles on the site directly to your email. We guarantee no spam!
Euphoria and depression
A depressive reaction, being the main cause, leads a person to seek help from a therapist and is the main complaint. The depressive reaction itself is part of a cycle, drawing the curve either down or up. In many cases, the depressive reaction is preceded by euphoria, and its collapse plunges the individual into depression. If we want to understand the depressive reaction, then we must understand the phenomenon of euphoria.
The signs of euphoria are easily recognizable. An individual in a euphoric state is hyperactive, speaks quickly, and is full of various ideas. Personal self-esteem is conspicuous, and the development of this condition leads to the development of mania.
Euphoria is only a lesser degree of depressive reaction. The ego of an individual who is in euphoria is so overexcited, as if it is taking part in a miraculous, unusual event that will fulfill secret dreams. This reaction is comparable to the reaction of a child who has been separated from his mother and now awaits her return with incredible excitement. For a baby, the return of his mother and her love is his most cherished desire. Mother's love embodies the fulfillment of all the needs of the child. The return of the mother gives a motivational energy surge that ends in euphoria.
Often, a person in a euphoric state is unable to realize the dynamics of his reaction, and also unconsciously perceives people as motherly figures who should care for, love and even feed him. People will initially be interested in him, but as it grows, his condition will begin to irritate people, and they will recoil from him.
There is no guarantee that people will satisfy his unconscious hopes, so over time the person will feel rejected. Self-confidence and self-esteem that accompany euphoria dissolve, and depression sets in, and with it the collapse of illusions.
The energy charge that overstimulates the peripheral structures of the body recedes, and the omnipotent ego turns into powerless. The lack of volitional efforts of an individual oppressed by depression leads to the fact that the person is unable to mobilize himself.
People suffering from depressive conditions have not satisfied the following needs: support, experience of physical contact, attention and approval, love and care. Unmet needs are reflected in a person’s inability to be alone, talkativeness, fear of separation, bragging, and dependent behavior (addiction). This means that a person who did not receive unconditional love in childhood will be constantly subject to cyclical mood swings: euphoria will be replaced by depression. Psychologists warn patients that euphoria carries with it the danger of approaching depression.
Psychiatrists attribute euphoria to a painful increase in emotional background, as well as a decrease in critical perception of reality. It can occur with increased motor and facial activity or, conversely, with deep retardation. It all depends on the reason that causes it.
Euphoria in case of morphine poisoning proceeds stunnedly, and in manic-depressive psychosis it proceeds violently. Such a warning to people always helps, because it brings a certain amount of reality into the patients’ thinking, softening and inhibiting sudden mood swings, and with the onset of depression it is no longer so destructive.
In a euphoric state, a person always thinks that everything will be fine, but good will not happen if hidden problems are not eliminated.
A person, falling from the heights of this state into depression, feels that all his illusions are crumbling, and there is no way out of depression. A healthy person does not experience sudden changes in mood from euphoria to depression. He is able to experience excitement due to any event, as well as prospects that will give a powerful energy flow. A person in this state will feel joy, pleasure, but will not feel euphoria. If the event, as well as the prospect, disappointed him, then he will be sad, but at the same time will not fall into the clutches of depression. A healthy person does not lose the ability to adapt to a new situation.
Symptoms of euphoria
Euphoria is quite difficult to recognize. Basically, it is mistaken for joy and happiness. In any case, even if a person understands that he is experiencing a feeling of euphoria, this does not make him puzzled by his condition, since people do not perceive this feeling as capable of causing harm to health.
However, in order to recognize euphoria, it is worth familiarizing yourself with its symptoms:
- Calmness and feeling of joy.
- Peace and lingering complacency.
- A feeling of boundless happiness.
- Positive reaction to external influences.
Many people compare euphoria to ecstasy. Ecstasy is essentially also heightened positive emotions, but more short-term. Euphoria is distinguished precisely by its duration and it is precisely this duration that carries danger. Therefore, if you notice that a person close to you has been radiating happiness and joy for a long time, then take a closer look at him.
Elevated mood can also be recognized by its physical manifestations. Among them it is worth mentioning such as:
- rapid pulse;
- slow body reactions;
- increased blood pressure.
Euphoria also carries with it negative mental symptoms:
- The feeling of being in another reality, that is, confusion. It seems to a person that he constantly experiences a feeling of “déjà vu”. If at first this may arouse interest or the person simply does not pay attention to “déjà vu,” then over time he will begin to experience discomfort that can develop into paranoia.
- Contrived experiences. Increased anxiety, fears and depression may occur. If at first a person feels a sharp attack of joy, then after some time the euphoria may subside and then everyday problems may be perceived as something insurmountable. Don’t think that euphoria always leaves behind a joyful aftertaste. There are often situations when after it a person falls into a prolonged depression.
However, in fairness, we note that euphoria sometimes manifests itself in positive signs:
- clarity of mind and speed of reactions;
- overflowing with energy and vigor;
- thirst for active action.
The duration of euphoria directly depends on the cause of its occurrence. If it appeared for natural reasons, then the “attack” of acute joy will last no more than half an hour. But if euphoria is a consequence of artificial causes (alcohol, drugs), then it can last from half an hour to several hours, depending on the amount of drugs used.
Drug euphoria
How to explain that young people use drugs? This is an attempt to escape the depressive feelings that young people hide inside themselves. This is the only way to explain despair and the desire to fly high so as not to feel reality.
Drug euphoria makes it possible to fly high, away from sad, despondent feelings. Young people should not be blamed for this, since they see no other way out. Unfortunately, there is no drug that will help forever, and after the high that it brings, there is always a fall and psychological dependence, which is as destructive in its power as physiological dependence. Therefore, our salvation is the understanding and acceptance of such falls, which create solid ground for the perception of our sensations.
Euphoria from marijuana occurs in the form of apathy, which feels like depression. Some people note that the sensations are reminiscent of an exciting journey that gives them an upbeat mood. Everything is individual. Some people, desperate, try to forever remain at the height of their sensations. These include heavy drug addicts. They try to get their buzz at any cost.
What is euphoria? Meaning
In science, the hormone of good mood is endorphin, located in the pituitary gland (upper part of the brain), as well as dopamine. They are produced in the processes (wirings) of neurons. How is idleness born in people in the medical sense? The first hormone interacts with certain nerve endings, which gives rise to a biochemical process, as a result of which euphoria is formed. The second substance (dopamine) is responsible for transmitting signals, and it provokes a positive psycho-emotional change.
But despite this, the formation of the euphoric effect is quite difficult to explain, since many physiological processes are involved in this.
Alcohol euphoria
After drinking a glass of wine, you can feel inexplicable enthusiasm and joy, an improvement in your mood. This occurs due to two processes that occur in the body. A sharp increase in the amount of morphine-like substances in the blood and brain, as well as increased synthesis of dopamine (an enzyme that is responsible for energy, mood, vascular tone, and performance).
Alcoholic euphoria is associated with hypoxia (oxygen starvation). Hypoxia occurs when blood vessels in the brain become clogged and the delivery of oxygen to brain cells through the blood stops.
Alcoholic euphoria is no different from manic, drug or euphoric states. A person who drinks obviously also needs a remedy that can pull him out of despondency and depression. It is clear that not everyone who drinks is trying to avoid depression, but if there is a need to drink, then this is a bad sign. In this case, the reference is to a person who needs alcohol to “take off.” After the alcoholic high, there comes a fall - a hangover, while the mood decreases and becomes depressed. If a person cannot cope with depression on his own, the need to take alcohol arises.
A fall from a drug high is different from an alcoholic one. The narcotic effects of drugs last longer than those of drinking alcohol. A person may not feel depressed after taking drugs, since the drug blocks feelings much more strongly than alcohol.
Is euphoria fraught with danger?
The safest euphoria is the love variety, the manifestations of which are found in a wide variety of people, regardless of their age. All other varieties of this state are dangerous due to addiction, since people naturally like this blissful state, and therefore they strive to experience it again. The absence of euphoria for a long period causes despondency and apathy in a person, which can gradually develop into full-fledged depression.
Different people achieve euphoria in different ways: some prefer extreme sports and recreation, trying to get adrenaline, others experience true bliss from listening to music at home or attending concerts, others induce artificial euphoria through the use of alcohol or drugs. The most dangerous is artificial euphoria - it entails addiction to drugs or alcohol, moreover, in order to obtain the usual state, a person has to gradually increase the dose of the substance taken , which can cause serious harm to health and lead to death.
Euphoria also leads to a distortion of the sense of reality, therefore, a person under its influence is not able to adequately assess the situation around him, which can result in an offense or crime.
Why does euphoria occur?
A state of euphoria and exaltation develops in the human body against the background of the influence of internal and external factors.
The reasons for the appearance of a feeling of euphoria in a person are divided into:
- natural;
- toxic;
- pathological.
The most harmless type of euphoria is considered to be natural. It develops against the backdrop of falling in love, playing sports, and joyful events. A pathological type that is formed as a result of brain diseases or prolonged mental disorders is considered dangerous.
Natural causes
Many people have experienced euphoria caused by natural factors.
It is not a pathological condition and does not mean the presence of serious pathologies in the human body. Most often, in this case, the winged state is caused by:
- Joyful events
. Events that are regarded by a person as joyful, positive and pleasant lead to a rise in mood and the development of causeless happiness. An emotional uplift can occur as a result of receiving an unexpected but long-awaited gift, successfully passing a test, or a promotion at work. - Physical exercise
. Many athletes experience bursts of happiness when overcoming long distances and setting record numbers. Some experience euphoria in cases where they manage to overcome themselves: overcome laziness, get rid of weakness and fatigue. In psychology there is even such a thing as runner's euphoria. - Music
. Musical euphoria occurs when listening to pleasant and rhythmic melodies. It is believed that such states are caused by meditation compositions, as well as melodies performed using a tambourine, rattles or drum. When musical euphoria appears, a person feels exaltation, pleasure, his body is covered with goosebumps, and a slight trembling appears. - Love
. The period of falling in love, lasting more than 2 months and accompanied by a strong feeling of attachment, is accompanied by intense production of happiness hormones and an increase in the functioning of the central nervous system. This leads to the onset of a slight intoxicating feeling of joy, happiness, and inspiration. However, euphoria in the case of falling in love can be replaced by a bad mood, namely a feeling of melancholy, sadness, obsessive thoughts about the object of love, and fear of separation. As the relationship strengthens and lovers get used to each other, euphoria begins to appear less frequently and less intensely. - Events that threaten life
. Extreme cases (road accidents, fire) lead to temporary changes in mental state. Severe stress provokes the appearance of emotional shock, which is replaced by a euphoric state, a feeling of alienation, unity with one’s body. Most often, such a mood develops in those who were in a dangerous situation, but were not harmed in it.
Important!
Prayers, breathing exercises, and creative activities can also lead to euphoria.
Toxic causes
Toxic euphoria appears against the background of alcohol or drug intoxication.
Most often, such conditions do not last long. They are replaced by a depressive mood, a feeling of loneliness and devastation. Sometimes the feeling of euphoria leads to severe aggression. The following lead to improved mood:
- Alcohol
. Causeless joy and increased strength are the typical state of a person who has consumed alcohol slightly more than the permissible limit. The surge of strength in this case can last from 30 minutes to several hours. At this time, people observe increased physical and speech activity, high self-esteem, self-confidence, and disinhibition. Often alcoholic euphoria is replaced by a depressive mood, moral devastation or irritability. - Drugs
(smoking mixtures). When smoking narcotic weed, a person gets a feeling of inspiration, carelessness, and joy. People may feel a surge of strength, a desire to share a joyful mood with someone, or lack of restraint. Using drugs in unlimited quantities leads to an uncontrollable feeling of joy. Impaired coordination of movements, severe retardation. Toxic happiness is replaced by aggression and a feeling of depression.
Euphoria also develops in those people who take drugs belonging to the group of opiates and hallucinogens.
These products have a psychostimulating effect on the human body. It causes attacks of causeless happiness, severe agitation, and difficulty speaking. Under the influence of drugs, a person may have difficulty recognizing the speech of interlocutors, wandering into happy thoughts, and answering questions late.
Pathological causes
Euphoria, which appears frequently and lasts a long time, is the cause of some psychological abnormalities and brain pathologies.
In this case, the patient experiences regular bouts of elevation, complacency, and bliss. These conditions are typical for:
- Bipolar disorder
. With bipolar disorder, a person experiences bouts of unreasonable joy and happiness, which are replaced by a depressive mood, a feeling of loneliness, irritability, and self-hatred. The duration of euphoria in bipolar disorder can last up to 1 day. - Hyperthymic psychopathy
. The disease is accompanied by euphoric states, which manifest themselves in the form of excessive sociability, excitement, and energy. A good mood periodically gives way to depression. However, it doesn't last long. Most of the time a person is in a state of mania and an eternal search for new experiences. These people need new emotions, so they periodically get involved in various adventures. - Schizophrenia
. Euphoric mood is characteristic of many forms of schizophrenia. It is accompanied by the development of causeless joy, foolishness, and emotional inadequacy. Pathological euphoria is replaced by anxiety, depression, and a feeling of loneliness. Causeless joy and happiness also manifest themselves in diseases such as mental retardation and Pick's disease.
Important!
There are frequent cases of euphoric mood during the development of malignant tumors in the brain. Oncological processes are often accompanied by emotional attacks, inadequate humor, and physical inactivity.