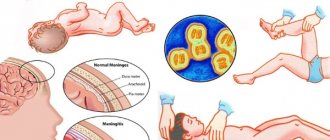
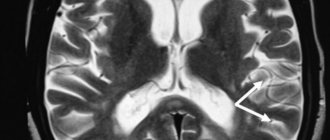
What is purulent meningitis?
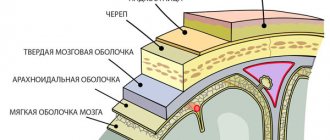
The disease is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process in the pia mater of the brain. The main cause is infection by pathogenic microorganisms.
Purulent meningitis manifests itself in the same way as most colds. The disease is accompanied by high body temperature and headache. After a few hours, nausea and vomiting occur.
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the clinical picture and the results of laboratory tests of cerebrospinal fluid. When a purulent form is detected, complex therapy is carried out, several groups of medications are used.
Routes of infection
The cause of purulent meningitis is various pathogenic microorganisms that can enter the body in several ways:
- Contact. Viruses and infections enter the brain tissue through open wounds during traumatic brain injuries, inflammation of the bones of the skull, certain parts of the organ, during surgery when the instruments were not properly processed.
- Airborne. The most common route for most microorganisms to enter the body. They penetrate from the environment through the respiratory system.
- Lymphogenic and hematogenous. Infection occurs through the lymph, when viruses and infections are transferred from other organs.
Also, purulent meningitis can be transmitted from mother to child. This method of infection is called placental.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from 2 to 5 days. During this time, microorganisms multiply and penetrate the brain tissue, after which characteristic symptoms appear.
Prevention
The main role in the prevention of childhood meningitis is vaccination against the main pathogen - meningococcus and pneumococcus, as well as quarantine measures in children's institutions when purulent meningitis is detected and a complete examination of children who have been in contact with the sick person.
If possible, you should scan all foci of chronic infections in the body (chronic otitis media, carious teeth), pay attention to the general strengthening of the immune system (hardening, proper nutrition, taking vitamins), and also teach children to observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Classification of purulent meningitis
Depending on how the disease develops and what causes it occurs, purulent meningitis is divided into two types:
- Primary. An independent pathology in which the infection enters the body through airborne droplets and lingers on the mucous membrane of the sinuses. The viruses then enter the brain. Infection also occurs due to open injuries to the skull, improper or insufficient sterilization of surgical instruments.
- Secondary purulent meningitis. This form develops against the background of an existing disease characterized by an inflammatory process.
In accordance with the location of the focus of the pathological process, the following types are distinguished:
- Basal. Inflammation affects the base of the brain. Along with signs of purulent meningitis, symptoms of damage to nerve endings appear.
- Total. The process extends to the entire soft shell of the organ.
- Spinal. The lesion is located in the membrane of the spinal cord.
- Convexital. The pathological process is located in the tissues of the cortex and is accompanied by psychomotor agitation.
Based on the nature of the course, several types of purulent meningitis are also distinguished. These include:
- Spicy. Signs appear suddenly and are quite pronounced. It is considered the most common type of disease.
- Fulminant. The pathology develops rapidly, and cerebral edema is observed.
- Recurrent purulent meningitis. Develops against the background of an existing chronic lesion.
- Abortive. Difficult to diagnose. It is characterized by pronounced signs of poisoning of the body by waste products of microorganisms.
Establishing the type, nature of the course and type of disease is carried out on the basis of diagnosis and clinical picture.
Causes of the disease
The cause of purulent meningitis is most often a bacterial infection of the membranes.
Helpful information
Based on the research results, it was established that the causative agents are pneumococci, Haemophilus influenzae and meningococci A, B and C.
In rare cases, purulent meningitis occurs as a result of the proliferation of Staphylococcus aureus.
Risk factors that increase the risk of developing the disease include:
- The rehabilitation period after surgery.
- Low immunity due to prolonged illness, hypothermia.
- Stress, psycho-emotional and physical stress.
- Diseases of the ENT organs of the purulent type.
- Chronic alcoholism.
- Traumatic brain injuries of varying severity.
Lifestyle is also of particular importance. The risk group includes patients who smoke, eat poorly, and lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Symptoms
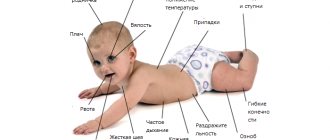
Purulent meningitis in the early stages of its development is similar to other colds and infectious diseases. After 2-5 days, the signs become more pronounced. If they occur, you should immediately consult a doctor, as the lack of therapy leads to various complications.
Symptoms of purulent meningitis include:
- High body temperature. The indicators exceed 39 degrees.
- Intense headache.
- Nausea and repeated vomiting.
- Cramps.
- Blurred consciousness.
- Psychomotor agitation.
- Delirium.
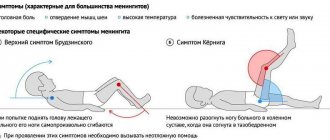
Also, purulent meningitis is accompanied by Kerning syndrome. It manifests itself as the inability to fully straighten the lower limbs. Patients report uncontrolled flexion of the knee and hip joint.
In severe cases, damage to the nerve endings of the skull, strabismus, paresis, and double vision are noted. Already on days 3-5 with purulent meningitis, a rash appears on the lips.
Purulent meningitis in children manifests itself in the form of skin rashes. There is increased pressure, as a result of which cerebrospinal fluid may leak. It is cloudy and contains pus.
The pathology is accompanied by increased vascular permeability and disruption of the blood clotting process. As a result, hematomas, areas of hemorrhage and necrosis appear on the surface of the skin.
Therapy
Classical medicine recognizes only drug treatment and surgery if necessary. Therapy with traditional methods is life-threatening and cannot be considered as separate from basic medical treatment.
Traditional
At the slightest suspicion of this pathology, the doctor prescribes therapy without obtaining laboratory tests. If this is not done, the consequences can be dire. The first remedy will be a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. The patient is sent to the hospital.
An antibiotic is used until an accurate diagnosis is obtained. Once the pathogen is identified, the doctor prescribes penicillin, cephalosporins, or macrolides to target the pathogen.
The dose of the drug will be maximum per patient every 4 hours until the patient gets better. Antibacterial therapy lasts up to 30–40 days.
Symptomatic treatment is carried out:
- Cerucalom to relieve nausea and eliminate vomiting;
- Baralgin and Ketanol to reduce headaches;
- sodium chloride solution, glucose, osmotic compounds to eliminate dehydration and intoxication;
- diuretics to relieve swelling of the brain.
The operation is performed to remove pus when there is a lot of it. For secondary pathology, medications are used to suppress the primary one. After completing therapy in the hospital, the patient will continue to receive treatment at home. He will be prescribed a diet and observation at the dispensary.
Important! Children who have had a purulent form of meningitis are observed by doctors for a couple of years. Every quarter after recovery, they are examined by a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist, and a neurologist. After a year - every 6 months.
In adults, the pediatrician is replaced by a therapist and the above list is supplemented by a psychiatrist. After discharge, the patient must visit doctors twice a month for 90 days, after - once a quarter, after a year - once every six months. All this applies only if there is no deterioration in health.
WE RECOMMEND SEEING: How to take a puncture for meningitis
Folk
The main methods of traditional therapy are aimed at eliminating negative symptoms. For this use:
- thistle infusion to relieve cramps;
- chamomile tea to relieve tension and calm;
- lavender infusion relieves cramps and relieves swelling;
- a tandem of lavender, primrose roots, valerian, mint, rosemary in equal parts soothes and relieves headaches.
Until the ambulance arrives, the patient should lie in a darkened room and silence. Not only the body, but also the soul should be in a calm state.
Diagnostics
If purulent meningitis is suspected, the patient is prescribed blood and urine tests and cerebrospinal fluid puncture.
The specialist also surveys the patient about existing symptoms and the time of their occurrence. The rigidity of the muscle tissue of the back and neck is determined, which does not allow the patient to tilt his head. Upon examination, an increase in deep and decrease in abdominal reflexes is determined.
The doctor pays attention to the presence of a rash on the skin around the mouth. Fragments of the rash are also sent for laboratory testing.
Treatment
Therapy for purulent meningitis is carried out with the help of antibiotics. Drugs are selected taking into account the type of microorganisms that caused the disease. Their intravenous administration is often prescribed. The duration of treatment is from 10 days.
To relieve unpleasant symptoms, a number of medications from different groups are prescribed. These include:
- antihistamines;
- diuretics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- cardiac glycosides;
- anticonvulsants;
- tranquilizers.
The dosage and duration of medication for purulent meningitis are selected individually in accordance with the individual characteristics of the body and the severity of the disease.
Complications and prognosis
Purulent meningitis is dangerous because it develops rapidly and can cause serious complications. Among them are:
- Severe headache.
- Fatigue quickly.
- Cerebral syndrome.
- Psycho-emotional state disorder.
- Thinking disorder.
The most dangerous consequences of purulent meningitis are cerebral edema and hydrocephalus. As a result of the ongoing processes, compression of the organ trunk occurs, where vital centers are located.
As a result of all the changes that occur, in the absence of therapy, death can occur. That is why you should not delay treatment and consult a doctor if symptoms occur.
Helpful information
Death of patients in the case of purulent meningitis occurs in approximately 14% of cases. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Forecast
The prognosis directly depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and initiation of antibiotic therapy. The later specific treatment is started, the greater the likelihood of developing life-threatening complications and death.
The mortality rate from purulent meningitis if untreated is approximately 50%. Pneumococcal meningitis has the most unfavorable prognosis, the probability of death in which (even with timely antibiotic therapy) is recorded in 15–25% of cases.
Preventive measures
In order to reduce the risk of developing primary or secondary purulent meningitis, it is important to undergo vaccinations in a timely manner and observe the rules of personal hygiene. If symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor and undergo treatment.
It is important to maintain immunity. During colds, take multivitamin complexes and avoid staying in crowded places.
Purulent meningitis is a dangerous disease of an infectious nature. When a disease is detected, immediate complex therapy is carried out, since the consequences of the pathology can be quite severe. Lack of therapy leads to death.
That is why it is important to follow the rules of prevention, and if characteristic symptoms occur, you must contact a specialist who will carry out treatment. Purulent meningitis requires the use of strong antibiotics, which only a doctor can choose correctly.
Is there an incubation period?
Translated from Latin – incubatio – means thoughtful, hidden. And we introduced the word incubator into the Russian language - “breeder,” for example, of chicks. This process means that what is hidden becomes apparent.
That's why the incubation period of meningitis is named so that it does not manifest itself in any way, and there are no symptoms. Nothing bothers a person, and until “quantity turns into quality,” he lives an ordinary life.
About deadlines
The incubation period for meningitis in adults and children is most often 5-7 days , after which clinical symptoms appear. Most often, a shorter duration is characteristic of purulent infections, and with serous inflammation the latent process can be long.
Thus, serous meningitis with mumps (mumps) has an incubation period of 15-30 days. But, at the same time, serous enteroviral meningitis can have an incubation period of 2-3 days.
There are no special calculation rules here, but the higher the immune system tension and the healthier the person, the longer there are no clinical symptoms.