The cardiovascular system is an important element of the human body; it is quite easy to upset the balance. Some people have heart pain after fright, stress, or nervous strain, which can lead to unpleasant consequences, so this problem should not be ignored. The myocardium is capable of withstanding heavy workloads every day, but at the same time the organ requires special careful treatment and can fail at the most unexpected moment under the influence of quite ordinary life factors. The pain can radiate to the hypochondrium, to the back, manifest as heaviness in the chest area, and cause a feeling of lack of air. In the process, your fingers may go numb, your head may become dizzy, your lips may turn blue.
Causes
With strong excitement, a feeling of fear, and fright, disruptions in the functioning of the autonomic part of the central nervous system occur. This leads to disturbances in the regulation of the heart muscle and the occurrence of vegetative-vascular dystonia and cardioneurosis. Pathology appears against the background of a complex combination of internal disorders and external factors.
The symptom of pain in the heart after a fright very often appears in people with existing diseases of the cardiovascular system, leading a sedentary lifestyle, abusing junk food, smoking, alcohol, psychotropic and narcotic substances. An anxious state in this case is a litmus test that indicates the presence of health problems.
Emotions have a direct impact on the state of the myocardium, since the muscle is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. Constant stress, worries, anxiety can negatively affect the signals coming from this department, especially if there are some predisposing factors for this, such as:
- heredity, tendency to heart disease, weak nervous system;
- regular stress, nervous strain;
- lack of oxygen;
- sudden climate change;
- hormonal imbalance;
- depression, neuroses, various mental disorders.
Also, pain in the heart due to fear can develop in the presence of respiratory diseases or a pinched nerve.
You can relieve pain at home, but after that you should urgently make an appointment with a cardiologist. A specialist will help you find the cause, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective, safe treatment.
Symptoms
How painful and pronounced the signs of heart rupture will be depends on how severely the myocardium is damaged, the degree of change in hemodynamic processes, and the presence of hemopericardium formation. If the defect is small in size, when blood does not enter the area of the organ’s lining or there is a small volume of it there, then the symptoms of the pathology will appear gradually, intensifying over time.
Signs:
- Severe pain behind the sternum on the left, occurring suddenly.
- Fear of death, anxiety, restlessness, psychomotor agitation may appear.
- Blue discoloration of the skin.
- Swelling of the limbs.
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath even at rest.
- Increased heart rate.
- Sticky sweat.
- Severe decrease in blood pressure.
- Cough with sputum that is foamy and pink in color.
If the heart rupture is of a slowly progressing type, then the person behaves restlessly, tries to neutralize the pain with the help of Nitroglycerin, but does not achieve the desired effect. Discomfort behind the sternum may subside slightly, but after a while it returns with renewed vigor. The course of the pathology is further worsened by the fact that the heart vessels do not receive the required volume of blood, as a result of which the myocardium experiences severe oxygen starvation, which inevitably leads to its failure.
The acute nature of the disease can rupture the tissues of the organ sharply, which in any case leads to the flow of blood into the heart sac (hemopericardium), and the systemic blood flow suddenly deteriorates. This can mean a rapid onset of death, since the ambulance team usually does not have time to help the patient
In order to prevent such a serious outcome, it is necessary to pay attention in time to the harbingers of such a pathology. People suffering from heart disease need to know what symptoms may occur before a major organ ruptures
Danger signs:
- loss of consciousness;
- pronounced cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin);
- the veins in the neck area swell greatly;
- tissue swelling becomes more and more noticeable;
- measuring the pulse becomes impossible, it cannot be felt;
- pronounced shortness of breath suddenly stops, the patient’s breathing stops.
Hemotamponade of the pericardial zone can occur not only due to myocardial infarction, but also due to heart injuries, as well as rupture of the aorta in the area of its initial section. Sharp pain and the development of cardiogenic shock are the main symptoms of tamponade. Such signs have increasing manifestations; within a few minutes after their disappearance, the patient’s death is usually recorded.
Any disturbances in the myocardium cannot go unnoticed, and the risk of death increases significantly if a large-focal transmural type of infarction is detected. It is especially dangerous when a person is additionally diagnosed with arterial hypertension and the patient is already advanced in age.
Associated symptoms
A nervous condition can lead to additional symptoms:
- arrhythmia;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- feeling of anxiety;
- dyspnea;
- heaviness and compression in the chest area;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- increased sweating;
- decreased performance, general loss of strength;
- lack of air, fainting;
- problems with urination;
- failures in thermoregulation;
- a sharp decrease or increase in blood pressure.
All of the above symptoms may indicate the presence of different diagnoses that are associated not only with the cardiovascular system.
What is heart break
The most complex and tragic consequence of myocardial infarction, which affects at least five percent of all who have suffered this disease, is rupture of the heart muscle.
Although popular rumor has made heart rupture something like a common noun, this misfortune has nothing to do directly with the state of fear, since here an exclusively mechanical process takes place, as a result of real damage.
The risk zone for a critical post-infarction state covers a fairly wide range of patients suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system. The risk area includes people over sixty years of age (more often women of this age), hypertensive patients, diabetic patients and, of course, patients of all degrees of coronary heart disease.
Symptoms
The relatively mild nature of damage to the heart muscle entails a sluggish rupture, with symptoms that come in waves or spasmodically. A person, for a long time, may feel a temporary lack of air, anxiety, pulsating, severe pain in the heart. The skin will most likely take on a bluish tint and swelling may occur.
Urgent measures by taking conventional medications, in this case, are completely ineffective. The remaining symptoms of heart rupture gradually increase, acting as if in slow motion - sweating, palpitations. But the phenomenon of gradual rupture is not so common in practice.
The percentage of immediate rupture, with a sudden rush of blood into the heart sac, is much higher.
Following an acute attack, in this case, the patient immediately becomes unconscious, his neck swells and bulges with veins.
For one or two minutes a person tries to compensate for the lack of oxygen by rapid, heavy breathing and death occurs. On the electrocardiogram (ECG of the heart) this moment is expressed as a solid isoline.
Swelling of the veins in the neck is a hallmark symptom of a ruptured heart
The defect of the heart muscle itself, which precedes the rupture, is impossible not to notice - it will be indicated by such an abundance of symptoms, ignoring which leads to death in the shortest possible time.
All of the above referred to gaps of an external nature. Disruptions with internal specifics are no less serious and entail exactly the same outcome if measures for high-quality and multifaceted rehabilitation after a heart attack are not taken in time.
Treatment
Depending on the diagnosis, the cardiologist prescribes a comprehensive therapeutic program that includes different treatment methods:
- Drug therapy: sedatives, tranquilizers, antidepressants.
- Traditional medicine: herbal preparations, teas, infusions, soothing baths with essential oils, special relaxing salts.
- Physiotherapy: magnetic, laser therapy, electrophoresis, massage, acupuncture, inductothermy, darsonvalization, aeroionotherapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Psychotherapy sessions.
- Spa treatment.
- Correction of diet, diet.
If pain appears in the heart area after a strong fright, you need to give yourself first aid. First of all, if possible, you need to take a lying position on a flat surface, unfasten the top buttons on your clothes, remove all excess, which can interfere with the normal flow of oxygen into the lungs and compress the chest. After this, it is important to establish uniformity of breathing; the process should occur slowly and measuredly. It is also necessary to exclude all irritating factors and take Corvalol or valerian tincture. If the condition does not improve, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Prescribed drugs
Sedatives reduce nervous conditions, dilate coronary vessels, and help stimulate the body's production of endorphins:
- Tricardin;
- Corvalment.
Magnesium and potassium preparations restore vascular tone, neuromuscular transmission, and normalize electrolyte balance:
- Magnerot;
- Asparkam.
Tranquilizers relieve anxiety, remove the feeling of fear and panic:
- Atarax;
- Phenazepam.
The selection of medications and their dosage should only be carried out by a qualified physician.
Rupture of the heart, myocardium: prerequisites, forms, signs, help, prognosis
A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university
Without exaggeration, the heart is considered the main organ in the circulatory system, without which blood delivery to the internal organs is impossible. When it is damaged, hemodynamics are disrupted, and cardiac rupture (HR) makes blood movement impossible, and the patient dies from shock.
Rupture of the heart muscle - myocardium - is a violation of its integrity, which most often occurs due to a heart attack. Contrary to popular belief, fright or severe fear cannot cause a rupture on its own, because the heart is a powerful muscular organ, and for its damage prerequisites are needed in the form of changes in the myocardium.
Elderly people, especially women, as well as patients suffering from diabetes, hypertension, and chronic cardiac ischemia are more susceptible to heart rupture.
Taking certain medications and late initiation of treatment for a heart attack may be accompanied by a slowdown in scar formation, which creates the preconditions for rupture.
Rupture of the heart vessels, the initial part of the aorta, is provoked by a deep atherosclerotic process, vasculitis.
Causes and types of heart rupture
Among the causes of heart rupture are:
The reasons for rupture of the heart wall lie in structural changes, because healthy myocardium is quite strong and, at the same time, elastic, so it cannot rupture.
The most common cause of heart rupture is considered to be infarction (necrosis) of the heart muscle . With this disease, rupture occurs in approximately 3% of cases and in approximately half of the patients it occurs on the first day from the onset of necrosis. Over the next two weeks, the likelihood of rupture increases significantly.
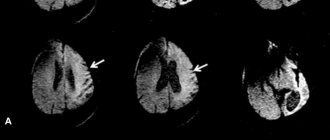
heart rupture as a result of a heart attack (arrows indicate areas of necrosis)
With myocardial infarction, rupture of the left ventricle of the heart usually occurs, since it is this section that experiences the greatest load during the operation of the organ, and it is in it that necrosis usually appears.
Up to 3% of cases may be accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the septum between the ventricles. The precursor to rupture is an extensive infarction, affecting a significant volume of the heart muscle, and the risk of damage is maximum in the first two weeks.
The right sections and atria are ruptured extremely rarely.
Endocarditis (inflammation of the inner layer of the heart), tumors, metabolic disorders (amyloidosis) lead to changes in the condition of the heart muscle, which becomes very susceptible to stress and can rupture. With endocarditis involving the valvular apparatus, rupture of the heart valve is likely, which is fraught with acute heart failure.
Other causes of heart wall rupture include trauma. For example, in case of an accident, a knife wound, a strong blow in certain sports or a fight.
Many people think that there is a rupture of the heart from fear, and this is evidenced by cases of sudden death with severe emotional shock. Indeed, with a post-mortem examination of the heart, it is possible to diagnose its tamponade from a rupture, but the cause of a defect in the myocardium is more often a heart attack, which, among other things, can be provoked by stress, fear, or severe anxiety.
on the left – post-infarction rupture of the myocardium (heart muscle), on the right – external rupture of the heart with hemotamponade
In addition to the immediate causes, there are also predisposing factors:
- Old age - after 50 years, regeneration processes slow down, and most people of this age already have some signs of ischemia or wear and tear of the heart muscle;
- High blood pressure, creating additional stress on the myocardium;
- Delayed treatment of acute infarction;
- Early activation of the patient with extensive heart attacks - even walking on the street or walking around the ward requires an increase in myocardial work, so the motor mode is usually limited;
- Exhaustion and low body weight of the patient contribute to slower scar formation in the necrosis zone, which is fraught with rupture in the acute period of a heart attack;
- Taking medications containing hormones, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, slows down the formation of connective tissue at the site of the infarction.
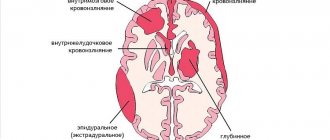
Depending on the area undergoing rupture and the time of manifestation of the pathology, various types of heart rupture are distinguished. Depending on the location of the damage zone, the following are possible:
different types of heart ruptures
- External ruptures, when a through defect is formed in the wall of the heart, through which blood enters the heart sac.
- Internal ruptures, when the structures of an organ located inside it are damaged: rupture of the papillary muscles, formation of a defect in the septum.
The blood inside the heart moves under high pressure, and when defects appear in the myocardium, it immediately rushes into the cavity of the heart sac, limited by the pericardium. The rapid filling of the pericardial cavity with fluid disrupts the contraction of the heart, causing tamponade and cardiac arrest. There is a deficiency of blood flow in the organs, and the patient dies from shock.
Internal ruptures can occur more easily than external ones. Thus, with a partial rupture of the papillary muscle, the patient can live up to two weeks, but this condition anyway requires urgent surgical treatment.
Incorrect movement of the valve leaflets when the papillary muscles or chordae are damaged causes acute heart failure and is fatal.
Ruptures of the septum are accompanied by the movement of blood through the defect from the left half of the heart to the right and can also lead to the death of the patient.
If the rupture occurred within three days from the moment of necrosis or injury, then it will be called early. After 72 hours, when recovery processes have already begun, but the scar is very tender, the rupture is provoked by excessive physical activity and is called late.
With extensive heart attacks, a simultaneous rupture is possible, and then death occurs suddenly. If the defect does not extend to the entire depth of the myocardium or is relatively small, then immediate death does not occur, blood circulation progressively worsens, and the damage is called slow flowing.
How does MS manifest?
Symptoms of cardiac rupture depend on the area of damage in the myocardium, the presence of hemopericardium, and the degree of hemodynamic impairment. With a relatively small defect, when blood does not enter the cavity of the cardiac membrane or its amount there is insignificant, the signs of the disease increase over several hours, ten minutes, and the patient is bothered by:
- Sharp, very intense pain behind the sternum, in the heart;
- Severe anxiety, possibly psychomotor agitation;
- Dyspnea;
- Blueness of the skin;
- Swelling.
As the symptoms of acute heart failure progress, the pulse becomes thready, blood pressure drops, and a change in consciousness or even loss of consciousness is possible. Pain appears in the right hypochondrium, associated with an enlarged liver due to stagnation of venous blood, and swelling increases.
A patient with slowly progressing MS is restless, tries to relieve pain with the usual nitroglycerin, but does not get any effect, the pain may decrease somewhat, but then appears again.
Characterized by cold clammy sweat, palpitations and hypotension.
The condition is further aggravated by the fact that the arteries of the organ do not receive enough of the blood they need, the myocardium experiences severe hypoxia, and its failure is inevitable.
An acute rupture of a large heart inevitably leads to bleeding into the heart sac (hemopericardium), the systemic blood flow is sharply disrupted, and the death of the patient occurs.
In more than 90% of cases, doctors encounter precisely such sudden and large myocardial ruptures.
Often, the called ambulance team simply does not have time to provide first aid and is only forced to ascertain the sudden death of the patient.
Harbingers of heart rupture can be intense pain that is not relieved by nitroglycerin and even narcotic analgesics, blood pressure drops sharply, the pulse becomes thread-like and can be palpated with great difficulty, the patient turns pale, the skin becomes bluish, and consciousness becomes confused.
Symptoms of external rupture are reduced to signs of pericardial hemotamponade and acute heart failure:
- The patient loses consciousness;
- The neck veins swell, swelling increases;
- Severe cyanosis appears;
- Severe shortness of breath gives way to respiratory arrest;
- The pulse cannot be felt, hypotension is replaced by shock with a lack of pressure.
Hemotamponade of the pericardium is possible not only with ruptures due to a heart attack, but also with traumatic injuries of the heart, rupture of the aorta in its initial section.
Sudden pain and signs of cardiogenic shock are the main manifestations of hemotamponade.
Both aortic rupture and myocardial infarction may have common development mechanisms, so all patients with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries and aorta are at risk.
hemotamponade in post-infarction cardiac rupture
Such symptoms increase over several minutes, after which death occurs from a ruptured heart - the pupils do not respond to light, breathing and heartbeat are not detected, and there is no consciousness. The ECG at this moment will show an isoline, that is, a complete absence of cardiac activity.
Myocardial damage does not occur unnoticed, and the risk of dying from cardiac rupture increases significantly if a large-focal transmural infarction is diagnosed, especially against the background of arterial hypertension and in an elderly patient.
Internal ruptures are no less dangerous than external ones. Thus, a violation of the integrity of the papillary muscles of the left ventricle is fraught with the rapid development of pulmonary edema - the main complication when blood flow in the left half of the heart is disrupted. Significant ventricular septal defects manifest themselves as symptoms of increasing cardiogenic shock. There is practically no chance to save the patient in these cases.
Treatment of heart rupture
Treatment of patients with cardiac rupture involves emergency cardiac surgery and intensive care. It is not always possible to provide all the necessary measures on time, because death occurs suddenly and very quickly. In addition, the patient may be far from the cardiac surgery hospital, and the time for preparation and transportation is extremely limited.
Surgical operations that can be performed for heart ruptures:
- Suturing the defect and installing special “patches”;
- Coronary artery bypass grafting;
- Valve replacement;
- Donor organ transplantation.
Surgical treatment consists of suturing the myocardial defect during open surgery, possibly strengthening the site of damage using a special “patch” made of synthetic materials.
In case of ruptures of the interventricular wall, their correction by endovascular intervention is applicable, without open access to the heart, but even in this case, a “patch” is installed in the damaged area.
Fluid from the pericardial cavity is removed using puncture.
In case of deep atherosclerotic damage to the coronary vessels, cardiac plastic surgery can be supplemented with coronary artery bypass grafting, aimed at restoring blood flow and, thus, accelerating scar formation at the site of ischemia and rupture.
If the pathology is accompanied by damage to the papillary muscles, chords, and other elements of the heart valve apparatus, then surgery to install an artificial valve (prosthetics) may be the method of choice.
Large ruptures against the background of extensive infarctions are extremely difficult to “correct” due to severe ischemia in the necrosis focus, where tissues are poorly connected to each other, regeneration slows down, and a significant area of the heart muscle may need to be removed. In these cases, a heart transplant can save the patient, but serious difficulties with its implementation are due to limited time and the lack of a suitable donor.
Drug therapy is aimed at maintaining acceptable blood pressure levels and the function of vital organs. The use of diuretics, peripheral vasodilators, analgesics, and cardiac glycosides is indicated. Infusion therapy consists of administering fresh frozen plasma and saline solutions.
Heart rupture is a pathology that requires emergency medical care, so patients suffering from coronary artery disease or who have suffered a myocardial infarction must not only carefully follow the regimen and prescriptions of the cardiologist, but also take every attack of chest pain seriously, and if it lasts more than five minutes, then contact medical attention must be sought immediately.
Source: https://sosudinfo.ru/serdce/razryv-serdca/
Prevention
To reduce the risk of unpleasant and sometimes dangerous symptoms, it is recommended:
- regularly visit the doctor and undergo medical examination;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- improve your diet by eliminating unhealthy foods and increasing the amount of cottage cheese, kefir, lean meat, fish, vegetables, and herbs in your diet;
- do not overuse physical activity and give up a sedentary lifestyle, in this case it is important to find a middle ground;
- control blood sugar, cholesterol, blood pressure levels;
- get rid of excess weight.
Pain in the heart area after a fright is a symptom that there are health problems that should not be taken lightly. Such a manifestation may signal the need to urgently visit a doctor and change your lifestyle.
FacebookvKontakteTwitterWhatsApp
Prayer for fear for children
It is a petition to the Lord that can heal both a child and an adult from causeless fear. Below is a prayer request for relief from fear.
Come out, enemy, Satan, childish fear, from the servant of God (name). From her body, from her head, from her legs, from her arms, from her heart, from her stomach, from her veins, half-veins, bones. You shouldn’t stand here, don’t walk on bones, don’t break bones, don’t dry the body and don’t drink blood. Come out, enemy, Satan, childish fear, from the servant of God (name) into the swamps, into low places where the sun does not rise, where people do not walk. It is not I who send you away, pour you out, reprimand you, but the Lord Jesus Christ commands you to get rid of all illnesses from the servant of God (name). Amen. Amen. Amen
It is recommended to read this prayer three times for three days in a row.
Prayer to Matrona of Moscow from the fright of a child
Help me, Blessed Elder, to find peace in my sinful soul. Drive away my random fear and bring peace of faith. Protect me from destructive fear and give me strength for a speedy recovery. Ask the Lord God for mercy and righteous fear about his punishment. Thy will be done. Amen
Possible consequences
Before choosing a treatment technique, you need to understand what the causes and consequences of fear may be. This disease is psychological, and its results can be very unpredictable. There can be any reaction to fear.
Being frightened, a woman causes embarrassment in the eyes of a man. By nature, the weaker sex is more timid. A slight fear most often does not lead to severe pathologies.
In childhood, the most common consequences are loss of speech and isolation. In rare cases, fear can cause speech delay for up to 5 years. In adults, fear can even lead to death.