Osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome is a dystrophic disorder in articular cartilage, accompanied by damage to the roots of the spinal endings. Depending on the location, the disease is accompanied by sudden, cramping pain in the chest, neck, back, and shoulder blades.
In this article we will tell you about the most effective and safe methods of treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome. Take just 5-7 minutes to read and get the most up-to-date information.
Causes
Degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs develop gradually, starting at the age of 25. With age, the risk of joint ossification, the appearance of growths and limited vertebrae increases.
Radicular osteochondrosis is a consequence of damage to the nerve roots emerging from the spinal cord. This process is accompanied by severe pain and numbness of the skin in the affected area.
The development of osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome can be provoked by the following factors:
- Congenital or acquired deformities of the spine.
- Excessive stress on the spine during heavy sports, pregnancy, and prolonged physical work.
- Spinal injuries.
- Obesity, leading to excessive stress on the spinal column.
- Walking for a long time in high heels.
- Static loads on the spine during sedentary work.
- Infectious diseases.
What it is
In neurology, several stages of osteochondrosis are distinguished. Each of them is accompanied by disruption of the ligamentous apparatus of the spinal column. What is subacute osteochondrosis complicated by radicular syndrome?
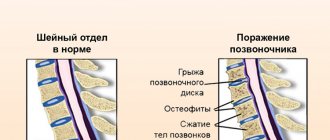
After 25 years, a person experiences gradual wear and tear of cartilage tissue, ligaments and intervertebral discs. The spine becomes less mobile, and the distance between the vertebral bodies decreases. Further progression of degenerative processes leads to the fact that the fibrous rings of the discs begin to deform, compressing the roots of the spinal nerves. The same radicular syndrome occurs in osteochondrosis, which was previously considered a “disease of the elderly.”
One of the “advanced” stages of pathology is considered to be a herniated disc. It occurs when the fibrous ring is completely ruptured and, depending on the location, can lead to serious complications, including paralysis of the lower extremities.
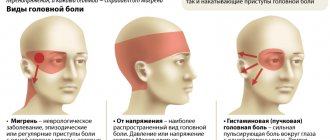
Symptoms of radicular syndrome in cervical osteochondrosis
After watching the video, you will learn about the typical manifestations of radicular osteochondrosis in the neck:
Cervical osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome is rarely observed. Usually the disease appears against the background of pinched artery of the spinal roots. Doctors preliminarily diagnose the pathology based on the following signs:
- Headaches, often accompanied by numbness in the parietal or occipital part of the skull.
- Numbness of the tongue, leading to problems with swallowing and speaking.
- Decreased chin muscle tone.
- Numbness of the skin on the left or right side of the neck.
- Decreased mobility of the upper limbs.
With cervical osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome, pain often radiates to the forearm, collarbone or scapula. Unpleasant sensations intensify when turning the head, bending, or sudden changes in the position of the body.
CS for thoracic osteochondrosis
Thoracic osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome has a pronounced course. When visiting a doctor, the patient complains of the following symptoms:
- Aching pain in the chest or shoulder blades, aggravated by coughing, sneezing, or sudden movements.
- Dryness and pain in the throat.
- Numbness of the skin.
- Tingling sensation in the forearm and upper limbs.
- Unpleasant sensations in the stomach area.
Due to the special symptoms, thoracic osteochondrosis with radicular symptoms is often confused with diseases of the cardiovascular, digestive or respiratory systems, which makes diagnosis much more difficult.
First aid: how to treat an acute attack of pain
The pain usually occurs suddenly and is very frightening for patients. The first step is to calm the person, because additional stress will increase the pain syndrome. For shooting in the neck or chest, the victim must be seated with support on his back and shoulder blades.
If an attack affects the lumbar spine, it is better to place the patient on a flat and hard surface - on the stomach, and place a cushion under the chest.
What not to do when providing first aid:
- massage the damaged area;
- apply wet and hot compresses and rubbing;
- use warming gels and ointments.
You can give a person any painkiller (for example, Analgin, Ketorolac), collect ice from the refrigerator, wrap it in thick cloth and apply it to the source of inflammation.
If the attack does not go away, you should call an ambulance. After the patient has received first aid, you need to insist on contacting a neurologist as soon as possible.
Be sure to read this good article:
TOP 10 methods for quick treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis at home: gymnastics, medications, prevention
CS for lumbar osteochondrosis
The lumbar region experiences regular physical activity, and the muscles here are usually weak, so osteochondrosis develops here most often.
With radicular syndrome in the lower back, the patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- Pain in the groin, thigh, sacrum. Often the unpleasant sensations spread to the lower leg and knee area.
- Numbness of the skin.
- Decreased sensitivity in the toes.
- There is a possibility of involuntary urination or defecation.
- Sexual dysfunction in men.
Typically, pain progresses with prolonged physical activity and goes away with rest. When treating lumbar osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome, the patient is prescribed to wear a support bandage.
Diagnostics
Common symptoms of radicular syndrome:
When the first pain and other unpleasant sensations appear, you should consult a doctor. The specialist examines the patient, collects anamnesis, and issues a referral for additional examinations. During the initial examination, the doctor must evaluate the condition of the spine, muscle tone, and tendon reflexes.
Osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome can be determined using the following studies:
- X-ray is one of the popular methods that allows you to determine the exact location of osteochondrosis, displacement of the vertebrae, the presence of salt deposits and intervertebral hernia.
- MRI is a highly informative research method that allows you to obtain a detailed picture of the condition of internal organs.
- Ultrasound is a safe method of examining the spine using ultrasonic waves.
- Myelography is a method of x-ray examination in which a special contrast agent is injected into the cervical or lumbar spine using a puncture.
If it is difficult to diagnose radicular syndrome, you may need the help of specialized specialists: urologist, general practitioner, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, oncologist, gynecologist, general practitioner.
Treatment
First of all, treatment of osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome is aimed at relieving pain and restoring a person’s physical activity. Further, the treatment results are consolidated using conservative treatment methods.
Osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome never goes away on its own, so when such a diagnosis is made, you should immediately begin to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and the causes of their occurrence. The sooner treatment begins, the faster the patient can return to their normal lifestyle. Stable results can only be achieved with an integrated approach.
All changes in the structure of the vertebrae are irreversible, but thanks to drug treatment, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and swimming, it is possible to significantly reduce the manifestations of the disease.
Drug therapy
All medications for osteochondrosis complicated by radicular syndrome should be taken only after being prescribed by a doctor, who determines the type and duration of medication intake individually for each patient.
The following drugs will help normalize the condition of a patient with osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
- Analgesics are medications intended to relieve pain. Available in the form of tablets, injections or solutions.
- Muscle relaxants - relax spastic muscles, reduce pain, improve blood circulation.
- Novocaine blockades - for severe pain, a potent drug is injected directly into the epidural area.
- Psychotropics - indicated in cases where, as a result of severe long-term pain, a person has developed psycho-emotional stress.
- B vitamins – promote the rapid restoration of nerve fibers.
You can also get rid of pain due to osteochondrosis using local creams and gels that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Exercise therapy
When osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome goes into remission, physical therapy is used to restore the patient’s condition. The doctor determines the amount and type of exercise individually for each patient, taking into account the degree of the disease, age, general health of the body and the presence of contraindications.
With regular exercise, the back muscles are strengthened, their elasticity increases, and the spine itself becomes more flexible.
Swimming
Swimming is one of the effective ways to improve the condition of radicular syndrome. There are practically no contraindications for exercising in the pool. Two or three workouts a week are enough and within a few months your condition will noticeably improve.
Other physical activities that are carried out in water are also useful for osteochondrosis complicated by radicular syndrome. For example, water aerobics or gymnastics. Loads in the pool are much easier to bear, so water training causes minimal fatigue.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
To increase the effectiveness of treatment for osteochondrosis, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Electrophoresis is a method of introducing drugs into the body through the skin.
- Phonophoresis is a method in which medicinal substances enter the body under the influence of ultrasound.
- Diadynamic therapy is a method of impulsive therapy that uses electric current.
- Acupuncture is one of the safest auxiliary methods of treating radicular syndrome, which has an excellent analgesic effect.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out in clinics or sanatoriums. The effect is noticeable only after completing the entire course, the duration of which depends on the degree of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Surgical intervention
If conservative treatment does not lead to a positive result or osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome causes spinal deformities, surgical treatment is indicated.
In what cases is surgery performed for osteochondrosis:
- Intense pain that even strong medications cannot cope with.
- Severe numbness or complete paralysis of the limbs.
- The appearance of an intervertebral hernia.
- Neurological disorders of the pelvic organs.
Spinal surgery is a complex and responsible procedure. During the rehabilitation period, the patient is recommended to undergo sanatorium-resort treatment.
Nutrition in the treatment of osteochondrosis
During the treatment of osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome, the patient's diet should be as balanced and healthy as possible. Be sure to include foods rich in chondroitins and vitamins into your diet. The menu should regularly include fish, meat, dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits. To strengthen joints, iron-containing products are recommended - jellied meat, aspic, jelly. Avoid foods that are too salty, fatty and smoked. It is also recommended to give up an abundance of sweets, strong tea, coffee, and alcohol. If you are overweight, watch your calorie intake.
It is also important to monitor your drinking regime. In the acute stage of the disease, it is recommended to reduce the amount of fluid consumed in order to reduce the swelling that compresses the nerve bundle. During the period of remission, the amount of fluid consumed per day should be at least two liters.
Lifestyle during CS treatment
In the acute period, when the pain has not yet been completely relieved, the patient is recommended to remain in bed for at least three days. Then you can gradually begin to move, excluding strong physical exertion.
Even during the period of remission of radicular syndrome, it is recommended to lead a measured and calm lifestyle. Do therapeutic exercises, spend as much time as possible in the fresh air, sleep on an orthopedic mattress and pillow.
Types of massage
Depending on the stage of the pathology, patients may be prescribed the following types of massage:
- medicinal (classical). The massage therapist works with his hands on the muscles and subcutaneous fat layer, promoting general relaxation, relieving tension and pain;
- spot. The specialist gently presses the “trigger points” and stimulates the biologically active zones of the body;
- honey Honey is a natural anti-inflammatory agent. This type of massage can be done independently, but provided there are no allergies;
- vacuum (or can). Glass or plastic medical jars are used. The purpose of this massage is to stimulate blood circulation in the affected area, relax muscles and relieve pain.
Cupping massage effectively relieves spasms and severe pain
Interesting article in continuation:
TOP 20 best patches for osteochondrosis: painkillers, Chinese, warming, orthopedic
Prevention
Prevention of osteochondrosis should be taken care of at a young age. Strong back muscles will maintain the spine in a normal position, preventing the development of degenerative processes.
Measures to prevent osteochondrosis:
- Lead an active lifestyle - it is not necessary to go to the gym every day and do strength training. To strengthen the spine, therapeutic exercises, swimming, and regular courses of preventive massage are sufficient.
- Calculate physical activity - do not lift heavy objects, if your work involves physical labor, distribute the load evenly.
- Eat right - for the health of the skeletal system, the human body must receive a sufficient amount of useful elements: vitamins B and D, protein, phosphorus, calcium.
- Choose comfortable shoes - excessive stress on the feet has a negative impact on the condition of the musculoskeletal system. Often, women, sacrificing their comfort, wear too high heels and do not take them off throughout the day. This is a huge load on the spine, so periodically wear comfortable shoes with low speed.
- Seek medical help in a timely manner - any pathologies at an early stage can be successfully corrected. Therefore, if you are experiencing severe pain in any part of your back, do not rush to take painkillers, but consult a neurologist.
Symptoms
General symptoms of degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system are as follows:
- pain syndrome of varying degrees of intensity;
- decreased sensitivity in the innervation zone;
- “crawling of goosebumps” along the nerve fibers;
- muscle spasm in the affected area.
Muscle spasm in the back is one of the symptoms of the disease
Constant compression of the spinal roots leads to the fact that severe pain can occur suddenly: for example, with a sudden careless movement. This manifestation is called reflex radicular syndrome.