Cephalgia is a disease that manifests itself in severe or moderate pain in the head. They can signal the presence of more serious diseases. Pain can affect both the entire head area and specific areas. In this case, a different nature of pain may be observed. It can be constant or paroxysmal. Hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult interferes with fruitful work and interferes with enjoying life.
The disease is divided into several types. There are infectious-toxic, vascular, neuralgic, liquorodynamic cephalgia, as well as muscle tension (vasomotor). Each type has a different mechanism of injury and clinical manifestations, which is especially important to consider when selecting the correct treatment.
Cephalgic syndrome (Cephalgia)
Cephalgic syndrome or, in other words, headache is a special pathological condition, which, despite its simplicity, can significantly reduce the comfort of a person’s life, and also serve as a clear symptom of more serious diseases. Correct diagnosis and timely treatment of cephalalgia, especially in children, is a rather difficult task, but absolutely necessary. Recently, in our society, due to numerous lifestyle disorders, cephalgic syndrome is actively gaining momentum and occurs quite often. Therefore, it is worth paying special attention to the standard rules that serve as the key to good good health.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Before we look at the main symptoms of cephalgic syndrome, it is worth finding out what causes headaches most often.
Click to enlarge
- Alcohol poisoning, smoking, excessive use of medications, drugs.
- Spasm of the neck, head vessels and muscles.
- Poor sleep, frequent stress.
- Poor nutrition of the brain: blockage of blood vessels, insufficient blood supply.
- Compression of the membranes of the brain.
The intensity of the manifestation of cephalalgia (headaches) may vary. This may be minor discomfort, which many are accustomed to endure, or severe pain. In the latter case, pain may affect the upper spine and neck.
Among the main symptoms of the disease are the following:
- Increased body temperature.
- Pupil dilation.
- Nausea and in some cases vomiting.
- Irritability and anxiety for no reason.
- Confusion.
- Acute reaction to external stimuli.
Pay attention to factors that can trigger the disease. These include the following:
- Meningitis.
- Stress.
- Diabetes.
- Hypertension.
- Aneurysm and, as a result, cephalalgia of the brain.
- Cervical osteochondrosis.
- Trigeminal neuralgia.
- Cardiac pathologies.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Eye strain.
- Diseases of internal organs.
- Arteritis of the temporal region.
- Psycho-emotional stress.
- Starvation.
- Spending a long time at the computer.
- Lack of fresh air.
- Passive lifestyle.
Often, cephalgic syndrome develops after a head injury. Warning factors include a sharp increase in pain during intense exercise, nausea, vomiting, mental abnormalities, rigidity, point pain, and minor stroke.
Click to enlarge
If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should be wary and, if possible, consult a specialist.
- If, during a cough or other strain, you feel pain in the head area. One of the reasons for this symptom is cerebral edema.
- If there is constant pain on one side of the head in the temple area, this may be a symptom of temporal arteritis. As a result, a person may lose vision or have a stroke.
- During vomiting or an attack of nausea, sharp pain occurs, mental abnormalities and changeable mood are also observed. Often such signs indicate the presence of a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Tension headache (one of the types of cephalgia) is expressed in the sensation of a tight hoop on the head. In this case, the pain can be severe or moderate. In any case, this interferes with concentration and full functioning. The development of these symptoms may be caused by muscle tension in the neck, head, or emotional stress.
- If you have recently suffered a traumatic brain injury and are still experiencing pain, you should see a doctor immediately. These symptoms may indicate cerebral hemorrhages.
- Often, cephalalgia is the result of a small stroke. Confusion, amnesia, impaired coordination, vision and hearing, and numbness of the limbs are also consequences of this disease.
- With the development of acute glaucoma, throbbing pain is observed in the eyes and forehead. In addition, redness of the mucous membrane of the organs of vision is observed.
- Constant muscle tension in the back of the head (stiffness), along with headache and fever, can signal the development of meningitis.
- A symptom of a rupture of an aneurysm is a sharp and pinpoint pain in the head area.
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, the disease is divided into several types. Let's look at the symptoms of each type of cephalic syndrome so you can determine the type of disease.
Infectious-toxic cephalalgia
When the human body fights disease and harmful microorganisms, some of the cells disintegrate and they are toxic. During blood circulation throughout the body, dead cells can enter the head area, which is why this type of disease develops. This situation is typical for ARVI and influenza. As for headaches, they usually spread gradually. It all starts with one point, which gradually covers the entire head area. In this case, patients note pulsation, a feeling of fullness, pressure, heat. There is a feeling that there is a cast-iron helmet on your head that is being hit.
Infectious-toxic cephalgic syndrome develops for the following reasons:
- Colds.
- Alcohol poisoning, food or medication.
- Inflammatory processes of ENT organs and head tissues.
- Infectious diseases.
The asthenocephalgic type of syndrome manifests itself as follows:
- Prostration.
- Feeling tired.
- Confusion.
- Temperature increase.
- Irritation from bright lights and loud music.
- Vomit.
- Feverish condition.
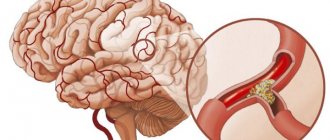
Vascular cephalgia
Click to enlarge
When the walls of the blood vessels in the brain swell or stretch, a vascular-type cephalgic syndrome occurs as a result. This happens for various reasons: an increase in blood viscosity, an increase in pulse volume, overflow of blood in a separate area of the vessels, insufficiency of venous tone. Depending on the cause, different types of headaches are observed: bursting, dull, throbbing.
We recommend reading: Dizziness with VSD
The following symptoms are observed:
- “Floaters”, stars and sparkling circles before the eyes, darkening.
- Dizziness.
- Facial pallor.
- Pulsating noise in the ears.
- Heaviness and swelling of the lower eyelids.
- Nasal congestion, throat redness.
- Arterial spasm.
Vascular cephalgia occurs for the following reasons:
- Emotional stress.
- Migraine.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Physical fatigue.
Neuralgic cephalgia
When this type of cephalgic syndrome develops, pain is observed in certain parts of the body. For example, pain in the occipital region or trigeminal nerve. When the patient touches this part of the body, a sharp pain occurs, which spreads to other parts of the head. Most often it is burning and sharp. As a result, the patient is afraid to touch his head, so as not to provoke another attack. Among the symptoms, sometimes there are “shots” under the eye socket, in the ear, and also in the jaw when chewing food, moving and swallowing.
Liquorodynamic cephalgia
Click to enlarge
Pain during liquorodynamic cephalgia directly depends on the amount of cerebrospinal fluid. It can either increase in volume or decrease, which leads to changes in intracranial pressure. Due to injuries and inflammatory processes that interfere with proper circulation, fluid stagnation occurs. As a result, headaches develop, which intensify with sneezing, coughing, tilting or turning the head, sudden rise and other strains.
The main reasons for the development of this type of cephalgia:
- Growth of cystic formation.
- Failure of venous outflow.
- Development of a cancerous tumor.
- Hydrofecal.
- The meninges lose their integrity.
Muscle tension
Headaches due to vasomotor cephalgia, or as they say in the medical community, tension cephalgia, are usually moderate, squeezing and encircling the head. This happens due to excessive muscle spasm in the neck, head, and shoulder girdle.
Psychological factors:
- Neurosis.
- Stress.
- Depression.
Physiological:
- Rachiocampsis.
- Incorrect posture.
- Damage to the eyes, pharynx, ears, paranasal sinuses.
- Osteochondrosis.
Symptoms:
- Moderate headaches.
- Weakness.
- Sensitivity to sunlight or loud music.
- Feeling of head being compressed.
The main reason for the development of this type of disease is an insufficient amount of oxygen in the vessels due to muscle spasms.
Diagnostics
Cephalgia with VSD should be distinguished from the pain syndrome that occurs with other diseases. Headaches can be a consequence of organic brain damage with:
- tumors (benign and malignant);
- strokes (ischemic and hemorrhagic);
- hydrocephalus;
- encephalitis and meningitis;
- congenital anomalies of the development of the brain and skull bones;
- head injuries with contusion of brain tissue and hemorrhages.
To exclude organic brain damage, instrumental studies will be required:
- x-ray,
- CT,
- MRI,
- vascular angiography.
Having excluded the above diseases, proceed to the next stage of diagnosis: it is necessary to differentiate dystonia from primary forms of headache (migraine, cluster headache).
During the examination, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease and clarifies the nature of the pain, studying the connection of the cephalgic syndrome with the influence of external factors.
- Migraine attacks may include nausea and vomiting, an aura, and sensitivity to light and noise. But unlike VSD, migraine pain is prolonged - from several hours to several days. Analgesic medications help with migraine pain.
- Based on the localization of the cephalgic syndrome, migraine and dystonia cannot be distinguished. Both pathologies can be either bilateral or unilateral.
- Cluster headache occurs on one side and is pronounced. Pain sensations are focused on the temples and eyes. Swelling of the upper eyelid and lacrimation may occur. The disease differs from dystonia by uniform symptoms.
To facilitate the diagnosis of cephalgia during VSD, attention should be paid to the appearance of numerous accompanying symptoms that occur as paroxysms:
- anxiety attacks;
- heartbeat;
- respiratory disorders;
- unstable blood pressure;
- sensations of heat;
- sudden pallor of the skin.
Many symptoms of dystonia go away on their own after a certain period of time.
Features of VSD with cephalgic syndrome
Due to the numerous causes of cephalalgia and the subjectivity of the perception of this disorder, identifying reliable symptoms is somewhat difficult for the doctor. The patient needs to describe in detail and accurately all his sensations so that the primary source of cephalalgia can be determined.
Headache has the following characteristics of conditions and symptoms:
- localization of pain;
- short- and long-period fluctuations in the intensity of cephalalgia;
- the presence of secondary nervous disorders.
According to sensations, cephalgia syndrome can be confidently defined as diffuse (pain spreads evenly over a large volume of the head without concentration) or localized (cephalgia manifests itself in a certain concentration in some areas). The first type of chronic headache indicates nervous pathologies or mental overstrain. If cephalgia tends to be localized, it means that the root cause lies in vascular disorders: very often this type of headache is characteristic of increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma). Expanding cephalgic syndrome is usually caused by manifestations of hypertension - primarily high intracranial pressure. If pain is acutely felt in one of the lobes of the brain, then this may be a local pre-stroke condition, or simple irradiation (redirection of cephalalgia) caused by a malfunction of the sympathetic nervous system.
The periodization of cephalgic syndrome is divided into two levels. The first determines the presence of a pulsating chronic headache, which can sometimes coincide with the beat of the heart (especially typical for hypertension and other central vascular disorders). The second level determines how often an attack of cephalgia occurs and how sharply the pain syndrome manifests itself. In vascular disorders, pain is associated with the occurrence of an imbalance in intracranial pressure, appears at a certain period and increases relatively sharply. If cephalalgia develops as a result of nervous overstrain and neuronal conduction disorders, then the pain appears at different times with a long period of increase.
Any secondary signs of headache are important for the correct diagnosis of cephalgic syndrome. For example, with a fairly acute course of cephalgia, a person develops a fear of bright light (photophobia) and sharp sounds (phonophobia). Such conditions are more typical for adults than for children. The body requires absolute rest and responds inadequately to stimuli associated with the activity of the central nervous system.
Doctors associate pain in the head area with disorders in the functioning of the blood vessels of the brain. They also manifest VSD, a similar type of which is called vasomotor.
There are three types of vegetative-vascular dystonia, each of which can cause cephalgic syndrome in a patient. The division into types is based on changes in vascular tone:
- Sympathetic type. The lumen of cerebral vessels periodically narrows through a spasm mechanism. As a result, parts of the brain experience a severe deficiency of blood, and with it oxygen. This is what causes the pain syndrome.
- The parasympathetic type is manifested, on the contrary, by excessive dilation of blood vessels and their oversaturation with blood. In this case, there is also a deficiency of blood flow, but there is also swelling and congestion of the brain tissue.
- The mixed version is considered the heaviest. With this type of VSD, a regular alternation of spasm/dilation of blood vessels occurs, which makes headache attacks severe and prolonged.
VSD of mixed type with cephalgic syndrome is considered one of the most difficult options for selecting effective treatment methods.
In the presence of such a pathology, in diagnosis, special attention is paid to the condition of the vessels of the brain and neck.
The diagnosis of VSD with cephalgia is made not only on the basis of complaints of periodic attacks of headaches. The connection between the pain syndrome and vegetative-vascular dystonia is indicated by additional manifestations characteristic of this syndrome.
With VSD of cerebral vessels, additional symptoms include:
- blurred vision, black dots moving in front of the eyes;
- nausea, vomiting, sweating;
- dizziness, fainting;
- development of panic syndrome, panic attacks;
- changes in body temperature, it either decreases or slightly exceeds 37 degrees
We recommend reading: Attacks of VSD: how they manifest themselves and how to help yourself
It is possible that other symptoms characteristic of VSD may appear in a particular patient under specific circumstances.
Reasons for development
VSD is not considered as an independent disease, but as a symptom of other diseases.
It is characterized by impaired functioning of the muscular layer of blood vessels with the subsequent development of dystonia. The following types of violations are distinguished:
- dystonia of the sympathetic type;
- parasympathetic dystonia;
- mixed type.
Under the influence of the sympathetic nervous system, vascular tone increases, which leads to their short-term narrowing like a spasm. As the lumen of the vessels decreases, blood flow also decreases, causing some areas to receive less blood. Hypoxia of brain tissue can lead to the development of cephalgic syndrome.
The parasympathetic nervous system produces the opposite effect - the tone of the blood vessels decreases and they become overfilled with blood. As a result, brain cells receive less oxygenated blood.
Another reason for headaches is venous congestion and overflow of the blood pools of the brain. With the development of persistent dystonia, cerebral venous hypertension may be observed. Overflow of the sinuses of the dura mater with venous blood leads to congestion and increased intracranial pressure (ICP).
With autonomic dysfunction, this almost never happens. If a person experiences a symptom of increased intracranial pressure:
- venous congestion in the fundus;
- bursting headache;
- vomiting without nausea;
– you need an MRI or CT scan and consultation with a neurosurgeon.
With a mixed type of VSD, pathological processes alternate with each other: vascular hypotension is replaced by hypertension and vice versa.
Cephalgia with vegetative-vascular dystonia
Headaches or cephalalgia syndrome may appear as a separate disease or signal other health problems. Very often, pain appears against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia. At the same time, during the diagnosis of physical organs, the doctor does not observe any deviations from the norm.
Features and nature of pain
Click to enlarge
Vegetative-vascular dystonia can manifest itself in the form of various headaches. There is often a feeling of emptiness, as well as a feeling of numbness. Many patients report pain attacks in the temples and forehead. Sometimes pain can spread to the eye area, leading to light intolerance.
VSD with cephalgic syndrome can also manifest itself as localization in a specific hemisphere, an additional burning sensation, and increased blood pressure. Very often the pain resembles a migraine, and it appears both suddenly and gradually increases the pain threshold. In most cases, nausea and dizziness are additionally observed.
Dystonia is often aggravated by muscle tension and, as a result, compression of blood vessels occurs. As a result, VSD develops as a vasomotor cephalgic syndrome.
Characteristics of headache
With a vegetative disease, symptoms can manifest in different ways. Cephalgia with VSD is divided according to the nature of the pain into:
- intense,
- permanent,
- pulsating,
- pressing,
- short-term
- impulsive.
When the pain is intense, the symptom is pronounced, the person’s general condition sharply worsens, and their performance decreases. Any movement can cause pain, which is aggravated by loud noise or bright light.
The patient experiences constant pain for a long period of time. At the same time, it does not become weaker or stronger. This is observed with venous stagnation in the vessels of the brain.
Pulsatile syndrome is characterized by the presence of pulsation in the vessels. This is observed when large vessels are affected. The pulsation is located in one place. This often causes blood pressure to rise. This type of headache is often observed in children with vegetative-vascular dystonia and acute hypertensive encephalopathy.
The pressing nature of the pain occurs over a large area. Patients feel that the head is being squeezed on both sides or around the entire circumference.
Short-term - appears for a short time and passes quickly. It can be easily relieved with painkillers. For some, the symptom becomes more frequent and takes on a different character.
Impulsive is manifested by tingling from mild sensations to sharp local pain. With frequent manifestations, the patient loses ability to work.
Symptoms associated with cephalgia
Patients often experience various symptoms of VSD. The occurrence of only headache in the clinical picture of VSD is almost never encountered. With VSD, in addition to headache, the following symptoms are observed:
- increased fatigue;
- dizziness;
- fainting, nausea, vomiting;
- spots before the eyes;
- anxiety, panic attack;
- blood pressure surges;
- dyshidrosis (dysfunction of the sweat glands);
- deterioration of body temperature regulation.
Cephalgia with dystonia can occur as a reaction to weather changes. Pain syndrome occurs suddenly without external causes. After this, the patient feels a loss of strength.
Cephalgia often causes discomfort, attacks are frequent and prolonged, and painkillers do not help. Weakness gradually develops and performance deteriorates.
Diagnosis and treatment
To finally determine what type of cephalgia the patient has developed, certain laboratory tests are prescribed. In particular, your doctor may recommend the following:
- Get a CT scan and MRI of the head and neck.
- Take an encephalogram.
- Examine the condition of the fundus, check intraocular pressure and visual acuity.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the cervical spine and head.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
- Rheoencephalogram to check blood flow in the head.
Treatment of cephalalgia will primarily depend on the type of disease. The diagnosis can be made either after an initial examination by a doctor, when leading questions are asked, or after tests have been completed (in uncertain situations). For example, if cephalgia develops due to VSD, a neurologist may prescribe mild sedatives, motherwort, and valerian to slightly calm the nervous system. Most likely he will recommend physical therapy, baths, vitamins.
If you have vasomotor cephalgia (muscle tension), then you should do therapeutic exercises, sign up for a massage, go to the pool, or possibly take medication. In this situation, it is important to maintain a daily routine, get good sleep and experience less stress.
If you have been experiencing headaches for a long time, you should definitely consult a doctor to rule out the most unfavorable consequences for your health.
When hydrocephalus of the brain is observed in an adult during work, it is worth stopping the work process and resting or going for a walk (this will ease the condition of the body), otherwise the chronic stage will develop. If this is not possible, you need to moisten a towel with cold water and apply it to your forehead. You can use other methods, for example, a contrast shower. Treatment of cephalalgia should be based on eliminating the cause of overexertion or a stressful situation, as well as facilitating general well-being in accessible ways.
If we talk about the treatment of cephalalgia in general, then most often it is prescribed:
- Physiotherapy.
- Drug treatment.
- Aromatherapy.
- Surgical intervention.
- Manual therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Reflexology.
- Osteopathy.
Now you know what cephalalgia is and how it manifests itself. To exclude the development of the disease, it is important to follow certain recommendations. These include sleep (the required number of hours to rest), reducing the number of stressful situations, regular walks in the fresh air, increasing immunity and giving up bad habits. Do not forget that a diagnosis can only be made by an appropriate specialist and observation by a doctor is an integral part of recovery.
We recommend reading: Betaserc for VSD
Drug treatment
Therapy for severe syndrome should include medication, adherence to a daily routine, proper nutrition and traditional medicine. Due to the large number of causes that lead to the syndrome, its treatment varies greatly. But with any form of cephalalgia, you should definitely put everything aside and just relax.
Further actions depend on the source of pain:
- To relieve pain in persistent cephalgic syndrome, you need to take any painkiller, for example, Analgin, Solpadeine, Panadol. If the pain is too severe, the drug should be administered intravenously or intramuscularly. It must be remembered that Analgin is contraindicated for use by people suffering from bronchospasms or bleeding.
- In order to get rid of pain due to vascular disorders, blood pressure should be normalized. For low levels, “Eleutherococcus extract” and “Pantocrine” will help; for high levels, “No-shpa” and “Curantil”. Each drug has contraindications and side effects, so before using them you should definitely consult your doctor.
- If cephalgia is a consequence of VSD, you should massage the temple area, take a walk outside, and then put a cool compress on your forehead or take a contrast shower. All this should help the body cope with the disease. It will also not hurt to take the following medications simultaneously: Eufillin, Caffeine, Cavinton, Furosemide and Veroshpiron.
- For migraines, you need to take: Paracetamol. If relief does not come - “Imigran”.
- Pain during tension cephalgia is relieved with conventional analgesics, but the treatment itself most often requires the inclusion of antidepressants: Aleval, Paroxin, Zalox, Aminotriptyline.
- In order to relieve tension and relax the body, specialists can prescribe muscle relaxants: Dillacin, Clindamycin, Milagin.
- For almost any form of cephalgic syndrome, various physiotherapeutic procedures and psychotherapeutic effects help: therapeutic massage of the cervical-collar area, pine, hydrogen sulfide, salt and radon baths, as well as contrast showers in the morning.
Non-drug forms of treatment
Before giving headache tablets to children, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate possible triggers. Among the activities of paramount importance:
- normalization of the daily routine,
- eliminating the likelihood of physical and mental overload,
- ensuring a favorable psychological climate in the family and children's team,
- creating conditions for good sleep,
- restrictions on the use of gadgets and watching television programs,
- involving the child in active physical activity: attending sports clubs, regular walks in the fresh air.
In many cases, food allergies act as triggers in the development of migraine attacks. Doctors recommend excluding the following foods from your diet or limiting them to a minimum:
- hard cheese,
- chocolate,
- milk,
- oranges,
- eggs.
For headaches of a psychogenic nature, it is advisable to do morning exercises every day and place the child in the wushu or yoga section.
If you experience emotional disorders, changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, or severe adolescence, you must contact a child psychologist or psychotherapist and resort to psychotherapy techniques.
Acupuncture shows good results in the treatment of patients with cephalgia.
To improve the general condition of the body with cephalgic syndrome, you can also use traditional medicine. But before using them you should also consult your doctor.
- Attacks of cephalalgia can be relieved with warm compresses of freshly brewed mint and teas made from it.
- A lemon peel and a cabbage leaf, which should be applied to the temple area, will also help.
- An infusion of St. John's wort will help relieve pain. It should be taken throughout the day in small sips.
- Calendula tincture with alcohol will relieve migraines if applied behind the ear. In this case, you should wrap your throat with a wool scarf and lie down for a while. Within 20 minutes the condition should improve.
- To reduce pressure, you can take foot baths, put mustard plaster on the calf muscle or shin. Apple cider vinegar compresses applied to the sole of the foot will also help.
- Baked potatoes or beet juice with lemon, honey or currants will help cope with hypertension.
- To increase blood pressure, you can drink coffee or strong tea with sugar, or eat dark chocolate.
During treatment of cephalgic syndrome, you should not try to treat headaches without the advice of a doctor. The therapy chosen by the patient may be incorrect, which will ultimately lead to the development of the disease and the appearance of associated complications. Also, frequent use of painkillers can worsen the condition of other organs in the body.
Before you begin treating pain, you need to undergo a full examination of the body and find out the true cause of the anomaly.
A truly experienced and competent doctor should not only prescribe medication, but also adjust the patient’s daily routine, recommend a set of physical exercises, therapeutic massage, manual therapy, psychological training and psychotherapy to improve health.
Prevention and complications
Rather than carry out long-term treatment for cerebral vascular dystonia, it is better to take timely care to prevent the development of pathology. In many ways, preventive and therapeutic measures are similar. To avoid the development of corresponding symptoms, it is recommended to lead a correct lifestyle (exclude bad habits), observe a work and rest schedule, proper nutrition, rational physical activity, and avoid emotional stress.
Among the complications of cerebral vascular dystonia are vegetative crisis and the development of panic attacks. If left untreated, the pathology is complicated by heart disease and mental illness.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not a dangerous disease, but it significantly worsens a person’s quality of life. Therefore, in order to reduce the severity of unpleasant symptoms, you need to start appropriate treatment as early as possible and adhere to the doctor’s prescriptions.