Causes
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, the performance of the autonomic system and blood vessels is extremely unstable. Functional dysfunction can occur under the influence of environmental factors.
Fainting is a fairly common symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia. They are usually preceded by physical and emotional stress, a sharp change in climatic conditions, changes in body position, and alcohol intake.
In this case, the function of the autonomic system is disrupted, the lumen of blood vessels expands, blood pressure decreases and the development of hypoxia leads to short-term loss of consciousness.
Often the causes of loss of consciousness are:
- Physical or emotional stress. After a person diagnosed with VSD has experienced strong emotions, a pre-fainting state may occur. If measures are not taken, the person loses consciousness.
- Overfatigue, which occurs when there is no rest during work.
- Stressful situations that have a negative impact on the nervous system and blood vessels, resulting in a disruption in their performance.
- A sharp change in climatic conditions. Changes in the weather also affect blood vessels, which leads to loss of consciousness.
- Prolonged stay in a stuffy room. As a result, oxygen deficiency develops.
- Sudden change position . Fainting often occurs after moving from a horizontal to a vertical position. When the VSD is established, it is not recommended to bend over sharply, stand up or lie down.
- Drinking alcohol also has a negative effect on the cardiovascular system.
Nutrition for vegetative-vascular dystonia
VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia) is a functional disorder of the autonomic nervous system.
When exposed to negative factors, a number of the following changes occur in the body:
- The functions the autonomic system are disrupted, smooth muscle elements relax.
- The lumen in large and small vessels expands significantly
- Blood pressure decreases .
- Blood flow to the brain decreases several times.
- Oxygen develops .
As a result of changes occurring in the body under the influence of negative factors, a short-term cessation of brain function occurs. Brain tissues are highly sensitive to lack of oxygen, and protective mechanisms are activated.
To avoid fainting when playing sports with a diagnosis of VSD, strength gymnastics, high jumps, exercises with high amplitude, sudden and fast movements are strictly contraindicated.
Also, you should not exercise in an upside-down position and use those exercise machines where the position of the head is lower than the level of the body.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
What happens in the body during the progression of vegetative-vascular dystonia
With the development of VSD, a disorder of nerve communications occurs between the brain and body systems: gastrointestinal, hormonal, urinary and reproductive, vascular, and nervous.
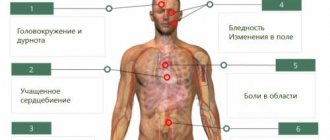
These disorders contribute to fainting during VSD and have the following manifestations:
- increased irritability;
- dizziness;
- increased heart rate;
- pain in the heart area;
- respiratory rhythm intensity;
- feeling of lack of air;
- vomit;
- disorders of the bladder emptying process;
- sexual dysfunctions;
- jumps in body temperature;
- surges in blood pressure.
Presyncope signs of VSD
Autonomic dysfunction (VSD) is a disease that occurs against the background of various disorders of the cardiovascular and autonomic systems. It is she who controls everything in the body and with any minor changes in functioning they suffer:
- genitourinary;
- nervous;
- hormonal;
- digestive;
- respiratory;
- cardiovascular.
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Even highly qualified specialists can find it difficult to recognize vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD).
A minor malfunction in the performance of any of these systems leads to the appearance of signs of VSD, presyncope and loss of consciousness.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia include:
- Irritability, sudden onset of dizziness.
- Pain in the heart muscle, breathing problems.
- Oxygen deficiency, shortness of breath.
- Decrease and increase in blood pressure.
- Disruption of the urination process.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Increase and decrease temperature .
Typically, a person does not lose consciousness suddenly. The pre-fainting state is accompanied by certain symptoms and after their occurrence, several minutes pass before fainting, which is quite enough to stop the attack.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Signs of fainting include:
- Severe dizziness.
- Trembling in the fingers.
- Nausea, in some cases vomiting may occur.
- General weakness.
- Short-term darkening of the eyes.
- Impaired coordination .
- Cold sweat.
- State of panic, fear of death.
- Paleness of the skin surface.
- Great fright.
- Tinnitus .
- Numbness in the limbs.
All symptoms of presyncope occur suddenly, regardless of time, place and human activity. At the same time, the patient gets scared, which significantly worsens their course.
Symptoms of approaching loss of consciousness
The pre-fainting state does not last for an hour or two, it comes on suddenly and lasts from 3 seconds to 3 minutes. During this period of time, a person experiences the following changes in his own state:
- heart rhythm disturbances occur;
- sudden emptiness and lethargy sets in, accompanied by a drop in blood pressure;
- the outflow of blood from the brain causes darkness before the eyes;
- a sharp decrease in consciousness is accompanied by weakness;
- dizziness and fainting are interspersed with symptoms such as the appearance of black spots before the eyes and tinnitus.
We recommend reading: Dizziness with VSD
From a medical point of view, the human body in a state of fainting shows the following:
- consciousness is lost or fleetingly clears up;
- pupils dilate;
- eyes react to light slowly and reluctantly;
- the pulse becomes weak, thread-like;
- blood pressure becomes extremely low;
- There may be tremors in the legs and some urine leakage.
After a person returns to consciousness, he may feel weak, have difficulty standing, sweat profusely, and complain of dry mouth mucous membranes. The speech of such a person will be clear, understandable, but somewhat slow. All these signs make it possible to distinguish fainting in a person with dystonia from the consequences of cerebrovascular accidents or TBI.
How to stop an attack
Patients who have suffered from a disease such as VSD for a long time know what precedes fainting and how to prevent it. The main task in this case is to dilate blood vessels so that blood begins to flow into the brain.
To do this you need:
- Sit on a chair and lower your head as low as possible. This will help restore blood circulation in the brain for a while.
- Sniff a substance that has a strong odor, such as ammonia, cologne, or perfume.
- Restore breathing. To do this, you need to take a paper bag and inhale and exhale into it.
- Engage in mental work, such as reading.
When the first signs of dizziness appear, you need to calm down, restore breathing and blood circulation.
How dangerous are fainting?
If a person loses consciousness for the first time, even for a few seconds, he needs to visit a specialist. This may be a sign of severe pathologies. Sometimes they do not make themselves felt for a long time, manifesting themselves only as fainting.
When a patient is diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dysfunction, usually no other serious pathologies are detected. However, this does not mean that the disease does not need treatment.
A constant feeling of anxiety, disruption of normal blood circulation, and surges in blood pressure lead to dangerous pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, which can cause a person to have a heart attack or stroke.
How to prevent fainting
Regular exercise plays an important role in the prevention of fainting during VSD. In this case, you need to choose a set of exercises that the patient will tolerate well and not overwork. Swimming, yoga, cycling, aerobics, and race walking have a positive effect on the nervous system and blood vessels. Constant physical activity will help keep your body in good shape.
In addition, regular walks in the fresh air help restore strength. It is preferable to perform them in a quiet place, for example, in a park, near water bodies for three to four hours. It is very important to take into account weather conditions, wear a hat, and keep your feet warm.
Every patient diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia has a tendency to faint. That is why it is necessary to regularly go out into the fresh air and take oxygen baths, since one of the reasons for the development of a pre-fainting state is a lack of oxygen in the brain.
Symptoms and treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women
The term “vegetative-vascular dystonia” is commonly used to describe a disorder of the autonomic nervous system, which affects women twice as often as men.
Mental stress is of particular value in the prevention of fainting during VSD. Patients with this diagnosis are recommended to devote time to mental activity every day, for example, reading books, solving riddles, crosswords, learning foreign languages, solving mathematical equations and problems.
But it should be remembered that mental overstrain can also cause fainting. Therefore, there is no need to overload your brain and take breaks. In cases where work activity involves constant mental stress, after a hard day you should give preference to active types of recreation.
What to do if the condition worsens
If you feel fainting approaching, you should sit down or take a horizontal position. If this is not possible, you should at least simply lean on any stable object located nearby. Sometimes a person feels better if he bends down. You also need to try to tense your muscles as much as possible. Next, you need to fully concentrate on breathing. You need to breathe with your stomach, deeply and slowly.
You can rub your ears with your palms and press your finger on the dimple under your nose. In addition, a person who often experiences fainting conditions should always have ammonia or fresh ginger with him.
There is no need to get up suddenly, as soon as the condition begins to improve, you need to remain calm for a few more minutes. Then you can drink a glass of water or a cup of warm tea with sugar.
We recommend that you read: What causes loss of appetite during VSD?