Causes of pineal cysts
The main risk factors for development include:
- disruption of outflow through the excretory duct due to compression by a neoplasm, a focus of inflammation, can be a consequence of an anatomical defect (for example, an excessively narrow or tortuous duct), blockage with pus particles;
- infection with a parasitic infection, often echinococcosis;
- the formation of a cyst at the site of hemorrhage during a hemorrhagic stroke or a lesion during ischemia (insufficient blood flow);
- traumatic brain or birth injury.
We recommend reading the article about the pineal gland in the brain. From it you will learn about what the pineal gland of the brain is, the structure and functions of the pineal gland, characteristics in children, as well as the main diseases that you may encounter.
And here is more information about the hormone serotonin.
Preventive actions
It has been determined that hypoxia of the central nervous system is an almost unambiguous factor.
Therefore, one of the prevention options is regular moderate physical activity in the fresh air (always in the fresh air), and sometimes taking vasodilating drugs.
Since echinococcus is one of the causes, it is necessary to observe appropriate sanitary safety measures.
Types of epiphysis formation
Depending on the morphological (structural) characteristics and mechanism of appearance, several types of pineal cysts have been identified.
Sizes: small, large
If the cavity has a diameter of up to 0.5-0.9 mm, then its course is asymptomatic in most cases. During MRI, such formations are found by chance, their prevalence reaches about 5-7% of all studies. A large cyst is considered to be a structure larger than 1 cm. It causes compression of blood vessels, epiphysis tissue, and outflow tracts of intracerebral fluid. Its course resembles a tumor process.
Brain pineal cyst
Simple and false
When neuroglia (non-functioning tissue) grows in patients with severe hypertension, rheumatism, or renal hypertension, a false cyst is formed.
In the depths of such accumulations, cells are destroyed, and a cavity appears in their place. Unlike a simple cyst, it does not have a lining layer inside. False formations also occur with drowning, rabies, tetanus infection, acute inflammation, acute swelling of the epiphysis.
Simple true cysts are covered with cells on the inside and have a well-defined outer shell of connective tissue fibers. Between these layers there is a middle one, formed by the tissue of the epiphysis. It may also contain calcium deposits.
Congenital in a child
The formation of a cyst in the fetus is associated with maternal infections, alcohol, smoking, and lack of blood flow through the placenta due to circulatory disorders. Oxygen starvation of the child’s brain also occurs with diabetes mellitus or its gestational form in a pregnant woman.
Acquired cyst in the epiphysis of the brain in an adult
Most often, cystic formations appear after trauma or neuroinfection affecting the brain. The formation is also caused by circulatory disorders due to blockage or rupture of cerebral vessels. It should be taken into account that a tumor of the pineal gland can also undergo cystic degeneration over time.
Treatment
Asymptomatic formations are under constant medical supervision: twice a year a person undergoes CT and MRI. Treatment of cerebral epiphysis cysts in such situations is not carried out as unnecessary. In circumstances where the formation causes unpleasant symptoms, the doctor selects possible treatment options. As a rule, such neoplasms are treated conservatively, that is, with medication or surgery. Drug treatment is aimed at eliminating symptoms, and surgery is performed when there is a threat to life.
Diagnosis of cerebral epiphysis cyst
Drug therapy for large cystic formations of the epiphysis includes the following drugs.
- Diuretics (Diacarb, Mannitop, Furosemide). They are prescribed to reduce intracranial hypertension and eliminate signs of brain swelling.
- Anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Finlepsin). Effective for convulsive manifestations that are characteristic of parasitic lesions.
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Ketorol, Naproxen). Taken for intense migraines.
- Neuroleptics and tranquilizers. They are used for obvious psychotic disorders.
This medical therapy is not often used for true genetic cysts, since they rarely grow large enough to cause seizures, but diuretics and painkillers are prescribed for many patients. In addition, the doctor may recommend adaptogens, as well as the drug melatonin for sleep problems.
Surgical intervention for an epiphysis cyst is indicated in the following cases:
- echinococcosis;
- acute occlusive hydrocephalus;
- rapid growth of formation, causing tissue compression;
- formation more than 1 cm in diameter, causing neurological disorders.
Surgical removal of an epiphysis cyst is carried out through craniotomy.
Surgical removal of an epiphysis cyst is carried out through craniotomy. This is a very complex intervention, associated with serious consequences - the pineal gland is located very deep and when trying to get to it, damage to neighboring tissues is likely. Although the problem will disappear after trephination, residual side effects are likely.
That is why such intervention is carried out purely based on vital signs. Naturally, any intervention in brain tissue is associated with enormous risks, so neurosurgeons approach the treatment of true epiphysis cysts with great caution, but echinococcosis leaves no other options. In this case, surgery is not just the only alternative to improve the condition, but often the last chance to save a person’s life.
Signs of an epiphysis cyst
Small cysts are asymptomatic. Manifestations usually occur when the mass is larger than half the size of the pineal gland itself. There are no typical signs by which this particular disease could be suspected. Problems with health depend both on the size of the cysts and the direction of tissue compression. The most common are:
- headache, almost not relieved by painkillers;
- loss of clarity of vision, double vision;
- feeling of fullness, pressure on the eyes;
- nausea, vomiting;
- gait instability, impaired coordination of movements;
- increased fatigue;
- seizures.
Parasitic cysts can cause decreased sensation and motor function.
More rare symptoms are also possible, caused by the pressure of a large cyst on neighboring tissues:
- convergent strabismus;
- inability to look up;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- refusal to eat or constant feeling of hunger;
- elevated or extremely low body temperature;
- unusual drowsiness;
- diabetes insipidus (unquenchable thirst, excessive urination);
- obesity.
Drooping of the upper eyelid
Hydrocephalus and cyst in a child
The most serious manifestation of a pineal cyst is blockage of the outflow of intracranial fluid. This leads to dropsy of the brain - hydrocephalus. Increased blood pressure causes headaches, nausea and vomiting. They have no connection with food intake, may be accompanied by nosebleeds, and the child holds his head in an unnatural position to relieve pain. Often there is simultaneous visual impairment, tinnitus, and convulsions.
In newborns, the accumulation of fluid in the cranial cavity causes frequent regurgitation and anxiety. Upon inspection you can see:
- head enlargement,
- divergence of cranial sutures,
- protrusion of the fontanelle,
- dilation of veins on the skin.
Such children are weakened, their skin is pale, they experience sweating and fatigue when feeding.
Consequences for the patient
When the cyst completely blocks the outflow of liquor fluid from the skull, an attack occurs. Its manifestations may be:
- intense headache;
- repeated vomiting;
- first redness, then pallor of the skin;
- eye movement disorders;
- fainting state.
In extremely severe cases, after an attack, there is a displacement of brain tissue and wedging of the medulla oblongata into the foramen magnum. This leads to compression of the centers regulating the work of the heart and lungs. If medical assistance is not provided immediately, death occurs.
For epiphysis cysts, such complications are rare; they are most often provoked by trauma, severe hypertensive crisis, or acute circulatory disorders in the pineal gland area.
Peculiarities
A benign tumor develops in the pineal region—the epiphysis. This area is located in the deep layers of the brain; the full range of its functions is not fully defined. When the pineal gland is damaged by a cyst, the outflow of hormones responsible for the cycle of sleep and wakefulness and puberty changes.
The outflow of hormones responsible for the cycle of sleep and wakefulness and puberty changes.
A cavity with liquid contents is rarely identified during a routine visit to a therapist. This usually occurs during a comprehensive examination for the presence of other pathologies.
Sometimes a cyst in the pineal region of the brain forms before birth. The patient can live with it all his life, sometimes experiencing minor symptoms.
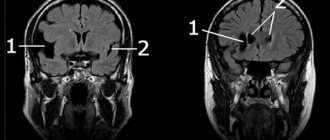
MRI and other diagnostic methods
Since the clinical picture of the disease is often absent, the detection of an epiphysis cyst is accidental during brain tomography. MRI has an advantage over CT in terms of the frequency of detecting small cysts. Additional contrast can help with targeted searches. The accumulation of contrast occurs only in the capsule of cystic formations, which distinguishes them from tumors of the epiphysis.
The remaining methods are uninformative. They can only detect signs of intracranial hypertension when the cyst compresses the outflow tract of cerebrospinal fluid:
- examination by a neurologist - disturbances in eye movements, poor performance of coordination tests, hypothalamic dysfunction;
- examination by an ophthalmologist - swelling of the optic discs;
- EchoEG - signs of displacement of brain structures, absence of foci of pathological activity characteristic of epilepsy.
Pineal cyst on MRI
Symptoms
Pinealoma refers to such neoplasms, in the presence of which a person can live his entire life without even knowing about their existence. This is especially true for small cysts (5 – 8 mm). Sometimes a headache may occur, but it quickly stops after taking conventional analgesics. But an increase in the amount of fluid in the cyst and its “swelling” to 1–2 cm is already accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms. Attacks of pressing headaches become frequent, noises appear in the head, night insomnia and daytime drowsiness appear (disruption of circadian biorhythms). Impaired motor coordination and the development of visual disturbances (doubling or blurriness of objects) are possible. In case of parasitic infection, the decay products of echinococci accumulated in the cystic cavity can cause symptoms of intoxication - nausea, vomiting.
In special cases, when pinealoma reaches very large sizes (more than 2 cm) and begins to put pressure on neighboring parts of the brain, its presence causes serious health problems: increased intracranial pressure, tremors of the limbs, disorientation in space, the appearance of neuroses and even epileptic attacks . And the most serious complication of an overgrown pineal gland cyst is the development of hydrocephalus (dropsy). This pathology occurs due to blockage of the excretory tract and disruption of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which often leads to irreversible mental and neurological disorders.
Treatment of children with hydrocephalus and epiphysis cyst
If there are signs of blockage in the movement of intracerebral fluid, it is necessary to prevent the possibility of brain displacement. Therefore, osmotic diuretics, magnesium sulfate, are prescribed. They do not allow long-term stabilization of the child’s condition, so surgical treatment is indicated.
In children, the method of choice is bypass surgery. Drainage is installed from the third ventricle of the brain into the right atrium or abdominal cavity. This operation can be performed with an endoscope, which significantly reduces the risk of damage to adjacent brain structures. Open access to the epiphysis is extremely difficult; it rarely allows one to avoid postoperative complications.
Modern shunt systems provide the ability to regulate intracranial pressure using a valve whose movement can be programmed. However, even these operations cannot provide a 100% guarantee of the absence of relapses and the need for re-intervention.
A child after bypass surgery should be under regular supervision of a neurologist, since the possibility cannot be excluded:
- addition of infection;
- displacement or separation of parts of the shunt;
- blocking the movement of liquor fluid.
If there is a valve failure, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid becomes rapid, which is accompanied by dizziness, fainting, and severe headache.
Neurosonography for a child
Cyst removal in adults
Small formations that do not compress surrounding tissue do not require removal. Patients are advised to undergo dynamic monitoring - at least once every 6 months they need to undergo an MRI. If there is significant growth or clinical symptoms, surgery is prescribed. It may involve shunting or removing the contents of the cyst.
Removing the contents of an epiphysis cyst
In cases where there is a threat of bleeding or rupture, and there is also a confirmed diagnosis of echinococcosis, then the operation is performed using open access with craniotomy. The cystic formation must be completely excised.
If there are no complications, then endoscopic removal through an opening in the skull is possible. An endoscope is inserted into it, fluid is pumped out from the cyst cavity, and its connections with neighboring ventricles or other natural accumulations of cerebrospinal fluid are established.
We recommend reading the article about hemorrhage in the pituitary gland. From it you will learn about the causes of hemorrhage in the pituitary gland, the main symptoms of hemorrhage of adenoma and microadenoma, as well as methods for diagnosing and treating hemorrhage in the pituitary gland.
And here is more information about melanostimulating hormone.
A pineal cyst occurs during fetal development or appears after birth due to injuries, infections, vascular disorders, or compression of the pineal duct from the outside. Depending on the characteristics, small and large cysts, simple and false, and parasitic are distinguished.
Small formations are asymptomatic, but large ones are manifested by hydrocephalus, compression of adjacent brain structures. If the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is completely disrupted, there is a risk of severe complications. Treatment is surgical, it is carried out in the form of bypassing the cyst cavity or its removal.
Possible complications
As already mentioned, severe complications with an epiphysis cyst arise only when the formation reaches an impressive size. And if left untreated, it can eventually cause hydrocephalus. In addition, compression of brain tissue is observed, which leads to an increase in intracerebral pressure, and this is fraught with the appearance of general cerebral symptoms: deterioration of memory, hearing, decreased level of intelligence and a drop in visual acuity.
Also, do not forget about the consequences of surgical intervention discussed above. But in any case, none of the manifestations should be left unattended. If there is a sharp deterioration in the condition, you should immediately contact a neurologist, especially if alarming symptoms are observed in the child. And you need to approach alternative treatment methods with great caution: unfortunately, they not only do not reduce formations, but can also lead to serious consequences (for example, intoxication).
Useful video
Watch the video about pinealoma - a tumor of the pineal gland:
Similar articles
- The pineal gland of the brain: the size of the pineal gland...
The third eye, the place of the soul in the human body, the internal compass - this is the name of the pineal gland of the brain (epiphysis). Its size and structure differ in children and adults. The main functions are the influence on hormonal levels, the release of three hormones. Read more - Thyroid cyst: main causes, symptoms...
A thyroid cyst is often found. But not all of them require treatment. The main reasons are organ dysfunction, iodine deficiency; symptoms may be absent at first. There are follicular, colloid, small, multiple, of both lobes. Why are they dangerous? When is removal surgery necessary? Read more
- Serotonin, the hormone of happiness: what it is responsible for, the main...
Serotonin is believed to be the hormone of happiness. In general, this is true, because its main functions help regulate the condition. It is also responsible for mood, for example, with a deficiency, depression develops. It is important to get tested for the hormone. Read more
- Hemorrhages in the pituitary gland: main symptoms, MRI with...
Often, hemorrhage into the pituitary gland occurs with adenoma and microadenoma. Unfortunately, the symptoms are similar to a heart attack or stroke, and it is not always possible to diagnose it in a timely manner. For an accurate determination, CT and MRI are used. Read more
- Melanostimulating hormone (melanotropin): how...
In the body, melanostimulating hormone not only gives pigmentation to the skin, hair, and mucous membranes, but also acts as a kind of protection from rays. It is also called melanotropin. What is the effect of excess and deficiency? Read more
Reasons for development
As a rule, the formation of a cyst-like cavity in any part of the endocrine system is a consequence of blockage of the excretory pathways of a hormonal substance produced by a certain organ. Pinealoma of the epiphysis is no exception. The most common causes of the appearance of a cyst, a violation of the outflow of melatonin and its accumulation in a kind of sac, are associated with a traumatic factor - a concussion, the formation of an internal hematoma and subsequent hemorrhage into the pineal body. This pinealoma usually does not grow and does not cause pronounced negative symptoms.
It is much worse if the formation of a cyst in the pineal gland is caused by a parasitic infection. In particular, it has been revealed that cystic transformation of the pineal gland often occurs after infection of the body with echinococci (tapeworms or helminths). These harmful microorganisms penetrate the pineal gland through the bloodstream, creating a protective encapsulated shell in the gland, where the products of their vital activity accumulate. In such cases, pinealoma gradually increases in size and begins to have an adverse effect on nearby brain structures.
In addition to the main reasons for the development of this pathology, sometimes a cyst is detected in the pineal gland in infants. This is an extremely rare phenomenon that occurs due to birth injuries, hypoxia, infectious infection or autoimmune disorders. Pinealoma in young children is usually small in size, does not cause any particular concern, and therefore does not require special treatment. However, children with such an anomaly should be monitored by a pediatrician.