Rating: 5/5 (2)
When a baby is born, doctors conduct various studies to determine its health status. One of them is an ultrasound, which can detect cysts in the brain - they are diagnosed very often in newborns (according to some sources, in every fourth child).
However, this disease is not a reason for parental panic, since some types of cysts do not require intervention at all, while others can be cured. Let's figure out what kind of disease this is, how it is diagnosed, treated, and what consequences a cyst in the head of a newborn may have.
What is a cyst
Doctors use this term to refer to benign formations that are localized in various parts of the brain or near it and are cavities with fluid inside. Depending on the time and cause of its appearance, the cyst may disrupt the development of the baby, but may not have a negative effect on health.
Diagnostic methods
Primary diagnosis is based on an ultrasound examination of a pregnant girl. Using ultrasound, the doctor simultaneously performs two tasks: assesses the condition of the internal organs of the expectant mother and her baby. If, during an ultrasound examination, a hollow capsule was discovered in the embryo’s brain, the doctor decides to carefully monitor the pregnant girl.
Neurosonography is used for secondary diagnostics in infants. This procedure is based on performing an ultrasound examination of the internal organs of a newborn using a non-overgrown fontanel. If during the diagnosis the doctor discovers a tumor in the brain, six months later the little patient is re-examined to exclude the possibility of cyst growth.
In order to determine the cause of the formation of a benign formation in the baby, the doctor removes blood for laboratory diagnostics. The use of computed tomography as an auxiliary diagnostic method is strictly prohibited.
Causes
The question of why cysts form in infants is quite complex even for neurosurgeons themselves.
There can be many reasons, and the time of cyst formation plays a role. If it is congenital, most likely the appearance of the neoplasm is caused by the genetic characteristics of the fetus or the mother herself, or a “failure” in the process of intrauterine development. Sometimes cysts are formed due to infectious or inflammatory processes that occurred during pregnancy.
As for cysts that appeared after the birth of a little person, the following reasons are identified:
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- encephalitis, meningitis, entry into the body of the herpes virus;
- birth or other injuries;
- congenital pathologies of the central nervous system or cerebrovascular accidents.
Prevention
In order to reduce the risk of developing a vascular cyst in a baby, a girl needs to follow simple rules during pregnancy:
- Eat a balanced diet: provide the fetus with healthy vitamins and minerals.
- Maintain an active lifestyle: regularly take walks, visit the pool, and perform special exercises.
- Strengthen the immune system by regularly taking vitamin complexes.
- Prevent the risk of hypothermia: select clothing appropriate to the weather conditions.
Since a benign formation develops asymptomatically, a pregnant girl should regularly attend an ultrasound scan so that the doctor can detect the pathology in a timely manner.
Symptoms
Mothers do not always suspect that something is wrong with their baby. Often, the brushes in the baby’s head do not manifest themselves in any way and do not bother the newborn. However, there are some signs that suggest that the baby has cysts:
- swelling of the fontanel or its pulsation;
- frequent causeless vomiting, regurgitation;
- developmental delay, motor skills;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- blurred vision.
Although cysts most often do not change in size, they can sometimes become larger. This is evidenced by the following symptoms:
- disturbances in the functioning of the sense organs;
- headache;
- change in intracranial pressure;
- epileptic seizures or fainting;
- lack of coordination.
Examination and diagnosis
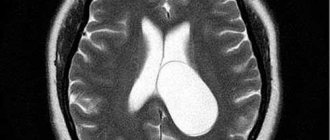
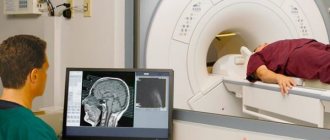
MRI or CT will provide unambiguous information about the presence, size and location of the cyst. A study with intravenous contrast helps to distinguish a cyst from a tumor You can perform such a study at the Clinic of the Academy of Sciences .
MRI scans of the brain. 1. Cyst after cerebral hemorrhage 2. Cerebellar cysts after ischemic stroke (blockage of cerebral arteries) 3. Cystic adhesive arachnoiditis
To avoid the enlargement and appearance of new cysts , we must clearly understand and treat the root cause of their occurrence. Therefore, we carefully examine you for circulatory disorders, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
Doppler ultrasound of the head and neck vessels (USDG) will help detect narrowing of the vessels that supply the brain with arterial blood. Lack of blood supply can lead to focal death of the brain matter and the appearance of cysts.
Heart studies (ECG, Echo-CG) . The brain may not have enough blood supply due to rhythm disturbances or heart failure.
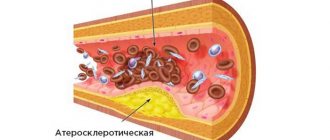
Blood test for clotting and cholesterol. An increase in cholesterol concentration in the blood and increased clotting are the main causes of blockage of brain vessels with subsequent formation of cysts. This problem is easily solved with the help of modern medications.
Blood pressure monitoring. Episodic increases in pressure are a common cause of strokes and post-stroke cysts. A monitor is a small device that is constantly with you for 1 day and records your blood pressure on a memory card. The data is then read by a computer and gives the doctor a complete picture of the pressure for the day.
blood tests for infections and autoimmune diseases of the nervous system in cases of suspected neuroinfections, arachnoiditis, and multiple sclerosis.
Types of cysts
Important! A cyst is not a death sentence! In some cases, after diagnosis, doctors do not prescribe treatment, but simply observe over time. Most types of such neoplasms resolve on their own.
Today, doctors identify several types of brain cysts in a newborn, which differ both in the localization of the formations and in the possible consequences or treatment methods.
- Formations that are located in the area of the choroid plexus (or “pseudocyst”). They appear during the fetal development of the baby - in this case, the prognosis is favorable, and cysts in most cases do not require treatment. They also form at a later age as a result of the penetration of the herpes virus, difficult childbirth or complications during pregnancy. Unpleasant consequences are possible here, so you should choose the right treatment strategy.
- Subependymal formations in most cases are the result of intrauterine infection of the baby. Poor circulation in the ventricles of the brain leads to the fact that some tissues die, and in their place a cyst forms, which is filled with fluid. Birth trauma can also manifest itself in this form. Most often, such formations also disappear on their own, but in all cases the child must be monitored and ultrasound and other examinations regularly repeated. The fact is that such cysts in the head of a newborn can increase in size, which is fraught with negative consequences, including increased intracranial pressure and deterioration of well-being.
- Arachnoid cysts of the brain are more common in male newborns. At the same time, the pathology itself is quite rare, and the prognosis for such a diagnosis is positive. The formation is located between the arachnoid membrane and the brain itself. There are primary cysts (that is, congenital) and secondary ones (appearing as a result of surgery, an inflammatory process).
- Periventicular cysts form during fetal development and are localized in the periventicular region of the white matter. They can be caused by hereditary pathologies, developmental abnormalities, and infection. They are treated comprehensively, sometimes with mandatory surgical intervention.
- Choroidal formations localized in the brain plexus of the same name, they arise as a result of injuries or infections that affect the fetus in the womb. Such cysts rarely resolve, so in most cases they are removed surgically. It has characteristic symptoms - the baby’s fontanel does not close, coordination of movements is impaired, and convulsive twitching of the body is possible.
If several cysts are found as a result of the study, they speak of multicystic brain disease, which can be localized in one department or in different ones. Moreover, the formations themselves may vary in type and require different treatment strategies.
Kinds
There are different types of cysts, more precisely two:
- Arachnoid.
- Cerebral (retrocerebellar).
The arachnoid is located between the brain and the membrane. Cerebral appears in the brain itself, where the area of inflammation is directly located.
There are also types of cysts:
- Colloidal. It is characterized by the fact that it grows very slowly, and no symptoms are observed for a long time.
- Epidermoid. It consists of horny scales, which are surrounded by an epithelial capsule.
- Dermoid. It consists of the germinal parts of the skin (dermis). This neoplasm consists of hair follicles and pigment cells.
- Pineal. This rare variety affects the pineal gland.
Another type is a cyst located in the choroid plexuses. It is often diagnosed in the womb, in the early stages of fetal development. The brain has a plexus of blood vessels that produce cerebrospinal fluid. It is they that can often be affected, becoming the area where the cyst is located. With such a neoplasm, brain functions are not impaired; it develops normally. Choroid plexus cysts are often diagnosed in newborns. Often it goes away on its own without requiring any treatment, but you still need to consult a pediatric neurologist.
A subependemal cyst is considered a serious pathology. If it is diagnosed in a newborn, the child must be constantly monitored by a doctor. Among the causes are circulatory disorders in the vessels of the ventricles of the brain. Because of this, brain tissue suffers from oxygen deficiency. As a result, they begin to die off and are replaced by cavities with liquid.
Treatment options
First of all, it is worth remembering: if a child has been diagnosed with this disease, examinations should be repeated regularly. Their frequency, depending on the type of formation, is determined by the neurosurgeon.
- As for the treatment strategy, depending on the size, type and location of the cyst, it may not be prescribed.
- If the neoplasm does not disappear on its own, medications are selected and surgical intervention is used, which can be palliative or radical.
Important! Most often, operations are performed on children after one year of age; before one year of age, they are performed only in exceptional cases.
- Palliative techniques include endoscopic operations (cysts are punctured using an endoscope, suctioning out the contents) and shunting (the fluid that “filled” the cyst is removed using shunts). It should be emphasized that shunting can lead to infection of the brain due to the long stay of the shunt itself in the body.
- In the most difficult cases, open surgery is performed, that is, craniotomy. It allows you to remove the tumor as completely as possible, with its walls and all its contents.
Surgery
Endoscopic surgery
In cases where medications do not eliminate the pathological neoplasm, surgical intervention is resorted to. The following methods can be used for this:
- Endoscopic surgery. It is a microsurgical method that allows fluid to be removed from the pathological cavity through an opening in the cyst. This method allows you to temporarily relieve symptoms;
- Shunting. The essence of this method is to remove liquid from the formation into other cavities;
- Cyst removal. The most radical method, which is carried out through opening the skull and allows you to completely remove the pathology.
Cyst in a baby’s head – video from Dr. Komarovsky
This diagnosis is very frightening for parents, but pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky is convinced that there is no reason to panic. By watching the following video, you can find out what he advises parents. In addition, Komarovsky explains the essence of such a diagnosis.
In most cases, a brain cyst is not as scary as it might seem to parents at first glance. Most often it goes away on its own, but if not, neurosurgeons select an appropriate treatment strategy. However, you should not ignore the disease - at a minimum, you should undergo regular examinations. What do you know about this disease, have your kids had it? Tell us about it in the comments.