Ischemic cerebral stroke occurs predominantly in older people, but the disease is increasingly affecting 30-40 year olds. Pathology is assigned several codes in ICD-10. It is based on a severe disruption of the blood supply. A stroke occurs unexpectedly and it is impossible to predict its occurrence. Lack of treatment in the first three hours leads to irreparable consequences and often death.
Ischemic stroke - what is it?
Ischemic stroke is a pathology associated with a lack of blood supply due to impaired blood circulation in a certain area of the brain. As a result, tissue necrosis develops. Ischemic stroke is also called cerebral infarction.
For reference. The disease is distinguished from a hemorrhagic stroke. In the latter case, hemorrhage occurs, while with ischemia, tissues die due to insufficient blood supply.
According to ICD-10, the disease is coded 163 or 164 (unspecified stroke).
Treatment
Diagnostics and basic therapy for IS include the implementation of emergency measures in the most acute period of IS in an intensive care unit under constant monitoring of the vital functions of the body and taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
In the acute period of IS, pressure stabilization, oxygen therapy, rehydration (in case of possible dehydration) or dehydration (in the presence of cerebral edema confirmed by CT) are carried out.
During the acute period of the event, the goals are as follows:
- relieve swelling and inflammation, thus improving blood circulation in the brain;
- monitor and maintain normal blood parameters (clotting, viscosity);
- maintain normal blood pressure and cardiovascular system activity;
- prevent the development of relapses;
- carry out specific treatment according to clinical algorithms.
Classification
The variety of symptoms, causes, and manifestation features allows us to create a classification of ischemic stroke.
By the nature of the lesion
Taking into account the nature and characteristics of the course of the disease, there are several types of stroke:
- Transient ischemic attack. The damage is concentrated in a small area. Signs of pathology last no more than a day.
- Minor stroke. Functional recovery is noted within 3 weeks.
- Progressive. Symptoms increase gradually over several hours or days. The normalization of the condition is not complete; residual effects persist.
- Total. Characterized by brain damage and developing functional deficits.
Because of
Types of diseases are described based on the reasons that led to them:
- Atherothrombotic stroke occurs during sleep. It is characterized by slow development - cholesterol formations gradually reduce the diameter of the cerebral vessels.
- The lacunar form does not appear immediately. On the first day, signs of this disease cannot be detected. With this disease, spasm occurs in the cerebral arteries passing through several meninges. It is associated with arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis and embolism. With lacunar syndrome, small capillaries that bring blood to tissues located deep in the brain are affected.
- On the contrary, a cardioembolic stroke occurs suddenly. A broken clot blocks blood flow in medium-sized arteries.
- Hemodynamic is caused by a sharp decrease in pressure or a decrease in the filling volume of the heart. The impact is not associated with physical activity.
- Hemorheological develops due to a blood clotting disorder.
For reference. A disease of unspecified origin occurs for unclear reasons. This type of ischemic stroke is also spoken of when several factors lead to the disease. In particular, an increase in pressure and an increase in lipid plaques.
On the side
An ischemic stroke on the right side is called right-sided. The processes of processing sensory information, perception, and fantasy are disrupted. Creative abilities are narrowed. The patient loses the ability to sympathize, memory deteriorates. If the patient is left-handed, his speech suffers. It turns out that the left side is paralyzed, the arm and leg cannot move, sensitivity disappears.
With an ischemic stroke on the left side, paralysis covers the right side of the body. The patient is prone to depression, short temper, and impulsiveness. Systemic and motor memory and speech suffer. A person loses the ability to analyze and learn new things.
By localization
The violation zone allows us to distinguish several types of stroke. Vertebro-basilar syndrome is characterized by atrophy in the area of the brainstem, cerebellum, and occiput.
When a disorder develops in the basilar part of the brain stem, the functioning of the heart and respiratory organs worsens. Death occurs most often due to the lesion located in this department.
For reference. A common form is the death of nerve tissue in the cerebellum area. This occurs due to blocking of blood flow in the superior basilar artery and its basin.
Patients suffer from coordination, tremor appears when trying to make a purposeful movement, vomiting, and coma develops. The most common outcome is death, and drug therapy rarely helps.
A circulatory disorder in the vertebrobasilar region is characterized by confusion, nausea, and inability to swallow.
With a stroke of the middle cerebral artery, sensitivity is impaired and paralysis develops. Patients are distinguished by their fixed gaze. Often they do not understand their illness.
In some cases, an ischemic crisis causes a disruption of the blood supply to the spinal cord. In this case, patients have paralyzed arms and legs, and have problems with bowel control.
For reference. Separately, they talk about an extensive cerebral infarction. This pathology develops in the event of a disruption of the blood supply in large arteries and their basins.
The researchers identified the volume of the lesion:
- extensive atherothrombic – 115 cm3;
- cardioembolic – 62 cm3;
- hemodynamic – 32 cm3;
- lacunar – 2 cm3.
A rheological lesion is characterized by an area of 1.5 cm3.
Rehabilitation
To improve the patient's prognosis, it is important to carry out timely rehabilitation immediately after the crisis.
After an atherothrombotic stroke, the following rehabilitation measures are carried out:
- proper nutrition with a balanced amount of fermented milk and plant foods in the diet;
- when consuming fluids, proceed from 30 ml of water per 1 kg of patient weight per day;
- therapeutic massage to reduce muscle tone;
- the work and rest regime should be without excessive stress, but also with a maximally active lifestyle;
- physical therapy classes;
- physiotherapeutic procedures to improve blood flow and speed up metabolic processes;
- drug treatment.
For patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke, regular visits to sanatoriums are important.
Preventive measures after a stroke
The following steps can help prevent another stroke:
- regular visits to a neurologist, especially if there are changes in your health status;
- proper nutrition;
- active lifestyle, but without heavy physical activity;
- constant exercise therapy;
- regular massage course;
- visiting specialized resorts for vascular health;
- regular and proper rest;
- correct intake of all prescribed medications, including preventative ones.
With proper prevention of recurrent strokes, you can avoid and still have a full-fledged work activity.
Stages of development
In the process of developing an ischemic stroke, there are several stages. The first of them, acute, lasts up to 21 days from the onset of the attack. It can be divided into the most acute stage, lasting five days, when symptoms increase. This is the stage where most people die.
The second lasts up to six months. Reversible changes occur in cells during this period. Compensation for disturbances begins, blood circulation around the affected nuclei is restored. The stage is called the early recovery stage.
The third conditionally begins 6 months after the impact and lasts up to a year. During this period, cysts and glial formations form in the affected areas.
For reference. A year after the attack, the fourth stage begins. It is called the stage of residual manifestations. It lasts for the rest of a person’s life.
Pathogenesis and causes of development
The pathogenesis centers on the formation of an area of dead brain tissue around which swelling occurs.
Attention. It takes approximately 8 minutes for irreversible consequences to occur in the area where the blood flow rate has decreased significantly (less than 10 ml/100 g per minute). This area is called the core or core of ischemia.
For several hours after the impact, the core is surrounded by still living tissue. However, she had already begun to experience nutritional deficiencies. The rate of cerebral blood flow here is 20 ml/100 g per 1 minute.
This zone is usually called the penumbra or ischemic penumbra. In the cells of this area, a metabolic disorder occurs, as a result of which it loses functionality due to a lack of nutrients.
Ischemic stroke - symptoms
Stopping the blood supply leads to the death of neurons, as a result of which intercellular connections and brain functions suffer.
Beginning of development
People are often confused about how ischemic stroke manifests itself. The fact is that it begins to develop in different ways. In an acute process, the severity of symptoms manifests itself within one to two hours. During this time, the person falls into a coma. Typically, paralysis and other severe impairments subsequently develop.
However, the symptoms of ischemic cerebral stroke can increase in waves. The condition worsens gradually due to brain hypoxia. Sometimes symptoms appear and then disappear, and the patient feels well for a week. With rapid diagnosis, cerebral functions are restored.
The tumor-like onset of the course of ischemic stroke is similar in pace and nature of development. However, tissue swelling and high blood pressure are considered to be the trigger of the process.
General cerebral symptoms
For reference. Regardless of the location of the lesion core, patients experience neurological symptoms: severe pain in the head, eyes, dry mouth, vomiting, fever, stupor.
Many lose consciousness, and some patients develop coma.
In some cases, convulsions are observed. Motor and sensory disturbances are observed.
Focal symptoms
Damage to the arteries of the brain is indicated by poor coordination, visual disturbances, dizziness, paralysis, speech disorders, and swallowing.
Damage to the anterior artery causes loss of the ability to move, asynchrony of eye movements, inability to speak, and increased grasping reflexes.
Violation of the posterior artery leads to a narrowing of the breadth of vision and a decrease in its acuity. The patient still understands the speech addressed to him, but he himself is lost and does not remember many words.
Extensive blocking of the middle artery causes paralysis, limits the sensitivity of the hands and face, misunderstanding of oral speech, and the inability to find the right words.
For reference. In the case of an extensive ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere, the functioning of the left part is reduced, up to its complete paralysis. With left-sided, the right side of the body suffers.
Ischemic stroke: stages of the disease
This type of stroke develops according to the cascade principle with the following stages:
- decreased blood flow;
- release of aspartate and glutamate followed by excitotoxicity;
- accumulation of calcium inside cells;
- activation of intracellular enzymes, development of oxidative stress, appearance of local inflammation reactions;
- process of neuronal death.
Due to the penetration of fluid into neurons and swelling of cells, cerebral edema inevitably appears. There is an increase in brain volume and an increase in intracranial pressure.
Diagnostics
If there is a suspicion of a blood supply disorder, a special technique is used to determine ischemic stroke. If a person with an acute cerebrovascular accident is conscious, his ability to speak and hold his hands up is checked. A characteristic sign of ischemic stroke is drooping of one of the corners of the mouth.
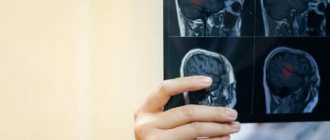
For reference. To confirm the diagnosis of ischemic stroke, CT or MRI is performed. These studies make it possible to detect the boundaries of the lesion and the approximate time of its appearance. The resulting tomogram allows one to distinguish between ischemia and hemorrhagic stroke.
Angiography is indicated to determine the exact site of the lesion. The patient is given an electrocardiogram and their blood pressure is measured.
To diagnose ischemic stroke, blood tests are performed - general, cholesterol, sugar, coagulability.
Ischemic stroke - treatment
Before the doctors arrive, the patient is placed on a horizontal plane, the head is raised 30°, and all compressive clothing is removed. A cold compress is applied to the forehead.
Mustard plasters or a heating pad are placed on the hands and feet; if they are paralyzed, they are rubbed with oil or alcohol solutions. It is important to provide a flow of fresh air.
Attention. No pills should be given to the patient.
The first therapeutic measures using medications are carried out immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis using CT and MRI. For stroke, thrombolysis is performed. Drugs are administered whose action is aimed at resolving the blood clot.
At this stage, it is important to understand that we are talking about an ischemic stroke, and not a hemorrhagic one.
Basic treatment for ischemic cerebral stroke includes:
- Normalization of blood pressure. It is treated with drugs - diuretics, alpha and beta blockers.
- Reducing the risk of blood clots. Anticoagulants and antiplatelet tablets (Cavinton, Vasobral) are used.
- Reducing the volume of cerebral edema.
- Regulation of homeostasis.
- Prevention of concomitant diseases and complications. A person who has experienced a stroke, especially an atherothrombic one, has a high probability of developing pneumonia, thrombosis, and bedsores.
- Maintaining body temperature below 37.5 °C.
Vitamin therapy is indicated. If necessary, thrombolytic therapy is carried out for ischemic stroke. Actiliz and Alteplase are prescribed.
Medicines prescribed for ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere are no different from the treatment of pathology of the left hemisphere.
For reference. Ischemic stroke is often treated only with surgery. They are aimed at creating an additional blood flow bypassing the affected area. Dilatation of arteries with stents is indicated. In the presence of a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaques, carotid endarterectomy is used to treat ischemic stroke.
As the acute symptoms of stroke disappear, the patient is recommended to undergo restorative therapy. It includes exercise therapy, massage, and physiotherapy methods. Classes with a psychiatrist or speech therapist are recommended. To restore coordination, a stabiloplatform is used.
Recovery course
The rehabilitation program includes many methods of influencing paralyzed limbs, learning to walk, eat, maintain personal hygiene, and self-care. It includes areas such as kinesiotherapy (movement therapy), speech and memory training, dietary nutrition, medication, physical therapy, and massage.
Watch the video about recovery after a stroke:
Motor program
You need to start moving as early as possible. At first, this may include flexion and extension of the fingers, hands and feet of the healthy side of the body. This speeds up the recovery of brain cells in the affected area. Subsequently, usually simultaneously with the massage, the physical therapy instructor performs gentle flexion, extension, and sequential rotation in all joints of the arm and leg.
Restoring finger movement after a stroke
To restore the function of the upper limb, a towel is hung over the bed, and the patient grabs it and moves back and forth, sideways, up and down. After mastering these exercises, the towel is hung higher.
Also, a rubber bandage is used as a training device; it is tied into a ring (the length of the strip is approximately 80 cm) and fixed on a stationary object or between the arms, legs, arm and leg. During training you need to stretch the ring.
The lower limbs in bed can be developed with passive movements in the ankle, knee and hip joints, and then the patient is asked to slide his heel along the bed . To eliminate the spasm, you need to place a hard cushion under the knee.
Exercises in bed
The next stage of training is training while sitting on the bed, and then standing on the floor. The following exercises may be included in the rehabilitation complex:
- pick up a box of matches from the table and then from the floor;
- stand on your toes with your arms raised above your head;
- expander compression;
- body bends;
- scissor-type hand movements;
- squats.
Special simulators for recovery after a stroke significantly speed up the rehabilitation process and can be used from the first days
Speech training
Speech is restored later than movements in the limbs; it may even take several years. To restore the ability to speak, it is important that the patient constantly hears the conversation addressed to him, even if he is not yet able to respond. Even the perception of someone else's speech activates the corresponding centers of the brain, which contributes to their disinhibition. If speech is completely absent, then the following techniques can be used for training:
- the patient finishes the word (the part without the last letter or syllable is pronounced to him), then the sentence;
- repetition of simple phrases;
- well-known poems;
- Tongue Twisters;
- singing together.
Advice from a speech therapist for speech restoration
In order to force the muscles involved in articulation to develop, the patient is asked to move his lower jaw daily, stick his tongue forward, lick his lips in different directions, and curl them into a tube.
Memory recovery
Against the background of drug therapy (nootropic drugs), special exercises are also carried out to develop memory:
- repeating a number sequence with your eyes closed;
- learning proverbs, sayings, poems;
- retelling a text read or a song heard;
- Board games.
Board games for memory restoration
The best results can be obtained if classes are combined with the patient’s previous hobbies so that the training process is accompanied by positive emotions.
Nutrition
It is most difficult to feed patients with impaired swallowing and sensitivity in one half of the oral cavity. They have to learn to eat again. To do this, you can use exercises to restore lost abilities:
- the patient imitates coughing, swallowing and yawning;
- puffs out cheeks;
- rinses your mouth and throat.
Exercise “Puffing up the cheeks”
When organizing nutrition for patients with impaired chewing and swallowing functions, the following features must be taken into account:
- food should only be warm and smell appetizing;
- exclude viscous and hard foods - rice, dry cottage cheese, dried bread, crackers;
- the side dish should have the consistency of thick puree, and soup or juice can be added to meat and fish;
- eating takes at least 40 minutes, the patient should not be rushed;
- it is necessary to feed in such a way that the food gets to the healthy side;
- For drinks and water, it is convenient to use a sippy cup or a cocktail straw.
The easiest foods for stroke patients with eating problems to swallow are:
- boiled carrots, potatoes, mashed or diced;
- cauliflower, broccoli;
- minced meat;
- baked flounder, sardines;
- omelette;
- avocado, banana;
- soft pear cubes;
- baked or pureed apples;
- jelly, pudding;
- soft cheese;
- porridge made from flakes or grains (thoroughly boiled).
Puree soups from vegetables, meat, fish.
It is unacceptable to include fatty meat, broths, fried and spicy foods, alcoholic and caffeinated drinks in the diet.
Drugs
The choice of medications for rehabilitation is carried out exclusively by a neurologist. The following groups of drugs are used:
| Groups | Medicines |
| Vasodilators (with caution, under pressure control) | Cavinton, Sermion, Instenon; |
| Neuroprotectors | Somazina, Semax, Cerebrolysin, Encephabol; |
| Antioxidants | Mexidol, Tanakan; |
| Nootropic | Lucetam, Phenotropil. |
If indicated, antiplatelet agents (Tiklid, Aspirin) and cholesterol-lowering drugs (Atokor, Vasilip) are used.
Physiotherapy
The appointment of procedures can be no earlier than 1 - 2 months from the onset of the stroke. The following techniques are indicated during the recovery period:
- electrophoresis on the collar area;
- sulfide baths on hands;
- magnetic therapy on the neck area;
- general baths with sea salt, pine extract, carbon dioxide and pearl;
- ozokerite or paraffin, mud or galvanic mud on the affected limbs;
- reflexology – acupressure or acupuncture;
- electrical stimulation with sinusoidally modulated currents;
- Darsonvalization of limbs.
Massage
Indicated from the first week of illness daily, starting from 10 minutes to half an hour. All movements are slow and low-intensity, especially if there is muscle spasm. On the healthy side, the technique of massage movements can be classic. Massaging sequence:
- Scapular region.
- Shoulder.
- Forearm and hand.
- Pelvic, femoral area.
- Shin and foot.
The course requires from 30 to 50 sessions, after which a break is needed for a month, then for maintenance therapy, massage can be performed in 10 sessions 3 - 4 times a year.
Watch the video about massage and exercise therapy after a stroke:
Complications
In ICD-10, the consequences of ischemic stroke are assigned code 169. If the diagnosis is incorrect and thrombolysis is performed during an attack, the course of the latter may worsen.
For reference. With right-sided and left-sided lesions, disturbances occur in the motor area. The limbs are paralyzed, muscle weakness develops, which does not allow the patient to care for himself or move around. Discoordination of movements, especially voluntary ones, is noted.
Sensitivity suffers, and it takes longer to restore it than to normalize motor activity.
Most patients experience consequences such as psycho-emotional disorders. Ischemic stroke is characterized by a tendency to depression, emotional lability, in many cases, aggressiveness, and the appearance of fears.
Impairments in the intellectual sphere with left-sided lesions lead to memory impairment, inability to analyze the situation, childishness, and disorientation in space and time. With right-sidedness, fantasy suffers.
Speech disorders are manifested by incoherent speech, repetition of the same phrases or words. In left-handed people they are observed with pathology of the right hemisphere.
In approximately 10% of cases, victims develop epilepsy. There is often a risk of a second strike.
Prevention
Researchers are confident that ischemic cerebral infarction can be prevented. They identified a number of preventive measures that can reduce the risk of disease:
- Treat hypertension. Normal blood pressure is 130/80. When it rises to 140/90 or higher, it is necessary to take medications to reduce it.
- If you have heart pathologies, follow medical recommendations and take prescribed medications.
- Take measures to prevent diabetes by taking prescribed medications. It is recommended to follow a diet, not consume sugar, and control glucose levels.
- If there is a tendency to thrombosis, perform thrombolysis. If blood clots are detected, carotid endarterectomy is indicated.
- Monitor your cholesterol levels. It increases the risk of developing plaques in the coronary and carotid arteries. If lipid formation is unstable, carotid endarterectomy is also performed.
- Do computed tomography periodically.
- Forget about bad habits. Tobacco smoke increases the likelihood of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. Drinking alcohol-containing drinks provokes an increase in blood pressure and the development of heart pathologies.
- Do not use oral contraceptives. Researchers note that the likelihood of developing ischemic stroke increases if a woman takes hormonal drugs. The use of any medicine must be agreed with a doctor.
- Exercise regularly. Physical exercise, exercise, jogging every day is an excellent way to prevent ischemic stroke and other diseases.
Ignoring preventive measures leads to repeated attacks.
Causes of pathology
Most often, the development of atherothrombotic stroke occurs in men over 40 years of age who lead a sedentary lifestyle, are exposed to stress, and experience excessive physical activity.
Causes causing pathologies:
- excess weight;
- age-related changes;
- alcohol and smoking abuse, drug addiction;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- blood pressure changes sharply and frequently;
- thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system, such as anemia, leukemia, hemorrhagic diathesis;
- connective tissue rheumatism;
- venereal diseases;
- consequences of heart valve replacement surgery;
- autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis;
- long-term or excessive use of drugs with hormonal supplements.
Heart diseases lead to strokes: myocarditis and endocarditis, coronary disease and arrhythmia. The cause of vascular pathologies of the brain can be diabetes mellitus and the complications caused by it.
Forecast
How long a person will live after an ischemic attack depends on the location, size of the damage, time of initiation of treatment and concomitant diseases.
For reference. According to statistics, up to 25% of patients who have suffered a major ischemic stroke die within the first month. These are mainly those people whose attack occurred due to atherosclerosis or blood clot rupture.
The main cause of death in cerebral infarction is cerebral edema and its displacement. Sometimes exacerbation of cardiovascular diseases leads to death.
In the next 14-21 days of acute ischemic stroke, death occurs due to heart failure, the formation of a blood clot in the pulmonary artery, and pneumonia.
Survival rates for ischemic stroke are up to 70% at the end of the first 12 months. After 5 years, about 50% are still alive, after ten – a quarter. With a repeated attack, the prognosis worsens.
It is noted that the recovery of patients is best in the first three months, and the strength and movements of the leg muscles are normalized faster and better than in the arms.
For reference. The prognosis for complete paralysis is unfavorable. If recovery does not occur within a year, after this period normalization of the condition is unlikely. The exception is speech.
Doctors use several scales that allow them to assess the prospects for recovery.
NIHSS scale
The grading system is based on the manifestation of symptoms of the disease at the acute stage. The degree of consciousness, speech preservation, ability to control movements and their coordination, muscle strength, facial expressions, attention, eye movements, field of vision are analyzed. Moreover, if a person scores few points, the prognosis is satisfactory; if a person scores high, the prognosis is unfavorable.
For reference. If the patient scores up to 8-10 points on this scale, the probability of recovery is 70%, the observed disorders are characterized as mild. From 9 to 12 – medium; up to 15 – heavy; up to 33 – extremely severe. Indicator 34 characterizes coma. The probability of recovery for a patient who scores more than 20 points is no more than 16%.
Rankin scale
The Rankin scale is also often used. Based on various pathological symptoms, it describes the levels of the patient’s condition and the prognosis for the preservation of functions. A patient diagnosed with grade zero does not have any limitations or residual symptoms.
In the first degree, minor disturbances associated with speech, movements, and sensitivity are noted. The person remains able to work.
With the second, the patient loses some functions and cannot take care of himself fully.
With the third, a person walks independently with the help of a frame or a cane, but cannot fully take care of himself - cook, clean, go to the store. In some cases of left-sided lesions, a decrease in intellectual functions is observed.
The fourth characterizes patients who need help every day with dressing, moving, and eating.
With the fifth, the patient needs help and care constantly, he cannot be left alone.